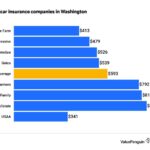
States that do not require auto insurance offer a unique perspective on driving regulations, prompting questions about financial responsibility and potential risks. While some might see this as a relaxed approach, it’s essential to understand the nuances of these laws and the implications for drivers and accidents.
In these states, drivers are not mandated to have traditional auto insurance policies, leaving them to navigate alternative options or rely on financial responsibility laws. This approach can be appealing for some, offering potential cost savings, but it also presents challenges in case of accidents or legal liabilities. This article delves into the complexities of these laws, exploring the potential risks and consequences of driving without insurance, examining alternatives to traditional insurance, and providing insights for residents of these states.
States Without Mandatory Auto Insurance
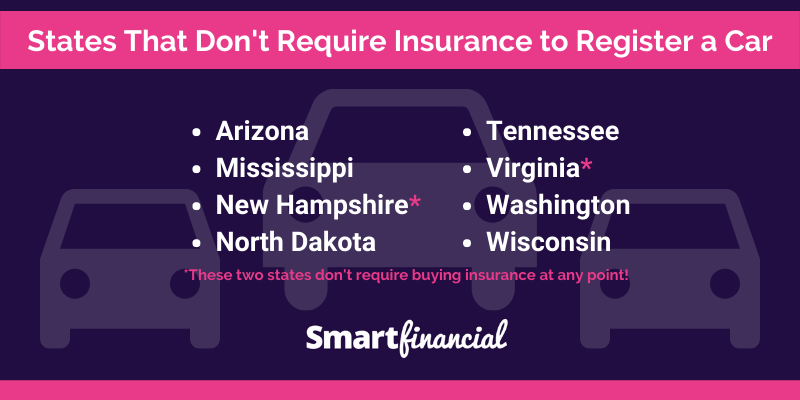
While most states in the US require drivers to carry auto insurance, a handful do not mandate it. The absence of this requirement is often linked to a combination of factors, including historical context, political considerations, and a desire to limit government intervention in personal choices.
States Without Mandatory Auto Insurance
A limited number of states have opted out of mandatory auto insurance requirements. These states are:
- New Hampshire
- Virginia
Potential Risks and Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without insurance in states that do not require it can lead to significant financial and legal repercussions.
- Financial Burden: In the event of an accident, drivers without insurance will be solely responsible for covering all related costs, including medical expenses, property damage, and legal fees. This can lead to substantial financial hardship, potentially forcing individuals into bankruptcy.
- Legal Consequences: Driving without insurance can result in various legal penalties, such as fines, license suspension, and even jail time. The severity of these penalties may vary depending on the state and the circumstances of the incident.
- Difficulty Obtaining Future Insurance: Having a history of driving without insurance can make it challenging to secure coverage in the future. Insurance companies often view drivers without insurance as high-risk, leading to higher premiums or even denial of coverage.
It’s important to remember that even in states without mandatory auto insurance, driving without insurance is a risky decision. The potential consequences far outweigh the perceived benefits.
Financial Responsibility Laws in Non-Insurance States
While some states do not mandate auto insurance, they still have financial responsibility laws in place to ensure drivers can cover damages caused by accidents. These laws differ from those in states with mandatory insurance, primarily focusing on demonstrating financial capability rather than requiring continuous insurance coverage.
Financial Responsibility Requirements
These laws generally require drivers to prove their ability to pay for damages caused in an accident. This proof can come in various forms, including:
- Financial Responsibility Bond: A bond issued by an insurance company guaranteeing payment for damages up to a certain amount. This bond typically acts as a substitute for insurance.
- Cash Deposit: Drivers can deposit a specific amount of money with the state, acting as a guarantee to cover potential damages.
- Self-Insurance: Some states allow drivers to self-insure, demonstrating financial capacity through a certificate of self-insurance, proving they can cover potential damages.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Drivers who fail to comply with financial responsibility laws face various penalties, including:
- License Suspension: The most common penalty is the suspension of the driver’s license. This can prevent the driver from operating a vehicle legally.
- Vehicle Registration Suspension: In some cases, the state may also suspend the registration of the vehicle, preventing it from being driven on public roads.
- Fines: Non-compliance can result in hefty fines, which can vary depending on the state and the specific violation.
- Legal Action: If a driver causes an accident without meeting financial responsibility requirements, they may face legal action from the injured party, leading to potential financial liabilities and legal consequences.
Examples of Financial Responsibility Laws in Non-Insurance States, States that do not require auto insurance
- New Hampshire: Requires drivers to provide proof of financial responsibility, such as a bond or cash deposit, only after an accident. The state offers a “No-Fault” insurance system, where drivers are responsible for their own injuries, but not for the injuries of others.
- Virginia: Requires drivers to maintain a minimum amount of liability insurance, even though it is not mandatory for all drivers. This is known as “Financial Responsibility” insurance, and drivers can choose to self-insure if they meet certain financial requirements.
Alternatives to Traditional Auto Insurance
In states without mandatory auto insurance, drivers face the risk of significant financial hardship in the event of an accident. Fortunately, several alternatives to traditional auto insurance offer coverage and financial protection. These alternatives provide varying levels of coverage, cost, and benefits, allowing drivers to choose the option that best suits their needs and budget.
Alternative Options to Traditional Auto Insurance
Here are some alternative options to traditional auto insurance:
- Self-Insurance: This involves setting aside funds to cover potential costs associated with accidents or damages. Self-insurance can be an option for drivers with a strong financial foundation and a low risk tolerance. However, it requires careful financial planning and the ability to absorb significant costs in the event of a major accident.
- Cash-Based Coverage: This involves paying for repairs or damages out of pocket, often with the help of a credit card or personal loan. While this option offers flexibility and potentially lower costs, it carries significant financial risk, as drivers are fully responsible for all costs associated with accidents.
- Ride-Sharing Services: Using ride-sharing services like Uber or Lyft can reduce the need for personal vehicle ownership and associated insurance costs. However, this option may not be suitable for all drivers, as it relies on the availability of rides and may not be cost-effective for frequent or long-distance travel.
- Memberships in Automobile Clubs: Some automobile clubs offer limited coverage, such as roadside assistance, emergency towing, and legal representation. These memberships can provide some protection in the event of an accident, but they typically do not cover liability or property damage.
- Surety Bonds: Surety bonds can be used to guarantee financial responsibility in the event of an accident. These bonds typically require a premium payment and may be a viable option for drivers with a strong credit history. However, they are not as comprehensive as traditional insurance policies and may not cover all potential costs.
- High-Risk Insurance: Some insurance companies offer high-risk insurance policies for drivers with poor driving records or other factors that make them ineligible for standard policies. These policies typically have higher premiums and may have limited coverage.
Comparison of Alternatives
The following table compares and contrasts the different alternatives based on their coverage, cost, and benefits:
| Alternative | Coverage | Cost | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Insurance | Limited | Potentially low | Flexibility, control over costs | High risk, potential for significant financial loss |
| Cash-Based Coverage | Limited | Potentially low | Flexibility | High risk, potential for significant financial loss |
| Ride-Sharing Services | Not applicable | Variable | Convenience, reduced ownership costs | Limited availability, may not be cost-effective for frequent travel |
| Automobile Club Memberships | Limited | Low | Roadside assistance, emergency towing | Limited coverage, does not cover liability or property damage |
| Surety Bonds | Limited | Variable | Financial responsibility guarantee | Not as comprehensive as traditional insurance, may require a strong credit history |
| High-Risk Insurance | Limited | High | Limited coverage for high-risk drivers | Higher premiums, limited coverage |
Impact on Drivers and Accidents

The absence of mandatory auto insurance in certain states can significantly impact drivers and the aftermath of accidents. Drivers in these states face increased financial and legal risks, potentially leading to severe consequences.
Financial Ramifications
The lack of mandatory auto insurance creates a higher risk of financial burden for drivers involved in accidents. Uninsured drivers are responsible for covering all accident-related expenses, including medical bills, property damage, and legal fees. This can lead to significant financial hardship, especially for those with limited resources.
Here’s a comparison of the potential outcomes for drivers with and without insurance:
| Outcome | Driver with Insurance | Driver Without Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Expenses | Covered by insurance | Out-of-pocket expenses |
| Property Damage | Covered by insurance | Out-of-pocket expenses |
| Legal Fees | Covered by insurance | Out-of-pocket expenses |
Legal Ramifications
Uninsured drivers who cause accidents face potential legal repercussions. Victims can sue uninsured drivers to recover damages, leading to significant financial penalties and even jail time.
“In some states, driving without insurance is considered a criminal offense, resulting in fines and even license suspension.”
Consequences for Uninsured Drivers
The lack of insurance can also lead to:
- Difficulty obtaining a loan or financing a vehicle
- Higher insurance premiums if they decide to obtain coverage later
- Negative impact on their credit score
Considerations for Residents: States That Do Not Require Auto Insurance
Living in a state without mandatory auto insurance can present unique challenges and opportunities. While it may seem appealing to avoid insurance premiums, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks and take proactive steps to protect yourself financially.
Financial Responsibility Laws
Understanding the financial responsibility laws in your state is paramount. These laws require drivers to demonstrate financial responsibility, typically through insurance or proof of financial resources, in case of an accident. Failing to meet these requirements can result in penalties, including fines, license suspension, or even imprisonment.
Alternatives to Traditional Auto Insurance
While traditional auto insurance may not be mandatory, residents have several alternative options to fulfill financial responsibility requirements and mitigate risks:
Self-Insurance
Self-insurance involves setting aside a substantial amount of money to cover potential accident costs. This option requires careful financial planning and risk assessment.
Surety Bonds
A surety bond is a financial guarantee issued by a surety company. It ensures that the bondholder will fulfill their financial obligations, such as covering accident-related expenses.
Cash Deposit
Some states allow drivers to make a cash deposit with the state to meet financial responsibility requirements. This deposit acts as a guarantee to cover potential accident costs.
Mitigating Risks and Protecting Yourself Financially
Here are some tips to mitigate risks and protect yourself financially in the absence of mandatory auto insurance:
Maintain a Clean Driving Record
A clean driving record is crucial in minimizing potential liability costs. Avoid traffic violations, accidents, and reckless driving.
Invest in Comprehensive Vehicle Maintenance
Regular vehicle maintenance helps prevent accidents and breakdowns. This includes regular oil changes, tire rotations, and brake inspections.
Consider Increasing Your Deductible
A higher deductible on your alternative insurance options can lower your premiums. However, ensure you have sufficient funds to cover the deductible in case of an accident.
Maintain a Strong Financial Reserve
Having a substantial financial reserve is essential to cover potential accident costs, including medical expenses, property damage, and legal fees.
Essential Steps for Financial Well-being
To ensure your financial well-being in a state without mandatory auto insurance, consider the following steps:
- Thoroughly research and understand the financial responsibility laws in your state. Familiarize yourself with the specific requirements, penalties, and alternative options available.
- Choose a suitable alternative insurance option or method to meet financial responsibility requirements. Carefully assess your financial situation, risk tolerance, and potential costs to determine the best option for you.
- Maintain a clean driving record and practice safe driving habits. This will help minimize the likelihood of accidents and associated costs.
- Invest in comprehensive vehicle maintenance and ensure your vehicle is in good working order. This can help prevent accidents and breakdowns.
- Establish a strong financial reserve to cover potential accident costs. This will provide a safety net in case of unexpected expenses.
- Consult with a financial advisor or insurance broker to discuss your specific needs and options. They can provide expert advice and guidance tailored to your situation.
Last Point

Driving without mandatory insurance comes with its own set of considerations. While it might seem like a cost-saving measure, the potential consequences of accidents or legal liabilities can outweigh any perceived benefits. It’s crucial to weigh the pros and cons carefully, explore available alternatives, and prioritize financial protection. Understanding the intricacies of these laws, the potential risks, and the available options empowers drivers to make informed decisions that ensure their safety and financial well-being.
Detailed FAQs
What are the financial responsibility laws in states without mandatory insurance?
These laws require drivers to prove their ability to pay for damages caused in an accident, typically through a bond, deposit, or self-insurance.
Are there any benefits to driving without mandatory insurance?
Some drivers might find potential cost savings as they are not required to purchase traditional insurance policies.
What are the potential consequences of driving without insurance in these states?
Drivers could face legal penalties, fines, license suspension, and difficulty in obtaining insurance in the future.
How can I protect myself financially if I live in a state without mandatory auto insurance?
Explore alternative insurance options, consider self-insurance, and ensure you meet the financial responsibility requirements of your state.