Which states do not require auto insurance? It’s a question that often surprises many drivers, as most of us assume that car insurance is a universal requirement. However, there are a handful of states in the U.S. that don’t mandate auto insurance for all drivers. These states often have alternative financial responsibility laws in place, such as surety bonds or self-insurance, to ensure that drivers can cover the costs of accidents they might cause. While this approach may seem appealing on the surface, it can have significant implications for both uninsured motorists and the overall insurance landscape.
The decision of whether or not to require auto insurance is a complex one, with arguments on both sides. Supporters of mandatory insurance argue that it promotes public safety by ensuring that drivers are financially responsible for any accidents they cause. They also point to the fact that uninsured motorists can pose a significant financial burden on accident victims and the insurance industry. On the other hand, opponents of mandatory insurance argue that it can lead to higher insurance premiums and create an unnecessary burden on low-income drivers. They also argue that individuals should have the freedom to choose whether or not to purchase auto insurance.
States Without Mandatory Auto Insurance: Which States Do Not Require Auto Insurance
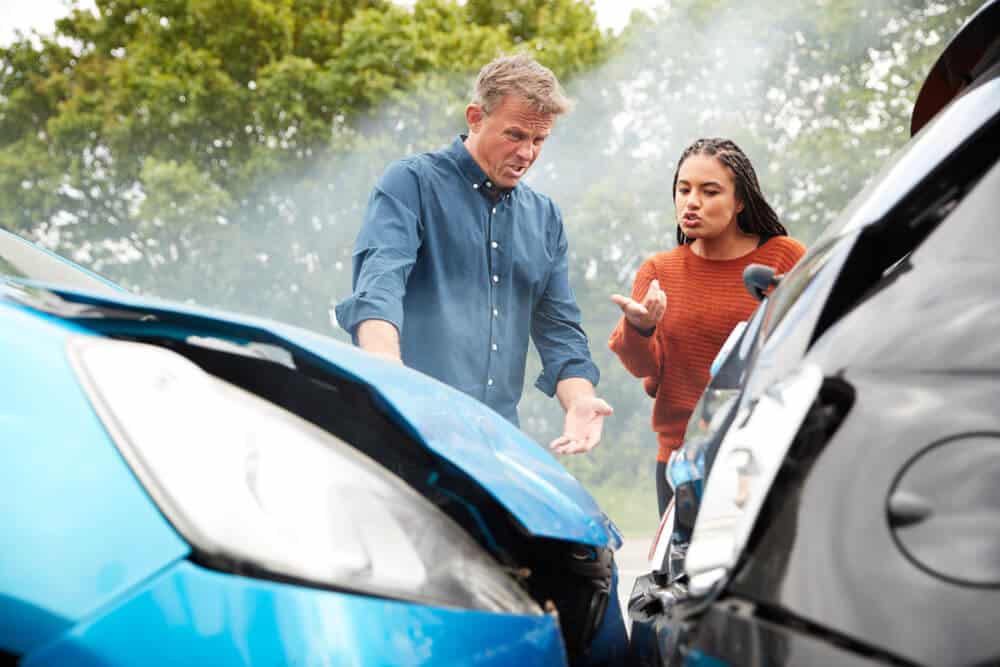

In the United States, most states require drivers to carry auto insurance to protect themselves and others from financial losses in case of an accident. However, there are a few states that do not mandate auto insurance coverage. This can lead to potential risks for drivers and other road users, as well as for the state’s financial system.
States Without Mandatory Auto Insurance
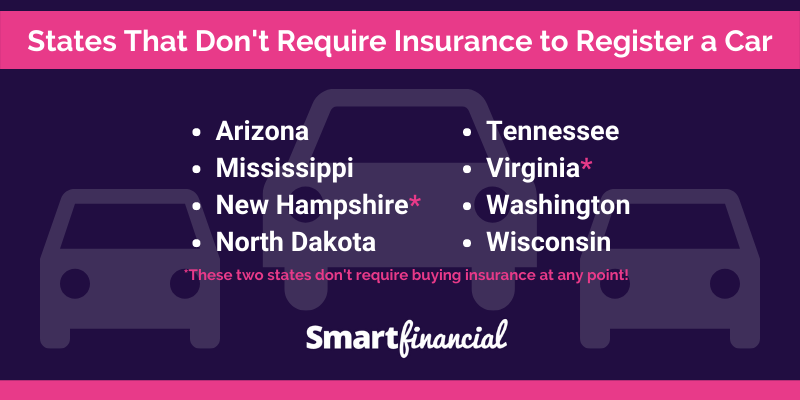
There are only two states in the US that do not require drivers to carry auto insurance:
- New Hampshire: New Hampshire is the only state that does not require any form of auto insurance. Instead, it relies on a system of financial responsibility laws. This means that drivers must prove they can pay for damages they cause in an accident.
- Virginia: Virginia does not require drivers to carry auto insurance, but it does require them to provide proof of financial responsibility. This can be done through a variety of means, such as carrying a surety bond, a certificate of self-insurance, or a deposit of cash or securities with the state.
Legal Basis for Exemption
- New Hampshire: The state’s legal basis for not requiring auto insurance stems from a long-standing belief in individual liberty and limited government intervention. The state’s legislature has consistently rejected attempts to introduce mandatory auto insurance laws, arguing that they are unnecessary and infringe on individual rights.
- Virginia: Virginia’s exemption from mandatory auto insurance is based on its history of relying on a system of financial responsibility laws. This system was established in the early 20th century to address concerns about uninsured drivers. The state’s legislature has maintained this system, believing it to be an effective way to ensure that drivers can pay for damages they cause.
Alternative Financial Responsibility Requirements
- New Hampshire: Drivers in New Hampshire must demonstrate their ability to pay for damages they cause in an accident. They can do this through a variety of means, including:
- Surety bond: A surety bond is a financial guarantee provided by a surety company that promises to pay damages up to a certain limit.
- Certificate of self-insurance: A certificate of self-insurance is issued to companies or individuals who have sufficient financial resources to cover their own liability.
- Cash deposit: Drivers can also deposit a certain amount of cash with the state to prove their ability to pay for damages.
- Virginia: Drivers in Virginia have several options to meet the financial responsibility requirements, including:
- Auto insurance policy: While not mandatory, drivers can choose to purchase auto insurance to meet the financial responsibility requirements.
- Surety bond: Similar to New Hampshire, drivers can purchase a surety bond to guarantee their ability to pay for damages.
- Certificate of self-insurance: Individuals or businesses with sufficient financial resources can obtain a certificate of self-insurance.
- Cash deposit: Drivers can deposit a certain amount of cash with the state to demonstrate their ability to pay for damages.
Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
- New Hampshire: While drivers are not required to carry auto insurance, they are still responsible for any damages they cause in an accident. If they cannot demonstrate their ability to pay for damages, they can face serious consequences, including:
- License suspension: Drivers who cannot prove financial responsibility may have their licenses suspended.
- Vehicle registration suspension: Their vehicle registration may also be suspended.
- Civil lawsuits: They could face civil lawsuits from injured parties or property owners.
- Criminal charges: In some cases, drivers who are involved in accidents and cannot prove financial responsibility may face criminal charges.
- Virginia: Similar to New Hampshire, drivers in Virginia who are involved in accidents and cannot prove financial responsibility face serious consequences, such as:
- License suspension: Their driver’s license may be suspended.
- Vehicle registration suspension: Their vehicle registration may be suspended.
- Civil lawsuits: They may be sued by injured parties or property owners.
- Criminal charges: In some cases, they could face criminal charges.
Financial Responsibility Laws in Non-Compulsory Insurance States
While some states require drivers to carry auto insurance, others rely on financial responsibility laws to ensure that drivers can cover the costs of accidents they cause. These laws are designed to protect victims of accidents and ensure that they can receive compensation for their injuries and damages.
Types of Financial Responsibility Laws
States without mandatory insurance typically use various financial responsibility laws to ensure drivers can cover accident-related costs. These laws often involve alternatives to traditional auto insurance, such as:
- Surety Bonds: Drivers can purchase a surety bond from a licensed surety company. This bond guarantees payment for damages up to a specific amount, typically $30,000 to $50,000, in case of an accident.
- Cash Deposits: Drivers can deposit a sum of money with the state, usually around $20,000 to $30,000, to demonstrate financial responsibility. This deposit serves as a guarantee for covering accident-related costs.
- Self-Insurance: Drivers with significant financial resources can apply for self-insurance certification. This allows them to demonstrate their ability to cover accident costs without purchasing traditional insurance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Alternatives to Traditional Auto Insurance
These alternatives to traditional auto insurance have both advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Lower Costs: Surety bonds and cash deposits can often be less expensive than traditional auto insurance, especially for drivers with good driving records and low risk profiles.
- Flexibility: These alternatives offer more flexibility than traditional insurance, allowing drivers to tailor their coverage to their specific needs and circumstances.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Coverage: These alternatives typically provide limited coverage compared to traditional auto insurance. For example, surety bonds and cash deposits may not cover all accident-related costs, such as medical expenses, lost wages, and property damage.
- Financial Risk: Drivers who choose these alternatives bear the financial risk of accidents. If they cause an accident, they are responsible for paying all damages out of their own pocket.
- Potential for Bankruptcy: In the event of a significant accident, drivers who choose these alternatives could face financial ruin if they are unable to cover the costs.
Enforcement of Financial Responsibility Laws
States with financial responsibility laws have mechanisms in place to enforce these requirements. Typically, these mechanisms involve:
- Proof of Financial Responsibility: Drivers are required to provide proof of financial responsibility, such as a surety bond, cash deposit, or self-insurance certification, when they register their vehicles.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Drivers who fail to comply with financial responsibility laws face penalties, such as fines, suspension of driving privileges, or vehicle impoundment.
- Accident Reporting Requirements: Drivers are required to report accidents to the state, even if they are not at fault. This allows the state to verify that drivers have met their financial responsibility obligations.
Potential Risks and Liabilities for Drivers
Drivers who choose alternatives to traditional auto insurance face several potential risks and liabilities:
- High Financial Risk: Drivers are responsible for covering all accident-related costs, even if the accident was not their fault. This could lead to significant financial hardship, especially in the event of a serious accident.
- Legal Liability: Drivers can be sued for damages resulting from accidents, even if they have met their financial responsibility requirements.
- Limited Legal Protection: Alternatives to traditional auto insurance may not provide the same legal protection as traditional insurance. For example, they may not cover legal fees or other expenses associated with defending a lawsuit.
Impact on Uninsured Motorists
In states without mandatory auto insurance, the absence of a financial safety net for accident victims can have significant repercussions for uninsured motorists. The lack of insurance can expose them to substantial financial burdens and legal complexities in the event of an accident.
Challenges in Recovering Compensation
The absence of mandatory insurance creates significant challenges for accident victims seeking compensation from uninsured drivers. Victims may face difficulties in identifying the at-fault driver, proving negligence, and obtaining financial resources to cover medical expenses, lost wages, and property damage. In the absence of insurance coverage, victims may have to pursue legal action against the uninsured driver, which can be a lengthy and expensive process.
The Role of Uninsured Motorist (UM) Coverage
While mandatory insurance may not be required in these states, many insurers offer optional uninsured motorist (UM) coverage. UM coverage protects policyholders in the event of an accident with an uninsured or underinsured driver. It acts as a safety net, providing financial compensation for damages and losses incurred in such accidents. However, the availability and extent of UM coverage vary depending on the insurer and the specific policy terms.
Real-World Examples
A real-world example highlights the challenges faced by uninsured motorists in states without mandatory insurance. In a recent case in [State Name], a pedestrian was struck by an uninsured driver while crossing the street. The pedestrian suffered severe injuries, requiring extensive medical treatment and rehabilitation. Due to the driver’s lack of insurance, the pedestrian faced significant financial hardship and had to navigate a complex legal process to seek compensation for their injuries.
Implications for the Insurance Industry
The absence of mandatory auto insurance in certain states significantly impacts the insurance industry, creating both challenges and opportunities. The lack of compulsory coverage alters the risk landscape for insurers, influencing their pricing strategies, coverage options, and risk management practices.
Impact on Insurance Rates and Coverage Options, Which states do not require auto insurance
In states without mandatory auto insurance, insurers face a higher risk of insuring drivers who may not be financially responsible. This increased risk is reflected in higher insurance premiums for drivers in these states. To mitigate this risk, insurers may offer limited coverage options, such as higher deductibles or reduced coverage limits, or they may decline to insure high-risk drivers altogether.
Public Safety Considerations

The absence of mandatory auto insurance in certain states raises concerns about public safety. While proponents of non-compulsory insurance argue that it promotes individual freedom and reduces costs, opponents emphasize the potential risks associated with uninsured drivers. This section delves into the potential impact of non-compulsory insurance on public safety, examining arguments for and against mandatory insurance in terms of road safety and exploring the potential consequences of increased uninsured driving.
The Relationship Between Insurance and Road Safety
The presence of mandatory auto insurance is widely believed to enhance road safety. This is primarily because insurance incentivizes drivers to be more responsible on the road. The financial burden of potential accidents, medical expenses, and property damage acts as a deterrent to reckless driving and encourages drivers to prioritize safety measures. Additionally, insurance coverage ensures that victims of accidents have access to financial compensation for medical expenses, lost wages, and property damage, mitigating the financial strain associated with accidents.
Arguments for Mandatory Insurance
- Financial Protection for Accident Victims: Mandatory insurance guarantees that victims of accidents have access to financial compensation, regardless of the driver’s financial status. This is crucial for ensuring that victims can cover medical expenses, lost wages, and property damage, preventing them from facing significant financial hardship.
- Reduced Uninsured Driving: By requiring all drivers to carry insurance, mandatory insurance policies significantly reduce the number of uninsured drivers on the road. This is because drivers who cannot afford insurance are less likely to drive, reducing the risk of accidents involving uninsured drivers.
- Deterrent to Reckless Driving: The financial consequences of accidents, including higher insurance premiums or even policy cancellation, serve as a deterrent to reckless driving. This incentivizes drivers to prioritize safety and reduce risky behaviors, contributing to a safer driving environment.
- Increased Road Safety: Studies have shown a strong correlation between mandatory insurance laws and reduced accident rates and fatalities. This is attributed to the factors mentioned above, such as reduced uninsured driving, increased financial responsibility, and a deterrent effect on reckless driving.
Arguments Against Mandatory Insurance
- Individual Freedom: Opponents of mandatory insurance argue that it infringes upon individual freedom, claiming that drivers should have the right to choose whether or not to purchase insurance. They believe that individuals should be responsible for their own choices and financial decisions, even if it means accepting the risks associated with driving without insurance.
- Increased Costs: Some argue that mandatory insurance increases the overall cost of driving, as insurance premiums are factored into the price of goods and services. They contend that this burden falls disproportionately on low-income individuals, who may struggle to afford insurance and face higher costs for essential goods and services.
Consequences of Increased Uninsured Driving
- Higher Accident Rates: Uninsured drivers are more likely to engage in risky driving behaviors, such as speeding, driving under the influence, and failing to maintain their vehicles. This increases the likelihood of accidents, leading to a higher number of collisions and injuries.
- Financial Strain on Accident Victims: When uninsured drivers are involved in accidents, victims often bear the financial burden of their injuries and property damage. This can result in significant financial hardship, especially for those who are unable to afford medical expenses or lost wages.
- Increased Costs for Insured Drivers: Uninsured drivers contribute to higher insurance premiums for insured drivers. This is because insurance companies must factor in the risk of accidents involving uninsured drivers, which increases their overall costs.
Evidence Supporting the Relationship Between Insurance and Road Safety
Numerous studies and research findings support the claim that mandatory insurance laws contribute to safer roads. For example, a study by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) found that states with mandatory insurance laws have significantly lower rates of uninsured drivers and lower accident rates than states without such laws. Additionally, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has reported that states with mandatory insurance laws experience lower rates of traffic fatalities and injuries. These findings demonstrate a strong correlation between mandatory insurance and improved road safety.
Economic Consequences
The absence of mandatory auto insurance in certain states carries significant economic implications, impacting healthcare costs, insurance premiums, and overall economic stability. These states face unique challenges in managing the financial fallout from uninsured motorists.
Impact on Healthcare Costs
The lack of mandatory auto insurance can lead to increased healthcare costs, particularly for those involved in accidents with uninsured drivers. When an uninsured motorist causes an accident, injured parties may be left to cover their medical expenses themselves, potentially leading to:
- Higher medical bills: Without insurance coverage, individuals are responsible for the full cost of their medical treatment, which can be substantial, especially in severe cases.
- Increased reliance on public healthcare: Uninsured individuals may rely on public healthcare systems, such as Medicaid, to cover their medical expenses, putting a strain on government resources.
- Financial burden on hospitals: Hospitals may be left to absorb the costs of treating uninsured patients, leading to higher healthcare costs for everyone.
Impact on Insurance Premiums
While states without mandatory auto insurance may have lower average insurance premiums, this can be misleading. The lack of mandatory insurance creates a higher risk pool, as it attracts individuals who may be less likely to purchase insurance due to financial constraints or risk tolerance. This can lead to:
- Higher premiums for insured drivers: Insurance companies may increase premiums for insured drivers to compensate for the higher risk of claims from uninsured motorists.
- Increased risk of insolvency: Insurance companies face a higher risk of financial instability if they are unable to adequately price their policies to account for the increased risk of claims from uninsured drivers.
- Limited availability of insurance: Some insurance companies may be hesitant to offer coverage in states without mandatory insurance, limiting choices for consumers.
Impact on Economic Stability
The economic consequences of non-compulsory insurance states can extend beyond individual finances and healthcare costs. These states may experience:
- Reduced economic activity: The increased risk and uncertainty associated with uninsured motorists can deter businesses from investing in these states, impacting economic growth and job creation.
- Higher litigation costs: The absence of insurance coverage can lead to more lawsuits, as injured parties seek compensation for their losses directly from uninsured drivers.
- Increased burden on taxpayers: The financial burden of uninsured motorist accidents may fall on taxpayers, as states may need to provide assistance to victims or cover costs associated with public healthcare.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, the debate over mandatory auto insurance is a multifaceted one with no easy answers. While the absence of mandatory insurance in certain states may seem like a cost-saving measure, it can have significant consequences for both individuals and the overall insurance landscape. Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to require auto insurance is a complex one that must be weighed carefully, taking into account the potential risks and benefits for all stakeholders.
Question Bank
What are the consequences of driving without insurance in a state that doesn’t require it?
Even in states without mandatory insurance, driving without financial responsibility can lead to serious consequences, including fines, license suspension, and even jail time. Additionally, if you cause an accident without insurance, you could be held personally liable for all damages, which could be substantial.
How can I ensure I’m financially protected if I live in a state without mandatory auto insurance?
If you live in a state that doesn’t require auto insurance, it’s crucial to explore your options for financial responsibility. You can choose to purchase traditional auto insurance, secure a surety bond, or self-insure. It’s important to carefully evaluate each option and choose the one that best suits your individual needs and financial situation.
Is it cheaper to drive without insurance in states that don’t require it?
While you might avoid the cost of insurance premiums, driving without insurance can be incredibly risky. In the event of an accident, you could face significant financial repercussions, including hefty legal fees and medical expenses. It’s generally not advisable to forgo insurance, even if it’s not legally required.







