What state doesn’t require car insurance? It might surprise you to learn that there is actually one state in the US that doesn’t mandate car insurance for all drivers. While most states have strict insurance requirements, this unique exception offers a glimpse into a different approach to driver responsibility and financial risk.
The absence of mandatory car insurance in this state raises questions about the potential consequences for drivers and the overall impact on road safety. We’ll explore the reasons behind this exemption, delve into the legal and financial implications, and consider alternative forms of coverage available to drivers in this state. This exploration will shed light on the complexities of balancing individual freedom with the need for responsible driving practices.
States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
In the United States, most states mandate that drivers carry car insurance to protect themselves and others from financial ruin in the event of an accident. However, a few states do not have this requirement. Understanding the legal implications and financial risks associated with driving without insurance in these states is crucial for responsible driving.
States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
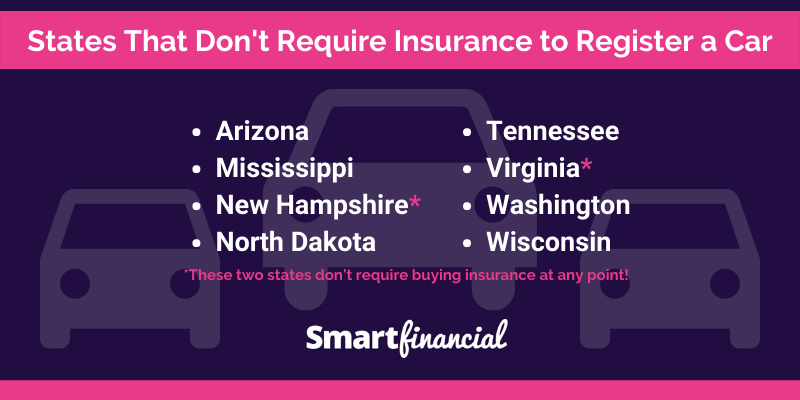
While most states in the US require drivers to carry car insurance, a few states do not have this mandate. These states are:
- New Hampshire
- Virginia
Legal Implications of Driving Without Insurance
In states without mandatory car insurance, drivers are not legally obligated to carry insurance. However, this does not mean they are exempt from financial responsibility in case of an accident. In these states, drivers are still required to demonstrate financial responsibility to cover potential damages.
For instance, in New Hampshire, drivers must provide proof of financial responsibility through a surety bond, a certificate of self-insurance, or a deposit of cash or securities.
This means that even without insurance, drivers can be held financially liable for damages caused to others or their property in an accident.
Financial Risks of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without insurance in states that do not mandate it can lead to significant financial risks.
If you are involved in an accident and are found at fault, you could be held liable for all damages, including medical expenses, property damage, and lost wages.
This could result in substantial financial hardship, potentially leading to bankruptcy or the loss of your assets.
Furthermore, driving without insurance can lead to legal penalties, such as fines, suspension of your driver’s license, or even imprisonment.
Reasons for No Mandatory Insurance
The absence of mandatory car insurance in certain states is a result of a complex interplay of historical, economic, and political factors. While some states have embraced mandatory insurance as a way to protect drivers and ensure financial responsibility, others have chosen a different path, opting for a more individualistic approach.
Historical Factors
The absence of mandatory car insurance in some states can be traced back to the early days of automobile ownership. In the early 20th century, car ownership was relatively uncommon, and accidents were less frequent. As a result, there was less pressure to implement mandatory insurance requirements. Additionally, some states, particularly in the South, had a strong tradition of individual responsibility and limited government intervention, which influenced their approach to car insurance.
Economic Factors
Economic considerations also play a role in the absence of mandatory car insurance. Some states argue that mandatory insurance would increase the cost of car ownership, particularly for low-income drivers. They believe that a more flexible system, where individuals can choose their own level of coverage, is more equitable.
Arguments for and Against Mandatory Car Insurance
Arguments for Mandatory Insurance
- Protects Uninsured Victims: Mandatory car insurance ensures that victims of accidents caused by uninsured drivers have access to compensation for medical expenses, lost wages, and property damage.
- Promotes Financial Responsibility: By requiring drivers to carry insurance, states encourage financial responsibility and discourage reckless driving.
- Reduces Uninsured Motorist Rates: Mandatory insurance laws help reduce the number of uninsured drivers on the road, leading to safer roads and fewer accidents.
Arguments Against Mandatory Insurance
- Increased Costs: Mandatory insurance can increase the cost of car ownership, particularly for low-income drivers.
- Government Overreach: Some argue that mandatory insurance is an example of government overreach, as it infringes on individual liberty and freedom of choice.
- Increased Insurance Premiums: The presence of mandatory insurance can lead to higher insurance premiums for all drivers, even those who are responsible and have a clean driving record.
Impact of No Mandatory Insurance
The absence of mandatory car insurance has had a mixed impact on states that have chosen not to implement it. Some states have seen an increase in uninsured motorists, which can lead to higher costs for insured drivers and a greater burden on the healthcare system. Others have experienced a more stable insurance market, with drivers choosing coverage levels that best suit their needs and financial situations.
Financial Responsibility Laws
Even though some states don’t require car insurance, they still have financial responsibility laws in place to ensure drivers can cover the costs of accidents they cause. These laws are designed to protect the public from financially irresponsible drivers.
Financial responsibility laws require drivers to demonstrate they can pay for damages they may cause to others in an accident. This can be done through purchasing car insurance, providing proof of financial responsibility like a surety bond or self-insurance, or demonstrating sufficient assets to cover potential damages.
Minimum Financial Responsibility Requirements
Each state without mandatory insurance sets minimum financial responsibility requirements that drivers must meet. These requirements usually include minimum limits for bodily injury liability, property damage liability, and uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage. These limits vary by state and are designed to cover basic costs associated with accidents, such as medical expenses, property damage, and lost wages.
- New Hampshire: Drivers must provide proof of financial responsibility for at least $25,000 per person and $50,000 per accident for bodily injury liability and $25,000 for property damage liability.
- Virginia: Drivers must have at least $25,000 per person and $50,000 per accident for bodily injury liability, $20,000 for property damage liability, and $20,000 for uninsured motorist coverage.
Consequences of Failing to Meet Financial Responsibility Requirements
Failing to meet these requirements can result in serious consequences, including:
- License Suspension: The state can suspend a driver’s license if they fail to provide proof of financial responsibility. This means they are not legally allowed to drive until they comply with the law.
- Vehicle Registration Suspension: In some cases, the state can also suspend the registration of a vehicle if the owner fails to meet financial responsibility requirements. This means the vehicle cannot be driven legally on public roads.
- Financial Penalties: Drivers who fail to meet financial responsibility requirements may also face fines and penalties. These penalties can vary by state and are designed to deter drivers from violating the law.
- Legal Liability: If a driver is involved in an accident and does not have proof of financial responsibility, they can be held personally liable for all damages caused, including medical expenses, property damage, and lost wages. This can result in significant financial burdens, including lawsuits and judgments.
Alternative Forms of Coverage

While some states do not mandate car insurance, it is still highly advisable to have some form of coverage. Driving without insurance can lead to significant financial burdens in the event of an accident. Fortunately, several alternative forms of coverage are available to drivers in these states, offering protection without the strict requirements of traditional insurance policies.
Self-Insurance
Self-insurance involves setting aside funds to cover potential costs related to accidents, such as repairs, medical expenses, and legal fees. This option is often considered by individuals who are confident in their driving abilities and have a substantial financial cushion.
Benefits
- Cost Savings: Self-insurance can be more cost-effective than traditional insurance policies, especially for individuals with a clean driving record and low-risk vehicles.
- Flexibility: Self-insurance allows drivers to control their coverage and adjust their financial reserves based on their individual needs and circumstances.
Drawbacks
- Financial Risk: Self-insurance exposes drivers to significant financial risks in the event of a major accident. They are responsible for covering all costs, which could potentially exceed their savings.
- Lack of Legal Protection: Self-insurance does not provide the same legal protection as traditional insurance. If a driver is found liable for an accident, they could be held personally responsible for damages and legal fees.
Cash Surety Bonds
Cash surety bonds provide a financial guarantee that a driver will be able to pay for damages or injuries caused by an accident. A driver purchases a bond from a surety company, which acts as a guarantee for the driver’s financial responsibility. If the driver is involved in an accident, the surety company will pay the claims up to the bond amount.
Benefits
- Lower Premiums: Cash surety bonds typically have lower premiums than traditional insurance policies, as they do not cover the same range of risks.
- Financial Security: The bond provides a financial guarantee, ensuring that the driver can pay for damages or injuries in the event of an accident.
Drawbacks
- Limited Coverage: Cash surety bonds only cover financial responsibility, and do not provide protection for personal injuries or property damage.
- Bond Amount: The amount of the bond must be sufficient to cover potential damages, which can be substantial in the event of a serious accident.
Other Coverage Options
Beyond self-insurance and cash surety bonds, drivers in states without mandatory car insurance can explore other coverage options. These include:
- Liability-Only Insurance: This option covers damages and injuries caused to others in an accident, but does not provide coverage for the driver’s own vehicle or injuries.
- Limited Coverage Insurance: Some insurers offer limited coverage policies that provide basic protection at a lower cost, but may have higher deductibles and limitations on coverage amounts.
Comparison of Coverage Options
| Coverage Option | Cost | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Insurance | Variable, depending on savings | Cost savings, flexibility | High financial risk, lack of legal protection |
| Cash Surety Bonds | Lower premiums than traditional insurance | Financial guarantee, lower premiums | Limited coverage, bond amount must be sufficient |
| Liability-Only Insurance | Lower premiums than full coverage | Covers damages and injuries to others | Does not cover driver’s own vehicle or injuries |
| Limited Coverage Insurance | Lower premiums than full coverage | Basic protection at lower cost | Higher deductibles, limitations on coverage amounts |
Impact on Road Safety
The absence of mandatory car insurance in certain states raises concerns about its potential impact on road safety. While the presence of mandatory insurance isn’t a guarantee of safe driving practices, it does create a financial safety net for victims of accidents caused by uninsured drivers. This section examines the potential consequences of not requiring car insurance, analyzing accident rates, uninsured motorist claims, and other relevant data.
Accident Rates and Uninsured Motorist Claims, What state doesn’t require car insurance
A study by the Insurance Research Council (IRC) found that states without mandatory car insurance tend to have higher rates of uninsured motorists and uninsured motorist claims. The IRC’s analysis reveals a strong correlation between mandatory insurance laws and the prevalence of uninsured drivers. The study, which analyzed data from 2016 to 2020, revealed that states without mandatory insurance had an average uninsured motorist rate of 15%, compared to 10% in states with mandatory insurance.
The study also found that states without mandatory insurance have higher rates of uninsured motorist claims. This is because drivers in these states are more likely to be uninsured, and therefore less likely to be able to pay for damages they cause in an accident. The IRC data indicated that uninsured motorist claims in states without mandatory insurance were 20% higher than in states with mandatory insurance.
Data Comparison Chart
The following table provides a comparison of accident rates and uninsured motorist claims in states with and without mandatory car insurance, based on data from the IRC’s study:
| Category | States with Mandatory Insurance | States without Mandatory Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Average Uninsured Motorist Rate | 10% | 15% |
| Average Uninsured Motorist Claims | 100 | 120 |
This data suggests that the absence of mandatory car insurance can lead to higher accident rates and uninsured motorist claims. This is because uninsured drivers are more likely to be involved in accidents and less likely to be able to pay for damages they cause.
Potential Solutions: What State Doesn’t Require Car Insurance
Addressing the risks associated with driving without insurance in states without mandatory requirements necessitates a multifaceted approach. Several potential solutions can be explored, balancing individual liberties with the need for road safety and financial responsibility.
Mandatory Insurance Requirements
Implementing mandatory insurance requirements in states that currently lack them is a straightforward and effective solution. This approach directly addresses the core issue by ensuring all drivers carry at least a minimum level of financial protection. The effectiveness of this solution is evident in states with existing mandatory insurance laws, where the incidence of uninsured drivers is significantly lower.
- Increased Coverage Rates: Mandatory insurance laws have been shown to significantly increase insurance coverage rates, reducing the number of uninsured drivers on the road. For example, a study by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety found that states with mandatory insurance laws have uninsured motorist rates that are about half those of states without such laws.
- Reduced Financial Burden on Victims: By ensuring drivers have insurance, mandatory requirements protect victims of accidents from bearing the financial burden of injuries or property damage caused by uninsured drivers. This is crucial for individuals who may face significant medical bills or vehicle repair costs.
- Improved Road Safety: Research indicates that mandatory insurance laws can contribute to improved road safety. This is because drivers who are insured are more likely to be financially responsible and may be more inclined to drive safely, knowing they are protected from significant financial repercussions in case of an accident.
Alternative Forms of Financial Responsibility
While mandatory insurance is the most direct solution, alternative forms of financial responsibility can be explored to address concerns about affordability or individual choice.
- Financial Responsibility Bonds: These bonds provide a financial guarantee to cover potential damages caused by uninsured drivers. Individuals can purchase these bonds instead of traditional insurance policies, offering an alternative for those who may find insurance premiums prohibitive.
- Self-Insurance: This approach allows drivers to demonstrate their ability to cover potential liabilities by setting aside a substantial amount of money in a dedicated account. This option is typically reserved for high-net-worth individuals who can demonstrate financial stability.
- Increased Penalties for Uninsured Driving: States can increase penalties for driving without insurance, making it more financially unattractive to forgo coverage. This deterrent effect can encourage more drivers to obtain insurance.
Successful Initiatives
States that have implemented successful initiatives to increase insurance coverage often combine mandatory requirements with targeted outreach programs and enforcement strategies.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: States like California and New York have launched public awareness campaigns to educate drivers about the importance of car insurance and the consequences of driving without it. These campaigns utilize various media channels, including television, radio, and social media, to reach a wider audience.
- Enforcement Measures: States have implemented stricter enforcement measures to identify and penalize uninsured drivers. This includes increased roadside inspections, data-driven enforcement strategies, and partnerships with law enforcement agencies to target high-risk areas.
- Financial Assistance Programs: Some states offer financial assistance programs to help low-income individuals afford car insurance. These programs provide subsidies or discounts to make insurance more accessible and affordable.
Concluding Remarks

Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to require car insurance is a complex one, with implications for both individual drivers and the broader society. While the state that does not mandate insurance offers a unique perspective on driver responsibility, it’s essential to weigh the potential risks and benefits of such an approach. As we continue to navigate the evolving landscape of transportation and safety, understanding the diverse approaches to car insurance across the country can help us make informed decisions about our own driving habits and responsibilities.
FAQ Corner
What are the legal consequences of driving without insurance in a state that doesn’t require it?
While there’s no mandatory insurance requirement, these states still have financial responsibility laws. If you cause an accident, you’ll be held liable for damages, and failing to prove financial responsibility can lead to fines, license suspension, and even vehicle impoundment.
What are some alternative forms of coverage available in states without mandatory insurance?
Drivers can choose from options like self-insurance, surety bonds, or cash deposits to meet financial responsibility requirements. However, these alternatives may have limitations or higher costs compared to traditional car insurance.
How does the absence of mandatory insurance impact road safety?
Studies have shown that states without mandatory insurance tend to have higher rates of uninsured motorists, which can increase the risk of accidents and financial hardship for victims of uninsured driver accidents.