State of Texas insurance requirements are a crucial aspect of responsible living in the Lone Star State. From protecting your vehicle and home to ensuring your health and financial well-being, understanding these regulations is essential. This comprehensive guide explores the various types of insurance required in Texas, providing insights into their purpose, coverage options, and potential exemptions.
Navigating the complex world of insurance can be overwhelming, but this guide aims to simplify the process by offering clear explanations and helpful resources. Whether you’re a new resident or a seasoned Texan, understanding the state’s insurance requirements is vital for protecting yourself and your loved ones.
Texas Insurance Requirements Overview
Texas has a robust system of insurance requirements designed to protect individuals, families, and businesses from financial hardship in the event of unforeseen circumstances. These requirements are essential for ensuring the well-being of the state’s residents and the stability of its economy.
Types of Insurance Required in Texas
Texas mandates various types of insurance coverage to safeguard individuals and property. Here’s a breakdown of the most common insurance requirements:
- Auto Insurance: All Texas drivers are required to have liability insurance, which covers damages to other vehicles and injuries to other individuals in the event of an accident. Minimum coverage levels are set by the state.
- Health Insurance: While not mandated for all Texans, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) requires most individuals to have health insurance. Those who do not have health insurance through their employer or government programs may be subject to a penalty.
- Homeowners Insurance: If you own a home in Texas, you are required to have homeowners insurance to protect your property against damages caused by fire, theft, or other perils.
- Liability Insurance: This type of insurance protects individuals and businesses from financial losses resulting from claims of negligence or wrongdoing. Liability insurance is often required for property owners, landlords, and businesses.
Evolution of Insurance Requirements in Texas
Insurance requirements in Texas have evolved over time to reflect changing societal needs and economic conditions.
Early insurance regulations in Texas focused primarily on protecting the public from financial losses caused by irresponsible or negligent individuals.
Over time, the state has expanded its insurance requirements to address a wider range of risks, including those related to natural disasters, healthcare costs, and environmental damage. For instance, the introduction of flood insurance requirements in areas prone to flooding reflects the state’s commitment to protecting its residents from the financial consequences of natural disasters.
Auto Insurance Requirements

Driving without auto insurance in Texas is illegal and can result in fines and license suspension. To ensure you are compliant with the law and protected in case of an accident, it is essential to understand the state’s auto insurance requirements.
Minimum Liability Coverage Requirements
Texas law mandates that all drivers carry a minimum amount of liability insurance to cover damages caused to others in case of an accident. These requirements are designed to protect other drivers, passengers, and property owners in the event of a collision. The minimum liability coverage requirements in Texas are:
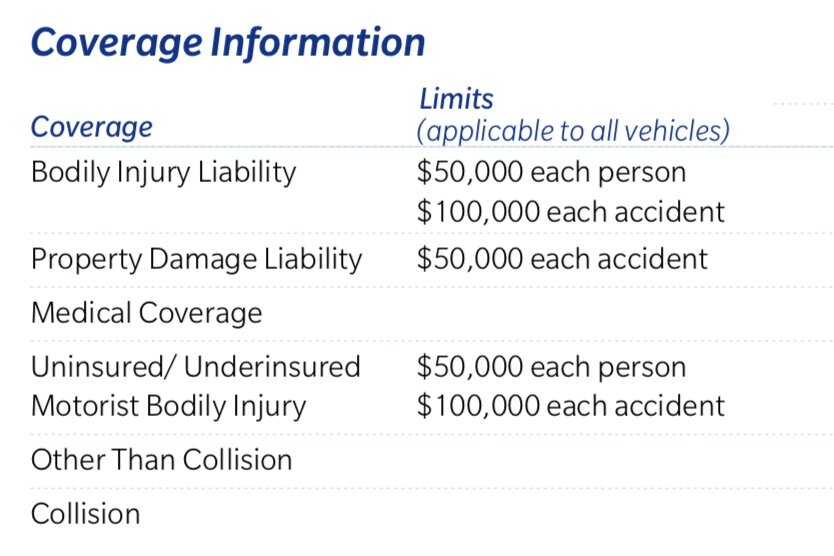
* Bodily Injury Liability: $30,000 per person / $60,000 per accident
* Property Damage Liability: $25,000 per accident
This means that if you cause an accident that results in injuries to another person, your insurance will cover up to $30,000 per injured person and up to $60,000 for all injuries in the accident. Similarly, your insurance will cover up to $25,000 in damages to another person’s property.
Types of Auto Insurance Coverage
While minimum liability coverage is required, there are several other types of auto insurance coverage available in Texas. These additional coverages can provide broader protection and financial security in the event of an accident. Some of the most common types of auto insurance coverage include:
- Collision Coverage: This coverage pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle if it is damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. It helps cover costs like repairs, towing, and rental car expenses.
- Comprehensive Coverage: This coverage protects your vehicle against damage caused by events other than collisions, such as theft, vandalism, fire, or natural disasters. It covers repairs or replacement costs for damage caused by these events.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage (UM/UIM): This coverage protects you and your passengers if you are involved in an accident with an uninsured or underinsured driver. It helps cover medical expenses, lost wages, and property damage caused by the other driver’s negligence.
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): While not mandatory in Texas, PIP coverage can help pay for medical expenses, lost wages, and other related costs for you and your passengers, regardless of fault. It provides valuable protection for injuries sustained in an accident.
- Medical Payments Coverage (Med Pay): This coverage pays for medical expenses for you and your passengers, regardless of fault, up to the policy limit. It can help cover costs like hospital bills, doctor visits, and prescriptions.
Comparing and Contrasting Auto Insurance Options
The cost of auto insurance can vary significantly depending on factors like your driving record, age, location, and the type of coverage you choose.
- Minimum Liability Coverage: This is the most affordable option, but it provides limited protection. It only covers damages you cause to others, not your own vehicle or injuries to yourself.
- Full Coverage: This includes collision, comprehensive, and liability coverage, providing comprehensive protection. While it is more expensive, it offers peace of mind and financial security in case of an accident.
- Customized Coverage: You can tailor your coverage to meet your specific needs and budget. You can choose to add or remove specific coverages, such as collision, comprehensive, or uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage, to customize your policy.
It is essential to carefully consider your individual circumstances and driving habits when choosing the right auto insurance coverage. You can consult with an insurance agent or broker to discuss your options and determine the most suitable coverage for your needs.
Homeowners Insurance Requirements
In Texas, homeowners insurance is not legally mandated, but it’s highly recommended for anyone who owns a home. While it’s not required by law, mortgage lenders often make it a condition for approving a loan. This means that most homeowners will end up purchasing homeowners insurance anyway.
Factors Affecting Homeowners Insurance Premiums
Homeowners insurance premiums are determined by a variety of factors, including:
- Property Value: The higher the value of your home, the more expensive your insurance will be. This is because you’re essentially insuring a larger amount of potential loss.
- Location: The risk of natural disasters and crime varies by location. Homes in areas prone to hurricanes, earthquakes, or wildfires will generally have higher premiums. Areas with higher crime rates can also lead to increased premiums.
- Coverage Options: The amount of coverage you choose will also impact your premium. More comprehensive coverage, including protection for things like floods or earthquakes, will generally cost more.
- Deductible: The deductible is the amount you agree to pay out of pocket before your insurance kicks in. A higher deductible means a lower premium, but you’ll have to pay more in case of a claim.
- Credit Score: Your credit score can also affect your insurance premiums. Insurance companies may use your credit score as a proxy for your risk assessment.
Common Homeowner Insurance Coverages
Homeowners insurance policies typically offer several types of coverage:
- Dwelling Coverage: This covers the structure of your home, including the walls, roof, and foundation. This is typically the largest part of your homeowners insurance policy.
- Other Structures Coverage: This covers structures on your property that are not attached to your home, such as a detached garage, fence, or shed.
- Personal Property Coverage: This covers your belongings inside your home, such as furniture, electronics, clothing, and jewelry. This coverage typically has limits, so it’s important to make sure you have enough coverage for all of your valuable items.
- Liability Coverage: This protects you from financial losses if someone is injured on your property or if you are found liable for damages to someone else’s property.
- Additional Living Expenses Coverage: This helps cover the cost of temporary housing and other living expenses if your home is damaged and uninhabitable due to a covered event.
Coverage Limitations, State of texas insurance requirements
It’s important to be aware of the limitations of homeowners insurance. Most policies have exclusions, which are events or situations that are not covered. Some common exclusions include:
- Earthquakes: Earthquake coverage is typically not included in standard homeowners insurance policies and must be purchased separately.
- Floods: Flood insurance is also typically not included in standard homeowners insurance policies and must be purchased separately.
- Acts of War: Most homeowners insurance policies do not cover damage caused by acts of war.
- Neglect: If damage is caused by your negligence, your insurance may not cover it.
Health Insurance Requirements
Texas has specific requirements regarding health insurance, largely influenced by the Affordable Care Act (ACA), also known as Obamacare. The ACA aims to ensure that most Americans have access to affordable health insurance. This section delves into the various aspects of health insurance in Texas, including the different types of plans available and the eligibility requirements for specific programs.
The Affordable Care Act’s Impact
The ACA significantly changed the health insurance landscape in Texas. It introduced several key provisions, including the individual mandate, which required most individuals to have health insurance or face a penalty. However, this mandate was repealed in 2019. The ACA also expanded Medicaid eligibility, created health insurance marketplaces, and provided subsidies to help individuals afford coverage.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
Texas offers a variety of health insurance plans to cater to different needs and budgets. The primary categories include:
- Individual Health Insurance: These plans are purchased directly by individuals, allowing them to choose the coverage that best suits their circumstances. They are often available through the Health Insurance Marketplace, a platform established by the ACA.
- Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance: Many employers in Texas offer health insurance as part of their benefits packages. These plans typically provide more comprehensive coverage than individual plans, and employees often pay a lower premium due to group rates.
- Government-Sponsored Health Insurance: Texas offers various government-sponsored health insurance programs, such as Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP). These programs are designed to provide affordable coverage to low-income individuals and families.
Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility
Medicaid is a government-funded health insurance program for low-income individuals and families. CHIP is a similar program specifically for children. Eligibility for both programs is based on income and household size.
- Medicaid: Texas has expanded Medicaid eligibility under the ACA, but it still has stricter eligibility requirements than some other states. Individuals can apply for Medicaid through the Texas Health and Human Services Commission website.
- CHIP: Texas CHIP provides health insurance to children from families with incomes above the Medicaid eligibility threshold. Children can be eligible for CHIP even if their parents are not eligible for Medicaid.
Liability Insurance Requirements
Liability insurance is a crucial aspect of risk management in Texas, particularly for businesses and professionals. It safeguards you from financial ruin by covering legal costs and settlements arising from injuries or damages caused by your actions or negligence. This insurance provides peace of mind and protects your assets from potential claims.
Types of Liability Insurance in Texas
Texas law mandates certain types of liability insurance for specific professions and businesses. The following list details some of the most common liability insurance types in Texas:
- General Liability Insurance: This type of insurance provides coverage for a wide range of potential liabilities, including bodily injury, property damage, and advertising injuries. It is essential for businesses with customer interactions or public exposure, as it protects them from lawsuits arising from various incidents.
- Professional Liability Insurance (Malpractice Insurance): Professionals like doctors, lawyers, accountants, and engineers need professional liability insurance to protect them from claims related to their professional services. This coverage helps cover legal fees and settlements if a client alleges negligence or malpractice during the professional’s services.
- Product Liability Insurance: Businesses that manufacture, distribute, or sell products need product liability insurance. This type of coverage protects them from claims arising from defective products that cause injuries or property damage to consumers.
Factors Influencing the Cost of Liability Insurance
Several factors contribute to the cost of liability insurance in Texas. Understanding these factors can help businesses and individuals make informed decisions about their insurance needs:
- Industry and Occupation: The risk associated with different industries and professions significantly influences insurance premiums. For example, healthcare professionals face higher premiums than retail businesses due to the higher risk of malpractice lawsuits.
- Location: The geographical location of a business or individual can impact insurance costs. Areas with higher population density or a history of lawsuits may have higher premiums.
- Business Size and Revenue: Larger businesses with higher revenues typically have higher liability insurance premiums. This is because they have a greater potential for claims and exposure to risk.
- Claims History: Businesses with a history of claims or lawsuits may face higher premiums. Insurance companies consider past claims as an indicator of future risk.
- Safety Measures and Risk Management Practices: Businesses that implement strong safety measures and risk management practices may qualify for lower premiums. Insurance companies recognize proactive measures as a sign of reduced risk.
Exemptions and Waivers
In Texas, certain individuals and situations may be exempt from specific insurance requirements or eligible for waivers. These exemptions and waivers are designed to address unique circumstances and alleviate the burden of insurance coverage in specific cases.
Exemptions from Auto Insurance Requirements
In Texas, individuals may be exempt from certain auto insurance requirements under specific circumstances. These exemptions are typically granted to vehicles that are not regularly used on public roads or are considered low-risk.
- Vehicles used solely for farm or ranch purposes: Vehicles used exclusively on private property, such as farms or ranches, may be exempt from auto insurance requirements. These vehicles are not considered to be operating on public roads and are not subject to the same risks as vehicles used for everyday transportation.
- Vehicles used for non-profit organizations: Vehicles used solely for charitable or non-profit purposes may be exempt from certain auto insurance requirements. These exemptions are typically granted to organizations that are not engaged in commercial activities and do not generate revenue from the use of their vehicles.
- Antique vehicles: Vehicles that are considered antiques, based on their age and historical significance, may be exempt from certain auto insurance requirements. These exemptions are typically granted to vehicles that are not driven regularly and are primarily used for display purposes.
Waivers for Homeowners Insurance Requirements
Homeowners insurance requirements in Texas may be waived or modified under certain circumstances. These waivers are typically granted to homeowners who meet specific criteria, such as those who own their homes outright or who have a low risk of property damage.
- Homes owned outright: Homeowners who own their homes outright, without any outstanding mortgage or lien, may be eligible for a waiver of certain homeowners insurance requirements. These homeowners are considered to have a lower risk of financial loss in the event of property damage, as they are not obligated to repay a lender.
- Low-risk properties: Homeowners who own properties that are considered low-risk, based on factors such as location, age, and construction, may be eligible for a waiver of certain homeowners insurance requirements. These waivers are typically granted to homeowners who have a lower probability of experiencing property damage.
Waivers for Health Insurance Requirements
Health insurance requirements in Texas may be waived or modified under certain circumstances. These waivers are typically granted to individuals who meet specific criteria, such as those who are eligible for other forms of health coverage or who have a pre-existing medical condition.
- Eligibility for other health coverage: Individuals who are eligible for other forms of health coverage, such as Medicare, Medicaid, or military health insurance, may be exempt from the individual health insurance mandate. These individuals are considered to have alternative sources of health insurance coverage.
- Pre-existing medical conditions: Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions may be eligible for waivers of certain health insurance requirements. These waivers are typically granted to individuals who have difficulty obtaining affordable health insurance coverage due to their pre-existing conditions.
Exemptions from Liability Insurance Requirements
Liability insurance requirements in Texas may be waived or modified under certain circumstances. These exemptions are typically granted to individuals or entities that are not considered to be at risk of causing significant financial harm to others.
- Government entities: Government entities, such as state agencies and local municipalities, may be exempt from certain liability insurance requirements. These exemptions are typically granted based on the assumption that government entities are already covered by other forms of insurance or indemnification.
- Non-profit organizations: Non-profit organizations may be exempt from certain liability insurance requirements, particularly if their activities are considered to be low-risk and do not involve significant financial exposure.
Resources and Support: State Of Texas Insurance Requirements

Navigating the world of Texas insurance can be a complex endeavor. Thankfully, a wealth of resources are available to help Texans understand their insurance requirements and find the right coverage for their needs.
State Agencies and Organizations
The Texas Department of Insurance (TDI) is the primary source of information on insurance regulations and consumer protection in the state. It offers various resources, including:
- Consumer Hotline: (800) 252-3439
- Website: https://www.tdi.texas.gov/
The Texas Department of Motor Vehicles (TxDMV) is responsible for regulating vehicle registration and insurance. Texans can access information about minimum auto insurance requirements, file complaints, and find resources on vehicle safety.
- Website: https://www.txdmv.gov/
The Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) provides information and resources on health insurance, including Medicaid and CHIP.
- Website: https://www.dshs.texas.gov/
The Texas Office of Consumer Credit Commissioner (OCCC) protects consumers from unfair or deceptive practices in the financial services industry, including insurance.
- Website: https://www.occc.texas.gov/
Insurance Companies and Brokers
Texas has a diverse landscape of insurance companies, each offering a range of products and services.
- Major Insurance Companies: State Farm, Allstate, Geico, Farmers Insurance, Progressive, USAA
- Independent Insurance Agents and Brokers: These professionals can help you compare quotes and find the best coverage for your needs. The Independent Insurance Agents & Brokers of Texas (IIABT) is a valuable resource for finding a local agent.
- Website: https://www.iiabt.org/
Consumer Protection Organizations
Several organizations advocate for consumers’ rights and provide information on insurance issues.
- Texas Legal Services Center: Offers legal assistance to low-income Texans on various issues, including insurance disputes.
- Better Business Bureau (BBB): Provides ratings and reviews of businesses, including insurance companies.
- Consumer Reports: Offers independent reviews and ratings of insurance companies and products.
Online Resources and Tools
The internet offers a wealth of information and tools for researching and obtaining insurance in Texas.
- TDI’s Consumer Information Website: https://www.tdi.texas.gov/
- Insurance Comparison Websites: Websites like Policygenius, The Zebra, and NerdWallet allow you to compare quotes from multiple insurers.
- Online Insurance Providers: Many insurance companies offer online quotes and purchase options, making it convenient to obtain coverage.
End of Discussion
By understanding and adhering to Texas insurance requirements, residents can safeguard themselves from unexpected financial burdens and ensure peace of mind. From the minimum auto liability coverage to the various options for homeowners and health insurance, this guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the essential aspects of insurance in Texas. Remember to consult with qualified professionals and explore the resources available to make informed decisions about your insurance needs.
Clarifying Questions
What happens if I don’t have the required insurance?
Failing to meet the minimum insurance requirements in Texas can result in hefty fines, license suspension, and even the inability to register your vehicle.
How often do I need to renew my insurance?
Insurance policies in Texas typically have a renewal period of six months or one year. It’s important to stay informed about your renewal dates to avoid any lapses in coverage.
Can I get a discount on my insurance?
Yes, many insurance companies offer discounts for various factors, including safe driving records, good credit scores, and bundling multiple insurance policies.