What state does not require car insurance? It’s a question that often surprises people, as most states mandate this coverage for drivers. However, there are a few exceptions, and understanding the reasons behind these policies can provide valuable insight into the complex world of car insurance and its impact on drivers and society.
This article explores the states that do not require car insurance, delving into the historical and economic factors that influenced these decisions. We’ll examine the arguments for and against mandatory car insurance, analyze the potential risks and consequences, and discuss alternative mechanisms for ensuring financial responsibility for drivers. By understanding the nuances of this topic, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the role of car insurance in protecting drivers, passengers, and pedestrians.
States That Do Not Require Car Insurance
In the United States, the requirement for car insurance varies from state to state. While most states mandate car insurance, there are a few exceptions. These states have chosen to forgo a mandatory car insurance requirement, opting for a different approach to financial responsibility for drivers.
States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
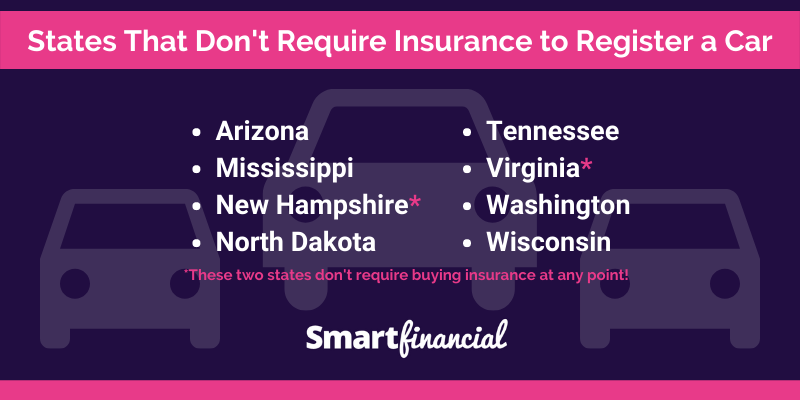
There are currently only two states in the US that do not require drivers to have car insurance:
- New Hampshire: New Hampshire has a unique system known as “financial responsibility.” Instead of requiring car insurance, the state mandates that drivers must prove they can pay for damages they cause in an accident. This can be done through a variety of methods, including posting a surety bond, providing proof of self-insurance, or demonstrating sufficient financial resources.
- Virginia: Virginia allows drivers to choose between purchasing car insurance or posting a surety bond as proof of financial responsibility. This means that drivers can opt out of traditional car insurance if they meet the state’s financial responsibility requirements.
Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
Even in states without a mandatory car insurance requirement, driving without insurance can still have serious consequences. These consequences can include:
- Financial Liability: In the event of an accident, drivers without insurance are personally responsible for all damages, including medical bills, property damage, and legal fees. This can result in significant financial hardship, even leading to bankruptcy.
- License Suspension: Driving without insurance can lead to license suspension or revocation, depending on the state and the severity of the offense. This means that drivers could lose their driving privileges and face difficulties getting around.
- Vehicle Impoundment: In some states, vehicles driven without insurance may be impounded until the owner can prove they have obtained insurance. This can lead to inconvenience and additional costs associated with retrieving the vehicle.
- Criminal Charges: In some cases, driving without insurance can be considered a criminal offense, leading to fines, jail time, or both. This is particularly true for repeat offenders or those who are involved in serious accidents.
Reasons for Not Requiring Car Insurance
The decision of certain states to not mandate car insurance is a complex issue influenced by various historical and economic factors. This lack of requirement can be viewed from different perspectives, with arguments both for and against it. Understanding these factors and their potential impact is crucial for assessing the overall implications of this policy choice.
Historical and Economic Factors
The historical context surrounding the decision of some states to not require car insurance is often linked to the development of the automobile industry and the growth of the insurance market. In the early days of automobiles, car ownership was relatively limited, and accidents were less frequent. This meant that the need for insurance was not as pressing as it is today. Additionally, some states, particularly those with strong agricultural economies, may have prioritized other forms of insurance, such as crop insurance, over car insurance.
Furthermore, economic factors can also play a role in the decision to not require car insurance. Some states may believe that mandatory car insurance would increase the cost of car ownership, making it less affordable for their residents. They may also argue that the potential benefits of mandatory insurance, such as increased financial protection for victims of accidents, are outweighed by the costs.
Arguments for and Against Mandatory Car Insurance
The debate surrounding mandatory car insurance often centers around the potential benefits and drawbacks of such a policy. Proponents of mandatory car insurance argue that it is essential for protecting victims of accidents, ensuring that they receive compensation for their injuries and damages. They also contend that it helps to stabilize the insurance market by reducing the risk of uninsured drivers, who are more likely to be involved in accidents and less likely to be able to pay for the damages they cause.
Opponents of mandatory car insurance argue that it infringes on individual liberty and forces people to purchase a product they may not need or want. They also contend that it can lead to higher insurance premiums, making car ownership more expensive, particularly for low-income drivers. Additionally, they may argue that the government should not be involved in regulating the insurance market.
Potential Impact on Public Safety and Financial Stability
The absence of mandatory car insurance can have both positive and negative impacts on public safety and financial stability. Some argue that the lack of insurance may lead to increased instances of uninsured drivers, who may be less likely to take precautions on the road and more likely to flee the scene of an accident. This can contribute to a higher number of accidents and injuries, ultimately impacting public safety.
On the other hand, proponents of voluntary insurance argue that it encourages drivers to take more responsibility for their actions, as they are personally liable for any damages they cause. They also suggest that the absence of mandatory insurance may result in lower insurance premiums, making car ownership more accessible for low-income individuals.
However, it is crucial to consider the potential financial instability that can arise from a lack of mandatory car insurance. Uninsured drivers who are involved in accidents may not be able to cover the costs of damages and injuries, leading to financial hardship for victims and potentially burdening the healthcare system. This can also create a ripple effect, impacting the financial stability of insurance companies and the overall economy.
Alternatives to Mandatory Car Insurance
States that do not require car insurance have to find alternative ways to ensure that drivers are financially responsible for accidents they cause. This means finding mechanisms to cover the costs of damages and injuries resulting from car accidents, even if the driver is not insured.
Financial Responsibility Laws, What state does not require car insurance
Financial responsibility laws are a common alternative to mandatory insurance. These laws require drivers to prove they have the financial means to cover potential accident-related costs. This proof can be in the form of:
- Self-insurance: Drivers can demonstrate financial responsibility by providing a certificate of self-insurance, which essentially guarantees they have sufficient funds to cover potential liabilities. This option is typically only available to individuals with significant financial resources.
- Financial responsibility bonds: Drivers can purchase a bond from an insurance company or surety company, guaranteeing payment for damages up to a certain amount. This option provides a financial safety net for drivers who cannot afford traditional insurance.
- Cash deposits: Some states allow drivers to deposit a specific amount of money with the state, which can be used to cover accident-related costs. This option is less common but can be an alternative for drivers who do not qualify for other financial responsibility options.
Effectiveness and Feasibility of Alternatives
While these alternatives can provide some financial protection, they are not as effective as mandatory insurance in ensuring financial responsibility for all drivers. Self-insurance, for example, is only accessible to a limited number of drivers. Financial responsibility bonds and cash deposits can be expensive, making them impractical for many individuals.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Alternatives
- Advantages: Alternatives to mandatory insurance can offer flexibility for drivers who can afford to self-insure or purchase a bond. They can also reduce the cost of insurance for some drivers by eliminating the requirement for mandatory coverage.
- Disadvantages: Alternatives are often less comprehensive than mandatory insurance, leaving drivers vulnerable to significant financial losses in the event of a serious accident. They also do not provide the same level of protection for victims of accidents, as uninsured drivers may not have sufficient funds to cover all damages.
Potential Risks and Consequences
Driving without car insurance in states that don’t mandate it poses significant risks for both drivers and other road users. The absence of a financial safety net can lead to substantial financial burdens and legal complications, particularly in the event of an accident.
Financial Burden on Accident Victims
The absence of mandatory car insurance creates a substantial risk for accident victims, who may face significant financial burdens. Without insurance coverage, the at-fault driver may be unable to cover the costs associated with the accident, leaving the victim responsible for their own medical expenses, property damage, and lost wages. This can have devastating consequences, especially for individuals with limited financial resources.
Financial Responsibility Laws

Even though some states don’t mandate car insurance, they still have laws in place to ensure drivers can cover the costs of accidents they cause. These laws are known as financial responsibility laws. They are designed to protect victims of car accidents and ensure that drivers have the means to pay for damages or injuries.
Financial Responsibility Laws in States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
Financial responsibility laws in states without mandatory car insurance are designed to ensure that drivers have the financial resources to cover the costs of accidents they cause. These laws typically require drivers to demonstrate proof of financial responsibility, which can be done through:
- Carrying a certain amount of liability insurance: This is the most common way to meet financial responsibility requirements. The specific amount of coverage required varies by state.
- Posting a security bond: This involves depositing a sum of money with the state, which can be used to cover accident costs if the driver is found liable.
- Providing a certificate of self-insurance: This option is typically available to large businesses or individuals with significant financial resources. It allows them to self-insure, meaning they assume the financial responsibility for accidents themselves.
Penalties for Failing to Meet Financial Responsibility Requirements
States without mandatory car insurance impose penalties on drivers who fail to meet financial responsibility requirements. These penalties can include:
- Suspension of driving privileges: This is the most common penalty. Drivers who cannot prove financial responsibility may have their driver’s licenses suspended until they comply with the law.
- Fines and court costs: Drivers may be fined for failing to meet financial responsibility requirements. They may also be required to pay court costs associated with the violation.
- Impoundment of vehicle: In some cases, the state may impound the driver’s vehicle until they can demonstrate proof of financial responsibility.
Situations Where Financial Responsibility Laws Are Triggered
Financial responsibility laws are triggered in a variety of situations, including:
- Being involved in a car accident: If a driver is involved in an accident that results in property damage or personal injury, they will be required to demonstrate proof of financial responsibility.
- Being cited for a traffic violation: Some states require drivers to demonstrate proof of financial responsibility after being cited for certain traffic violations, such as speeding or driving under the influence.
- Applying for a driver’s license: In some states, drivers must provide proof of financial responsibility when applying for a driver’s license or renewing their existing license.
Consequences of Failing to Meet Financial Responsibility Requirements
Drivers who fail to meet financial responsibility requirements face serious consequences, including:
- Inability to drive legally: Driving without proof of financial responsibility is illegal and can result in the suspension of driving privileges.
- Financial hardship: Drivers who are found liable for an accident without proof of financial responsibility may be held personally responsible for all damages and injuries, potentially leading to significant financial hardship.
- Criminal charges: In some cases, failing to meet financial responsibility requirements can result in criminal charges.
Examples of Situations Where Financial Responsibility Laws Apply
Here are some examples of how financial responsibility laws might apply in real-life situations:
- Driver A causes an accident: Driver A, who lives in a state without mandatory car insurance, causes an accident that results in $10,000 worth of damage to another driver’s car and $5,000 in medical bills for the other driver. Driver A is required to demonstrate proof of financial responsibility to cover these costs. If Driver A cannot provide proof, they may face penalties such as license suspension and financial responsibility for the damages and injuries.
- Driver B is cited for speeding: Driver B, who lives in a state without mandatory car insurance, is cited for speeding. The state requires drivers to demonstrate proof of financial responsibility after being cited for certain traffic violations. If Driver B cannot provide proof, they may face penalties such as fines and license suspension.
- Driver C applies for a driver’s license: Driver C, who lives in a state without mandatory car insurance, applies for a driver’s license. The state requires drivers to provide proof of financial responsibility when applying for a driver’s license. If Driver C cannot provide proof, they will not be issued a driver’s license.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the decision of whether or not to require car insurance is a complex one, with far-reaching implications for drivers, insurance companies, and society as a whole. While some states have chosen to forgo mandatory car insurance, it’s important to recognize the potential risks and consequences for all involved. By understanding the arguments for and against mandatory car insurance, we can engage in informed discussions about the best ways to promote safety and financial responsibility on our roads.
Common Queries: What State Does Not Require Car Insurance
What are the potential consequences of driving without insurance in a state that doesn’t require it?
Even in states without mandatory car insurance, you can still face serious consequences for driving without coverage. If you’re involved in an accident, you could be held financially liable for all damages and injuries, potentially leading to significant financial hardship. Furthermore, driving without insurance can result in fines, license suspension, or even jail time, depending on the specific state laws.
Is it cheaper to drive without insurance in a state that doesn’t require it?
While you might avoid paying insurance premiums, driving without insurance in a state that doesn’t require it is a risky gamble. The potential financial burden of an accident far outweighs any potential savings from not having insurance. It’s crucial to remember that accidents can happen to anyone, and being uninsured leaves you vulnerable to significant financial losses.







