What states require auto insurance? This question is crucial for anyone who owns or operates a vehicle in the United States. Across the country, laws mandate that drivers carry a minimum level of auto insurance to protect themselves and others in the event of an accident. This ensures financial responsibility and helps to mitigate the financial burden on individuals and families affected by collisions.
Understanding the legal requirements for auto insurance is essential for responsible driving. Each state has its own set of regulations, dictating the types and minimum amounts of coverage required. These requirements are designed to ensure that drivers have the financial resources to cover damages and injuries resulting from accidents they may cause. By complying with these laws, drivers contribute to a safer and more secure driving environment for everyone.
Legal Requirements for Auto Insurance
In the United States, all states except New Hampshire require drivers to have auto insurance. This requirement is based on the principle of financial responsibility, ensuring that drivers are financially prepared to cover the costs of accidents they may cause.
History of State-Level Auto Insurance Laws
The history of state-level auto insurance laws dates back to the early 20th century. The first state to enact a compulsory auto insurance law was Massachusetts in 1927. This law required drivers to prove financial responsibility, typically through the purchase of insurance. Following Massachusetts’s lead, other states gradually adopted similar laws, recognizing the need to protect the public from uninsured drivers.
- In the 1930s, several states enacted “financial responsibility laws” requiring drivers to demonstrate their ability to cover accident-related costs, often through proof of insurance or a bond.
- The 1940s saw a shift toward “compulsory insurance laws” that mandated drivers to purchase auto insurance, making it a legal requirement.
- By the 1960s, most states had adopted some form of compulsory auto insurance, establishing a framework for financial responsibility on the road.
Rationale Behind Requiring Auto Insurance
The rationale behind requiring auto insurance stems from a combination of factors:
- Protection for Accident Victims: Auto insurance provides financial protection to accident victims, covering medical expenses, property damage, and lost wages. Without insurance, victims may face significant financial hardship, potentially leading to legal action or bankruptcy.
- Financial Responsibility: Auto insurance promotes financial responsibility among drivers. By requiring drivers to purchase insurance, states ensure that drivers are prepared to cover the costs of accidents they may cause, preventing them from imposing financial burdens on others.
- Road Safety: Some studies suggest that mandatory auto insurance may contribute to safer roads by encouraging drivers to be more cautious. Knowing that they are financially responsible for accidents, drivers may be more likely to drive safely and avoid risky behaviors.
- Economic Stability: Mandatory auto insurance contributes to economic stability by reducing the number of uninsured drivers. Uninsured drivers are more likely to be involved in accidents and less likely to pay for damages, leading to higher costs for insured drivers. By requiring all drivers to be insured, states help stabilize the insurance market and prevent premiums from rising excessively.
States with Mandatory Auto Insurance

All states in the U.S. require drivers to carry auto insurance, with the exception of New Hampshire. However, even in New Hampshire, drivers are required to provide proof of financial responsibility in case of an accident.
The minimum coverage requirements vary from state to state. These requirements ensure that drivers are financially responsible for any damages or injuries they may cause to others in an accident.
Minimum Coverage Requirements
The table below Artikels the minimum coverage requirements for each state that mandates auto insurance.
| State Name | Liability Coverage | Property Damage Coverage | Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Alaska | $50,000 per person/$100,000 per accident | $25,000 | $50,000 per person/$100,000 per accident |
| Arizona | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $15,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Arkansas | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| California | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident | $5,000 | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident |
| Colorado | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $15,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Connecticut | $20,000 per person/$40,000 per accident | $10,000 | $20,000 per person/$40,000 per accident |
| Delaware | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident | $10,000 | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident |
| Florida | $10,000 per person/$20,000 per accident | $10,000 | $10,000 per person/$20,000 per accident |
| Georgia | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Hawaii | $20,000 per person/$40,000 per accident | $10,000 | $20,000 per person/$40,000 per accident |
| Idaho | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $15,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Illinois | $20,000 per person/$40,000 per accident | $15,000 | $20,000 per person/$40,000 per accident |
| Indiana | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Iowa | $20,000 per person/$40,000 per accident | $10,000 | $20,000 per person/$40,000 per accident |
| Kansas | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Kentucky | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Louisiana | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident | $10,000 | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident |
| Maine | $50,000 per person/$100,000 per accident | $25,000 | $50,000 per person/$100,000 per accident |
| Maryland | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident | $15,000 | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident |
| Massachusetts | $20,000 per person/$40,000 per accident | $5,000 | $20,000 per person/$40,000 per accident |
| Michigan | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Minnesota | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident | $10,000 | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident |
| Mississippi | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Missouri | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Montana | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Nebraska | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Nevada | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident | $10,000 | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident |
| New Hampshire | N/A (Financial Responsibility Required) | N/A | N/A |
| New Jersey | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident | $5,000 | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident |
| New Mexico | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| New York | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| North Carolina | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident | $25,000 | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident |
| North Dakota | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Ohio | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Oklahoma | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Oregon | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $20,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Pennsylvania | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident | $5,000 | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident |
| Rhode Island | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| South Carolina | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| South Dakota | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Tennessee | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $15,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Texas | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident | $25,000 | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident |
| Utah | $25,000 per person/$65,000 per accident | $15,000 | $25,000 per person/$65,000 per accident |
| Vermont | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Virginia | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $20,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Washington | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| West Virginia | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Wisconsin | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Wyoming | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
Visual Representation
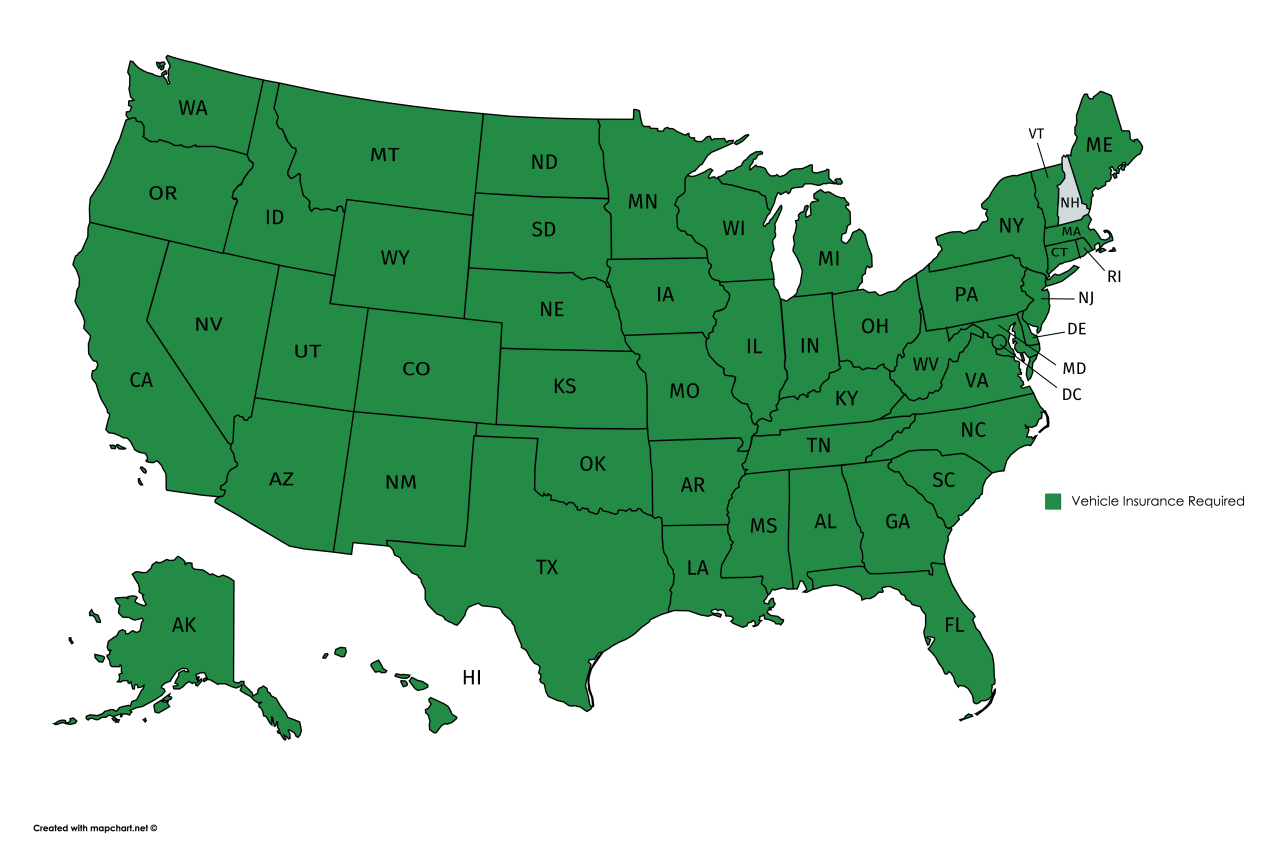
The map below illustrates the states with mandatory auto insurance requirements. The states shaded in blue require auto insurance, while New Hampshire (shaded in gray) requires proof of financial responsibility.
[Visual representation of a map of the United States with all states shaded in blue except for New Hampshire, which is shaded in gray.]
Exemptions and Exceptions to Auto Insurance Requirements
While most states mandate auto insurance, certain exemptions and exceptions exist. These exemptions are often granted to specific vehicle types, individuals, or situations. Understanding these exemptions is crucial for drivers, as failing to comply with insurance requirements can lead to penalties.
Exemptions Based on Vehicle Type
Some states exempt specific vehicle types from mandatory insurance requirements. This often applies to vehicles that are not typically driven on public roads, such as:
- Antique or classic cars: These vehicles are often exempt from insurance requirements if they are primarily used for exhibitions or special events and not for daily driving.
- Farm vehicles: Some states exempt farm vehicles used solely for agricultural purposes, such as tractors or combines, from mandatory insurance requirements.
- Construction equipment: Heavy equipment used for construction purposes may be exempt from insurance requirements if they are not driven on public roads.
It’s important to note that even if a vehicle is exempt from mandatory insurance, it’s still advisable to have some form of liability coverage to protect against potential accidents.
Exemptions Based on Individual Circumstances
In some cases, states may exempt individuals from mandatory insurance requirements based on specific circumstances. These exemptions may include:
- Financial hardship: Some states may allow drivers to apply for exemptions from insurance requirements if they can demonstrate financial hardship. This exemption may be granted on a case-by-case basis.
- Military service: Some states exempt active-duty military personnel from insurance requirements if they are stationed outside the state and their vehicles are not registered in the state.
- Age: Certain states may exempt drivers under a specific age from mandatory insurance requirements if they are driving a vehicle owned by a parent or guardian who has insurance coverage.
The criteria for these exemptions vary by state, and it’s important to consult with the relevant state agency for specific details.
Consequences of Driving Without Required Insurance
Driving without the required auto insurance can have severe consequences. Depending on the state, penalties may include:
- Fines: Drivers caught driving without insurance can face hefty fines, ranging from hundreds to thousands of dollars.
- License suspension: Driving without insurance can result in the suspension of your driver’s license. This can make it difficult to drive legally and may impact your ability to obtain employment or insurance in the future.
- Vehicle impoundment: Your vehicle may be impounded until you provide proof of insurance.
- Jail time: In some states, driving without insurance can lead to jail time, especially if you are involved in an accident.
- Increased insurance premiums: Even if you obtain insurance after being caught driving without it, you may face higher premiums due to your driving record.
It’s crucial to understand the insurance requirements in your state and ensure you have adequate coverage to avoid these penalties.
The Importance of Adequate Auto Insurance Coverage
Auto insurance is crucial for safeguarding yourself financially in the event of an accident, theft, or other unforeseen circumstances. It acts as a safety net, protecting you from potentially devastating financial losses. Having adequate coverage is not just a legal requirement but a wise financial decision.
Types of Auto Insurance Coverage
Different types of auto insurance coverage cater to various situations and provide financial protection for specific events. Understanding these coverage options allows you to choose the most suitable plan based on your individual needs and circumstances.
- Liability Coverage: This coverage is essential and covers damages caused to other people and their property in an accident for which you are at fault. It typically includes two types:
- Bodily Injury Liability: Covers medical expenses, lost wages, and other related costs for injuries caused to others in an accident.
- Property Damage Liability: Covers repairs or replacement costs for damage to another person’s vehicle or property.
- Collision Coverage: This coverage pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle if it is damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. Collision coverage is usually optional, but it is highly recommended for newer vehicles or those with significant loan balances.
- Comprehensive Coverage: This coverage protects your vehicle from damages caused by non-collision events such as theft, vandalism, natural disasters, or animal collisions. Comprehensive coverage is typically optional, but it can be crucial for protecting your investment in your vehicle.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: This coverage protects you if you are involved in an accident with a driver who has no insurance or insufficient insurance to cover your losses. It can help pay for your medical expenses, lost wages, and vehicle repairs.
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): This coverage, also known as no-fault insurance, covers your medical expenses and lost wages regardless of who is at fault in an accident. PIP is typically required in some states and can be a valuable addition to your policy.
Benefits of Adequate Auto Insurance Coverage
Having sufficient auto insurance coverage can provide peace of mind and financial security in various scenarios.
- Accidents: In case of an accident, liability coverage protects you from financial ruin by covering damages to other vehicles and injuries to others. Collision coverage helps with the repairs or replacement of your vehicle. If the other driver is uninsured or underinsured, uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage steps in to protect you.
- Theft: Comprehensive coverage protects you from financial losses if your vehicle is stolen. It can help cover the cost of replacing your vehicle or paying for the deductible on your policy.
- Natural Disasters: Comprehensive coverage can also help cover damages caused by natural disasters such as floods, earthquakes, or hailstorms.
Financial Impact of Inadequate Insurance Coverage
Insufficient auto insurance coverage can have severe financial consequences.
- High Out-of-Pocket Expenses: Without adequate coverage, you could be responsible for covering all medical expenses, vehicle repairs, and other costs related to an accident. This can lead to significant out-of-pocket expenses, potentially causing financial hardship.
- Legal Battles: If you are found liable for an accident, you may face lawsuits from the injured parties. Without adequate liability coverage, you could be forced to pay large settlements or judgments, potentially leading to bankruptcy.
- Loss of Your Vehicle: If your vehicle is damaged beyond repair or stolen, you may be left without transportation and responsible for replacing it. Without comprehensive coverage, you may have to bear the full cost of replacement.
Factors Influencing Auto Insurance Costs: What States Require Auto Insurance

Auto insurance premiums are calculated based on a variety of factors that assess the risk associated with insuring a particular driver and vehicle. These factors are designed to reflect the likelihood of an accident, the potential severity of the damage, and the overall cost of providing coverage.
Factors Affecting Insurance Costs, What states require auto insurance
Several key factors contribute to the cost of auto insurance. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions about their coverage and potentially reduce their premiums.
| Factor | Impact on Premium | Example | State-Specific Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Driving Record | Drivers with a clean driving record typically receive lower premiums. Accidents, traffic violations, and DUI convictions can significantly increase premiums. | A driver with multiple speeding tickets may face higher insurance rates compared to a driver with a spotless record. | Some states may have stricter penalties for certain offenses, leading to higher premiums. |
| Age | Younger drivers (especially those under 25) generally have higher premiums due to their inexperience and higher risk of accidents. Premiums tend to decrease with age as drivers gain experience. | A 18-year-old driver is likely to pay more for insurance than a 40-year-old driver with similar driving history. | Some states may offer discounts for young drivers who complete driver’s education courses or maintain good grades. |
| Vehicle Type | The make, model, and year of the vehicle can influence insurance costs. High-performance cars, luxury vehicles, and vehicles with a history of theft or accidents tend to have higher premiums. | A sports car may have a higher insurance premium than a compact sedan due to its higher repair costs and potential for higher speeds. | States may have different regulations regarding vehicle safety features, which can impact insurance rates. |
| Location | The geographic location where a vehicle is insured can significantly impact premiums. Areas with higher rates of accidents, theft, or vandalism typically have higher insurance costs. | A driver living in a densely populated urban area may face higher insurance rates than a driver living in a rural area. | States may have different laws regarding insurance coverage and minimum requirements, leading to variations in premiums. |
| Credit Score | In many states, insurance companies use credit scores as a factor in determining premiums. Drivers with good credit scores generally receive lower rates. | A driver with a credit score of 750 may receive a lower premium than a driver with a credit score of 550. | Some states have regulations that restrict the use of credit scores in insurance pricing. |
| Driving History | Drivers with a history of accidents or traffic violations are considered higher risk and typically pay higher premiums. | A driver who has been involved in a recent accident may see a significant increase in their insurance premiums. | States may have different rules regarding the duration of time that accidents and violations affect insurance rates. |
| Coverage Options | The type and amount of coverage selected can impact premiums. Higher coverage limits (e.g., higher liability limits) generally lead to higher premiums. | A driver who chooses comprehensive and collision coverage will likely pay more than a driver who only carries liability coverage. | States may have different minimum coverage requirements, which can influence the cost of insurance. |
| Driving Habits | Factors such as the number of miles driven, the purpose of driving (e.g., commuting, personal use), and driving habits (e.g., driving at night) can influence premiums. | A driver who commutes a long distance every day may pay more for insurance than a driver who primarily uses their vehicle for short trips. | Some insurance companies may offer discounts for drivers who use telematics devices to track their driving habits. |
Resources for Finding Auto Insurance Information
Navigating the world of auto insurance can be overwhelming, especially with the sheer number of insurance companies and coverage options available. Fortunately, there are reliable resources that can help you find the information you need to make informed decisions about your auto insurance.
State Insurance Departments
State insurance departments play a crucial role in regulating the insurance industry within their respective states. They provide valuable resources and information for consumers, including:
- Information on Auto Insurance Requirements: State insurance departments can provide detailed information about the specific auto insurance requirements in your state, including minimum coverage limits and types of coverage required.
- Complaints Against Insurance Companies: If you experience problems with your insurance company, you can file a complaint with the state insurance department. They investigate complaints and work to resolve issues between consumers and insurers.
- Consumer Guides and Resources: Many state insurance departments offer consumer guides and resources on various insurance topics, including auto insurance. These resources can help you understand your coverage options, compare different policies, and make informed decisions.
Consumer Protection Agencies
Consumer protection agencies, such as the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC), provide information and resources to help consumers understand and navigate the insurance industry. The NAIC, for instance, offers:
- Consumer Information and Resources: The NAIC website features a wealth of information on various insurance topics, including auto insurance. You can find guides, articles, and FAQs on issues like coverage options, claims procedures, and consumer rights.
- Consumer Complaint Database: The NAIC maintains a consumer complaint database where you can search for complaints filed against insurance companies. This information can help you identify potential problems with specific insurers.
- Model Laws and Regulations: The NAIC develops model laws and regulations that state insurance departments can adopt. These models help ensure consistency and consumer protection across state lines.
Comparing Insurance Quotes
Once you have a good understanding of your state’s auto insurance requirements and the coverage options available, it’s time to start comparing insurance quotes. Here are some tips for getting the best coverage at an affordable price:
- Get Quotes from Multiple Insurers: Don’t settle for the first quote you receive. Contact several insurance companies and compare their rates and coverage options.
- Use Online Comparison Tools: Many websites offer free online comparison tools that allow you to compare quotes from multiple insurers side-by-side.
- Consider Discounts and Bundling: Ask about discounts that may apply to your situation, such as safe driving discounts, good student discounts, or multi-policy discounts.
- Review Your Coverage Needs Regularly: Your insurance needs may change over time, so it’s essential to review your coverage periodically and make adjustments as necessary.
Checklist for Seeking Auto Insurance
Before you start shopping for auto insurance, consider these essential steps:
- Gather Your Information: Have your driver’s license, vehicle identification number (VIN), and other relevant information readily available.
- Determine Your Coverage Needs: Understand the minimum coverage requirements in your state and consider additional coverage options like collision, comprehensive, and uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage.
- Get Quotes from Multiple Insurers: Obtain quotes from at least three to five insurance companies to compare rates and coverage options.
- Compare Quotes Carefully: Pay attention to deductibles, premiums, and coverage limits when comparing quotes.
- Read Policy Documents: Before you finalize your policy, carefully review the policy documents to ensure you understand the terms and conditions.
Summary
Navigating the complexities of auto insurance can be daunting, but understanding the requirements in your state is crucial. Whether you’re a new driver or a seasoned veteran, staying informed about auto insurance laws is vital. By adhering to these regulations, you not only protect yourself financially but also contribute to a safer and more responsible driving community. Remember, driving without the required insurance can result in significant fines, license suspension, and even vehicle impoundment. Take the time to understand your state’s specific requirements and ensure you have adequate coverage to protect yourself and others on the road.
General Inquiries
How can I find out what the minimum auto insurance requirements are in my state?
You can find this information on your state’s Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) website or by contacting your state’s insurance department.
What happens if I get into an accident without the required auto insurance?
You could face significant penalties, including fines, license suspension, and even vehicle impoundment. You may also be held personally liable for any damages or injuries you cause.
Can I get a discount on my auto insurance if I have a clean driving record?
Yes, most insurance companies offer discounts for drivers with good driving records. This is a significant incentive to maintain safe driving habits.
What are some tips for finding affordable auto insurance?
Compare quotes from multiple insurance companies, consider increasing your deductible, and look for discounts for things like safety features, good driving records, and bundling your insurance policies.







