State minimum car insurance is a legal requirement in every state, designed to protect drivers and their victims in the event of an accident. It provides basic financial coverage, but it’s crucial to understand what’s included and whether it’s enough for your specific needs.
This guide explores the complexities of state minimum car insurance, from its purpose and coverage to the factors influencing its cost. We’ll also discuss the potential risks of driving with only minimum coverage and offer strategies for finding affordable insurance options that meet your individual needs.
State Minimum Car Insurance Requirements

Every state in the United States requires drivers to have a minimum amount of car insurance. This is to protect drivers and their passengers from financial hardship in the event of an accident. State minimum car insurance requirements ensure that all drivers have basic coverage, providing a safety net for those involved in accidents.
Types of Coverage Included
State minimum car insurance policies typically include liability coverage, which protects drivers from financial responsibility for damages or injuries caused to others in an accident. These policies often include:
- Bodily Injury Liability: This coverage pays for medical expenses, lost wages, and other damages caused to the other driver and their passengers if you are at fault in an accident.
- Property Damage Liability: This coverage pays for repairs or replacement costs of the other driver’s vehicle and any other property damaged in an accident if you are at fault.
Minimum Requirements Across States
State minimum car insurance requirements vary significantly. Some states require higher coverage limits than others. For example, in some states, the minimum bodily injury liability coverage might be $25,000 per person and $50,000 per accident, while in other states, it could be as high as $100,000 per person and $300,000 per accident.
Consequences of Driving Without Minimum Car Insurance
Driving without minimum car insurance can have serious consequences, including:
- Fines and Penalties: You can face hefty fines and penalties for driving without insurance. These fines can vary from state to state, and they can also increase with repeat offenses.
- License Suspension or Revocation: Driving without insurance can result in the suspension or revocation of your driver’s license. This can make it difficult or impossible to drive legally.
- Impoundment of Your Vehicle: In some states, your vehicle may be impounded if you are caught driving without insurance.
- Financial Responsibility: If you are involved in an accident without insurance, you will be personally responsible for all damages and injuries, even if you were not at fault. This can lead to significant financial hardship, including legal fees, medical bills, and repair costs.
Understanding Your Coverage Needs
While state minimum car insurance requirements ensure you meet the legal baseline, it’s crucial to understand that this coverage might not be sufficient for your specific needs. Factors beyond the state minimum can influence your car insurance needs, and having higher coverage limits can offer significant benefits in the event of an accident.
Factors Influencing Coverage Needs
Several factors can influence your need for coverage beyond the state minimum.
- Value of Your Vehicle: If you drive a newer or more expensive car, the minimum coverage may not be enough to fully cover the cost of repairs or replacement in case of an accident.
- Your Driving History: If you have a history of accidents or traffic violations, you might need higher coverage limits to mitigate potential risks.
- Your Financial Situation: Your financial stability plays a role. If you have significant assets or dependents, you might consider higher coverage limits to protect yourself from financial hardship in case of a major accident.
- Your Driving Habits: If you frequently drive in high-traffic areas or have a longer commute, the chances of being involved in an accident increase, making higher coverage more beneficial.
- Your Location: The cost of living and repair costs in your area can influence your coverage needs. Areas with higher living costs or frequent accidents may require higher coverage limits.
Benefits of Higher Coverage Limits
- Financial Protection: Higher coverage limits provide greater financial protection in case of an accident, ensuring you can cover medical expenses, property damage, and other related costs.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing you have adequate coverage can offer peace of mind, reducing the financial burden and stress associated with an accident.
- Legal Protection: Higher coverage limits can help protect you from potential legal liabilities, such as lawsuits arising from an accident.
- Improved Credit Score: Paying for higher coverage limits can improve your credit score, as it demonstrates responsible financial behavior.
Risks of Driving with Minimum Coverage
Driving with only minimum coverage exposes you to several risks:
- Insufficient Coverage: In the event of a major accident, minimum coverage may not be enough to cover all expenses, leaving you financially responsible for the difference.
- Financial Hardship: Without sufficient coverage, you might face significant financial hardship, including medical bills, legal fees, and repair costs.
- Legal Liability: Minimum coverage might not be sufficient to cover all legal liabilities in case of an accident, potentially leading to lawsuits and financial ruin.
- Limited Options: Minimum coverage may limit your options for repairs or replacements, forcing you to settle for less than what you deserve.
Real-World Scenarios
- Accident with Multiple Vehicles: If you’re involved in an accident involving multiple vehicles, minimum coverage might not cover the damages to all vehicles involved, leaving you liable for the remaining costs.
- Severe Injury: In case of a severe injury, minimum coverage may not cover all medical expenses, leaving you with a substantial medical debt.
- Property Damage: If you cause significant property damage, minimum coverage might not be enough to cover the repair or replacement costs, leading to financial hardship.
Types of Car Insurance Coverage
While state minimum car insurance requirements provide basic protection, they may not be enough to cover all potential expenses in the event of an accident. Understanding the different types of car insurance coverage beyond the minimum can help you make informed decisions about your insurance policy and ensure you have the right protection for your needs.
Comprehensive Coverage
Comprehensive coverage protects your vehicle against damages caused by events other than collisions, such as theft, vandalism, fire, hail, or natural disasters. This coverage pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle, minus your deductible.
- Example: If your car is stolen or damaged in a hailstorm, comprehensive coverage would help pay for repairs or replacement.
Collision Coverage
Collision coverage protects your vehicle against damages caused by a collision with another vehicle or object, regardless of who is at fault. This coverage pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle, minus your deductible.
- Example: If you are involved in an accident and damage your vehicle, collision coverage would help pay for repairs or replacement, even if you are at fault.
Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage
Uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage protects you and your passengers in case of an accident with a driver who is uninsured or has insufficient insurance. This coverage helps pay for medical expenses, lost wages, and other damages.
- Example: If you are hit by a driver who does not have insurance or has insufficient insurance to cover your injuries and damages, uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage would help pay for your losses.
Personal Injury Protection (PIP)
Personal injury protection (PIP) coverage, also known as no-fault insurance, covers your medical expenses and lost wages after an accident, regardless of who is at fault. It is typically required in some states.
- Example: If you are injured in an accident, PIP coverage would help pay for your medical bills and lost wages, even if you were at fault.
Medical Payments Coverage (Med Pay)
Medical payments coverage (Med Pay) is similar to PIP but covers medical expenses for you and your passengers regardless of fault, but only up to a certain limit.
- Example: If you are injured in an accident, Med Pay would help pay for your medical bills, even if you were at fault, but only up to the coverage limit.
Rental Reimbursement Coverage
Rental reimbursement coverage helps pay for a rental car while your vehicle is being repaired after an accident.
- Example: If your vehicle is damaged in an accident and you need to rent a car while it is being repaired, rental reimbursement coverage would help pay for the rental car.
Roadside Assistance Coverage
Roadside assistance coverage provides help with common roadside emergencies, such as flat tires, jump starts, and towing.
- Example: If you have a flat tire in the middle of the night, roadside assistance coverage would send a tow truck to help you.
Table Comparing Coverage Types
| Coverage Type | Purpose | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comprehensive Coverage | Protects your vehicle against damages caused by events other than collisions. | Pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle, minus your deductible. | Theft, vandalism, fire, hail, natural disasters. |
| Collision Coverage | Protects your vehicle against damages caused by a collision with another vehicle or object. | Pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle, minus your deductible. | Accidents with another vehicle, hitting a stationary object. |
| Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage | Protects you and your passengers in case of an accident with an uninsured or underinsured driver. | Helps pay for medical expenses, lost wages, and other damages. | Accidents with a driver who does not have insurance or has insufficient insurance. |
| Personal Injury Protection (PIP) | Covers your medical expenses and lost wages after an accident, regardless of fault. | Helps pay for medical bills and lost wages. | Accidents where you are injured, regardless of fault. |
| Medical Payments Coverage (Med Pay) | Similar to PIP but covers medical expenses for you and your passengers regardless of fault, but only up to a certain limit. | Helps pay for medical bills, even if you were at fault, but only up to the coverage limit. | Accidents where you are injured, regardless of fault. |
| Rental Reimbursement Coverage | Helps pay for a rental car while your vehicle is being repaired after an accident. | Provides transportation while your vehicle is being repaired. | Accidents where your vehicle needs to be repaired. |
| Roadside Assistance Coverage | Provides help with common roadside emergencies. | Provides assistance with flat tires, jump starts, towing, and other emergencies. | Flat tire, dead battery, lockout. |
Factors Influencing Insurance Costs

Your car insurance premium is determined by various factors, and understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your coverage and potentially save money.
Factors Affecting Insurance Costs
- Driving History: Your driving record significantly impacts your premium. Accidents, traffic violations, and DUI convictions can lead to higher premiums. Conversely, a clean driving record can result in lower rates.
- Age and Gender: Younger drivers, especially those under 25, generally pay higher premiums due to their higher risk of accidents. Gender can also play a role, with some insurers historically charging men slightly higher premiums than women.
- Vehicle Type and Value: The type of vehicle you drive and its value influence your premium. Sports cars and luxury vehicles are often associated with higher risks and therefore have higher premiums. Older vehicles, on the other hand, might have lower premiums due to their lower replacement value.
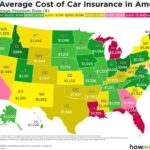
- Location: Your location, including the state and city you live in, impacts your premium. Areas with higher crime rates or more frequent accidents generally have higher insurance rates.
- Credit Score: In some states, your credit score can affect your car insurance premium. This is based on the idea that people with good credit are more financially responsible and less likely to file claims.
- Coverage Levels: The amount of coverage you choose, such as liability limits, collision coverage, and comprehensive coverage, directly impacts your premium. Higher coverage levels typically result in higher premiums.
- Deductibles: A deductible is the amount you pay out of pocket before your insurance kicks in. Higher deductibles generally lead to lower premiums, as you are taking on more financial responsibility.
Finding Affordable Insurance: State Minimum Car Insurance

Finding the right car insurance policy can be a challenging process, but it’s crucial to secure the coverage you need without breaking the bank. There are various strategies you can employ to find affordable car insurance options and navigate the buying process effectively.
Comparing Insurance Providers
It’s essential to compare quotes from multiple insurance providers to find the best rates for your needs. Different companies offer diverse coverage options and pricing structures. You can utilize online comparison tools or contact insurance agents directly to gather quotes. By comparing quotes, you can identify companies that offer competitive rates and coverage tailored to your specific requirements.
Negotiating Lower Premiums
Once you’ve identified potential insurance providers, consider negotiating lower premiums. Here are some effective strategies:
- Bundle Policies: Bundling your car insurance with other policies, such as homeowners or renters insurance, can often result in significant discounts. Insurance companies often offer discounts for multiple policyholders.
- Ask for Discounts: Inquire about available discounts, such as safe driving discounts, good student discounts, or discounts for anti-theft devices. Many insurance companies offer a variety of discounts that can reduce your premium.
- Increase Your Deductible: Raising your deductible, the amount you pay out of pocket before your insurance kicks in, can lower your premium. However, consider your financial situation and risk tolerance before making this decision. A higher deductible means you’ll pay more in the event of an accident.
- Shop Around Regularly: Insurance rates can fluctuate over time, so it’s advisable to shop around for new quotes periodically. You may be able to find better rates with a different provider or negotiate a lower premium with your current insurer.
Navigating the Buying Process, State minimum car insurance
The process of purchasing car insurance can be streamlined by following these steps:
- Gather Information: Before contacting insurance providers, gather essential information, including your driving history, vehicle details, and desired coverage levels. This information will help you get accurate quotes.
- Request Quotes: Contact multiple insurance providers to request quotes. Use online comparison tools or contact agents directly. Ensure you compare quotes with similar coverage levels to ensure a fair comparison.
- Review Coverage Options: Carefully review the coverage options offered by each provider. Ensure you understand the different types of coverage and their limits. Consider your individual needs and risk tolerance when selecting coverage.
- Compare Prices and Coverage: Compare the prices and coverage options from different providers. Identify the best balance between affordability and comprehensive coverage. Consider factors such as customer service, financial stability, and claims handling experience.
- Choose a Provider and Purchase Policy: Once you’ve selected the provider that best meets your needs, purchase your policy. Ensure you understand the terms and conditions of the policy before signing. Keep a copy of your policy for your records.
Concluding Remarks
Navigating the world of car insurance can be daunting, but understanding the fundamentals of state minimum car insurance is a vital first step. By carefully considering your individual needs, exploring different coverage options, and actively seeking affordable rates, you can ensure that you’re adequately protected on the road.
Key Questions Answered
What happens if I drive without minimum car insurance?
Driving without the minimum required car insurance in your state can result in fines, license suspension, and even jail time. Additionally, if you cause an accident, you could be held personally liable for all damages and injuries, potentially leading to significant financial burdens.
Is state minimum car insurance enough for everyone?
While state minimum car insurance fulfills legal requirements, it might not be sufficient for everyone. Consider factors like your assets, driving history, and the value of your vehicle to determine if you need additional coverage.
How often should I review my car insurance policy?
It’s a good practice to review your car insurance policy annually, or even more frequently if you experience significant life changes like getting married, buying a new car, or moving to a different state. This ensures your coverage remains adequate and your premiums are competitive.