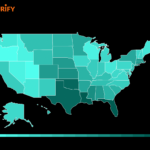
States where auto insurance is not required – In the United States, most drivers are required to carry auto insurance to protect themselves and others from the financial consequences of accidents. However, there are a few states that do not mandate auto insurance, leaving drivers with the choice of whether or not to purchase coverage. These states, often citing principles of individual liberty and economic freedom, have opted for a system where drivers are held financially responsible for any damages they cause. This approach presents a unique dynamic, with drivers weighing the risks and potential costs of driving without insurance against the benefits of greater financial autonomy.
This article delves into the intricacies of these states, exploring the financial responsibility laws, the potential risks and challenges of driving without insurance, and the alternative forms of financial protection available. We’ll also analyze the impact of this policy on the insurance industry and drivers, examining the implications for access to affordable coverage, risk management, and overall road safety.
States Without Mandatory Auto Insurance

In the United States, the majority of states mandate that drivers carry auto insurance to protect themselves and others from financial losses in the event of an accident. However, a few states have chosen to opt out of this requirement, leaving drivers with the choice of whether or not to purchase insurance. This decision is often based on a complex interplay of historical context, economic considerations, and philosophical beliefs about individual liberty.
States Without Mandatory Auto Insurance
The following states currently do not require drivers to carry auto insurance:
- New Hampshire
- Virginia
Historical Context
The historical context behind these states’ decisions is rooted in a combination of factors, including:
- Individual Liberty: New Hampshire’s decision to forgo mandatory auto insurance stems from a long-standing tradition of prioritizing individual liberty and minimal government intervention. This philosophy extends to the realm of personal responsibility, where individuals are expected to make informed choices regarding their own risk management.
- Economic Considerations: Virginia’s decision was influenced by economic considerations, particularly the belief that mandatory insurance would increase the cost of car ownership for many residents. Proponents of this view argue that it would be more cost-effective to rely on a system of financial responsibility laws, which hold drivers accountable for damages they cause, even without insurance.
Rationale Behind These States’ Decisions
The rationale behind these states’ decisions can be summarized as follows:
- Individual Liberty: New Hampshire’s approach emphasizes individual responsibility and freedom of choice. Drivers are allowed to choose whether or not to purchase insurance, with the understanding that they will be held financially liable for any damages they cause.
- Cost Reduction: Virginia’s decision is driven by the desire to minimize the financial burden of auto insurance on its residents. By avoiding mandatory insurance, the state hopes to keep costs lower and encourage greater competition within the insurance market.
- Potential Economic Benefits: Proponents of these states’ decisions argue that they can lead to economic benefits by encouraging greater competition in the insurance market and reducing the cost of car ownership. They also point to the potential for lower insurance premiums for those who choose to purchase insurance.
Financial Responsibility Laws in Non-Mandatory Insurance States
While these states do not mandate auto insurance, they all have financial responsibility laws in place to ensure that drivers can cover the costs of any accidents they may cause. These laws are designed to protect victims and ensure that they receive compensation for damages.
Financial Responsibility Requirements
These laws typically require drivers to prove their ability to pay for damages caused by accidents. This can be done by:
- Purchasing auto insurance: Although not mandatory, most drivers in these states choose to purchase auto insurance to meet financial responsibility requirements.
- Posting a surety bond: Drivers can post a bond with a financial institution to guarantee their ability to pay for damages. This bond serves as a financial guarantee, ensuring that the driver can cover the costs of an accident.
- Providing proof of financial responsibility: Drivers may be required to provide proof of financial responsibility in the form of a certificate of insurance or a surety bond.
The minimum financial responsibility requirements vary from state to state. These requirements typically specify the minimum amounts of coverage that drivers must have for bodily injury liability, property damage liability, and uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage. For example, a state might require drivers to carry at least $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident for bodily injury liability and $10,000 for property damage liability.
Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without meeting the financial responsibility requirements in these states can have serious consequences. These consequences can include:
- Fines and penalties: Drivers caught driving without meeting financial responsibility requirements can face hefty fines and penalties. These fines can vary from state to state but can be substantial, potentially reaching hundreds or even thousands of dollars.
- License suspension: In addition to fines, driving without insurance can lead to the suspension of your driver’s license. This suspension can last for a significant period of time, making it difficult to drive legally until the requirements are met.
- Asset seizure: In some states, if a driver is found liable for an accident and does not have insurance or the financial means to cover damages, their assets may be seized to compensate the injured party. This can include vehicles, property, and even wages.
- Criminal charges: In some cases, driving without insurance in a state that requires financial responsibility can result in criminal charges, leading to jail time or community service.
Comparison with Mandatory Insurance States
States with mandatory auto insurance laws have stricter requirements. Drivers are legally required to have a minimum amount of insurance coverage, and failing to do so can result in serious penalties, including license suspension, fines, and even vehicle impoundment. In non-mandatory insurance states, drivers have more flexibility, but they also bear the risk of significant financial consequences if they are involved in an accident and do not have the means to cover the damages.
Risks and Challenges of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without insurance in states where it is not mandatory can expose drivers to significant financial and legal risks. While not required by law, it is highly advisable to carry auto insurance, as the potential consequences of driving uninsured can be severe and financially crippling.
Financial Hardship in Accidents
The lack of insurance can lead to significant financial burdens for drivers involved in accidents. Without coverage, drivers are personally liable for all costs associated with the accident, including:
- Medical Expenses: In case of injuries to themselves or others, uninsured drivers are responsible for all medical bills, including hospital stays, surgeries, and ongoing rehabilitation.
- Property Damage: Damage to other vehicles or property involved in the accident must be covered by the uninsured driver, which can be substantial, especially in cases of serious collisions.
- Legal Fees: Uninsured drivers may face lawsuits from injured parties or property owners, resulting in hefty legal fees and potential judgments.
Alternative Forms of Financial Protection
In states that don’t require auto insurance, drivers have a few options for demonstrating financial responsibility and protecting themselves from liability in case of an accident. These alternatives to traditional insurance policies offer varying levels of coverage and come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these options is crucial for drivers in these states to make informed decisions about their financial protection.
Self-Insurance
Self-insurance, also known as “going bare,” involves assuming full financial responsibility for any accidents or damages caused by your vehicle. This means you would be personally liable for any medical bills, property damage, and legal expenses arising from an accident.
- Pros:
- Potentially lower costs compared to traditional insurance, as you’re not paying premiums.
- Greater control over your financial risk and how you manage it.
- Cons:
- Significant financial risk, as you’re responsible for all costs in case of an accident.
- Potential for substantial financial hardship if a major accident occurs.
- Limited legal protection compared to insurance.
Surety Bonds, States where auto insurance is not required
A surety bond is a type of financial guarantee issued by a surety company. It assures the public that the bondholder (the driver) will be financially responsible for any damages caused by their vehicle. In the event of an accident, the surety company will pay the damages up to the bond amount, and the driver is then responsible for reimbursing the surety company.
- Pros:
- Provides financial protection for third parties in case of an accident.
- May be more affordable than traditional insurance, especially for drivers with good driving records.
- Cons:
- The bond amount may not be sufficient to cover all potential costs of an accident.
- Requires a financial assessment and approval from the surety company.
- May not offer the same level of coverage as traditional insurance.
Cash Deposits
Some states allow drivers to make a cash deposit with the state government as proof of financial responsibility. The amount of the deposit varies by state and is typically based on the potential cost of damages from an accident. If the driver is involved in an accident, the state will use the deposit to pay for damages up to the deposit amount.
- Pros:
- May be a more affordable option than insurance for some drivers.
- Provides a simple and straightforward way to demonstrate financial responsibility.
- Cons:
- Requires a large upfront deposit, which may not be feasible for all drivers.
- The deposit amount may not be sufficient to cover all potential costs of an accident.
- Does not offer the same level of coverage or legal protection as traditional insurance.
Comparison of Alternative Financial Protection Options
| Option | Cost | Accessibility | Legal Implications | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Insurance | Potentially lower | High | High risk of personal liability | Limited, only covers what you can afford |
| Surety Bond | Moderate | Moderate | Provides financial protection for third parties | Limited to the bond amount |
| Cash Deposit | High upfront cost | Limited | Provides financial protection for third parties | Limited to the deposit amount |
Impact on the Insurance Industry and Drivers
States without mandatory auto insurance create a unique dynamic within the insurance industry, impacting both insurers and drivers in various ways. This dynamic can be analyzed by examining the market forces, pricing strategies, and overall profitability of insurers, as well as the accessibility of affordable coverage, risk management practices, and driving experiences for drivers.
Impact on the Insurance Industry
The absence of mandatory auto insurance in certain states can have a significant impact on the insurance industry. It affects market dynamics, pricing strategies, and overall profitability.
- Market Dynamics: The absence of mandatory insurance can lead to a higher concentration of high-risk drivers who are more likely to drive uninsured. This can result in increased claims costs for insurers, leading to higher premiums for those who do have insurance.
- Pricing Strategies: Insurers may employ more complex pricing strategies in states without mandatory insurance to mitigate the risk associated with uninsured drivers. This could involve using more sophisticated risk assessment models, implementing higher deductibles, or offering limited coverage options.
- Profitability: The presence of a significant number of uninsured drivers can negatively impact the profitability of insurers. Higher claim costs and the need for more complex pricing strategies can reduce profit margins.
Impact on Drivers
Drivers in states without mandatory auto insurance face a range of challenges and opportunities, impacting their access to affordable coverage, risk management practices, and overall driving experience.
- Access to Affordable Coverage: Drivers in these states may find it difficult to obtain affordable auto insurance due to the higher risk associated with uninsured drivers. Insurers may charge higher premiums or offer limited coverage options to compensate for the increased risk.
- Risk Management Strategies: Drivers may need to implement more comprehensive risk management strategies to protect themselves financially in the absence of mandatory insurance. This could involve increasing their deductibles, seeking alternative forms of financial protection, or driving more defensively.
- Overall Driving Experience: The presence of uninsured drivers can create a more hazardous driving environment, potentially leading to increased accidents and higher insurance costs for those who do have insurance. This can impact the overall driving experience, leading to increased stress and anxiety for drivers.
Increased Uninsured Motorists
The lack of mandatory auto insurance can lead to an increase in uninsured motorists, posing a significant risk to overall road safety.
- Financial Implications: Uninsured drivers are more likely to be involved in accidents and leave the victims financially responsible for their injuries and damages. This can result in significant financial hardship for victims and their families.
- Safety Concerns: Uninsured drivers are less likely to be held accountable for their actions, potentially leading to a higher incidence of reckless driving and accidents. This can create a more dangerous driving environment for everyone on the road.
- Social Costs: The presence of a significant number of uninsured motorists can increase the burden on society, leading to higher healthcare costs and social welfare programs to support victims of uninsured driver accidents.
Summary: States Where Auto Insurance Is Not Required

The decision of whether or not to require auto insurance is a complex one, with far-reaching implications for drivers, the insurance industry, and overall road safety. While some states choose to prioritize individual liberty and financial responsibility, others prioritize universal coverage and risk mitigation. Ultimately, the choice of how to manage auto insurance is a reflection of each state’s unique values and priorities, shaping the driving experience for millions of Americans.
FAQs
What are the benefits of driving without insurance in these states?
Drivers in states without mandatory auto insurance can potentially save money on insurance premiums. They may also have more flexibility in choosing their own coverage options or opting for alternative forms of financial protection.
What are the main concerns regarding driving without insurance?
The primary concern is the potential for significant financial hardship in the event of an accident. Without insurance, drivers are personally liable for any damages or injuries they cause, which could lead to substantial out-of-pocket expenses, including medical bills, property repairs, and legal fees.
Are there any specific situations where driving without insurance is particularly risky?
Driving without insurance poses a higher risk in situations involving serious accidents, especially those resulting in injuries or significant property damage. The financial consequences of such incidents could be devastating for drivers without insurance, potentially leading to bankruptcy or other financial ruin.