State Insurance USA encompasses the vast and complex landscape of insurance within the United States. This industry, a cornerstone of economic stability and individual well-being, is shaped by a dynamic interplay of federal and state regulations, market forces, and consumer needs.
From health and auto insurance to home and life coverage, the American insurance market offers a diverse array of products and services, catering to the unique needs of individuals and businesses across the country. This intricate system, however, is not without its challenges, as regulatory frameworks, consumer preferences, and technological advancements constantly reshape the industry.
State Insurance Landscape in the USA
The United States insurance industry is a vast and complex ecosystem, playing a vital role in protecting individuals and businesses against various risks. It encompasses a wide range of insurance products, catering to diverse needs across different sectors. This section provides an overview of the current state of the insurance industry in the USA, including key players, market trends, regulatory environment, and different types of insurance offered.
Major Players and Market Trends
The US insurance market is dominated by a few large players, including Berkshire Hathaway, UnitedHealth Group, and Anthem, among others. These companies hold significant market share and operate across multiple insurance segments. However, the industry is also characterized by a large number of smaller regional and niche players, offering specialized products and services.
The US insurance market is constantly evolving, driven by factors such as technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and regulatory reforms. Key trends shaping the industry include:
- Digital Transformation: Insurers are increasingly leveraging technology to enhance customer experience, streamline operations, and develop innovative products. This includes using artificial intelligence (AI) for risk assessment, chatbots for customer service, and mobile apps for policy management.
- Data Analytics: Data analytics is playing a crucial role in risk assessment, pricing, and fraud detection. Insurers are using advanced analytics to gain insights into customer behavior, market trends, and emerging risks.
- Focus on Customer Experience: The insurance industry is increasingly focusing on providing a seamless and personalized customer experience. This includes offering digital self-service options, personalized communication, and proactive customer support.
- Growth in Specialty Insurance: The demand for specialized insurance products is growing, driven by factors such as increasing complexity of risks and the emergence of new industries. This includes cyber insurance, drone insurance, and other niche products.
Types of Insurance Offered in the USA
The US insurance industry offers a wide range of insurance products, covering various risks and needs. Some of the most common types of insurance include:
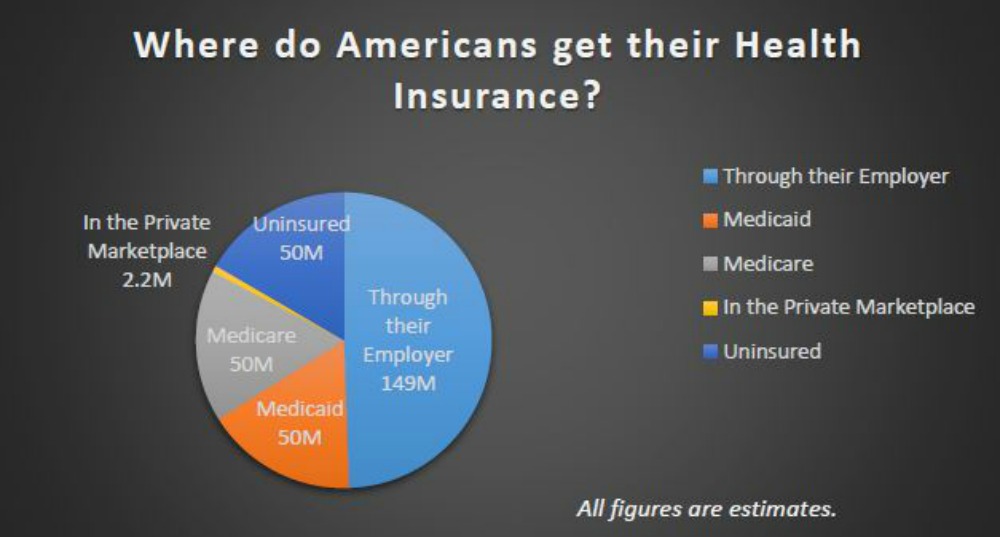
- Health Insurance: Provides coverage for medical expenses, including hospitalization, surgery, and prescription drugs. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) has significantly impacted the health insurance market, expanding coverage and regulating premiums.
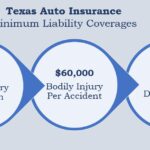
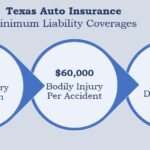
- Auto Insurance: Required by law in most states, auto insurance provides coverage for damages and injuries caused by car accidents. It typically includes liability coverage, collision coverage, and comprehensive coverage.
- Home Insurance: Protects homeowners against financial losses due to damage or destruction of their property, such as fire, theft, or natural disasters. It also provides liability coverage for injuries that occur on the property.
- Life Insurance: Provides financial protection to beneficiaries upon the death of the insured. It can be used to cover funeral expenses, debt repayment, or income replacement.
- Business Insurance: Covers various risks faced by businesses, including property damage, liability, and business interruption. This includes general liability insurance, workers’ compensation insurance, and property insurance.
Regulatory Environment
The US insurance industry is subject to a complex regulatory framework at both the federal and state levels. The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) is a non-governmental organization that provides guidance and uniformity in insurance regulation across states.
The regulatory environment plays a crucial role in ensuring the solvency of insurers, protecting consumers, and promoting fair competition. Key regulatory areas include:
- Solvency Regulation: Insurers are required to maintain adequate capital reserves to ensure they can meet their financial obligations to policyholders. Regulators monitor insurer financial health and intervene if necessary.
- Consumer Protection: Regulations protect consumers from unfair or deceptive insurance practices. This includes requirements for clear and concise policy language, fair pricing, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Market Conduct: Regulators oversee the conduct of insurers in the marketplace, ensuring fair competition and preventing anti-competitive practices. This includes monitoring advertising, underwriting, and claims handling practices.
Key Factors Driving Growth and Challenges in the US Insurance Market
The US insurance market is expected to continue growing in the coming years, driven by factors such as:
- Growing Population: The US population is growing, leading to increased demand for insurance products. This includes health insurance, life insurance, and property insurance.
- Rising Affluence: As the US economy grows, individuals and businesses have more disposable income, leading to increased demand for insurance products.
- Emerging Risks: The world is facing new and emerging risks, such as cyberattacks, climate change, and pandemics. This is driving demand for new and innovative insurance products.
However, the industry also faces challenges such as:
- Competition: The insurance market is highly competitive, with both large and small players vying for market share. This can lead to pressure on pricing and profit margins.
- Regulatory Changes: The regulatory landscape is constantly evolving, creating uncertainty for insurers and requiring them to adapt their operations. This can lead to increased compliance costs and operational challenges.
- Technological Disruption: The rapid pace of technological change is disrupting the insurance industry, requiring insurers to invest in new technologies and adapt their business models. This can be a significant challenge for traditional insurers.
State-Level Insurance Regulations: State Insurance Usa
The insurance industry in the United States is heavily regulated at the state level. Each state has its own unique set of laws and regulations governing insurance companies, products, and consumer protection. These regulations aim to ensure fair competition, protect consumers from unfair practices, and maintain the solvency of insurance companies.
State-Level Regulations: A Diverse Landscape
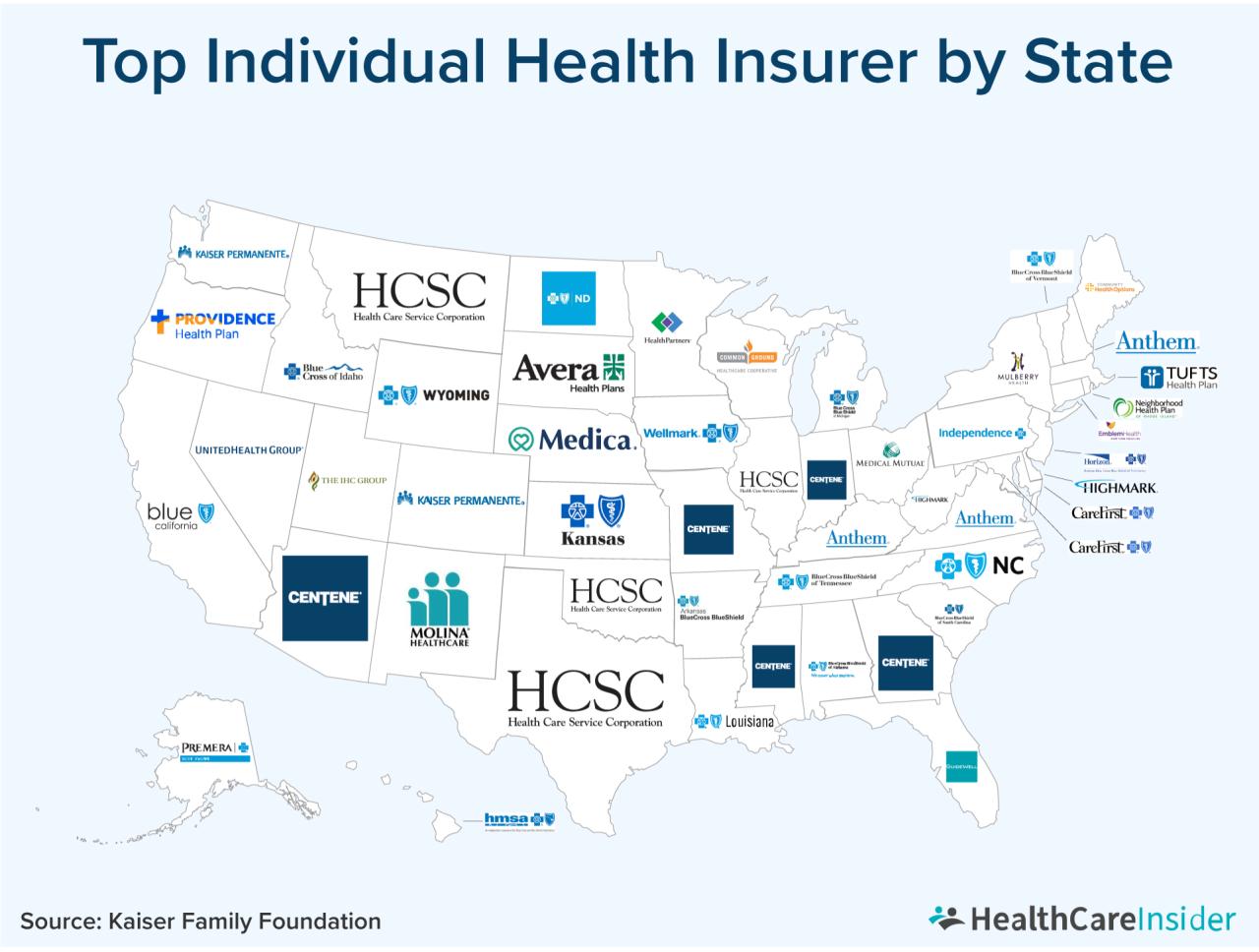
State insurance regulations vary significantly across the country. Some states have a more hands-off approach, while others are more stringent in their oversight. This variation in regulations can impact insurance pricing, availability, and consumer choices.
- Insurance Rates: State regulations influence the rates insurance companies can charge. Some states have strict regulations on rate filings and require companies to justify their rates, while others allow more flexibility. For instance, states like California and New York have strict rate regulation, leading to lower premiums compared to states like Texas and Florida, where rates are generally higher.
- Insurance Products: States may restrict or mandate the types of insurance products available. For example, some states require insurance companies to offer specific coverage, such as earthquake insurance in earthquake-prone areas. Others may limit the types of coverage available, such as health insurance plans.
- Consumer Protection: State regulations aim to protect consumers from unfair or deceptive practices. This includes regulations on advertising, claims handling, and consumer complaints. For instance, states like Massachusetts and New Jersey have strong consumer protection laws, while others have less stringent regulations.
Impact on Insurance Pricing, Availability, and Consumer Choices
State-level regulations can significantly influence the cost, availability, and choices consumers have in insurance.
- Insurance Pricing: Stricter rate regulations can lead to lower premiums for consumers but may limit insurance companies’ ability to price risk accurately. This can lead to less competition and fewer options for consumers in some states. For example, states with strict rate regulations often have lower auto insurance premiums, but fewer insurance companies may operate in those states.
- Insurance Availability: Certain regulations can make it challenging for insurance companies to operate in a state, leading to limited availability of certain products or coverage. For instance, states with strict requirements for financial reserves or risk management may discourage some companies from entering the market. This can result in fewer insurance options for consumers in those states.
- Consumer Choices: State regulations can impact the types of insurance products available to consumers. For example, states with strict regulations on health insurance plans may limit the choice of plans available to consumers. Conversely, states with more flexible regulations may offer a wider variety of plans, but consumers may need to navigate more complex options.
Role of State Insurance Departments
State insurance departments play a crucial role in overseeing and regulating the insurance industry. They are responsible for:
- Licensing and Regulating Insurance Companies: State insurance departments license and regulate insurance companies operating within their jurisdiction. They ensure companies meet financial solvency requirements and comply with state regulations.
- Reviewing and Approving Insurance Rates: State insurance departments review and approve insurance rates to ensure they are fair and non-discriminatory. They also monitor rate changes to ensure companies are not charging excessive premiums.
- Enforcing Insurance Laws and Regulations: State insurance departments enforce insurance laws and regulations, investigate consumer complaints, and take action against companies that violate state rules.
- Protecting Consumer Rights: State insurance departments educate consumers about their rights and responsibilities and provide resources for resolving insurance disputes.
Consumer Perspectives on State Insurance
Consumers’ experiences with state insurance programs and services vary widely across the United States. Consumer satisfaction levels are influenced by factors such as the quality of insurance products, the efficiency of claims processing, and the responsiveness of customer service. This section will delve into consumer perspectives on state insurance, examining their experiences, satisfaction levels, and key concerns.
Consumer Experiences with State Insurance
Consumers’ experiences with state insurance programs and services vary greatly. Many consumers find that state insurance programs offer affordable and reliable coverage, particularly for essential services such as health insurance and auto insurance. However, some consumers may encounter challenges, such as difficulty navigating complex regulations or delays in receiving claims payments. It is important to understand the nuances of consumer experiences to address potential areas for improvement.
Consumer Satisfaction with State Insurance Providers, State insurance usa
Consumer satisfaction levels with insurance providers in different states vary significantly. Studies conducted by independent organizations, such as J.D. Power, provide insights into consumer satisfaction with insurance providers across different states. These studies typically measure factors such as customer service, claims handling, and overall satisfaction with the insurance provider. Consumer satisfaction levels are influenced by factors such as the quality of insurance products, the efficiency of claims processing, and the responsiveness of customer service.
Key Concerns of Consumers Regarding State Insurance
Consumers have a number of key concerns regarding state insurance. These concerns often center around issues such as affordability, access to coverage, and the quality of insurance products. Consumers are increasingly concerned about the rising cost of insurance premiums, particularly for health insurance and auto insurance. Access to coverage is another significant concern, particularly for individuals with pre-existing conditions or those who live in rural areas. Additionally, consumers are concerned about the quality of insurance products, such as the adequacy of coverage and the ease of filing claims.
State Insurance and Economic Development
State insurance plays a crucial role in fostering economic growth and development by providing financial security and stability, promoting investment, and supporting businesses.
Impact on Employment, Investment, and Business Activity
Insurance contributes significantly to employment, investment, and business activity.
- Employment: The insurance industry is a major employer, providing jobs in various sectors, including underwriting, claims processing, sales, and customer service. Insurance companies also create indirect employment opportunities in related fields, such as legal services, accounting, and consulting.
- Investment: Insurance companies are major investors in the economy, allocating funds to various assets, including stocks, bonds, and real estate. This investment helps to stimulate economic growth by providing capital for businesses and infrastructure projects.
- Business Activity: Insurance provides businesses with financial protection against risks, such as property damage, liability claims, and business interruptions. This protection allows businesses to operate with greater confidence, invest in growth, and create new jobs.
Addressing Specific Economic Challenges
State insurance can be instrumental in addressing specific economic challenges, such as natural disasters, pandemics, and climate change.
- Natural Disasters: Insurance provides financial assistance to individuals and businesses affected by natural disasters, helping them to rebuild and recover. This reduces the economic impact of disasters and promotes resilience.
- Pandemics: Insurance can play a vital role in mitigating the economic impact of pandemics by providing coverage for business interruption, medical expenses, and other related losses. This helps to protect businesses and individuals from financial hardship.
- Climate Change: Insurance can help to address the economic risks associated with climate change, such as flooding, droughts, and extreme weather events. This can include developing innovative insurance products, promoting risk mitigation measures, and investing in climate-resilient infrastructure.
Emerging Trends in State Insurance
The insurance industry is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer expectations, and evolving regulatory landscapes. State insurance is no exception, with emerging trends reshaping how insurance is offered, purchased, and experienced.
The Role of Technology
The use of technology is profoundly impacting state insurance, enabling insurers to optimize operations, personalize products, and enhance customer interactions.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is revolutionizing insurance by automating tasks, improving risk assessment, and personalizing policy recommendations. AI-powered chatbots are becoming increasingly common for customer service, providing quick and efficient responses to inquiries.
- Big Data and Analytics: Insurance companies are leveraging vast amounts of data to gain deeper insights into customer behavior, risk factors, and market trends. This data-driven approach allows insurers to develop more accurate pricing models, personalize products, and offer targeted marketing campaigns.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain’s decentralized and secure nature offers potential for streamlining insurance processes, such as claims management and fraud detection. It can also facilitate peer-to-peer insurance models, where individuals can share risk directly.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Connected devices are generating valuable data that insurers can use to assess risk and offer tailored insurance products. For example, telematics devices in vehicles can track driving behavior, allowing insurers to offer discounts based on safe driving practices.
Impact on Insurance Products and Services
The adoption of these technologies is leading to the development of innovative insurance products and services.
- Micro-Insurance: Technology enables insurers to offer micro-insurance products, providing coverage for specific risks at affordable prices. This is particularly relevant for low-income populations and emerging markets.
- On-Demand Insurance: Digital platforms allow consumers to purchase insurance on an as-needed basis, providing coverage only when required. This offers flexibility and cost-effectiveness, particularly for short-term or temporary needs.
- Usage-Based Insurance: Technology enables insurers to price policies based on actual usage, rewarding safe and responsible behavior. For example, pay-per-mile car insurance programs are becoming increasingly popular.
Impact on Consumer Experiences
Emerging trends in state insurance are significantly improving consumer experiences.
- Enhanced Convenience: Digital platforms and mobile apps allow consumers to purchase insurance, manage policies, and file claims online or through their smartphones, providing 24/7 access and convenience.
- Personalized Experiences: Data analytics enable insurers to personalize policies and communications, offering customized products and services that meet individual needs.
- Improved Transparency: Digital platforms provide access to real-time information about policies, claims, and other insurance-related details, enhancing transparency and customer understanding.
Opportunities and Challenges
While emerging trends offer significant opportunities for state insurance, they also present challenges that need to be addressed.
- Data Privacy and Security: The increasing use of data raises concerns about privacy and security. Insurers need to implement robust data protection measures to safeguard sensitive information.
- Cybersecurity Risks: The reliance on technology increases vulnerability to cyberattacks. Insurers need to invest in strong cybersecurity measures to protect their systems and customer data.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Rapid technological advancements often outpace regulatory frameworks. States need to adapt their regulations to keep pace with emerging trends and ensure a level playing field for insurers and consumers.
Conclusive Thoughts

Understanding the nuances of State Insurance USA is crucial for both consumers and industry stakeholders. Navigating this complex landscape requires a comprehensive understanding of regulatory frameworks, market trends, and consumer perspectives. By analyzing these factors, we can gain valuable insights into the future of insurance in the United States and its impact on individuals, businesses, and the broader economy.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the main types of insurance offered in the USA?
The major types of insurance in the USA include health, auto, home, life, and commercial insurance, among others.
How do state insurance regulations impact consumers?
State regulations influence insurance pricing, coverage options, and consumer protections, ultimately affecting the choices and costs faced by individuals.
What are some emerging trends in state insurance?
Emerging trends include the use of technology, data analytics, and digital platforms, which are transforming insurance products, services, and consumer experiences.