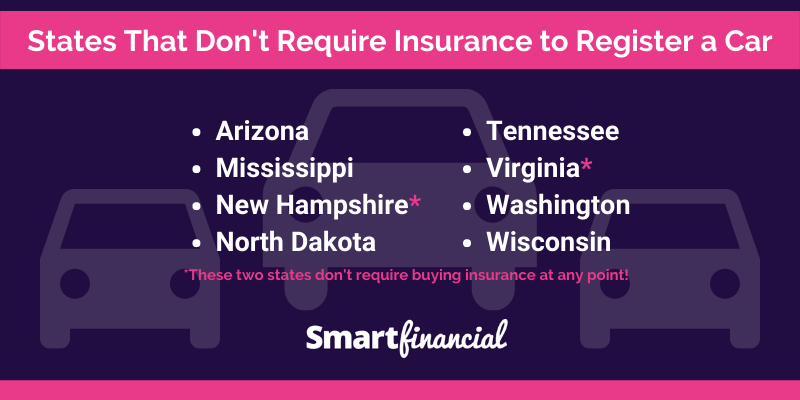
What states do not require auto insurance? This question may seem surprising, but in the United States, not every state mandates that drivers carry auto insurance. While most states have laws requiring drivers to prove financial responsibility, a handful have chosen a different approach. This decision has significant implications for drivers, insurance companies, and society as a whole.
The absence of mandatory auto insurance in certain states raises important questions about the balance between individual freedom and societal responsibility. These states rely on alternative mechanisms to ensure financial accountability for accidents, such as surety bonds or self-insurance. However, the potential consequences of driving without insurance in these states can be severe, leaving drivers vulnerable to significant financial hardship and potential legal repercussions.
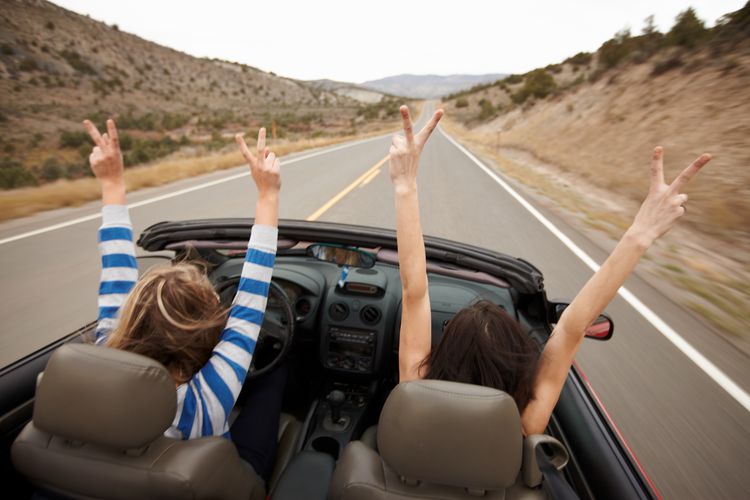
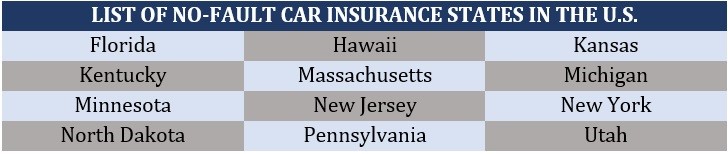
States Without Mandatory Auto Insurance
While most states in the U.S. require drivers to carry auto insurance, a handful of states do not mandate this requirement. This decision is rooted in a combination of factors, including philosophical beliefs about individual responsibility and the desire to minimize government intervention in personal affairs. However, choosing to drive without insurance in these states can have significant financial and legal repercussions, potentially leading to substantial out-of-pocket expenses and even criminal charges.
States Without Mandatory Auto Insurance
| State | Reason for No Requirement | Potential Consequences | Potential Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| New Hampshire | The state’s “financial responsibility law” requires drivers to demonstrate financial responsibility, but they can choose to do so through self-insurance or a surety bond instead of purchasing insurance. | Drivers without insurance who cause an accident could face significant financial liability, including medical bills, property damage, and legal fees. They may also be subject to fines, license suspension, and even jail time. | Drivers without insurance face a significant risk of financial ruin if they are involved in an accident. They may also be at a higher risk of being sued by the other party, and they could face difficulty obtaining future insurance coverage. |
| Virginia | Virginia’s “financial responsibility law” requires drivers to demonstrate financial responsibility, but they can choose to do so through self-insurance or a surety bond instead of purchasing insurance. | Similar to New Hampshire, drivers in Virginia without insurance who cause an accident could face substantial financial liability, including medical bills, property damage, and legal fees. They may also be subject to fines, license suspension, and even jail time. | Similar to New Hampshire, drivers without insurance face a significant risk of financial ruin if they are involved in an accident. They may also be at a higher risk of being sued by the other party, and they could face difficulty obtaining future insurance coverage. |
Financial Responsibility Laws in States Without Mandatory Insurance: What States Do Not Require Auto Insurance

Even though some states don’t require drivers to carry auto insurance, they still have laws in place to ensure financial responsibility in case of accidents. These laws aim to protect victims of accidents and ensure that they have access to compensation for their injuries and damages.
Types of Financial Responsibility Laws
These states have adopted various approaches to ensure financial responsibility. Here are some common methods:
- Surety Bonds: These bonds act as a financial guarantee. Drivers purchase a bond from an insurance company or a surety company. The bond promises to cover financial obligations in case of an accident. The amount of the bond varies depending on the state and can range from $10,000 to $50,000 or more.
- Self-Insurance: In some states, drivers can opt for self-insurance. This means they demonstrate the financial capacity to cover their own liability in case of an accident. They typically need to prove they have sufficient assets or income to meet potential financial obligations.
- Cash Deposits: Some states allow drivers to deposit a certain amount of money with the state government. This deposit acts as a guarantee for financial responsibility. The amount of the deposit varies depending on the state’s regulations.
- Proof of Financial Responsibility: Some states require drivers to provide proof of financial responsibility, such as a certificate of insurance from an insurance company. This ensures that drivers have a source of coverage in case of an accident.
Comparison of Financial Responsibility Laws
The specific requirements and enforcement mechanisms for financial responsibility laws vary across states. Some states might have stricter requirements, such as higher bond amounts or more stringent proof of financial responsibility, while others might have more lenient regulations.
For instance, New Hampshire, a state without mandatory insurance, requires drivers to provide proof of financial responsibility, which can be met through various options, including surety bonds, self-insurance, or a cash deposit. In contrast, Florida, another state without mandatory insurance, has a more comprehensive financial responsibility law that requires drivers to have a minimum amount of liability insurance coverage.
Enforcement of Financial Responsibility Laws
These laws are enforced through various mechanisms. If a driver is involved in an accident and fails to meet the financial responsibility requirements, they can face penalties, including:
- License Suspension: States can suspend the driver’s license until they meet the financial responsibility requirements. This ensures that drivers who are not financially responsible are prevented from driving on public roads.
- Registration Suspension: States can suspend the vehicle’s registration until the driver complies with the financial responsibility laws. This prevents uninsured vehicles from being driven on public roads.
- Fines and Penalties: Drivers who violate financial responsibility laws can be subject to fines and other penalties. These penalties act as a deterrent to encourage drivers to comply with the regulations.
The Impact of No Mandatory Auto Insurance on Drivers
In states without mandatory auto insurance, drivers face a unique set of challenges and risks. While they might save on premiums in the short term, the potential consequences of driving without insurance can be severe and financially devastating.
Financial Risks Without Insurance
Drivers without insurance in these states are essentially gambling with their financial security. In the event of an accident, they could be held personally liable for all damages, including:
- Medical expenses: If they cause injuries to others, they could be responsible for covering the victims’ medical bills, which can be substantial, especially in serious accidents.
- Property damage: If they cause damage to another person’s vehicle or property, they could be liable for repairs or replacement costs.
- Lost wages: If the accident results in a lawsuit, the driver could face significant financial losses due to legal fees and potential judgments against them.
- Legal fees: Even if the driver is not at fault, they may still incur legal expenses to defend themselves against claims.
The financial burden of these costs could be overwhelming for most drivers, potentially leading to bankruptcy or significant debt.
The Impact of No Mandatory Auto Insurance on the Insurance Industry
The absence of mandatory auto insurance in certain states presents unique challenges and opportunities for the insurance industry. While it might seem counterintuitive, these states can actually experience higher insurance premiums and more complex risk assessments.
Challenges for Insurance Companies in States Without Mandatory Auto Insurance
In states without mandatory auto insurance, insurance companies face several challenges in managing risk and ensuring profitability.
- Increased Risk of Uninsured Drivers: The lack of mandatory coverage means a higher probability of encountering uninsured drivers, increasing the risk of financial losses for insurance companies in case of accidents involving uninsured parties.
- Difficulty in Assessing Risk: Without mandatory coverage, it becomes more difficult for insurers to assess the risk profiles of drivers. This can lead to inaccurate pricing and potential losses for the company.
- Higher Claims Costs: The absence of mandatory coverage can result in more claims from uninsured drivers, leading to higher claims costs for insurance companies.
- Increased Fraud: The absence of mandatory coverage can make it easier for individuals to commit insurance fraud, as they may be less likely to have a valid insurance policy.
Strategies for Mitigating Risk in States Without Mandatory Auto Insurance, What states do not require auto insurance
To mitigate these risks, insurance companies in states without mandatory auto insurance employ various strategies.
- Higher Premiums: Insurance companies often charge higher premiums in states without mandatory coverage to compensate for the increased risk.
- Stricter Underwriting: Insurers may implement stricter underwriting criteria to assess the risk profiles of drivers more thoroughly. This can involve more comprehensive background checks, driving record reviews, and credit score analysis.
- Risk-Based Pricing: Insurance companies may use sophisticated risk-based pricing models to tailor premiums to individual drivers based on their specific risk factors. This can include factors like age, driving history, vehicle type, and location.
- Uninsured Motorist Coverage: Insurers may offer uninsured motorist coverage as an optional add-on to their policies. This coverage protects policyholders in case they are involved in an accident with an uninsured driver.
Insurance Claim Trends and Payouts in States Without Mandatory Auto Insurance
While data on insurance claim trends and payouts in states without mandatory auto insurance can vary depending on the specific state and insurer, general trends suggest that these states may experience higher claim costs and payouts.
- Higher Claims Frequency: Studies have shown that states without mandatory auto insurance tend to have higher rates of uninsured drivers, leading to an increased frequency of claims involving uninsured parties.
- Increased Average Claim Costs: The absence of mandatory coverage can lead to higher average claim costs as insurers may have to cover the costs of damages caused by uninsured drivers.
The Impact of No Mandatory Auto Insurance on Society
The absence of mandatory auto insurance in certain states has far-reaching consequences that extend beyond individual drivers. It creates a ripple effect, impacting various aspects of society, including healthcare, legal systems, and community well-being.
Increased Healthcare Costs
The lack of mandatory insurance can lead to higher healthcare costs for everyone. When uninsured drivers are involved in accidents, they are less likely to be able to cover their medical expenses. This burden often falls on hospitals, taxpayers, and those with health insurance, who end up paying for the uninsured through higher premiums and taxes. A study by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) found that uninsured motorists are more likely to be involved in fatal crashes, leading to increased healthcare costs for treating severe injuries.
Increased Litigation and Legal Disputes
The absence of mandatory insurance can also lead to an increase in litigation and legal disputes. When an uninsured driver is at fault in an accident, the injured party may have to pursue legal action to recover damages. This can be a lengthy and expensive process, and it can also strain the judicial system. Furthermore, the absence of insurance can complicate settlements and lead to protracted legal battles, further burdening the legal system and creating financial strain on both parties involved.
Impact on Communities
The lack of mandatory auto insurance can also have a negative impact on communities. Uninsured drivers are more likely to flee the scene of an accident, leaving victims without compensation for their injuries and property damage. This can create a sense of insecurity and distrust within communities. Additionally, uninsured drivers are more likely to be involved in hit-and-run accidents, which can have devastating consequences for victims and their families. For example, in states without mandatory insurance, uninsured drivers are more likely to be involved in accidents that result in fatalities, leaving families to grapple with the loss of a loved one and the financial burden of funeral expenses and medical bills.
Concluding Remarks
The debate surrounding mandatory auto insurance is complex and multifaceted. While some states choose to forgo mandatory coverage, the potential risks and consequences for drivers and society at large remain significant. Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to require auto insurance is a matter of public policy, with far-reaching implications for individuals, businesses, and the overall well-being of communities.
Questions Often Asked
What are the benefits of having car insurance even if it’s not required?
Even if a state doesn’t mandate car insurance, it’s highly advisable to have it. Insurance provides financial protection in case of an accident, covering costs like repairs, medical bills, and legal expenses. It can also help protect your assets and prevent significant financial hardship.
What happens if I get into an accident in a state that doesn’t require car insurance?
If you’re involved in an accident in a state without mandatory insurance, you could be held personally liable for damages. This means you could be sued and forced to pay for repairs, medical bills, and other expenses out of your own pocket. It’s essential to understand the financial responsibility laws in place in each state you drive in.
Are there any exceptions to the no-insurance requirement in these states?
While some states don’t require insurance, they often have exceptions for specific situations, such as commercial vehicles, rental cars, or vehicles used for certain types of transportation. It’s crucial to check with your state’s Department of Motor Vehicles for the most up-to-date information.







