Which state does not require auto insurance – In the vast landscape of American driving regulations, one state stands apart as a unique outlier: New Hampshire. This state doesn’t require drivers to carry auto insurance, a policy that has sparked debate and raised questions about financial responsibility and road safety.
While New Hampshire’s stance may seem unconventional, it’s rooted in a philosophy of personal freedom and individual responsibility. The state instead relies on a system of financial responsibility laws, requiring drivers to prove their ability to cover potential damages in case of an accident. This approach, however, presents a potential dilemma: while it allows for individual choice, it also carries the risk of leaving accident victims without adequate compensation.
States with No Mandatory Auto Insurance
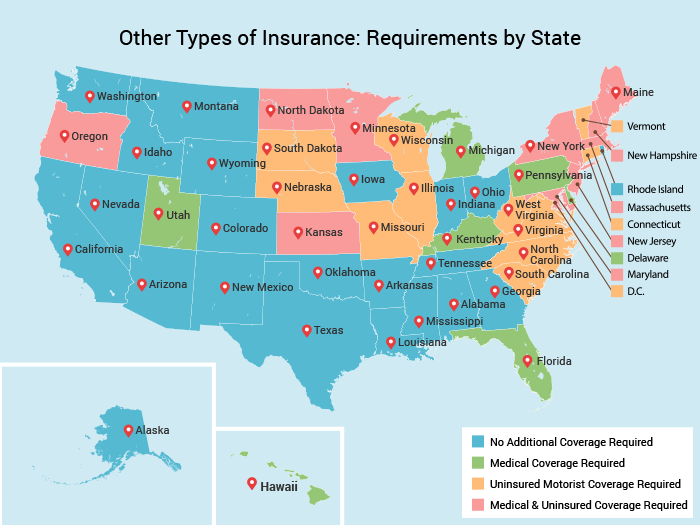
In the United States, most states mandate that drivers carry auto insurance to protect themselves and others from financial losses in the event of an accident. However, there are a few states that do not have this requirement.
States Without Mandatory Auto Insurance
These states have opted out of mandatory auto insurance for various reasons, including concerns about affordability, government intervention, and individual responsibility. The states that do not require drivers to carry auto insurance are:
- New Hampshire
- Virginia
Reasons for Not Mandating Auto Insurance
The decision of these states to forgo mandatory auto insurance stems from a combination of factors:
- Affordability Concerns: Some states argue that mandatory insurance requirements can burden low-income drivers with high premiums, making it difficult for them to afford to drive. They believe that individuals should be able to choose their own level of insurance coverage based on their financial situation.
- Government Intervention: Others believe that government mandates are an unnecessary intrusion into personal freedom and that individuals should be responsible for their own choices, including whether or not to purchase insurance. They argue that the free market can effectively address the issue of uninsured drivers without the need for government intervention.
- Individual Responsibility: Some states prioritize individual responsibility and believe that drivers should be held accountable for their actions, even if it means facing financial consequences for accidents they cause. They argue that mandatory insurance requirements can create a sense of entitlement and reduce personal accountability.
Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
While these states do not mandate auto insurance, it is important to understand the potential consequences of driving without it.
- Financial Liability: In the event of an accident, drivers without insurance are fully responsible for all damages and injuries they cause. This can include medical expenses, property damage, and lost wages. The financial burden can be substantial and potentially lead to bankruptcy.
- Legal Consequences: Depending on the state, driving without insurance can result in fines, license suspension, or even jail time. In some states, drivers may be required to pay a “financial responsibility” fee to reinstate their license.
- Difficulty Obtaining Coverage: Even if a driver decides to purchase insurance later, their lack of coverage history can make it difficult and expensive to obtain a policy. Insurance companies may consider them a high-risk driver and charge significantly higher premiums.
Financial Responsibility Laws in Non-Insurance States
States that do not require auto insurance typically have financial responsibility laws in place to ensure that drivers can cover the costs of accidents they cause. These laws aim to protect victims of accidents by ensuring that the responsible party can pay for damages, injuries, or other losses.
Differences from Mandatory Insurance Laws
Financial responsibility laws in non-insurance states differ from those in states with mandatory insurance in several key ways. Here are some of the most significant distinctions:
- Proof of Financial Responsibility: Instead of requiring drivers to maintain continuous auto insurance coverage, these states usually require drivers to demonstrate financial responsibility through other means. This can include providing proof of sufficient assets, posting a bond, or securing a surety bond.
- Triggering the Requirement: In states with mandatory insurance, the requirement is typically ongoing. However, in non-insurance states, the financial responsibility requirement is often triggered only after an accident or traffic violation. This means that drivers are not obligated to provide proof of financial responsibility until they are involved in an accident or receive a traffic ticket.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Penalties for failing to comply with financial responsibility laws can vary widely. Some states may suspend a driver’s license or registration, while others may impose fines or even jail time.
Effectiveness in Protecting Victims
The effectiveness of financial responsibility laws in protecting victims of accidents is a complex issue. While these laws aim to ensure that drivers can cover the costs of accidents they cause, their effectiveness can be limited by several factors:
- Lack of Continuous Coverage: Unlike mandatory insurance, financial responsibility laws do not require drivers to maintain continuous coverage. This means that a driver may not have the necessary financial resources to cover the costs of an accident if they have not met the financial responsibility requirements before the accident occurs.
- Limited Enforcement: The enforcement of financial responsibility laws can be challenging, especially in states with limited resources or a large number of uninsured drivers. This can lead to a situation where some drivers are able to avoid complying with the law and potentially leave victims without compensation.
- Potential for Higher Costs: In states with mandatory insurance, insurance companies spread the risk of accidents among all policyholders. However, in states with financial responsibility laws, victims may have to rely on the financial resources of the responsible party alone. This can result in higher costs for victims if the responsible party does not have sufficient assets to cover the damages.
Impact of No-Fault Insurance on Driving Habits
No-fault insurance is a system where drivers are compensated for their own injuries and damages, regardless of who caused the accident. This system contrasts with traditional fault-based insurance, where the at-fault driver’s insurance company covers the damages. In states without mandatory auto insurance, no-fault insurance may be a more common approach, as it can provide coverage for drivers who choose not to carry traditional insurance.
No-Fault Insurance Systems and Their Impact on Driving Habits
No-fault insurance systems have been implemented in various states, aiming to simplify the claims process and potentially reduce litigation costs. However, the impact of no-fault insurance on driving habits is a complex issue with both potential benefits and drawbacks.
Potential Benefits
- Reduced Litigation: No-fault systems aim to minimize litigation by removing the need to determine fault in every accident. This can lead to faster claim processing and reduced legal costs.
- Increased Coverage: No-fault insurance often provides coverage for medical expenses, lost wages, and other damages, regardless of who caused the accident. This can provide greater financial security for drivers, even if they are not at fault.
- Potential for Reduced Premiums: Some proponents of no-fault insurance argue that it can lead to lower insurance premiums, as the system eliminates the cost of fault determination and litigation.
Potential Drawbacks
- Increased Claims: No-fault systems may lead to an increase in the number of claims, as drivers may be more likely to file claims for minor injuries or damages. This could potentially increase insurance costs.
- Moral Hazard: Some argue that no-fault insurance creates a moral hazard, as drivers may be less careful if they know they will be compensated for their own injuries regardless of fault. This could lead to an increase in accidents.
- Limited Coverage for Serious Injuries: No-fault systems often have caps on the amount of coverage available for serious injuries. This can leave drivers with significant medical bills and other expenses if they are involved in a severe accident.
No-Fault Insurance in States Without Mandatory Insurance
In states without mandatory auto insurance, no-fault insurance may be more prevalent, as it can provide coverage for drivers who choose not to carry traditional insurance. However, the absence of mandatory insurance can lead to challenges in enforcing no-fault provisions and ensuring that drivers are adequately insured.
Impact on Driving Habits
- Increased Risk: The lack of mandatory insurance in these states may encourage drivers to take greater risks, as they may not be financially responsible for damages caused to others.
- Difficulty in Collecting Compensation: Victims of accidents involving uninsured drivers may face difficulties in collecting compensation for their injuries and damages, as there may be no insurance coverage to draw upon.
- Potential for Increased Costs: The presence of uninsured drivers can increase insurance costs for all drivers, as insurance companies need to account for the risk of uninsured drivers.
Potential Risks of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without insurance in states that do not require it comes with a range of significant risks. Not only can it leave you financially vulnerable in the event of an accident, but it can also lead to legal repercussions and damage your credit score.
Financial Risks
The financial risks of driving without insurance are substantial. In the event of an accident, you could be responsible for covering all the damages, including:
- Repair costs for your vehicle: Even if the accident was not your fault, you could be responsible for fixing your own vehicle if you are uninsured.
- Medical bills: If you or another driver is injured, you could be held liable for their medical expenses.
- Property damage: If you cause damage to another person’s property, you will be responsible for the repair or replacement costs.
- Lost wages: If you are unable to work due to an accident, you will not receive any compensation for lost income.
- Legal fees: If you are sued by the other party, you will be responsible for paying your own legal fees.
These costs can quickly add up, potentially leading to significant financial hardship.
Legal Consequences
Driving without insurance in a state that does not require it can still have serious legal consequences. Here are some examples:
- Fines and penalties: Most states have laws requiring drivers to prove financial responsibility, even if insurance is not mandatory. If you are involved in an accident and cannot demonstrate financial responsibility, you could face fines, license suspension, or even jail time.
- License suspension or revocation: If you are found to be driving without insurance after an accident, your driver’s license could be suspended or revoked.
- Criminal charges: In some states, driving without insurance can be considered a criminal offense, leading to fines, jail time, or both.
Impact on Credit Score and Future Insurance Premiums
Driving without insurance can also negatively impact your credit score and future insurance premiums. Here’s how:
- Negative marks on your credit report: If you fail to pay your debts from an accident, the unpaid bills could be reported to credit bureaus, potentially lowering your credit score.
- Higher insurance premiums: Even if you do not have an accident, driving without insurance can be viewed as a risk factor by insurance companies. When you eventually do decide to purchase insurance, you may face higher premiums than someone with a clean driving record and continuous insurance history.
Alternatives to Traditional Auto Insurance
Even without mandatory auto insurance, drivers in states without coverage requirements still need to protect themselves financially in case of accidents. Several alternative insurance options exist, offering varying levels of coverage and costs. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for making informed decisions about financial responsibility on the road.
Alternative Insurance Options
Here are some alternative insurance options available in states without mandatory auto insurance:
- Self-Insurance: This involves setting aside a significant sum of money to cover potential accident costs. This option is suitable for individuals with substantial financial resources and a high risk tolerance.
- Cash-Based Insurance: This type of insurance provides coverage in exchange for a lump sum payment upfront, often at a lower cost than traditional insurance. However, it offers limited coverage and may not be suitable for drivers with high accident risk.
- Ride-Sharing and Transportation Network Companies (TNCs): Some ride-sharing and TNC services offer insurance coverage for drivers while they are actively transporting passengers. This coverage may be limited to accidents occurring during rides, and drivers should carefully review the terms and conditions.
- Limited Liability Insurance: This option provides coverage for liability claims but does not cover damage to the insured vehicle. It is often cheaper than full coverage insurance and can be suitable for drivers with older vehicles or low financial risk.
- Short-Term Insurance: This type of insurance offers temporary coverage for a specific period, typically for a few days or weeks. It can be useful for occasional drivers or those needing temporary coverage for a specific event.
Cost and Benefits Comparison, Which state does not require auto insurance
Comparing the costs and benefits of alternative insurance options is crucial to determine the best fit for individual needs and circumstances.
| Option | Cost | Benefits | Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Insurance | High upfront cost | Full control over coverage and costs | High-income drivers with high risk tolerance |
| Cash-Based Insurance | Lower upfront cost | Limited coverage | Drivers with low accident risk and limited financial resources |
| Ride-Sharing/TNC Insurance | Variable cost | Coverage during rides | Ride-sharing drivers |
| Limited Liability Insurance | Lower cost than full coverage | Limited coverage | Drivers with older vehicles or low financial risk |
| Short-Term Insurance | Variable cost | Temporary coverage | Occasional drivers or those needing temporary coverage |
Suitability for Different Drivers
The suitability of each alternative insurance option varies depending on individual factors such as driving history, financial situation, and risk tolerance.
- High-risk drivers with a history of accidents or traffic violations may find it difficult to obtain traditional insurance at affordable rates and might consider alternatives like cash-based insurance or limited liability insurance.
- Drivers with older vehicles may find limited liability insurance or self-insurance suitable, as they may not need comprehensive coverage for their vehicle.
- Occasional drivers or those needing temporary coverage may find short-term insurance a cost-effective option.
- Ride-sharing drivers should consider the insurance coverage offered by their platform and may need additional insurance for situations outside of rides.
Final Review

Navigating the complexities of auto insurance requirements in the United States is essential for responsible driving. While New Hampshire’s unique stance offers a glimpse into alternative approaches, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks and implications associated with driving without insurance. Whether you’re a seasoned driver or a new motorist, being informed about your state’s regulations and the consequences of non-compliance is paramount for a safe and secure driving experience.
Questions and Answers: Which State Does Not Require Auto Insurance
What happens if I get into an accident in New Hampshire without insurance?
You could face significant financial consequences, including legal fees, medical bills, and repair costs. You may also be required to post a bond to cover potential future damages.
Is it cheaper to drive without insurance in New Hampshire?
While you won’t have to pay for insurance premiums, you’re essentially self-insuring, which means you’re responsible for all costs associated with an accident. In the long run, this could be much more expensive than having insurance.
Are there any other states that don’t require auto insurance?
Currently, New Hampshire is the only state in the US that doesn’t mandate auto insurance.







