What states don’t require auto insurance? This question is crucial for drivers who want to understand their legal obligations and the potential risks involved. While most states mandate auto insurance, a handful of states allow drivers to forgo coverage. These states have chosen to adopt a “financial responsibility” system, meaning drivers must prove they can cover the costs of an accident they might cause. However, this choice comes with significant financial and legal consequences, making it essential to weigh the pros and cons carefully.
The absence of mandatory insurance in these states can lead to a higher risk of uninsured drivers on the road. This lack of coverage can leave victims of accidents with substantial financial burdens, forcing them to bear the costs of their injuries and property damage. Additionally, driving without insurance in any state can result in hefty fines, license suspension, and even jail time, regardless of whether insurance is mandatory.
States Without Mandatory Auto Insurance: What States Don’t Require Auto Insurance
In the United States, most states require drivers to carry auto insurance. However, a few states have chosen to forgo this requirement, leaving drivers with the choice of whether or not to purchase insurance. This decision is based on various factors, including the state’s political climate, economic considerations, and the belief that individuals should have the freedom to choose whether or not to insure their vehicles.
States Without Mandatory Auto Insurance
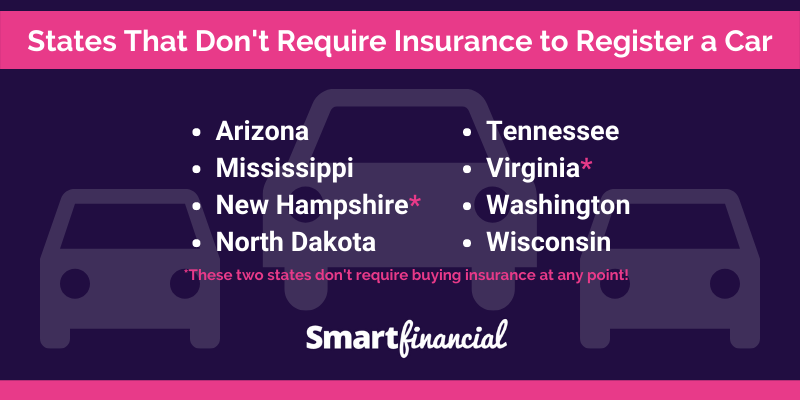
The following states do not require drivers to carry auto insurance:
- New Hampshire
- Virginia
Rationale for Not Requiring Auto Insurance
These states have chosen not to mandate auto insurance for a variety of reasons. Some argue that requiring insurance is an infringement on individual liberty, while others believe that it is an unnecessary government intrusion into the private lives of citizens. Additionally, some states believe that the cost of insurance is too high and that individuals should be free to choose whether or not to bear the financial risk associated with driving without insurance.
Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
While these states do not require drivers to carry insurance, it is important to understand that driving without insurance can have significant consequences.
Financial Liabilities
If you are involved in an accident while driving without insurance, you could be held financially responsible for all damages, including:
- Medical expenses for yourself and any other individuals involved in the accident
- Property damage to your vehicle and any other vehicles involved
- Lost wages due to time off work
- Legal fees associated with defending yourself against a lawsuit
In the absence of insurance, you would be personally responsible for covering these costs.
Legal Repercussions
Driving without insurance can also result in legal repercussions. Depending on the state, you could face:
- Fines and penalties
- Suspension of your driver’s license
- Imprisonment
These penalties can vary significantly from state to state.
“It is crucial to understand that even in states that do not require auto insurance, you are still financially and legally responsible for any damages or injuries you cause while driving.”
Financial Implications of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without insurance can have severe financial consequences, potentially leading to significant debt and financial hardship. The costs associated with an accident can quickly spiral out of control, leaving you with a heavy burden to manage.
Accident-Related Expenses
The costs of an accident without insurance can be substantial. You will be responsible for all medical bills, property damage, and other expenses related to the accident. These expenses can include:
- Medical Bills: Treatment for injuries sustained in an accident can be extremely expensive. These costs may include hospital stays, surgery, rehabilitation, and ongoing medical care.
- Property Damage: Repairing or replacing your vehicle and any other damaged property is your responsibility without insurance. This can include damage to the other vehicle, property, and even pedestrian injuries.
Legal Fees and Court Costs
Even if the accident is not your fault, you may still face legal fees and court costs. These expenses can include:
- Legal Representation: Hiring an attorney to represent you in court can be costly, especially if the case is complex or involves significant damages.
- Court Fees: Filing fees, witness fees, and other court-related expenses can quickly add up.
License Suspension and Fines
Driving without insurance is illegal in most states and can result in:
- License Suspension: Your driving privileges can be suspended, making it impossible to drive legally.
- Fines: You may face hefty fines, which can vary depending on the state and the severity of the offense.
Safety Considerations
Driving without insurance poses significant safety risks, not only for the uninsured driver but also for other road users. The absence of insurance can lead to dire consequences, both financially and physically, in the event of an accident.
Uninsured Drivers and Accident Involvement
Uninsured drivers are more likely to be involved in accidents. This is because they may be more inclined to engage in risky driving behaviors, such as speeding or driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs. Without the financial burden of insurance premiums, they may feel less pressure to drive safely.
Alternatives to Traditional Auto Insurance

In states without mandatory auto insurance, drivers have the option to explore alternative insurance arrangements to protect themselves financially in the event of an accident. These alternatives can offer varying levels of coverage, cost, and accessibility, allowing drivers to choose the option that best suits their individual needs and financial situation.
Self-Insurance
Self-insurance involves setting aside a specific amount of money to cover potential costs related to accidents, such as repairs, medical expenses, and legal fees. Drivers who choose this option assume full financial responsibility for any damages or injuries they may cause. This approach can be appealing for drivers with a strong financial history and a low-risk driving profile.
- Coverage: Self-insurance provides coverage only up to the amount of money set aside by the driver.
- Cost: Self-insurance can be less expensive than traditional insurance, as drivers avoid paying premiums. However, the cost of covering a major accident can be substantial.
- Accessibility: Self-insurance is accessible to anyone, but it requires a significant amount of financial discipline and a high level of risk tolerance.
Financial Responsibility Bonds
A financial responsibility bond is a type of insurance that provides financial protection for drivers who cannot obtain traditional insurance due to a poor driving record or other factors. This bond guarantees payment to the other party in case of an accident, up to a specific limit.
- Coverage: Financial responsibility bonds typically provide limited coverage, often covering only liability for property damage and injuries to others.
- Cost: The cost of a financial responsibility bond varies depending on the bond amount and the driver’s risk profile. It can be more expensive than traditional insurance.
- Accessibility: These bonds are typically available to drivers with a poor driving record or who have been denied traditional insurance.
High-Risk Insurance Plans, What states don’t require auto insurance
High-risk insurance plans are designed for drivers with a poor driving record, such as multiple accidents or traffic violations. These plans often have higher premiums and limited coverage compared to standard insurance policies.
- Coverage: High-risk insurance plans may offer limited coverage, with higher deductibles and lower limits on liability coverage.
- Cost: The cost of high-risk insurance is significantly higher than standard insurance, reflecting the increased risk associated with these drivers.
- Accessibility: These plans are specifically designed for drivers who have been denied standard insurance due to their driving history.
State-Specific Regulations and Exemptions
While some states have no mandatory auto insurance laws, they still have regulations in place to ensure financial responsibility for drivers. These regulations typically involve minimum financial responsibility requirements, exemptions for certain vehicle types, and penalties for driving without insurance.
Minimum Financial Responsibility Requirements
States without mandatory auto insurance typically require drivers to demonstrate financial responsibility, usually through proof of financial responsibility (e.g., insurance policy) or a surety bond. These requirements ensure that drivers have the financial resources to cover damages or injuries they may cause in an accident.
| State | Minimum Liability Coverage | Other Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| New Hampshire | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident for bodily injury, $25,000 for property damage | Drivers must provide proof of financial responsibility through an insurance policy, surety bond, or self-insurance |
| Virginia | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident for bodily injury, $20,000 for property damage | Drivers must provide proof of financial responsibility through an insurance policy or surety bond |
| Pennsylvania | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident for bodily injury, $5,000 for property damage | Drivers must provide proof of financial responsibility through an insurance policy or surety bond |
Exemptions for Specific Vehicle Types
Some states may exempt certain types of vehicles from mandatory insurance requirements. These exemptions often apply to vehicles used for specific purposes, such as farm vehicles or antique cars.
- New Hampshire exempts antique vehicles, farm vehicles, and vehicles used for specific purposes, such as transporting farm products or equipment.
- Virginia exempts antique vehicles and vehicles used for specific purposes, such as transporting farm products or equipment.
- Pennsylvania exempts antique vehicles, vehicles used for specific purposes, such as transporting farm products or equipment, and vehicles owned by government agencies.
Penalties for Driving Without Insurance
Driving without insurance in states that do not mandate coverage can result in significant penalties, including fines, license suspension, and even jail time. These penalties can vary depending on the state and the circumstances of the offense.
- New Hampshire: Fines of up to $500, license suspension, and potential jail time.
- Virginia: Fines of up to $500, license suspension, and potential jail time.
- Pennsylvania: Fines of up to $1,000, license suspension, and potential jail time.
Recommendations for Drivers in States Without Mandatory Insurance
Driving without insurance in states that do not require it presents significant financial risks. It is crucial to understand the potential consequences and explore strategies for mitigating those risks. This section will Artikel recommendations for drivers in these states, emphasizing the importance of financial protection and responsible driving practices.
Strategies for Mitigating Financial Risks
Drivers in states without mandatory auto insurance should prioritize strategies to minimize financial risks. This involves a comprehensive approach encompassing responsible driving habits, financial planning, and understanding potential liability.
- Practice Defensive Driving: Defensive driving techniques, such as maintaining a safe distance, anticipating potential hazards, and avoiding distractions, can significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents. This proactive approach minimizes the chances of incurring substantial financial burdens.
- Maintain a Clean Driving Record: A clean driving record with no traffic violations or accidents can help reduce insurance premiums if you choose to obtain coverage. This demonstrates responsible driving habits and may make you a more attractive candidate for insurance providers.
- Consider a High Deductible: A high deductible can lower your insurance premiums if you choose to obtain coverage. However, it’s essential to ensure you have the financial capacity to cover the deductible in case of an accident.
Ensuring Adequate Financial Protection
While states may not mandate auto insurance, drivers should still prioritize financial protection in case of an accident. This includes exploring options beyond traditional insurance, such as self-insurance, or creating a dedicated emergency fund.
- Self-Insurance: Self-insurance involves setting aside a substantial amount of money to cover potential accident costs. This approach requires careful financial planning and a high level of risk tolerance.
- Emergency Fund: Establishing a dedicated emergency fund specifically for potential accident costs can provide a safety net. Aim to accumulate enough funds to cover potential medical expenses, vehicle repairs, and other related expenses.
Resources for Obtaining Insurance Information and Assistance
Drivers in states without mandatory auto insurance can access resources to understand their options and make informed decisions about insurance coverage.
- State Insurance Departments: Contact your state’s insurance department for information about available insurance options, consumer protection laws, and potential penalties for driving without insurance.
- Insurance Agents and Brokers: Consult with insurance agents or brokers to explore different coverage options and compare rates. They can provide personalized guidance based on your individual circumstances.
- Consumer Advocacy Groups: Organizations like the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) and the Consumer Federation of America (CFA) provide information and resources on insurance matters.
Conclusive Thoughts
Navigating the complexities of auto insurance in states without mandatory coverage requires careful consideration. Drivers in these states must be fully aware of the financial and legal ramifications of driving without insurance. It’s crucial to explore alternative options, such as self-insurance, financial responsibility bonds, or high-risk insurance plans, to ensure adequate financial protection. Ultimately, responsible drivers in these states should prioritize safeguarding themselves and others by taking the necessary steps to secure appropriate coverage.
FAQ Guide
What happens if I get into an accident without insurance in a state that doesn’t require it?
Even in states without mandatory insurance, you’ll be held financially responsible for any damages or injuries you cause in an accident. This can include medical bills, property repairs, legal fees, and more. You could face significant financial hardship and even legal action.
Are there any exemptions for certain vehicle types in states without mandatory insurance?
Yes, some states may have exemptions for certain vehicle types, such as antique cars or vehicles used for specific purposes. However, these exemptions vary by state and require specific documentation.
Is it cheaper to drive without insurance in states that don’t require it?
While it may seem cheaper in the short term, driving without insurance in these states carries significant risks. You could face much higher costs in the long run due to potential accidents, legal fees, and fines.
How can I find out more about the specific regulations in my state?
You can visit your state’s Department of Motor Vehicles website or contact them directly for detailed information about auto insurance requirements and exemptions.







