States that dont require car insurance – States that don’t require car insurance might seem like a dream for some, but the reality is far more complex. While these states offer a temporary reprieve from mandatory coverage, they also present significant financial and legal risks. The absence of mandatory insurance creates a unique situation where drivers are solely responsible for covering the costs of any accidents they cause, potentially leading to significant financial hardship. This article delves into the complexities of driving without insurance, exploring the legal requirements, financial implications, and alternative options available in these states.
These states, typically known for their libertarian leanings, believe that individuals should have the freedom to choose whether or not to purchase car insurance. However, this freedom comes with a hefty price tag. Without insurance, drivers face the full weight of financial responsibility for any accidents they cause, potentially leading to devastating consequences. It’s a gamble that many might not be willing to take, especially considering the potential costs of medical bills, property damage, and legal fees.
States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
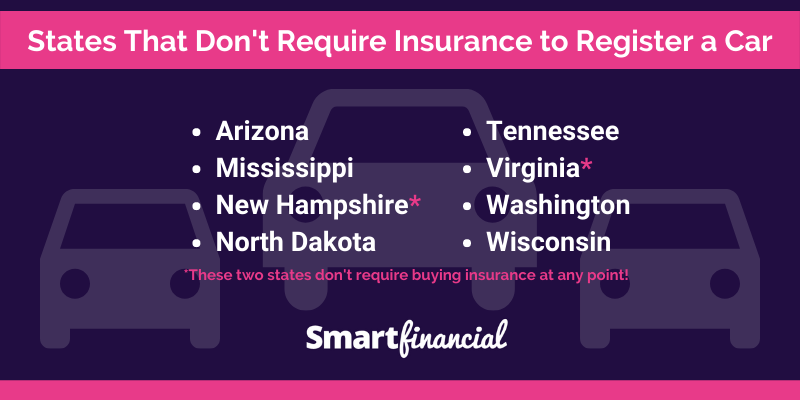
While most states in the U.S. mandate car insurance, there are a few exceptions. These states do not require drivers to have car insurance, but there are legal requirements and potential risks associated with driving without insurance.
States Without Mandatory Car Insurance, States that dont require car insurance
The following states do not require drivers to have car insurance:
- New Hampshire
- Virginia
However, it’s important to note that even in these states, drivers are still required to provide proof of financial responsibility in the event of an accident. This means that drivers must be able to demonstrate that they have the financial means to cover damages caused by an accident, even if they don’t have insurance.
Legal Requirements for Driving in States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
In New Hampshire, drivers are required to provide proof of financial responsibility in the form of a surety bond, a cash deposit, or a certificate of self-insurance. In Virginia, drivers are required to provide proof of financial responsibility in the form of a surety bond, a cash deposit, or a certificate of self-insurance.
Potential Risks and Consequences of Driving Without Insurance in States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
Even though these states don’t mandate car insurance, drivers face significant risks and potential consequences if they are involved in an accident without insurance.
- Financial Liability: If you are involved in an accident and are found to be at fault, you could be held financially responsible for all damages, including medical expenses, property damage, and lost wages. This could potentially lead to significant financial hardship.
- License Suspension: Even though these states don’t require car insurance, they still have laws that protect victims of accidents. If you are found to be at fault in an accident and do not have insurance, your license could be suspended.
- Legal Action: The injured party could sue you for damages, and you would be responsible for all legal fees and court costs.
It’s important to remember that even in states without mandatory car insurance, driving without insurance is a risky and potentially costly decision. If you are involved in an accident, you could face significant financial and legal consequences.
Financial Responsibility Laws
Financial responsibility laws are designed to ensure that drivers have the financial means to cover the costs of damages or injuries they may cause in an accident. These laws require drivers to prove their ability to pay for potential liabilities arising from accidents. This is typically accomplished through the purchase of car insurance, but other options may be available depending on the state’s specific requirements.
Types of Financial Responsibility Laws
States that require car insurance generally have one of two types of financial responsibility laws:
- Financial Responsibility Law: This type of law requires drivers to provide proof of financial responsibility after an accident. If a driver is involved in an accident, they must demonstrate that they have the financial resources to cover the costs of damages or injuries. This proof is usually provided in the form of an insurance policy or a surety bond.
- Compulsory Insurance Law: This type of law requires drivers to maintain car insurance at all times, regardless of whether they have been involved in an accident. This is the most common type of financial responsibility law, and it ensures that all drivers have insurance coverage to protect themselves and others on the road.
Penalties for Failing to Meet Financial Responsibility Requirements
The penalties for failing to meet financial responsibility requirements vary from state to state, but common consequences include:
- Suspension of driver’s license: This is a common penalty for drivers who fail to maintain the required insurance coverage.
- Fines: Drivers who violate financial responsibility laws may face fines, which can be substantial, depending on the state and the nature of the violation.
- Vehicle registration suspension: If a driver does not have the required insurance, their vehicle registration may be suspended, preventing them from legally driving the vehicle.
- Jail time: In some states, repeat offenders who fail to meet financial responsibility requirements may face jail time, especially if they are involved in accidents that result in serious injuries or property damage.
Benefits of Car Insurance

Even though some states don’t mandate car insurance, it’s still a smart decision to have it. Car insurance provides crucial protection, ensuring financial stability and peace of mind in case of unexpected events. This section will explore the key benefits of having car insurance, categorized into financial protection, legal protection, and peace of mind.
Financial Protection
Car insurance offers financial protection in various situations, covering costs associated with accidents, damage, and other unforeseen events.
- Coverage for Accidents: In the event of an accident, car insurance covers the costs of repairs, medical expenses, and other related expenses. This protection helps individuals avoid significant financial burdens. For instance, if you cause an accident that results in damage to another vehicle or injury to the other driver, your insurance will cover the costs of repairs and medical bills.
- Coverage for Damage to Your Vehicle: Car insurance protects your vehicle from damage caused by accidents, theft, vandalism, natural disasters, and other events. This coverage helps you avoid the expense of repairing or replacing your vehicle, ensuring you can get back on the road quickly.
- Liability Coverage: This type of coverage protects you from financial responsibility if you are found liable for an accident. Liability coverage covers the costs of damages to other vehicles, property, and medical expenses for the other driver and passengers involved in the accident.
- Medical Payments Coverage: This coverage provides financial assistance for medical expenses, regardless of who is at fault. This includes medical bills for you and your passengers, as well as any pedestrians injured in an accident.
Legal Protection
Car insurance also provides crucial legal protection in case of an accident.
- Legal Representation: If you are involved in an accident, car insurance companies provide legal representation to help you navigate the legal complexities of the situation. This can be invaluable, especially if you are facing a lawsuit or other legal proceedings.
- Defense Against Claims: Your insurance company will defend you against claims made by others, such as those related to property damage or personal injury. This protection can help you avoid significant legal costs and potential financial liabilities.
Peace of Mind
Car insurance offers peace of mind knowing that you are financially and legally protected in case of an unexpected event.
- Reduced Stress and Anxiety: Knowing that you have insurance coverage can reduce stress and anxiety, especially in the event of an accident. This allows you to focus on recovering and getting back on your feet without worrying about the financial implications.
- Financial Security: Car insurance provides financial security, knowing that you are protected from significant financial losses due to accidents or other events. This can be a significant benefit, especially for individuals who rely on their vehicles for transportation, work, or other essential needs.
- Compliance with Financial Responsibility Laws: Even if your state doesn’t require car insurance, most states have financial responsibility laws that require you to be able to pay for damages caused by an accident. Car insurance can help you meet these requirements, avoiding fines and penalties.
Types of Car Insurance Coverage
Here is a table that compares the costs and benefits of different types of car insurance coverage:
| Type of Coverage | Cost | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Liability Coverage | Low | Protects you from financial responsibility for damages to others. |
| Collision Coverage | Moderate | Covers damage to your vehicle in an accident, regardless of fault. |
| Comprehensive Coverage | Moderate | Covers damage to your vehicle from events other than accidents, such as theft, vandalism, or natural disasters. |
| Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage | Low | Protects you if you are hit by a driver without insurance or with insufficient insurance. |
| Medical Payments Coverage | Low | Covers medical expenses for you and your passengers, regardless of fault. |
Driving Without Insurance Risks: States That Dont Require Car Insurance
Even though some states don’t require car insurance, driving without it can be a risky and potentially costly decision. While you might be tempted to save money on premiums, the potential financial consequences of an accident without insurance can be devastating.
Financial Implications of an Accident Without Insurance
If you’re involved in an accident without insurance, you could face a range of financial burdens, including:
- Repair Costs: You’ll be responsible for paying for any damage to your own vehicle, even if you weren’t at fault. This can be extremely expensive, especially if your car is totaled.
- Medical Expenses: If you or someone else is injured in an accident, you’ll be responsible for all medical bills, including hospital stays, surgeries, and rehabilitation. This can easily amount to thousands of dollars, even for minor injuries.
- Legal Fees: If the other driver files a lawsuit against you, you’ll need to hire an attorney to represent you. Legal fees can be very expensive, especially if the case goes to trial.
- Lost Wages: If you’re injured and unable to work, you’ll lose income. This can put a significant strain on your finances, especially if you have dependents.
- Property Damage: If you cause damage to someone else’s property, you’ll be responsible for the repairs. This can include damage to vehicles, buildings, and other structures.
Real-World Scenarios
- Scenario 1: A driver without insurance causes an accident, totaling the other driver’s car and causing minor injuries. The driver without insurance is sued and faces significant legal fees, medical bills, and lost wages. The financial burden is so heavy that the driver is forced to declare bankruptcy.
- Scenario 2: A driver without insurance is involved in a hit-and-run accident. The driver flees the scene and is later caught by the police. They face criminal charges, including fines, jail time, and a permanent record. They are also responsible for the damage they caused, which can be substantial.
Alternative Options to Traditional Car Insurance
In states without mandatory car insurance requirements, drivers have the freedom to choose whether or not to purchase traditional insurance. However, this freedom comes with risks, as being uninsured can lead to significant financial consequences in case of an accident. Fortunately, alternative options exist for those seeking coverage without the traditional insurance model. These alternatives provide various levels of protection and cost-effectiveness, catering to different needs and risk profiles.
Self-Insurance
Self-insurance is a strategy where individuals set aside funds to cover potential costs associated with accidents. This approach is often considered by those with strong financial reserves and a high risk tolerance.
Advantages
- Cost Savings: Self-insurance eliminates monthly premium payments, allowing individuals to potentially save money over time.
- Flexibility: Self-insured individuals have complete control over how their funds are managed and invested.
Disadvantages
- Financial Risk: Self-insurance exposes individuals to the full financial burden of an accident, which can be substantial.
- Limited Coverage: Self-insurance typically does not cover third-party liability claims, leaving individuals vulnerable to lawsuits.
Cash-Based Coverage
Cash-based coverage involves paying for accident-related expenses out of pocket. This approach is suitable for individuals with a high risk tolerance and a strong financial cushion.
Advantages
- Cost Savings: Cash-based coverage eliminates the need for monthly premiums, potentially saving individuals money.
- Simplicity: This approach is straightforward, requiring no complex insurance policies or paperwork.
Disadvantages
- Financial Risk: Individuals are fully responsible for all accident-related costs, potentially leading to significant financial strain.
- Limited Protection: Cash-based coverage does not provide any financial protection for medical expenses, property damage, or legal costs.
Memberships and Associations
Some organizations offer membership benefits that include limited car insurance coverage. These benefits typically provide coverage for specific situations, such as accidents involving members of the organization.
Advantages
- Cost-Effective: Membership-based insurance options can be more affordable than traditional insurance.
- Community Support: Memberships often offer a sense of community and support, which can be beneficial in case of an accident.
Disadvantages
- Limited Coverage: Membership-based insurance usually provides limited coverage, often with specific exclusions and restrictions.
- Membership Requirements: Individuals may need to meet certain criteria or pay membership fees to access these benefits.
Pay-Per-Use Insurance
Pay-per-use insurance, also known as usage-based insurance, is a modern approach that charges drivers based on their actual driving habits. This model uses telematics devices or smartphone apps to track driving data, such as mileage, speed, and braking behavior.
Advantages
- Personalized Pricing: Pay-per-use insurance allows drivers with safe driving habits to potentially pay lower premiums.
- Cost-Effective: This option can be more affordable than traditional insurance for drivers who drive less frequently.
Disadvantages
- Data Privacy Concerns: Pay-per-use insurance requires sharing driving data, raising concerns about privacy.
- Limited Availability: This option is not available in all states or from all insurance companies.
Comparison Table
| Option | Features | Costs | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Insurance | Individuals set aside funds to cover accident costs. | No premiums, potential cost savings. | Cost savings, flexibility. |
| Cash-Based Coverage | Individuals pay for accident costs out of pocket. | No premiums, potential cost savings. | Cost savings, simplicity. |
| Memberships and Associations | Organizations offer limited insurance benefits to members. | Membership fees, potential cost savings. | Cost-effective, community support. |
| Pay-Per-Use Insurance | Premiums are based on actual driving habits. | Variable premiums based on usage. | Personalized pricing, cost-effective for low-mileage drivers. |
Conclusive Thoughts
While the allure of saving money on car insurance might be tempting, the potential risks of driving without insurance in states that don’t require it are substantial. It’s a gamble that could easily backfire, leaving drivers facing financial ruin and legal consequences. Understanding the legal requirements, financial implications, and alternative options available is crucial for making informed decisions about driving in these states. Ultimately, the choice is yours, but weigh the risks carefully before deciding to forgo car insurance.
Essential Questionnaire
What happens if I get into an accident without insurance in a state that doesn’t require it?
You will be personally liable for all damages and injuries caused by the accident, including medical bills, property damage, and legal fees. You could face lawsuits, wage garnishment, and even asset seizure to cover these costs.
What are the alternative options to traditional car insurance in these states?
Alternatives include self-insurance, surety bonds, and alternative risk transfer programs. These options may offer cost savings but often have limitations and may not provide the same level of protection as traditional car insurance.
Are there any exceptions to the “no car insurance required” rule in these states?
Yes, some states may require car insurance for specific situations, such as operating a commercial vehicle or having a history of driving violations. It’s important to check the specific requirements for your state.
Is it really cheaper to drive without insurance in these states?
While you might save on the cost of premiums, the potential costs of an accident far outweigh any potential savings. Without insurance, you’re taking a significant financial risk.







