States without mandatory car insurance present a unique landscape for drivers. These states, often driven by a belief in individual responsibility, choose not to require drivers to carry insurance. This approach raises questions about financial security, road safety, and the potential consequences for both uninsured drivers and the broader community.
While the absence of mandatory insurance may seem appealing to some, it’s crucial to understand the potential downsides. Drivers without insurance face significant financial risks in the event of an accident, potentially leading to crippling debt. This can also strain the healthcare system and create a burden on responsible drivers who are forced to pay higher premiums to compensate for uninsured drivers’ risks.
States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
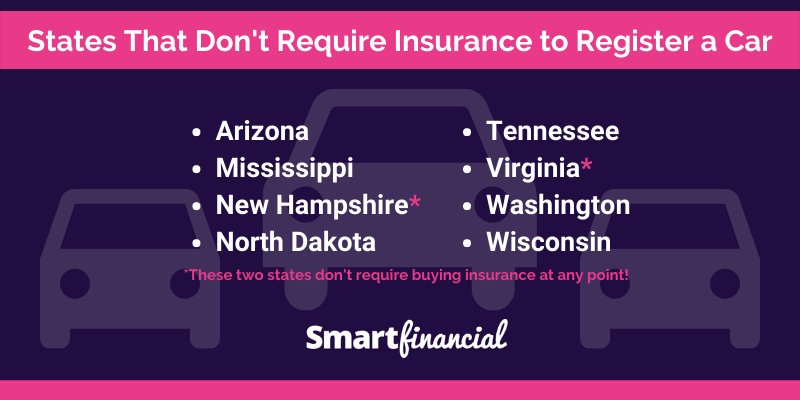
In the United States, car insurance is generally mandatory. However, there are a few states that do not have a requirement for drivers to carry car insurance. This means that drivers in these states are not legally obligated to purchase insurance coverage.
These states have chosen not to mandate car insurance for a variety of reasons, including a desire to limit government intervention in the private sector, concerns about the affordability of insurance, and the belief that individuals should be free to make their own choices about insurance coverage.
Reasons for Not Requiring Car Insurance
These states have chosen not to require car insurance for various reasons. The rationale behind these decisions is complex and multifaceted.
- Limited Government Intervention: Some states believe that government should not interfere in the private sector and that individuals should be free to make their own choices about insurance coverage. They argue that mandating car insurance would be an unnecessary government intrusion into the lives of citizens.
- Affordability Concerns: Some states are concerned about the affordability of car insurance, particularly for low-income drivers. They believe that mandating car insurance would place an undue burden on these drivers, making it difficult for them to afford to drive.
- Individual Choice and Responsibility: Some states believe that individuals should be free to make their own choices about insurance coverage and that they should be responsible for the consequences of their decisions. They argue that mandating car insurance would undermine personal responsibility and could lead to higher insurance premiums for everyone.
Financial Implications of Not Having Car Insurance
Driving without car insurance in states that don’t mandate it can have serious financial consequences, potentially leading to significant financial hardship. The lack of insurance can leave drivers vulnerable to substantial costs in the event of an accident, including medical expenses, property damage, and legal fees.
Costs Associated with Accidents
The financial impact of driving without insurance in an accident can be devastating. Without coverage, drivers are personally responsible for all expenses related to the accident, including:
- Medical Expenses: If you cause an accident and injure another driver or passenger, you could be held liable for their medical bills, which can be substantial, especially in cases of serious injuries.
- Property Damage: If you damage another person’s vehicle or property, you’ll be responsible for the repair or replacement costs, which can vary significantly depending on the extent of the damage.
- Legal Fees: Even if you’re not at fault for the accident, you may still need to hire an attorney to defend yourself against claims. Legal fees can be expensive, especially if the case goes to court.
Financial Implications Across Different States
The financial consequences of driving without insurance can vary depending on the state. Some states have stricter penalties for uninsured drivers than others, including:
- Higher Fines: Uninsured drivers may face significant fines, which can be much higher than the cost of insurance.
- License Suspension: Driving without insurance can result in the suspension of your driver’s license, making it impossible to legally operate a vehicle.
- Jail Time: In some states, driving without insurance can even lead to jail time, especially if the accident results in serious injuries or death.
It’s crucial to remember that even if you live in a state that doesn’t require car insurance, it’s still highly recommended to have coverage. The financial risks of driving without insurance are substantial, and the potential consequences can be devastating.
Alternatives to Mandatory Car Insurance
States without mandatory car insurance have implemented various alternative mechanisms to address the financial risks associated with car accidents. These alternatives aim to ensure that drivers and pedestrians are protected from financial hardship in the event of an accident.
Financial Responsibility Laws
Financial responsibility laws are a common alternative to mandatory car insurance. These laws require drivers to demonstrate their ability to cover the costs of damages they may cause in an accident. States without mandatory car insurance often have stringent financial responsibility laws.
- Proof of Financial Responsibility: Drivers in these states are typically required to provide proof of financial responsibility, which can be in the form of insurance, a surety bond, or a deposit of cash or securities with the state. This ensures that drivers have the means to cover potential damages.
- Minimum Financial Responsibility Limits: These laws usually set minimum limits for the amount of coverage drivers must have. These limits may vary by state but typically include coverage for bodily injury liability, property damage liability, and uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage. For example, in New Hampshire, drivers must carry a minimum of $25,000 in liability coverage for bodily injury per person, $50,000 for bodily injury per accident, and $25,000 for property damage.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Failure to comply with financial responsibility laws can result in significant penalties, such as fines, license suspension, or even vehicle impoundment. These penalties deter drivers from driving without adequate financial protection.
Self-Insurance
Some states allow drivers to self-insure, meaning they assume financial responsibility for any damages they cause in an accident.
- High Financial Responsibility Requirements: States that allow self-insurance typically have very high financial responsibility requirements, such as requiring drivers to demonstrate a substantial net worth or post a large bond. This ensures that self-insured drivers have the financial resources to cover significant damages.
- Limited Availability: Self-insurance is not available to everyone and is often limited to individuals with substantial assets. This is because the financial risk associated with self-insurance is significant, and states want to ensure that drivers have the financial capacity to handle potential claims.
Other Measures
In addition to financial responsibility laws and self-insurance, some states have implemented other measures to protect drivers and pedestrians from financial risks.
- State-Run Uninsured Motorist Funds: These funds provide compensation to victims of accidents caused by uninsured or hit-and-run drivers. The funds are typically financed through a surcharge on insurance premiums or a fee on vehicle registrations.
- Mandatory Accident Reporting: Some states require drivers to report all accidents, even minor ones, to the state. This helps ensure that accidents are documented and that drivers are held accountable for their actions.
Effectiveness of Alternatives
The effectiveness of these alternatives compared to mandatory insurance is a subject of debate.
- Pros of Alternatives: Alternatives can provide some level of protection for drivers and pedestrians, and they can be more affordable for some individuals than mandatory insurance. For example, drivers with clean driving records and substantial assets may find self-insurance to be a more cost-effective option.
- Cons of Alternatives: Alternatives may not provide the same level of protection as mandatory insurance. For example, financial responsibility laws may not adequately cover the costs of significant damages, and self-insurance can leave drivers exposed to significant financial risk. Additionally, alternatives can be more difficult to enforce than mandatory insurance, as it can be challenging to track down uninsured drivers and collect damages from them.
Impact on Uninsured Drivers
Driving without car insurance in states that don’t mandate it can have significant consequences. While some drivers may choose to forgo insurance due to financial constraints or a perceived low risk of accidents, the potential costs associated with an accident can be substantial and far outweigh any savings from not having insurance.
Financial Implications of Accidents
The financial implications of an accident for an uninsured driver can be devastating. In the event of an accident, the uninsured driver is personally liable for all damages, including:
- Medical expenses: If the driver or any passengers are injured, they will be responsible for all medical bills, including hospitalization, surgery, and rehabilitation.
- Property damage: The driver will be responsible for repairing or replacing any damaged vehicles or property, including their own vehicle and the other party’s vehicle.
- Legal fees: If the accident results in a lawsuit, the uninsured driver will be responsible for their own legal fees and potentially those of the other party.
- Lost wages: If the driver is injured and unable to work, they will lose income, adding to their financial burden.
Potential for Higher Premiums in Mandatory Insurance States
While drivers in states without mandatory car insurance may initially save money by not having insurance, their decision could lead to higher premiums in states with mandatory insurance. This is because insurance companies often use driving records to assess risk and determine premiums. A driver who has been involved in an accident without insurance will likely have a higher risk profile, resulting in higher premiums when they eventually obtain insurance.
Risks and Challenges Faced by Uninsured Drivers, States without mandatory car insurance
Uninsured drivers face a range of risks and challenges, depending on the specific state and the circumstances of the accident. Some of the most significant challenges include:
- Difficulty obtaining insurance: Once a driver has been involved in an accident without insurance, it can be challenging to find an insurance company willing to provide coverage, especially at an affordable rate.
- Financial hardship: The financial burden of an accident without insurance can be overwhelming, potentially leading to bankruptcy or other financial difficulties.
- Legal consequences: In some states, driving without insurance is a criminal offense, and drivers could face fines, license suspension, or even jail time.
Legal Considerations and Consequences
While states without mandatory car insurance may not require drivers to have coverage, it’s crucial to understand that driving without insurance can have serious legal consequences. In these states, driving without insurance is still considered a risky and potentially costly decision, as you’re responsible for covering the financial burden of any accidents you may cause.
Penalties and Legal Consequences
Driving without insurance in states that do not mandate it can result in a range of penalties and legal consequences. These consequences can vary depending on the state, the severity of the accident, and the specific circumstances.
- Fines and Penalties: Uninsured drivers involved in accidents may face hefty fines and penalties, which can significantly increase the financial burden of the accident. These fines can vary depending on the state and the specific circumstances of the accident.
- License Suspension or Revocation: Depending on the state and the circumstances of the accident, an uninsured driver’s license may be suspended or revoked. This can significantly impact their ability to drive legally and may require them to go through a lengthy process to regain driving privileges.
- Civil Liability: Even in states without mandatory insurance, uninsured drivers are still held financially liable for any damages or injuries caused by their negligence. This means that they can be sued by the other party involved in the accident, and the court may order them to pay substantial compensation for medical expenses, property damage, lost wages, and other related costs.
- Criminal Charges: In some cases, driving without insurance may lead to criminal charges, particularly if the accident results in serious injuries or fatalities. These charges can include reckless driving, hit-and-run, or even vehicular manslaughter.
Examples of Legal Cases and Rulings
- Case Example: In a recent case in [State Name], a driver who was involved in a car accident without insurance was found liable for over $100,000 in damages. The court ruled that the driver’s negligence caused the accident and that they were responsible for covering the medical expenses and property damage of the other party.
- Ruling Example: In another case in [State Name], a driver was convicted of reckless driving and hit-and-run after fleeing the scene of an accident without insurance. The court sentenced the driver to a significant jail term and a hefty fine.
Societal Impacts

The presence or absence of mandatory car insurance laws has profound implications for society, affecting road safety, financial stability, and overall well-being. These laws can influence individual behavior, impact the cost of insurance, and affect the accessibility of healthcare for accident victims.
Influence on Road Safety and Accident Rates
The influence of insurance requirements on road safety is a complex issue with varying perspectives. Proponents argue that mandatory insurance encourages responsible driving by deterring individuals from driving without financial protection. This, in turn, could potentially lead to a reduction in accidents. Conversely, opponents argue that insurance requirements may not directly translate to safer driving habits. They contend that other factors, such as driver education, road infrastructure, and law enforcement, play a more significant role in accident prevention.
Impact of Insurance Policies on Society in Different States
The impact of insurance policies on society varies across states, influenced by factors such as the prevalence of uninsured drivers, the cost of insurance, and the availability of alternative solutions. For example, states with higher rates of uninsured drivers often face higher healthcare costs and social burdens due to accidents involving uninsured individuals. These states may also experience a greater financial burden on their healthcare systems and emergency services. Conversely, states with mandatory insurance requirements tend to have lower rates of uninsured drivers and a more stable financial landscape for accident victims.
Closing Summary

The debate surrounding mandatory car insurance continues, with valid arguments on both sides. Ultimately, each state must weigh the benefits and drawbacks of requiring insurance, considering the unique needs and priorities of its citizens. Regardless of the stance taken, it’s essential for drivers to understand the potential risks and responsibilities associated with driving without insurance, ensuring they make informed decisions to protect themselves and others on the road.
Top FAQs: States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
What happens if I get into an accident without insurance in a state that doesn’t require it?
You could be held personally liable for all damages and injuries, potentially facing significant financial losses, legal battles, and even license suspension.
Are there any alternatives to car insurance in states that don’t require it?
Some states offer alternative mechanisms like financial responsibility laws, requiring drivers to demonstrate financial ability to cover potential damages. However, these often have limitations and may not provide the same level of protection as insurance.
Is it cheaper to drive without insurance in states that don’t require it?
It might seem cheaper in the short term, but the potential costs of an accident far outweigh any savings. Additionally, you might face higher premiums if you eventually decide to get insurance due to your prior uninsured status.







