Which states don’t require auto insurance? This question might seem surprising, but in the United States, there are a handful of states that don’t mandate car insurance for all drivers. These states, often with strong financial responsibility laws in place, offer a unique perspective on the traditional approach to auto insurance. While some may see this as a potential risk, others view it as a way to reduce the burden of insurance costs. This article explores the reasons behind these policies, the potential risks and benefits, and the alternatives available to drivers in these states.
The decision to not require auto insurance is a complex one, with arguments both for and against. Supporters of this approach point to the potential for lower insurance costs and greater freedom for individuals. However, critics argue that the lack of mandatory insurance creates a greater risk of uninsured drivers, leading to higher costs for those who do carry insurance and potentially impacting the overall safety of the roads.
States Without Mandatory Auto Insurance
In the United States, all states require drivers to have some form of liability insurance, but a few states do not mandate that drivers carry auto insurance. These states allow drivers to choose whether or not to purchase insurance, opting instead for a financial responsibility law. This means that drivers are only required to prove their ability to pay for damages caused in an accident, rather than having continuous insurance coverage.
States Without Mandatory Auto Insurance, Which states don’t require auto insurance
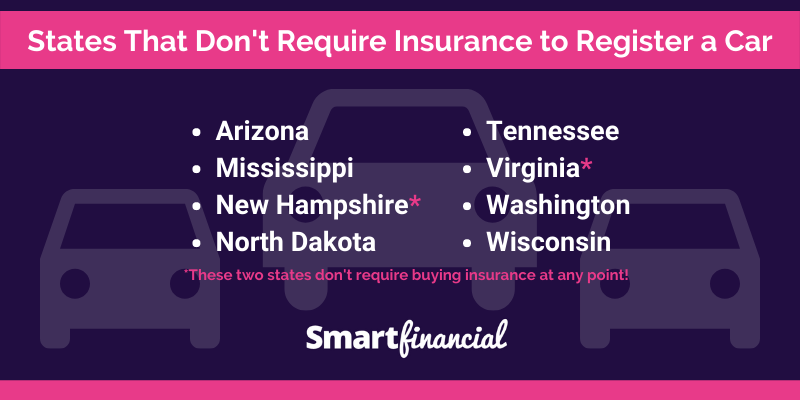
The states that do not require drivers to carry auto insurance are:
- New Hampshire
- Virginia
Reasons for Not Mandating Auto Insurance
The primary reason for not mandating auto insurance is often rooted in a desire to limit government intervention in personal choices. States like New Hampshire and Virginia prioritize individual liberty and believe that individuals should be free to make their own decisions regarding insurance coverage. These states argue that individuals are better equipped to assess their own risks and make informed choices about their insurance needs.
Potential Risks and Benefits of Living in a State Without Mandatory Auto Insurance
Living in a state without mandatory auto insurance presents both potential risks and benefits.
Potential Risks
- Higher Financial Risk: Drivers who choose not to carry insurance face a significant financial risk in the event of an accident. If they are at fault, they will be personally liable for all damages, including medical bills, property damage, and legal fees. This can lead to substantial financial hardship, potentially even bankruptcy.
- Limited Access to Financial Resources: In the absence of insurance, drivers may struggle to access the financial resources needed to cover accident-related expenses. This can create a cycle of debt and financial instability, especially for those who are already struggling financially.
- Increased Risk of Uninsured Motorists: A lack of mandatory insurance can lead to a higher number of uninsured motorists on the road. This increases the risk of being involved in an accident with an uninsured driver, further compounding the financial risk for all drivers.
Potential Benefits
- Lower Insurance Costs: The absence of a mandatory insurance requirement can potentially lead to lower insurance costs for those who do choose to purchase coverage. This is because insurance companies may face less competition in these states, allowing them to offer lower premiums.
- Greater Individual Choice: Drivers have the freedom to choose whether or not to purchase insurance, allowing them to make decisions based on their individual needs and financial circumstances. This can be beneficial for drivers who are confident in their ability to manage risk and are willing to take on more personal responsibility.
Financial Responsibility Laws in Non-Mandatory States
While some states require all drivers to have auto insurance, others do not. However, even in these states, drivers are still legally obligated to demonstrate their financial responsibility in case of an accident. This is accomplished through financial responsibility laws, which aim to ensure that drivers have the means to cover potential damages or injuries caused by their actions on the road.
These laws typically require drivers to provide proof of financial responsibility, usually in the form of insurance, a surety bond, or a deposit of cash or securities. These requirements vary from state to state and may differ from the mandatory auto insurance requirements found in other states.
Specific Requirements of Financial Responsibility Laws
Financial responsibility laws in non-mandatory states are designed to ensure that drivers are held accountable for the financial consequences of accidents they cause. These laws vary from state to state, but generally include the following requirements:
- Proof of Financial Responsibility: Drivers must provide proof that they can cover the costs associated with potential accidents. This proof can come in the form of an insurance policy, a surety bond, or a deposit of cash or securities.
- Minimum Coverage Limits: Each state sets minimum coverage limits for financial responsibility, which dictate the minimum amount of coverage drivers must have. These limits typically cover bodily injury liability, property damage liability, and uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage.
- Compliance with Financial Responsibility Requirements: Drivers must maintain compliance with the financial responsibility laws of their state. This means providing proof of financial responsibility when requested and ensuring that their coverage meets the minimum requirements.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Failure to comply with financial responsibility laws can result in penalties, such as fines, license suspension, or vehicle registration suspension.
Differences from Mandatory Auto Insurance Requirements
While financial responsibility laws share some similarities with mandatory auto insurance requirements, there are key differences. Here’s a breakdown of those differences:
- Coverage Requirements: Mandatory auto insurance laws require drivers to purchase specific types of coverage, such as liability, collision, and comprehensive, while financial responsibility laws focus on ensuring drivers have the financial means to cover potential damages, not necessarily requiring specific coverage types.
- Enforcement: Mandatory auto insurance laws are typically enforced through insurance verification checks and penalties for non-compliance, while financial responsibility laws rely on demonstrating financial responsibility through various means, including insurance, bonds, or deposits.
- Consequences of Non-Compliance: Failure to maintain mandatory auto insurance can result in immediate penalties, such as fines and license suspension, while non-compliance with financial responsibility laws often triggers penalties only after an accident occurs.
The Impact of No-Fault Insurance

In states that don’t require auto insurance, the concept of no-fault insurance can play a significant role. No-fault insurance systems, also known as personal injury protection (PIP) systems, operate differently from traditional fault-based insurance systems. Understanding how no-fault insurance works and its implications is crucial for drivers in these states.
How No-Fault Insurance Works
No-fault insurance operates on the principle that each driver’s insurer covers their own medical expenses and lost wages, regardless of who caused the accident. This eliminates the need for lengthy legal battles to determine fault, which can be time-consuming and costly.
Benefits of No-Fault Insurance
- Faster Claim Processing: No-fault insurance simplifies the claims process, as drivers file claims with their own insurer, regardless of fault. This can lead to quicker settlements and reimbursements for medical expenses and lost wages.
- Reduced Litigation: By eliminating the need to prove fault in court, no-fault insurance significantly reduces the number of lawsuits arising from car accidents. This reduces legal fees and court congestion.
- Lower Insurance Premiums: In some cases, no-fault insurance can result in lower premiums for drivers, as insurers can benefit from streamlined claims processing and reduced litigation costs.
Drawbacks of No-Fault Insurance
- Limited Coverage: No-fault insurance typically has limits on the amount of coverage available for medical expenses and lost wages. If these limits are exceeded, drivers may need to pursue additional compensation through traditional fault-based lawsuits.
- Potential for Abuse: In some cases, drivers may attempt to inflate their claims or file fraudulent claims to receive higher payouts. This can lead to higher premiums for all drivers.
- Limited Compensation for Serious Injuries: Drivers with serious injuries may find that no-fault insurance does not provide sufficient compensation for their losses, particularly if they have high medical expenses or long-term disability.
Comparison to Traditional Fault-Based Systems
- Fault Determination: In fault-based systems, the at-fault driver’s insurer is responsible for covering the other driver’s damages. This process involves investigating the accident to determine fault, which can be complex and time-consuming.
- Litigation: Fault-based systems often lead to lawsuits, as drivers seek compensation for their losses. This can be a lengthy and expensive process.
- Coverage: Fault-based insurance typically provides broader coverage than no-fault insurance, including compensation for pain and suffering, emotional distress, and punitive damages.
Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
While states without mandatory auto insurance laws provide drivers with a degree of flexibility, it’s crucial to understand the potential consequences of driving without insurance. Choosing not to have auto insurance exposes drivers to significant financial and legal risks, particularly in the event of an accident.
Financial Consequences
The absence of auto insurance can result in substantial financial burdens, particularly if you’re involved in an accident. Without insurance coverage, you become personally liable for all costs associated with the accident, including:
- Medical Expenses: If you injure yourself or others, you’ll be responsible for all medical bills, including hospital stays, surgeries, and ongoing care. This can quickly accumulate into substantial amounts, potentially leading to financial hardship.
- Property Damage: In the case of an accident, you’ll be responsible for repairing or replacing any damaged vehicles or property, including your own. This can be a significant financial burden, especially if you’re at fault.
- Legal Fees: If you’re sued by the other party involved in the accident, you’ll be responsible for legal fees and court costs. These costs can be substantial, adding to your financial strain.
- Lost Wages: If you’re injured and unable to work, you’ll be responsible for lost wages, further adding to your financial burden.
Alternatives to Traditional Insurance

While some states don’t require auto insurance, drivers in these states still face significant financial risks in case of an accident. Fortunately, various alternatives to traditional auto insurance exist, providing some level of protection without the usual premiums. These alternatives offer different levels of coverage and financial responsibility, catering to various needs and budgets.
Self-Insurance
Self-insurance involves setting aside a substantial sum of money to cover potential accident-related costs. This approach is suitable for individuals with a strong financial foundation and a low-risk driving history. It eliminates premium payments but requires significant financial discipline and a considerable financial reserve.
Self-insurance can be a viable option for individuals with a substantial financial cushion and a history of safe driving.
Cash-Based Insurance
Cash-based insurance involves paying for accident-related costs out of pocket, typically through a pre-paid plan or a cash-based membership program. These programs usually offer limited coverage and may have specific limitations on the types of accidents they cover.
Cash-based insurance is an alternative for drivers seeking lower premiums but with limited coverage and potentially higher out-of-pocket expenses.
Ride-Sharing and Public Transportation
Instead of owning a car, individuals can rely on ride-sharing services like Uber and Lyft or public transportation. These options offer convenience and cost-effectiveness, particularly for frequent commuters or those living in urban areas with robust public transportation networks.
Ride-sharing and public transportation can be economical alternatives to car ownership, reducing the need for insurance altogether.
Financial Responsibility Laws
States without mandatory auto insurance often have financial responsibility laws, requiring drivers to demonstrate financial capability to cover potential accident-related costs. This can be achieved through a surety bond, a deposit of funds, or a certificate of self-insurance. These options offer a level of financial protection but may not provide comprehensive coverage like traditional insurance.
Financial responsibility laws ensure that drivers have the financial means to cover accident-related costs, providing some protection for other drivers and pedestrians.
Safety Considerations
The absence of mandatory auto insurance in certain states raises concerns about potential safety implications. While it’s not a direct cause-and-effect relationship, the lack of insurance can influence driving behavior and contribute to road safety challenges.
The Impact of Uninsured Drivers on Road Safety
The presence of uninsured drivers can pose a significant risk to road safety. When a driver is uninsured, they may be less likely to take precautions and drive responsibly. This can lead to an increased likelihood of accidents and injuries.
- Financial Irresponsibility: Uninsured drivers may be less likely to maintain their vehicles properly, as they are not financially incentivized to do so. This can lead to breakdowns and accidents caused by mechanical failures.
- Risk-Taking Behavior: Uninsured drivers may feel less accountable for their actions, leading to reckless driving behaviors such as speeding, driving under the influence, and aggressive driving.
- Lack of Coverage: In the event of an accident, uninsured drivers may be unable to cover the costs of damages or injuries, leaving victims financially vulnerable.
Economic Considerations
The absence of mandatory auto insurance in certain states presents a unique economic landscape, influencing both individual financial burdens and the overall cost of accidents. This section delves into the financial implications of driving without insurance, exploring the potential costs associated with uninsured accidents and the financial implications for both individuals and the state.
Potential Costs Associated with Uninsured Accidents
Uninsured accidents can lead to substantial financial burdens for both individuals and the state. When an uninsured driver causes an accident, the injured party may face significant expenses, including medical bills, property damage repairs, lost wages, and legal fees. In the absence of insurance coverage, these costs can be substantial, potentially leading to financial hardship for the injured party.
- Medical Expenses: Uninsured accidents can result in severe injuries, leading to substantial medical bills for treatment, rehabilitation, and long-term care.
- Property Damage: Repairs for damaged vehicles or other property can be expensive, especially in cases of significant damage.
- Lost Wages: Injured parties may be unable to work, resulting in lost income and further financial strain.
- Legal Fees: Seeking compensation from an uninsured driver often requires legal representation, which can involve substantial legal fees.
Financial Implications for Individuals
Individuals in states without mandatory auto insurance face several financial implications, including the potential for significant out-of-pocket expenses and the risk of financial hardship.
- Out-of-Pocket Expenses: Individuals may be responsible for covering the full cost of accidents, including medical bills, property damage, and legal fees, if they are involved in an accident with an uninsured driver.
- Financial Hardship: The potential for high out-of-pocket expenses can lead to financial hardship, especially for individuals with limited financial resources.
- Credit Damage: Unpaid medical bills or legal judgments related to uninsured accidents can negatively impact credit scores, making it difficult to obtain loans or secure affordable credit in the future.
Financial Implications for the State
States without mandatory auto insurance may experience increased costs associated with uninsured accidents, impacting the state’s budget and potentially straining public resources.
- Increased Costs for Public Programs: States may see increased costs for public programs, such as Medicaid, which provide healthcare coverage for low-income individuals, as uninsured individuals may rely on these programs to cover accident-related medical expenses.
- Increased Costs for Law Enforcement: Law enforcement agencies may experience increased costs associated with investigating and responding to accidents involving uninsured drivers, as these accidents may require more extensive investigations and resource allocation.
- Increased Costs for Courts: The judicial system may see increased costs associated with resolving legal disputes arising from uninsured accidents, as these cases often involve complex legal issues and require extensive court resources.
Case Studies
Real-world examples of driving without insurance in states without mandatory coverage can provide valuable insights into the potential consequences. These cases illustrate the risks and challenges individuals face when operating a vehicle without insurance.
Financial Burden of Accidents
The financial burden of accidents can be substantial, especially when driving without insurance.
- In one instance, a driver in New Hampshire, a state without mandatory auto insurance, was involved in a collision that resulted in significant property damage and injuries. Without insurance, the driver was held personally liable for all damages, including medical expenses, repairs, and legal fees. The individual faced mounting debt and potential financial ruin due to the lack of insurance coverage.
- In another case, a driver in Delaware, another state without mandatory insurance, was involved in an accident that resulted in the death of another driver. The uninsured driver was sued by the deceased driver’s family and held liable for wrongful death damages. The driver was forced to sell their property and declare bankruptcy to cover the legal costs and settlements.
Legal Consequences
Driving without insurance can lead to legal consequences, including fines, license suspension, and even jail time.
- In Texas, a state with a financial responsibility law, a driver was stopped for a traffic violation and found to be driving without insurance. The driver was issued a citation and fined $350. The driver’s license was also suspended until proof of insurance was provided.
- In Florida, a driver was involved in an accident and found to be driving without insurance. The driver was charged with a misdemeanor offense and sentenced to six months in jail. The driver was also ordered to pay a fine of $1,000 and complete 100 hours of community service.
Impact on Victims
Victims of accidents involving uninsured drivers often face significant challenges in obtaining compensation for their injuries and damages.
- A pedestrian in Virginia, a state with a financial responsibility law, was struck by an uninsured driver. The pedestrian suffered serious injuries and incurred substantial medical expenses. The uninsured driver was unable to cover the costs, and the pedestrian was forced to file a claim with their own insurance company under their uninsured motorist coverage.
- In Pennsylvania, a state without mandatory insurance, a driver was involved in an accident with an uninsured driver. The driver’s vehicle was totaled, and they suffered minor injuries. The uninsured driver was unable to provide any compensation, and the driver was left to pay for the damages and medical expenses out of pocket.
Epilogue
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to carry auto insurance in a state that doesn’t require it is a personal one. Drivers need to weigh the potential risks and benefits, considering their individual circumstances and financial situation. By understanding the nuances of these policies and exploring alternative options, drivers can make informed decisions about their insurance needs and protect themselves on the road.
Expert Answers: Which States Don’t Require Auto Insurance
What are the potential consequences of driving without insurance in a state that doesn’t require it?
While these states may not mandate insurance, they still have financial responsibility laws. If you cause an accident, you could face significant financial penalties, including fines, license suspension, and even jail time. You could also be held liable for the full cost of damages, including medical bills and property repairs.
What are the benefits of living in a state without mandatory auto insurance?
Some argue that the absence of mandatory insurance can lead to lower costs for drivers, as they have the option to choose their coverage level. Additionally, it can provide more freedom for individuals who believe they can manage their own risk.
What are the alternatives to traditional auto insurance in non-mandatory states?
There are a few alternatives, including self-insurance, surety bonds, and alternative risk-sharing programs. These options vary in cost and coverage, so it’s crucial to research them carefully before making a decision.







