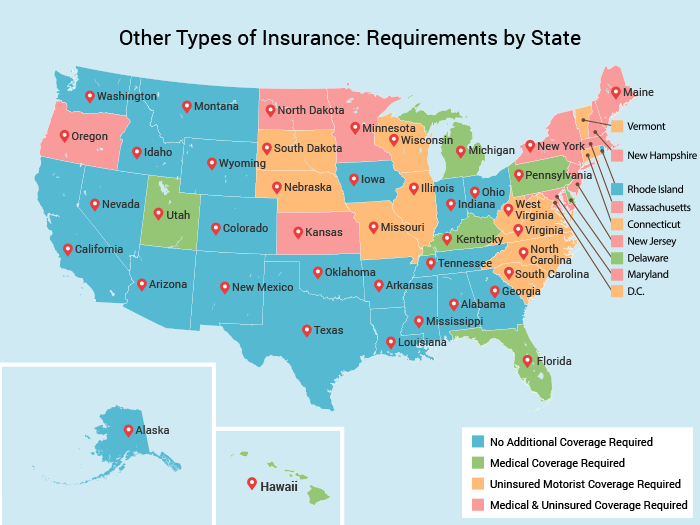
What states is car insurance not required? This question might surprise some, as most of us are accustomed to the idea that car insurance is a necessity. However, there are a handful of states in the United States that do not mandate car insurance for all drivers. While this might seem like a tempting option for some, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks and consequences of driving without insurance, as well as the legal implications involved.
The absence of mandatory car insurance in certain states is a reflection of the ongoing debate surrounding the role of government in regulating personal choices and the balance between individual liberty and public safety. These states often rely on financial responsibility laws, which require drivers to demonstrate their ability to cover damages in case of an accident, regardless of whether they have insurance. This approach can lead to a complex web of legal requirements and potential financial burdens for drivers who choose not to purchase car insurance.
States Without Mandatory Car Insurance: What States Is Car Insurance Not Required
While most states in the United States mandate car insurance, a few states do not have this requirement. This means that drivers in these states are not legally obligated to carry car insurance. However, this doesn’t mean that driving without insurance is risk-free. It is crucial to understand the legal implications and potential financial risks associated with driving without insurance in these states.
States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
Here is a list of states that do not require car insurance:
| State | Minimum Liability Coverage Requirements | Penalties for Driving Without Insurance | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|
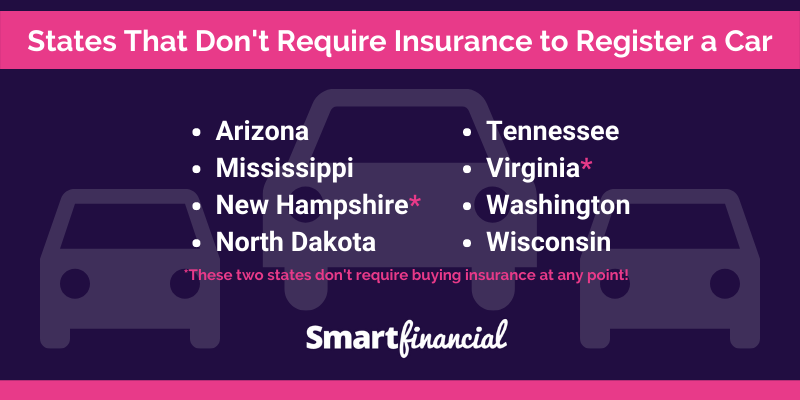
| New Hampshire | N/A | Drivers are required to prove financial responsibility in case of an accident, typically through a bond or cash deposit. | New Hampshire has a “financial responsibility” law, which means that drivers must be able to pay for damages they cause in an accident. They can fulfill this requirement by providing proof of insurance, posting a bond, or making a cash deposit. |
| Virginia | N/A | Drivers are required to carry a “financial responsibility” bond or certificate of self-insurance. | Virginia requires drivers to provide proof of financial responsibility, which can be achieved through a bond or certificate of self-insurance. |
Legal Implications of Driving Without Insurance in States Without Mandatory Coverage
Even though these states do not have a mandatory car insurance requirement, it is still highly advisable to carry insurance. Driving without insurance can have serious legal consequences, including:
- License Suspension: If you are involved in an accident and are found to be uninsured, your driver’s license can be suspended. This can make it impossible for you to legally drive.
- Fines and Penalties: You may face fines and penalties for driving without insurance, even if you are not involved in an accident. These penalties can vary from state to state.
- Jail Time: In some cases, driving without insurance can even lead to jail time, especially if you are involved in a serious accident.
Financial Risks and Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without insurance can expose you to significant financial risks and consequences. Here are some of the potential risks:
- Financial Responsibility: If you are involved in an accident, you will be fully responsible for covering all costs, including repairs, medical expenses, and lost wages, regardless of who is at fault.
- Legal Fees: If you are sued by the other party involved in the accident, you will be responsible for covering all legal fees, which can be substantial.
- Loss of Property: If you are involved in an accident and your vehicle is damaged, you will be responsible for covering the cost of repairs or replacement.
- Personal Bankruptcy: The financial burden of an accident without insurance can be overwhelming, potentially leading to personal bankruptcy.
Additional Considerations
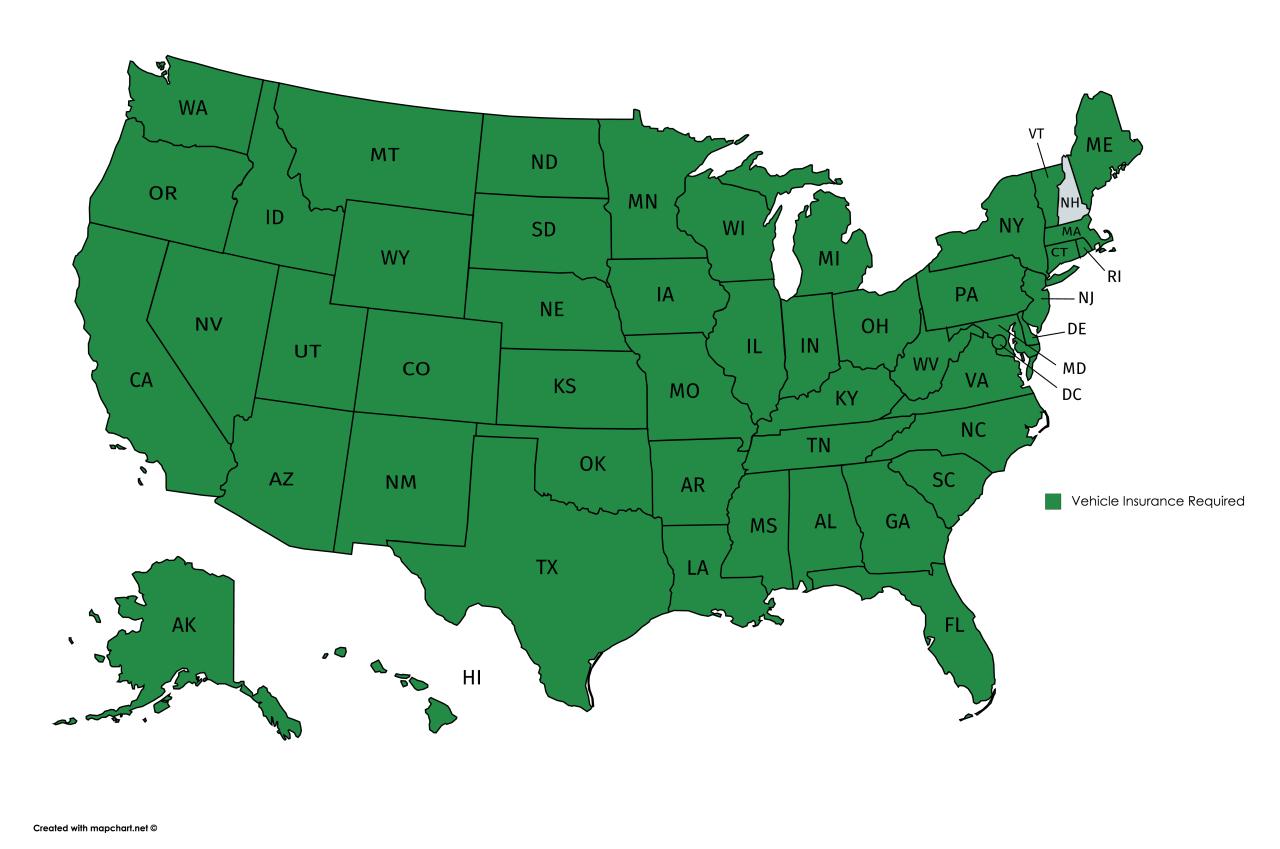
While states like New Hampshire and Virginia do not mandate car insurance, it is important to understand that they still have financial responsibility laws. These laws require drivers to be able to pay for damages they cause in an accident. Therefore, even in these states, it is highly advisable to carry insurance to protect yourself financially in case of an accident.
Financial Responsibility Laws
Financial responsibility laws are state regulations that require drivers to demonstrate their ability to pay for damages or injuries they might cause in a car accident. These laws are essential for ensuring that victims of car accidents receive compensation for their losses and for promoting road safety by deterring drivers who are unable or unwilling to cover potential liabilities.
Types of Financial Responsibility Laws
Financial responsibility laws in the United States generally fall into one of three categories:
- Financial Responsibility Insurance: This type of law requires drivers to carry a minimum amount of liability insurance, which covers damages and injuries caused to others in an accident. This is the most common type of financial responsibility law in the United States.
- Security Deposit: In some states, drivers can meet the financial responsibility requirement by providing a cash deposit or a bond, which acts as a guarantee that they can pay for damages in case of an accident. This option is less common than insurance.
- Proof of Financial Responsibility: These laws require drivers to provide proof of their ability to pay for damages, typically in the form of a certificate of insurance, a surety bond, or a self-insurance certificate. This proof is usually required when registering a vehicle or after an accident.
Enforcement of Financial Responsibility Laws
The enforcement of financial responsibility laws varies by state. Here are some common methods:
- Vehicle Registration: Most states require drivers to provide proof of insurance when registering their vehicles. If a driver fails to provide proof, they may be denied registration or have their registration suspended.
- Accident Reporting: Drivers involved in accidents are typically required to report the incident to the state. If a driver is found to be at fault and does not have insurance, they may face fines, license suspension, or other penalties.
- Financial Responsibility Forms: In some states, drivers may be required to file a financial responsibility form with the state after an accident, demonstrating their ability to pay for damages. Failure to do so can result in penalties.
Uninsured Motorist Coverage
Uninsured motorist coverage (UM) is an essential part of car insurance that protects you and your passengers in case you’re involved in an accident with a driver who doesn’t have insurance or doesn’t have enough insurance to cover your damages. It’s a safety net that helps you recover from the financial burden of accidents caused by negligent drivers.
Types of Uninsured Motorist Coverage
There are two main types of uninsured motorist coverage:
- Bodily Injury Coverage: This type of coverage pays for medical expenses, lost wages, and pain and suffering if you or your passengers are injured in an accident caused by an uninsured or underinsured driver.
- Property Damage Coverage: This coverage helps pay for repairs or replacement costs for your vehicle if it’s damaged in an accident caused by an uninsured or underinsured driver.
Situations Where Uninsured Motorist Coverage Can Be Beneficial
Here are some situations where uninsured motorist coverage can be vital:
- Hit-and-Run Accidents: When a driver hits your car and flees the scene, you might not be able to identify them or obtain their insurance information. UM coverage can help you recover your losses in such cases.
- Accidents with Drivers Who Have Minimal Coverage: If a driver has the minimum required insurance but it’s not enough to cover your medical expenses or vehicle damage, UM coverage can bridge the gap.
- Accidents with Drivers Who Are Uninsured: Many drivers operate vehicles without insurance. UM coverage protects you against financial ruin if you’re involved in an accident with such a driver.
Tips for Ensuring Adequate Uninsured Motorist Coverage
- Choose Coverage Limits That Reflect Your Needs: Consider the value of your vehicle and the potential medical expenses you might incur in case of an accident. You might need higher coverage limits if you have a newer car or live in an area with high medical costs.
- Review Your Coverage Regularly: Your insurance needs may change over time, especially if you acquire a new vehicle or your family situation changes. Ensure your UM coverage remains adequate to meet your current needs.
- Consider Underinsured Motorist Coverage: This coverage protects you if you’re involved in an accident with a driver who has insurance but not enough to cover your losses. Underinsured motorist coverage (UIM) is a valuable addition to your insurance policy.
Alternatives to Traditional Car Insurance
In states where car insurance isn’t mandatory, you have more options than just opting out entirely. Here are some alternatives to traditional car insurance that might be suitable for your situation.
Self-Insurance
Self-insurance means setting aside funds to cover potential costs associated with an accident, such as repairs, medical bills, or legal expenses. It’s often considered by individuals with a strong financial foundation and a low risk tolerance.
Advantages
- Potential Cost Savings: If you don’t file any claims, you can save money compared to paying premiums for traditional insurance.
- Control: You have complete control over how your funds are used.
Disadvantages
- High Risk: You are fully responsible for all costs associated with an accident, which could be significant.
- Financial Strain: A major accident could severely impact your finances.
- Limited Legal Protection: You might not have the same level of legal protection as traditional insurance in case of a lawsuit.
Cash-Based Insurance
Cash-based insurance involves paying a lump sum upfront for coverage. This is a popular option for drivers who want to avoid monthly premiums.
Advantages
- Lower Costs: Cash-based insurance can often be cheaper than traditional insurance, especially for drivers with a clean driving record.
- Flexibility: You can choose the level of coverage you need.
Disadvantages
- Large Upfront Payment: You need to have a significant amount of money available upfront.
- Limited Coverage: Cash-based insurance often provides limited coverage, such as liability only.
Membership-Based Insurance
Membership-based insurance programs offer coverage through a membership fee rather than traditional premiums. These programs often focus on specific groups of drivers, such as seniors or those with good driving records.
Advantages
- Lower Costs: Membership fees are typically lower than traditional premiums.
- Community Focus: Membership-based programs often offer additional benefits, such as discounts on car repairs or roadside assistance.
Disadvantages
- Limited Availability: Not all states have membership-based insurance programs.
- Limited Coverage: Coverage may be limited compared to traditional insurance.
Comparison Table
| Insurance Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Insurance | Potential cost savings, control | High risk, financial strain, limited legal protection |
| Cash-Based Insurance | Lower costs, flexibility | Large upfront payment, limited coverage |
| Membership-Based Insurance | Lower costs, community focus | Limited availability, limited coverage |
Choosing the Right Alternative
The best alternative for you will depend on your individual needs and circumstances. Consider your financial situation, driving history, and risk tolerance when making your decision. If you’re unsure, it’s always best to consult with a financial advisor or insurance professional.
Risks and Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without car insurance is a risky proposition that can lead to significant financial and legal repercussions. It’s crucial to understand the potential consequences to make informed decisions about your driving.
Financial Burdens
Driving without insurance can result in substantial financial burdens, especially if you’re involved in an accident. Here’s why:
- Medical Expenses: In case of an accident, you’ll be solely responsible for covering all medical expenses, including hospital bills, surgeries, and rehabilitation. These costs can easily reach tens of thousands of dollars, leaving you in a precarious financial situation.
- Property Damage: If you cause an accident, you’ll be responsible for repairing or replacing any damaged property, including the other vehicle, any personal property in the other vehicle, and any other property you may have damaged. These costs can also be significant, especially in the case of a serious accident.
- Legal Fees and Court Costs: You may face legal action from the other party involved in the accident. This can include lawsuits for damages and other legal fees, adding to your financial burden. In some cases, you may also be required to pay court costs and fines.
- Lost Wages: If you’re injured in an accident, you may be unable to work, resulting in lost wages. This can further exacerbate your financial difficulties.
Legal Liabilities, What states is car insurance not required
Driving without insurance can also lead to serious legal consequences. Here’s what you may face:
- Fines and Penalties: In most states, driving without insurance is a serious offense that can result in hefty fines, license suspension, and even jail time. These penalties vary by state and the severity of the offense.
- Criminal Charges: In some cases, driving without insurance can be considered a criminal offense, leading to criminal charges and a criminal record. This can have a significant impact on your future employment and life.
- Civil Lawsuits: Even if you’re not found criminally liable for an accident, you can still be sued in civil court for damages by the other party. This can result in a substantial financial judgment against you, which you may be unable to afford.
Real-Life Scenarios
The consequences of driving without insurance can be severe, as evidenced by numerous real-life cases. Here are some examples:
- A young driver, without insurance, was involved in a minor fender bender. While the damage was minimal, the other driver was seriously injured and required extensive medical treatment. The young driver was held liable for all medical expenses, totaling over $50,000. He faced a financial crisis and had to declare bankruptcy.
- A driver without insurance caused a major accident, resulting in significant property damage and injuries to multiple people. He was charged with reckless driving and multiple counts of driving without insurance. He faced hefty fines, a lengthy jail sentence, and civil lawsuits that drained his savings.
Mitigating Risks
While driving without insurance is not advisable, there are some steps you can take to mitigate risks:
- Consider High-Risk Insurance Options: If you can’t afford traditional car insurance, explore high-risk insurance options offered by some companies. These policies may be more expensive, but they provide some financial protection.
- Drive Safely and Defensively: Driving safely and defensively can reduce the likelihood of an accident, which can help you avoid the consequences of driving without insurance.
- Seek Legal Advice: If you’re facing legal action or have questions about your legal obligations, seek legal advice from a qualified attorney. They can help you navigate the legal system and protect your rights.
The Impact of Uninsured Drivers on Society
The presence of uninsured drivers on the road poses a significant threat to the well-being of individuals and the overall safety of communities. Their lack of financial responsibility creates a ripple effect, impacting not only accident victims but also the entire insurance system and healthcare infrastructure.
The Impact on Insurance Premiums
Uninsured drivers contribute to higher insurance premiums for everyone. When an uninsured driver causes an accident, the burden of covering the damages often falls on the insured party, leading to higher insurance claims. This, in turn, forces insurance companies to raise premiums for all policyholders to compensate for the increased risk.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, while some states do not mandate car insurance, it’s essential to understand the potential risks and consequences of driving without it. The absence of mandatory insurance doesn’t mean that drivers are absolved of responsibility for accidents they may cause. The financial burden and legal liabilities can be significant, and the impact on victims of accidents involving uninsured drivers can be devastating. Ultimately, responsible driving practices and ensuring adequate financial protection through insurance are crucial for safeguarding oneself, others, and the well-being of our communities.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the benefits of having car insurance even in states where it’s not mandatory?
Even in states without mandatory car insurance, having coverage provides crucial financial protection in case of accidents. It helps cover medical expenses, property damage, and legal fees, protecting you from potential financial ruin.
What are the different types of financial responsibility laws?
Financial responsibility laws can vary by state. Some require drivers to provide proof of financial responsibility, such as a bond or deposit, while others mandate minimum liability coverage. These laws aim to ensure that drivers can compensate for damages caused in accidents.
Can I be penalized for driving without insurance in a state where it’s not required?
While not all states require car insurance, you can still face penalties for driving without it. These penalties can include fines, license suspension, or even jail time if you’re involved in an accident and found liable.