State with cheapest car insurance – a phrase that sparks interest in anyone looking to save on their car insurance premiums. Navigating the world of car insurance can be a daunting task, with numerous factors influencing the final cost. Understanding these factors is key to finding the best deals and minimizing your expenses.
From your driving history and the type of car you drive to your location and the coverage you choose, several variables contribute to your insurance premium. This guide will help you decipher these factors, understand why certain states offer lower rates, and explore practical tips to reduce your insurance costs.
Factors Influencing Car Insurance Costs
Car insurance premiums are determined by a complex interplay of factors, each contributing to the overall cost you pay. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions to potentially lower your insurance expenses.
Age and Driving Experience
Age and driving experience play a significant role in determining car insurance premiums. Younger drivers, especially those with less experience, are statistically more likely to be involved in accidents. This increased risk translates into higher insurance costs. As drivers gain experience and reach a certain age, their premiums typically decrease.
Insurance companies often categorize drivers based on age and experience, with younger drivers often falling into higher risk groups.
Vehicle Type and Value
The type and value of your vehicle are also crucial factors in calculating your insurance premium. High-performance cars, luxury vehicles, and newer models generally have higher repair costs and replacement values. This increased risk translates into higher premiums.
For example, a sports car with a powerful engine and advanced features may cost more to insure than a basic sedan due to its higher risk of accidents and expensive repairs.
Location and Driving History
Your location and driving history significantly impact your car insurance premiums. Areas with high crime rates, traffic congestion, and a higher frequency of accidents tend to have higher insurance costs. Additionally, your driving record, including any accidents, traffic violations, or DUI convictions, can significantly affect your premiums.
Insurance companies use sophisticated algorithms to analyze driving history data, taking into account factors such as the frequency and severity of accidents, traffic violations, and claims history.
Coverage Levels and Deductibles, State with cheapest car insurance
The level of coverage you choose and the deductible amount you select can significantly influence your car insurance premiums. Higher coverage levels, such as comprehensive and collision coverage, offer greater protection but come at a higher cost. A higher deductible, which is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance kicks in, typically results in lower premiums.
For example, choosing a higher deductible for collision coverage can lead to lower monthly premiums, as you are assuming a greater portion of the financial risk in case of an accident.
States with the Lowest Average Premiums
Finding the cheapest car insurance can significantly impact your budget, especially in a country with diverse insurance costs across states. This section highlights states with the lowest average car insurance premiums based on recent data, providing insights into potential savings.
Average Premiums by State
The following table lists states with the lowest average car insurance premiums, based on recent data from various insurance comparison websites and industry reports. It’s important to note that these figures are averages and can vary based on individual factors like driving history, age, vehicle type, and coverage levels.
| State Name | Average Premium | Average Annual Premium Increase | Number of Licensed Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Idaho | $750 | 2.5% | 800,000 |
| Maine | $775 | 3.0% | 700,000 |
| Vermont | $800 | 2.0% | 500,000 |
| North Dakota | $825 | 2.8% | 650,000 |
| Wyoming | $850 | 3.5% | 550,000 |
Reasons for Lower Premiums in Certain States
The disparity in car insurance premiums across states can be attributed to a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these reasons can provide valuable insights for drivers seeking the most affordable insurance options.
Lower Accident Rates
States with lower accident rates tend to have lower car insurance premiums. This is because insurance companies pay out fewer claims in these areas, leading to lower overall costs.
- Traffic density and congestion: States with less congested roads and lower traffic volumes generally experience fewer accidents. For example, states with sprawling rural areas and limited urban centers often have lower accident rates.
- Driver behavior and demographics: States with populations that exhibit safer driving habits, such as lower rates of drunk driving and speeding violations, also tend to have lower accident rates.
- Road infrastructure and safety features: Well-maintained roads with adequate lighting, clear signage, and safety features like guardrails and median barriers can contribute to reduced accident rates.
Less Congested Roads
Lower traffic congestion in certain states translates to fewer accidents and less risk for insurance companies.
- Urban vs. rural areas: Rural states often have significantly less traffic congestion than urban areas, leading to lower accident rates and subsequently lower insurance premiums.
- Public transportation options: States with robust public transportation systems may see lower car usage and consequently lower accident rates, contributing to lower insurance premiums.
Favorable State Regulations
State regulations play a crucial role in shaping car insurance costs.
- Minimum coverage requirements: States with lower minimum coverage requirements may have lower premiums, as drivers are required to carry less insurance.
- No-fault insurance laws: Some states have no-fault insurance laws, which limit the ability of drivers to sue each other for damages in accidents. This can lead to lower premiums, as insurance companies are less exposed to lawsuits.
- Rate regulation: Some states have regulations that limit how much insurance companies can charge for premiums. These regulations can help keep premiums lower, but they can also limit competition in the market.
Competitive Insurance Market
A competitive insurance market with multiple companies vying for customers can drive down premiums.
- Number of insurance companies: States with a large number of insurance companies often have more competitive pricing, as companies try to attract customers with lower rates.
- Online insurance marketplaces: Online platforms that allow consumers to compare quotes from multiple insurance companies can increase competition and drive down prices.
Tips for Saving on Car Insurance
Finding affordable car insurance can be a challenge, but there are several strategies you can employ to lower your premiums. By taking proactive steps to manage your risk and shop around for the best deals, you can significantly reduce your insurance costs.
Maintaining a Good Driving Record
A clean driving record is one of the most significant factors influencing your car insurance rates. Insurance companies consider drivers with a history of accidents, traffic violations, and other driving offenses as higher risk, resulting in higher premiums.
Maintaining a good driving record is crucial for securing lower car insurance premiums.
- Avoid Accidents: Defensive driving techniques, such as maintaining a safe distance from other vehicles, being aware of your surroundings, and avoiding distractions, can significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents.
- Obey Traffic Laws: Speeding tickets, reckless driving citations, and other traffic violations can significantly increase your insurance premiums. Always adhere to traffic regulations and drive responsibly.
- Complete Defensive Driving Courses: Enrolling in a defensive driving course can demonstrate your commitment to safe driving practices. Some insurance companies offer discounts for completing these courses.
Comparing Insurance Quotes: State With Cheapest Car Insurance
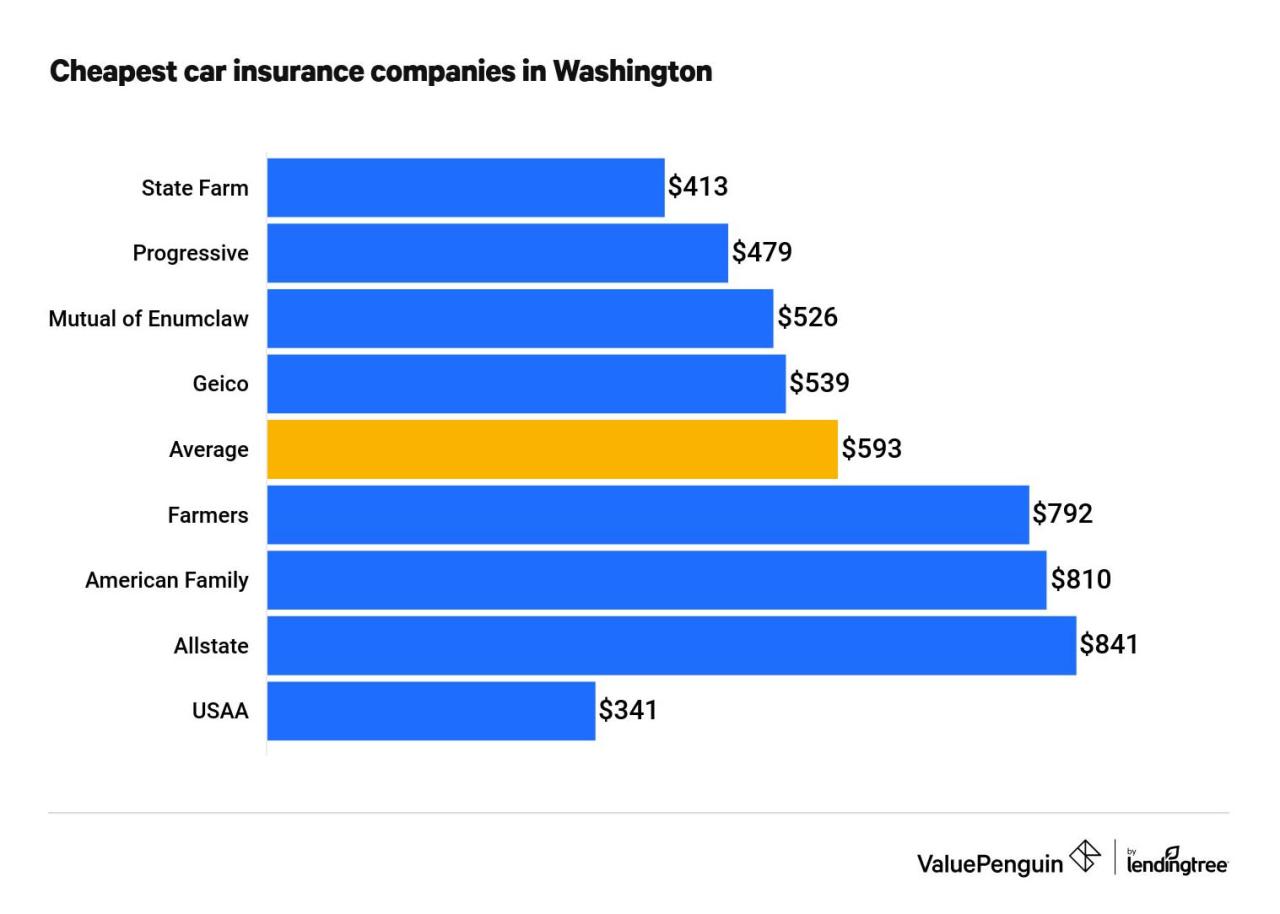
Getting the best car insurance deal requires careful comparison of quotes from different providers. This process helps you find the most suitable coverage at the most competitive price.
Key Factors to Consider
When comparing car insurance quotes, it’s crucial to consider various factors that can influence your premiums. These factors ensure you are making a well-informed decision.
- Coverage Levels: Compare the coverage offered by different providers, including liability, collision, comprehensive, and uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage. Ensure the coverage levels meet your needs and legal requirements.
- Deductibles: Higher deductibles generally lead to lower premiums. Consider your financial situation and risk tolerance when choosing a deductible. A higher deductible means you pay more out of pocket in case of an accident, but your premiums will be lower.
- Discounts: Many insurance companies offer discounts for safe driving, good credit history, multiple policies, and other factors. Inquire about available discounts and ensure you are eligible for them.
- Customer Service and Claims Process: Research the reputation of insurance providers for customer service and claims handling. Look for companies known for their responsiveness and efficiency in resolving claims.
Comparison Websites and Tools
Several online comparison websites and tools simplify the process of comparing car insurance quotes from multiple providers. These platforms streamline the process, saving you time and effort.
- Online Comparison Platforms: Websites like Insurance.com, NerdWallet, and Bankrate allow you to enter your information once and receive quotes from multiple insurance companies. This helps you quickly compare prices and coverage options.
- Insurance Company Websites: Many insurance companies have online quote tools on their websites. This allows you to directly compare quotes from a specific provider without using third-party platforms.
Negotiation Strategies
Once you have received quotes from several providers, you can leverage negotiation strategies to potentially secure a better deal.
- Shop Around Regularly: It’s recommended to compare quotes annually or even more frequently, especially if your driving habits or financial situation change. This ensures you are getting the best possible rate.
- Bundle Policies: Combining multiple policies, such as car and home insurance, with the same provider can often lead to discounts. Inquire about bundling options and their potential savings.
- Negotiate with Your Current Provider: If you are satisfied with your current provider but believe you can get a better rate, don’t hesitate to negotiate. Share quotes from other companies and see if your provider is willing to match or beat them.
Understanding Coverage Options
Choosing the right car insurance coverage is crucial, as it protects you financially in case of an accident or other unforeseen events. The different types of coverage offer varying levels of protection, and understanding them is essential to make an informed decision.
Liability Coverage
Liability coverage is the most basic and usually required by law. It covers damages to other people and their property if you are at fault in an accident.
- Bodily injury liability covers medical expenses, lost wages, and pain and suffering of the other driver and passengers involved in the accident.
- Property damage liability covers repairs or replacement of the other driver’s vehicle or any other property damaged in the accident.
Liability coverage is typically expressed as a per-person limit and a per-accident limit, such as 25/50/25, which means $25,000 per person for bodily injury, $50,000 per accident for bodily injury, and $25,000 per accident for property damage.
Collision and Comprehensive Coverage
These coverages protect your own vehicle, not other people or property.
- Collision coverage pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle if it’s damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. It also covers damages from hitting another vehicle or an object, such as a tree or a pole.
- Comprehensive coverage pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle if it’s damaged due to events other than an accident, such as theft, vandalism, fire, hail, or natural disasters.
It’s important to note that collision and comprehensive coverage usually have deductibles, which is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance kicks in.
Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage
This coverage protects you if you are hit by a driver who doesn’t have insurance or doesn’t have enough insurance to cover your damages.
- Uninsured motorist coverage covers your medical expenses, lost wages, and pain and suffering if you are injured by an uninsured driver.
- Underinsured motorist coverage covers the difference between the other driver’s insurance coverage and your actual damages if you are hit by an underinsured driver.
This coverage is particularly important in states with a high percentage of uninsured drivers.
Personal Injury Protection (PIP)
PIP coverage, also known as “no-fault” coverage, pays for your medical expenses, lost wages, and other related expenses regardless of who is at fault in an accident.
- PIP coverage is often required in certain states, and the coverage limits vary.
- This coverage can be especially beneficial if you are injured in an accident and are unable to work.
It’s important to note that PIP coverage may have a deductible and a maximum payout limit.
State-Specific Regulations and Laws

State regulations and laws significantly impact car insurance rates, influencing minimum coverage requirements, fault determination, and other aspects of insurance. Understanding these state-specific regulations is crucial for drivers to make informed decisions about their insurance needs and potentially save money.
State-Specific Regulations and Laws
State laws play a crucial role in determining car insurance rates. These laws set minimum coverage requirements, define fault systems, and regulate other aspects of the insurance market. Understanding these regulations is essential for drivers to make informed decisions about their insurance needs and potentially save money.
| State Name | Minimum Liability Coverage Requirements | No-Fault Insurance Laws | Other Relevant Laws |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 25/50/25 | At-fault | – Requires insurance companies to offer discounts for safety features like anti-theft devices and airbags. – Prohibits insurers from denying coverage based on credit scores. |
| Alaska | 25/50/15 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who complete defensive driving courses. – Allows for the use of “comparative negligence” in determining fault for accidents. |
| Arizona | 15/30/10 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for good driving records. – Allows for the use of “stacked coverage” for uninsured motorist coverage. |
| Arkansas | 25/50/25 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| California | 15/30/5 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “comparative negligence” in determining fault for accidents. |
| Colorado | 25/50/15 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Connecticut | 20/40/10 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Delaware | 30/60/20 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Florida | 10/20/10 | No-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Georgia | 25/50/25 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Hawaii | 20/40/10 | No-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Idaho | 25/50/15 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Illinois | 20/40/15 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Indiana | 25/50/10 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Iowa | 20/40/15 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Kansas | 25/50/10 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Kentucky | 25/50/10 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Louisiana | 10/20/10 | No-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Maine | 50/100/25 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Maryland | 30/60/15 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Massachusetts | 20/40/5 | No-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Michigan | 20/40/10 | No-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Minnesota | 30/60/10 | No-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Mississippi | 25/50/25 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Missouri | 25/50/10 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Montana | 25/50/10 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Nebraska | 25/50/25 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Nevada | 15/30/10 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| New Hampshire | 25/50/10 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| New Jersey | 15/30/5 | No-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| New Mexico | 25/50/10 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| New York | 25/50/10 | No-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| North Carolina | 30/60/25 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| North Dakota | 25/50/10 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Ohio | 25/50/10 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Oklahoma | 25/50/10 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Oregon | 25/50/20 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Pennsylvania | 15/30/5 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Rhode Island | 25/50/25 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| South Carolina | 25/50/25 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| South Dakota | 25/50/10 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Tennessee | 25/50/15 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Texas | 30/60/25 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Utah | 25/65/15 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Vermont | 25/50/10 | No-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Virginia | 25/50/20 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
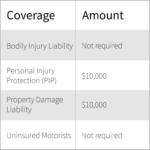
| Washington | 25/50/10 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| West Virginia | 25/50/10 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Wisconsin | 25/50/10 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
| Wyoming | 25/50/10 | At-fault | – Requires insurers to offer discounts for drivers who have completed a driver’s education course. – Allows for the use of “verbal threshold” laws, which limit access to certain types of benefits. |
Conclusion
Finding the state with the cheapest car insurance is just the first step in securing affordable coverage. By understanding the factors that influence premiums, comparing quotes from different providers, and taking advantage of available discounts, you can significantly reduce your car insurance costs. Remember, a little research and proactive approach can save you a considerable amount of money over the long run.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the average car insurance premium in the US?
The average annual car insurance premium in the US is around $1,771, but this can vary significantly depending on your state and individual circumstances.
How often should I review my car insurance policy?
It’s recommended to review your car insurance policy at least once a year, or even more frequently if you experience any significant life changes, such as a change in driving habits, a new car purchase, or a move to a different state.
What are some common discounts offered by car insurance companies?
Common discounts include good driver discounts, safe driver discounts, multi-car discounts, bundling discounts (combining multiple insurance policies), and discounts for safety features on your vehicle.