What states do not require car insurance? This question might surprise some, as most of us assume car insurance is mandatory everywhere. However, a handful of states have chosen to forgo this requirement, leaving drivers with a choice to opt in or out. This decision has far-reaching consequences, affecting both the financial responsibility of drivers and the safety of our roads.
While these states might not mandate insurance, they still hold drivers accountable for their actions on the road. Financial responsibility laws ensure that drivers are prepared to cover damages and injuries they might cause. This often involves providing proof of financial responsibility through various means, like surety bonds or self-insurance. The lack of mandatory insurance, however, raises concerns about uninsured drivers and the potential for financial hardship in the event of an accident.
States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
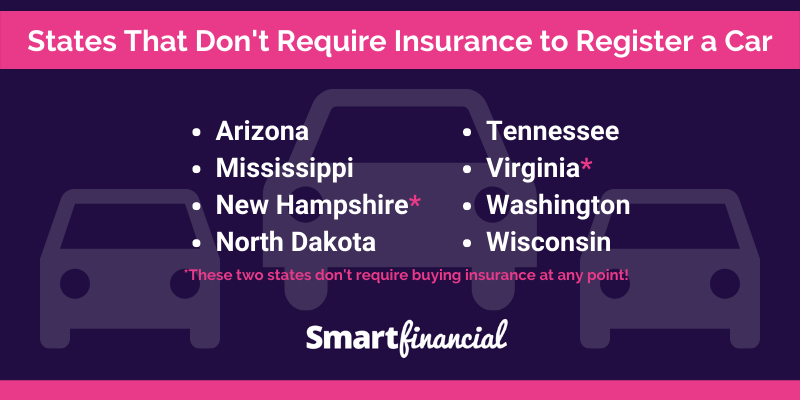
While most states in the U.S. mandate car insurance, a handful have opted for a different approach. These states do not require drivers to carry car insurance, which can seem like a significant advantage, but it’s essential to understand the potential consequences of driving without insurance in these states.
States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
These states do not have a mandatory car insurance requirement:
- New Hampshire
- Virginia
Rationale Behind the Decision, What states do not require car insurance
The rationale behind these states’ decisions to forgo mandatory car insurance is rooted in a combination of factors, including:
- Individual Freedom and Choice: These states believe that individuals should have the freedom to choose whether or not to purchase car insurance, arguing that it’s a personal financial decision. They see mandatory insurance as an infringement on individual liberty.
- Potential for Lower Insurance Costs: Proponents argue that the absence of a mandatory requirement could lead to lower insurance premiums for those who choose to purchase coverage, as insurance companies might offer more competitive rates in a less regulated market.
Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
While these states don’t mandate car insurance, it’s crucial to understand that driving without insurance can have serious consequences.
- Financial Responsibility: In the event of an accident, drivers without insurance are fully responsible for all damages and injuries they cause. This can result in substantial financial burdens, potentially leading to lawsuits, debt, and even bankruptcy.
- License Suspension: Even though these states don’t require insurance, they may still suspend the driver’s license if they are involved in an accident without insurance. This can significantly impact their ability to drive legally and could lead to additional fines and penalties.
- Higher Costs in the Long Run: While drivers might save on insurance premiums in the short term, the potential for significant financial losses due to an uninsured accident can far outweigh any short-term savings.
Financial Implications
The financial implications of not having car insurance in states that do not require it can be significant.
- Accident-Related Costs: In the event of an accident, drivers without insurance are fully responsible for all costs, including:
- Medical Expenses: Covering medical bills for injuries to themselves and others involved in the accident.
- Property Damage: Repairing or replacing damaged vehicles and other property.
- Legal Fees: Paying for legal representation if they are sued by the other party.
- Potential for Bankruptcy: The financial burden of an uninsured accident can be overwhelming, potentially leading to debt and even bankruptcy.
- Higher Insurance Rates in the Future: Even if drivers manage to avoid an accident, not having insurance can negatively impact their ability to obtain insurance in the future. Insurance companies might view them as higher-risk individuals and charge significantly higher premiums.
Financial Responsibility Laws in Non-Mandatory Insurance States
While some states require drivers to carry car insurance, others rely on financial responsibility laws to ensure drivers can cover the costs of accidents they cause. These laws are designed to protect victims of accidents by ensuring that the at-fault driver has the financial means to pay for damages.
Financial Responsibility Requirements
Financial responsibility laws in states without mandatory car insurance typically require drivers to demonstrate their ability to pay for damages resulting from accidents they cause. These requirements can vary from state to state but often include:
- Proof of Financial Responsibility: This can be shown through various means, such as:
- Car insurance policy: Even in states without mandatory insurance, drivers may choose to purchase a car insurance policy to fulfill this requirement.
- Surety bond: A surety bond is a guarantee issued by a surety company that ensures payment for damages up to a certain limit.
- Cash deposit: Some states allow drivers to deposit a specific amount of cash with the state to demonstrate financial responsibility.
- Self-insurance: In some cases, drivers with substantial assets may be able to self-insure, proving they have sufficient financial resources to cover potential liabilities.
- Minimum Financial Responsibility Limits: Each state sets minimum limits for the amount of coverage required. These limits typically include:
- Bodily injury liability: This covers injuries to others in an accident.
- Property damage liability: This covers damage to another person’s property in an accident.
- Uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage: This protects drivers in case they are hit by an uninsured or underinsured driver.
Comparison with Mandatory Insurance States
While states with mandatory insurance require drivers to purchase a minimum level of coverage, states with financial responsibility laws allow drivers to choose how to demonstrate their financial responsibility. This can offer flexibility but also carries a higher risk for drivers who choose not to purchase insurance.
| Requirement | States with Mandatory Insurance | States with Financial Responsibility Laws |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Mandatory minimum liability insurance | Proof of financial responsibility (insurance, bond, cash deposit, self-insurance) |
| Enforcement | Regular insurance checks and penalties for non-compliance | Enforcement primarily after an accident occurs |
| Risk | Lower risk for drivers as they are required to have insurance | Higher risk for drivers who choose not to purchase insurance, as they may be financially liable for damages in an accident |
Risks and Considerations for Drivers in Non-Mandatory Insurance States

Driving without insurance in states that do not require it presents significant risks and potential financial burdens. Even though these states do not mandate car insurance, drivers are still responsible for any damages or injuries they cause in an accident. This means that if you are involved in an accident without insurance, you could be held personally liable for all associated costs.
Financial Burdens
In the event of an accident, drivers without insurance may face substantial financial burdens. These can include:
- Medical expenses: If you injure someone in an accident, you could be responsible for their medical bills, including hospitalization, surgery, and rehabilitation.
- Property damage: You may be required to pay for repairs or replacement of the other vehicle, as well as any property damage, like a fence or building.
- Lost wages: If the other party is unable to work due to injuries, you could be liable for their lost wages.
- Legal fees: If the case goes to court, you will likely incur significant legal fees to defend yourself.
These costs can quickly add up, potentially leading to financial ruin.
Legal Consequences
Driving without insurance in non-mandatory insurance states can also have legal consequences.
- Civil lawsuits: The injured party can sue you for damages, potentially leading to a large judgment against you.
- License suspension: Even though insurance is not mandatory, many states have financial responsibility laws that require drivers to demonstrate proof of financial responsibility, often through insurance. Failing to comply can lead to license suspension or revocation.
- Criminal charges: Some states have laws that specifically criminalize driving without insurance. This could result in fines, jail time, or both.
Potential Risks
The potential risks associated with driving without insurance in states that do not require it are significant and can have far-reaching consequences. Here’s a table summarizing these risks:
| Risk | Financial Burden | Legal Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Accident causing injury or property damage | Medical expenses, property damage, lost wages, legal fees | Civil lawsuits, license suspension, criminal charges |
| Inability to afford necessary repairs or compensation | Financial ruin, potential bankruptcy | Civil lawsuits, license suspension, potential garnishment of wages |
| Lack of coverage for legal defense | High legal fees, potential unfavorable judgment | Civil lawsuits, license suspension, potential imprisonment |
Alternatives to Traditional Car Insurance: What States Do Not Require Car Insurance
In states that do not mandate car insurance, drivers have the option of exploring alternative insurance solutions to mitigate the financial risks associated with driving. These alternatives offer varying levels of coverage and protection, catering to different needs and budgets.
Self-Insurance
Self-insurance involves setting aside funds to cover potential costs related to accidents or damages. This approach allows drivers to avoid premium payments but requires significant financial discipline and a large emergency fund to handle unexpected expenses.
- Benefits: Potential for cost savings, control over financial decisions.
- Drawbacks: Requires substantial financial reserves, potential for significant financial losses in case of a major accident, limited coverage options.
Cash-Based Coverage
This option involves paying for repairs or damages out of pocket in the event of an accident. It is often preferred by drivers who have substantial savings or are willing to take on the risk of financial responsibility.
- Benefits: No premium payments, full control over financial decisions.
- Drawbacks: Requires significant financial resources, potential for substantial financial losses, limited protection against legal liabilities.
Limited Liability Coverage
This type of coverage provides protection against legal liabilities in case of an accident, but it does not cover damages to the insured vehicle. It is often a more affordable alternative to traditional insurance, offering basic protection without comprehensive coverage.
- Benefits: Lower premiums compared to traditional insurance, protection against legal liabilities.
- Drawbacks: Limited coverage, no protection for vehicle damages.
Ride-Sharing Programs
Some ride-sharing companies offer insurance coverage to their drivers, providing protection against accidents and liability claims. This option can be beneficial for drivers who frequently use ride-sharing services as a primary mode of transportation.
- Benefits: Potential for coverage while driving for ride-sharing services, may offer additional benefits like accident forgiveness.
- Drawbacks: Coverage is limited to ride-sharing activities, may have specific requirements or limitations.
Other Alternative Options
Other alternative insurance options may include:
- Umbrella Insurance: This type of insurance provides additional liability coverage beyond the limits of primary insurance policies, offering greater protection against significant financial losses in case of a major accident.
- Gap Insurance: This coverage protects against financial losses when the value of a vehicle is less than the outstanding loan balance after an accident or theft.
Impact of No-Fault Insurance Systems on Non-Mandatory Insurance States
No-fault insurance systems, which shift the focus from assigning blame to providing coverage for injuries, can have a significant impact on states that do not require car insurance. These systems can alter the financial responsibility requirements, potentially offering both advantages and disadvantages for drivers.
Financial Responsibility Requirements in No-Fault States
No-fault insurance systems typically establish a set of minimum coverage requirements for personal injury protection (PIP), which covers medical expenses and lost wages regardless of fault. These requirements replace or supplement traditional liability coverage, which compensates for damages caused to others. In states without mandatory car insurance, no-fault systems can introduce a layer of financial responsibility, even if the state does not mandate car insurance.
Benefits of No-Fault Insurance Systems in Non-Mandatory Insurance States
- Reduced Litigation: No-fault systems aim to streamline the claims process by eliminating the need to determine fault in minor accidents. This can lead to fewer lawsuits and quicker settlements, reducing legal costs and delays for everyone involved.
- Guaranteed Coverage for Injuries: Drivers are assured of coverage for their own medical expenses and lost wages, regardless of who caused the accident. This can provide peace of mind and financial security in the event of an accident.
- Potential Cost Savings: The streamlined claims process and reduced litigation can potentially lead to lower insurance premiums for drivers.
Drawbacks of No-Fault Insurance Systems in Non-Mandatory Insurance States
- Limited Coverage for Serious Injuries: No-fault systems often have caps on PIP benefits, which can leave drivers with significant out-of-pocket expenses for serious injuries.
- Increased Premiums for High-Risk Drivers: Drivers with a history of accidents or violations may face higher premiums in no-fault systems, as they are more likely to file claims.
- Potential for Abuse: Some drivers may be tempted to file fraudulent claims or exaggerate injuries to maximize their benefits.
Examples of States with No-Fault Systems and No Mandatory Car Insurance
- New Hampshire: New Hampshire is the only state that does not require any form of car insurance. However, drivers are required to provide proof of financial responsibility, which can be met through a surety bond, self-insurance, or a no-fault insurance policy.
Conclusive Thoughts
Navigating the world of car insurance can be complex, especially in states that don’t require it. Understanding the financial responsibility laws, the potential risks, and available alternatives is crucial for drivers in these states. While choosing not to purchase traditional car insurance might seem appealing, it’s essential to weigh the potential financial burdens and legal consequences. Ultimately, the decision comes down to personal risk tolerance and financial preparedness.
Questions and Answers
What happens if I get into an accident without car insurance in a state that doesn’t require it?
You could face significant financial repercussions, including paying for damages and injuries out of pocket. You might also be subject to legal action and penalties.
Is it cheaper to drive without car insurance in states that don’t require it?
It might seem cheaper in the short term, but the potential costs of an accident far outweigh any savings. Remember, you are still responsible for any damages or injuries you cause.
What are some alternative insurance options available in states without mandatory car insurance?
Some alternatives include self-insurance, surety bonds, and limited liability insurance policies. These options often have specific requirements and limitations.
What are the benefits of having car insurance even if it’s not mandatory?
Car insurance offers financial protection in case of an accident, helps cover medical expenses, and can provide legal representation. It also protects your assets and provides peace of mind.
Are there any states that are considering making car insurance mandatory?
Yes, some states are considering making car insurance mandatory due to concerns about uninsured drivers and the financial burdens on victims of accidents.







