Out of state insurance – Out-of-state insurance is a crucial topic for anyone who frequently travels across state lines or relocates to a new state. It involves obtaining insurance coverage from a provider in a state other than your primary residence, and understanding its implications is essential for ensuring proper protection and avoiding legal complications.
This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of out-of-state insurance, covering its various types, factors influencing costs, legal considerations, and practical tips for navigating the process. We’ll delve into the benefits and drawbacks of having out-of-state insurance, shedding light on situations where it might be necessary and providing insights on how to make informed decisions regarding your coverage.
Understanding Out-of-State Insurance
Out-of-state insurance refers to an insurance policy purchased from an insurance company that operates in a state different from where the insured individual or property is located. It’s a common scenario for individuals who relocate to a new state, have property in multiple states, or engage in activities that require coverage in another state.
Situations Requiring Out-of-State Insurance
Out-of-state insurance can be necessary in several situations.
- Relocation: When moving to a new state, individuals often need to obtain insurance from a company licensed in that state. This ensures compliance with local regulations and provides coverage for potential risks in the new location.
- Property Ownership: Owning property in multiple states may necessitate separate insurance policies for each location. This ensures adequate coverage for all properties, regardless of the state where the primary residence is located.
- Business Operations: Businesses operating in multiple states often need out-of-state insurance to comply with state-specific regulations and protect their interests in each jurisdiction.
- Travel and Recreation: Individuals traveling or engaging in recreational activities in other states may require temporary out-of-state insurance to cover potential accidents or incidents.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Out-of-State Insurance
Having out-of-state insurance can offer advantages and disadvantages.
- Benefits:
- Competitive Rates: Out-of-state insurers may offer more competitive rates than local companies, especially if the individual’s risk profile is considered low.
- Specialized Coverage: Some insurers specialize in certain types of coverage, such as high-value property or niche industries, which may not be readily available from local companies.
- Broader Network: Out-of-state insurers often have a wider network of providers, offering more options for medical care, repair services, or other claims-related needs.
- Drawbacks:
- Limited Local Knowledge: Out-of-state insurers may lack familiarity with local regulations, specific risks, or available resources, potentially leading to challenges in claim processing or coverage disputes.
- Accessibility Issues: Obtaining assistance from an out-of-state insurer might be more challenging due to geographical distance or differences in communication practices.
- Regulatory Differences: State regulations governing insurance can vary significantly, leading to potential inconsistencies in coverage or claim handling procedures.
Types of Out-of-State Insurance
Out-of-state insurance refers to obtaining insurance coverage from a company that is licensed and operates in a different state than where you reside. This can be a viable option for individuals who are relocating, traveling frequently, or simply seeking more competitive rates. Understanding the various types of out-of-state insurance and their specific requirements is crucial for making informed decisions.
Auto Insurance
Out-of-state auto insurance is a common need for individuals who move to a new state or drive across state lines frequently. The requirements for obtaining out-of-state auto insurance vary depending on the state.
- Minimum Coverage Requirements: Each state has minimum coverage requirements for auto insurance, which are usually defined by the state’s financial responsibility laws. These requirements typically include liability coverage, which protects you financially if you cause an accident, and personal injury protection (PIP) coverage, which covers medical expenses and lost wages for you and your passengers. Additionally, some states may require uninsured/underinsured motorist (UM/UIM) coverage, which protects you if you are involved in an accident with a driver who does not have adequate insurance.
- No-Fault States: In no-fault states, drivers are required to file claims with their own insurance company, regardless of who caused the accident. These states often have higher PIP coverage requirements, and drivers are typically prohibited from suing the other driver unless the injuries are severe.
- At-Fault States: In at-fault states, the driver who caused the accident is responsible for paying for the other driver’s damages. These states typically have lower PIP coverage requirements, and drivers have the right to sue the other driver for damages.
Health Insurance
Obtaining out-of-state health insurance can be complex and depends on your current residency status and eligibility for state-specific programs.
- Individual Health Insurance Marketplace: If you are not eligible for employer-sponsored health insurance or government-sponsored programs like Medicare or Medicaid, you can purchase individual health insurance through the Health Insurance Marketplace. This marketplace allows you to compare plans from different insurers and choose the plan that best meets your needs and budget.
- Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance: If you are employed by a company that offers health insurance, you may be able to obtain coverage through your employer’s plan, even if you live in a different state. However, the availability of coverage and the specific plan options may vary depending on your employer’s policies and the state where you reside.
- Government-Sponsored Programs: Medicare and Medicaid are government-sponsored health insurance programs that provide coverage to eligible individuals. Medicare is a federal program for individuals aged 65 and older or those with certain disabilities, while Medicaid is a state-administered program for low-income individuals and families. The eligibility requirements and benefits of these programs vary depending on the state.
Homeowners Insurance
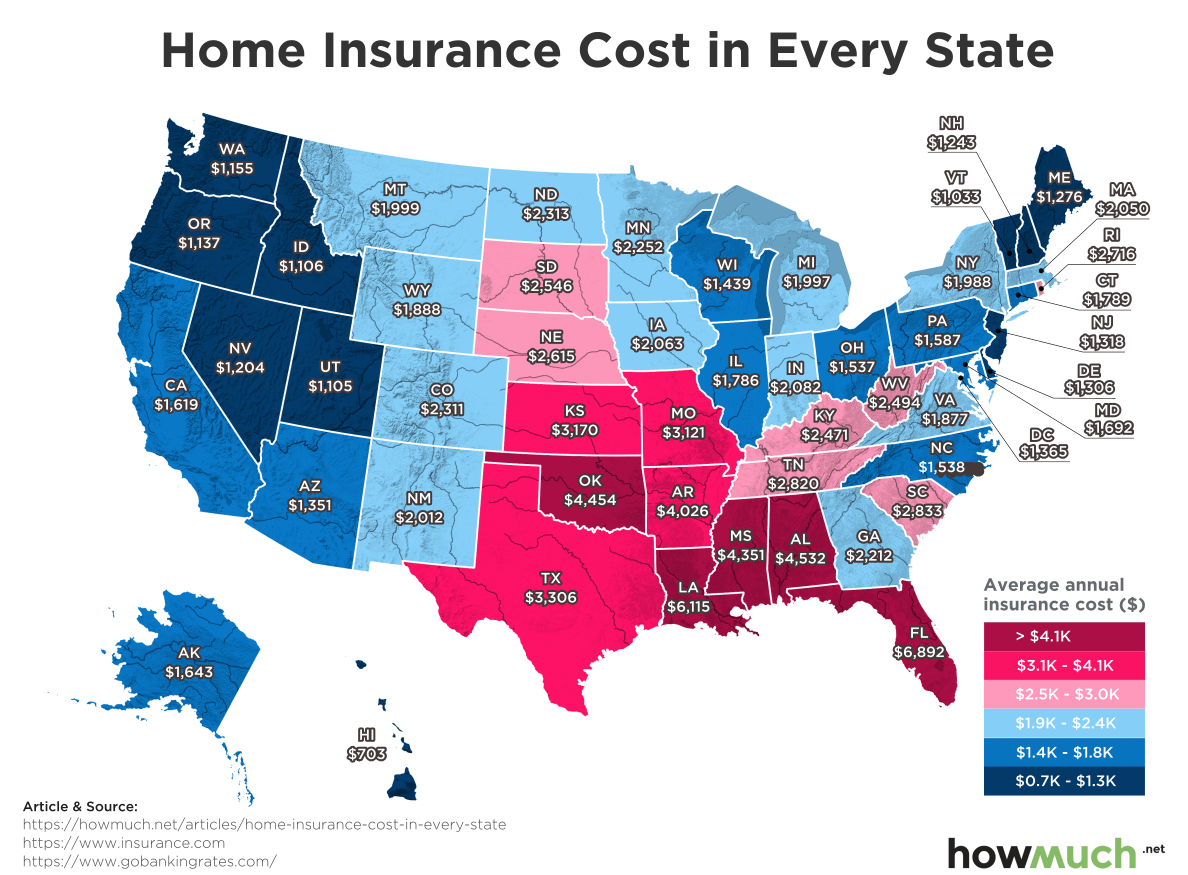
Out-of-state homeowners insurance can be obtained if you own a property in a different state than where you reside. The requirements for obtaining out-of-state homeowners insurance vary depending on the state and the insurer.
- Property Location: The location of your property is a major factor in determining your homeowners insurance premiums. Factors such as the property’s value, the risk of natural disasters, and the crime rate in the area can all affect your premiums.
- Coverage Options: Homeowners insurance policies typically include coverage for dwelling, personal property, liability, and additional living expenses. The specific coverage options available and the limits of coverage may vary depending on the insurer and the state.
- State Regulations: Each state has its own regulations regarding homeowners insurance, which can affect the coverage options and the premiums you pay. For example, some states require insurers to offer specific coverage options, such as flood insurance, while other states do not.
Life Insurance
Out-of-state life insurance is available to individuals who want to obtain coverage from a company that is licensed in a different state than where they reside. The requirements for obtaining out-of-state life insurance are generally less stringent than for other types of insurance.
- State Licensing: The life insurance company must be licensed to sell insurance in the state where you reside. This ensures that the company is subject to the state’s regulations and consumer protection laws.
- Coverage Options: Life insurance policies are available in various forms, such as term life insurance, whole life insurance, and universal life insurance. The specific coverage options and premiums vary depending on the insurer and the state.
- Underwriting: Life insurance companies typically require an underwriting process to assess your risk and determine your premiums. This process may involve a medical exam, a review of your health history, and a financial evaluation.
Factors Affecting Out-of-State Insurance Costs
When you’re moving to a new state, you’ll need to get insurance for your car. But did you know that your insurance premiums can vary significantly depending on where you live? Several factors can affect the cost of out-of-state insurance, and understanding these factors can help you get the best possible rate.
State Regulations
State regulations play a crucial role in determining insurance costs. Each state has its own set of rules and regulations regarding insurance coverage, minimum requirements, and pricing practices.
- For instance, some states require drivers to carry higher liability limits than others. This means that if you’re involved in an accident, you may have to pay more in damages in a state with higher liability limits.
- Additionally, states may have different regulations regarding no-fault insurance, which covers your own medical expenses regardless of who is at fault in an accident. States with no-fault insurance laws tend to have higher insurance premiums.
Driving History
Your driving history is a significant factor in determining your insurance premiums. This includes your past accidents, traffic violations, and driving record.
- A clean driving record with no accidents or violations will typically result in lower premiums. On the other hand, if you have a history of accidents or traffic violations, your premiums will likely be higher.
- The severity of your past accidents and violations also matters. A major accident, such as a DUI, will generally lead to a more substantial increase in your premiums than a minor fender bender.
Vehicle Type
The type of vehicle you drive also plays a role in your insurance costs. Some vehicles are considered riskier to insure than others due to factors such as:
- Safety features: Vehicles with advanced safety features, such as anti-lock brakes, airbags, and stability control, tend to have lower insurance premiums. These features help reduce the risk of accidents and injuries.
- Value: More expensive vehicles are generally more expensive to insure. This is because they are more costly to repair or replace in the event of an accident.
- Performance: High-performance vehicles, such as sports cars, often have higher insurance premiums. These vehicles are typically driven faster and may be more likely to be involved in accidents.
Comparing Quotes
To find the best value for your out-of-state insurance, it’s essential to compare quotes from different insurers. You can do this online, by phone, or through an insurance broker.
- When comparing quotes, make sure you’re comparing the same coverage levels and deductibles. This will ensure that you’re getting a fair comparison.
- You should also consider the insurer’s financial stability and customer service ratings.
Navigating the Out-of-State Insurance Process
Obtaining out-of-state insurance can seem daunting, but with the right steps and preparation, it can be a smooth process. This section will guide you through the process, outlining the necessary steps, required documents, and essential considerations to ensure a successful transition.
Steps Involved in Obtaining Out-of-State Insurance
The process of obtaining out-of-state insurance typically involves several steps. It’s crucial to understand the specific requirements of the new state you’re moving to.
- Research and Compare Insurance Providers: Begin by researching insurance providers in your new state. Consider factors like coverage options, pricing, customer service, and financial stability. Online comparison tools can help you gather quotes from various providers.
- Contact the Insurance Provider: Once you’ve chosen a provider, contact them directly to discuss your insurance needs. Provide them with details about your vehicle, driving history, and coverage preferences.
- Gather Necessary Documents: Prepare all the required documentation for the application process. This might include your driver’s license, proof of residency, vehicle registration, and insurance information from your previous provider.
- Complete the Application Process: Fill out the insurance application form accurately and thoroughly. Provide all the necessary information, including your personal details, vehicle information, and coverage preferences.
- Pay the Premium: Once your application is approved, you’ll need to pay the premium for your insurance policy. Payment options may vary depending on the provider.
- Receive Your Policy: After payment, you’ll receive your insurance policy documents. Carefully review the policy details to ensure you understand the coverage and terms.
- Notify Your Previous Provider: Inform your previous insurance provider about your move and policy cancellation. Ensure you understand the cancellation process and any potential fees involved.
Checklist of Documents and Information
Having the necessary documents readily available will streamline the application process. Here’s a checklist to ensure you have everything you need:
- Driver’s License: A valid driver’s license from your previous state.
- Proof of Residency: Documents demonstrating your new address, such as a utility bill, lease agreement, or voter registration card.
- Vehicle Registration: The current registration for your vehicle.
- Insurance Information: Your current insurance policy details, including policy number, coverage details, and expiration date.
- Driving History: A copy of your driving record, which you can obtain from your previous state’s Department of Motor Vehicles.
- Social Security Number: You may need to provide your Social Security number for identification and verification purposes.
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN): The unique identification number of your vehicle.
Guide for Individuals Seeking Out-of-State Insurance
Consider these factors to ensure a smooth transition and obtain the best possible insurance coverage:
- State-Specific Requirements: Each state has its own insurance regulations. Research the specific requirements of your new state, including minimum coverage limits and any unique regulations.
- Coverage Needs: Evaluate your insurance needs based on your vehicle type, driving habits, and personal circumstances. Determine if you require additional coverage beyond the state minimums.
- Compare Quotes: Obtain quotes from multiple insurance providers to compare prices, coverage options, and customer service.
- Consider Discounts: Explore potential discounts offered by insurance providers, such as good driver discounts, multi-car discounts, or safe driving discounts.
- Read the Policy Carefully: Before finalizing your policy, carefully review the terms and conditions. Pay close attention to coverage limits, exclusions, and any specific requirements.
- Ask Questions: Don’t hesitate to ask questions if you’re unsure about any aspect of the insurance process or policy details.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations

Navigating the complex world of out-of-state insurance requires understanding the legal framework that governs it. This section delves into the legal and regulatory considerations surrounding out-of-state insurance, including reciprocity agreements and state-specific regulations.
Reciprocity Agreements
Reciprocity agreements between states play a crucial role in determining the coverage and validity of out-of-state insurance. These agreements essentially allow insurers licensed in one state to sell insurance in another state, subject to certain conditions. The impact of these agreements on coverage varies depending on the specific terms of the agreement and the type of insurance involved. For instance, some reciprocity agreements might only cover certain types of insurance, while others might have broader applicability.
State-Specific Regulations
Each state has its own set of regulations governing insurance, including out-of-state insurance. These regulations can vary significantly from state to state, impacting aspects such as coverage requirements, minimum coverage limits, and insurance rates. It’s essential to understand the specific regulations of the state where you’re seeking coverage to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
Key Legal Aspects of Out-of-State Insurance by State
The following table summarizes key legal aspects of out-of-state insurance by state, providing a general overview of the regulatory landscape:
| State | Reciprocity Agreements | Coverage Requirements | Minimum Coverage Limits | Insurance Rates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| California | Reciprocity agreements with most states | Complies with California’s minimum coverage requirements | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident (liability) | Subject to California’s insurance rate regulations |
| Texas | Reciprocity agreements with most states | Complies with Texas’s minimum coverage requirements | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident (liability) | Subject to Texas’s insurance rate regulations |
| New York | Reciprocity agreements with some states | Complies with New York’s minimum coverage requirements | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident (liability) | Subject to New York’s insurance rate regulations |
| Florida | Reciprocity agreements with most states | Complies with Florida’s minimum coverage requirements | $10,000 per person/$20,000 per accident (liability) | Subject to Florida’s insurance rate regulations |
Tips for Out-of-State Insurance: Out Of State Insurance
Navigating out-of-state insurance can be complex, but with some proactive planning and informed decision-making, you can ensure smooth transitions and optimal coverage. Here are some key tips to help you manage your out-of-state insurance policies effectively.
Understanding Your Coverage Needs
It is crucial to understand your specific coverage needs before making any changes to your insurance policies. This involves carefully considering your individual circumstances, including your location, vehicle type, driving history, and any unique assets you need to protect.
Communicate with Your Insurer
Open and clear communication with your current insurer is essential when moving to a new state. Inform them about your relocation plans well in advance to avoid any potential coverage gaps or policy lapses. Be prepared to provide them with your new address and other relevant information.
Explore Your Options, Out of state insurance
Once you’ve moved to a new state, it’s wise to explore your insurance options to ensure you’re getting the best possible coverage at a competitive price. Compare quotes from multiple insurers in your new state to find the best fit for your needs.
Review Your Policy Documents
Thoroughly review your insurance policy documents, including the declarations page, coverage details, and any exclusions. Pay close attention to the state-specific requirements and regulations that apply to your new location.
Consider State-Specific Requirements
Each state has its own set of insurance laws and regulations, including minimum coverage requirements. Ensure you understand the specific requirements in your new state and adjust your coverage accordingly.
Maintain Accurate Information
It’s crucial to keep your insurer informed of any changes to your personal information, such as your address, contact details, and vehicle information. This helps ensure that your insurance policy remains accurate and up-to-date.
Review Your Coverage Periodically
Regularly review your insurance policy to ensure it continues to meet your needs. Life circumstances can change, and your coverage requirements may need to be adjusted accordingly.
Keep Records of Your Insurance Documents
Maintain organized records of all your insurance documents, including policies, declarations pages, and communication with your insurer. This can be helpful for reference purposes and in case of any future claims.
Conclusion
In conclusion, out-of-state insurance presents both opportunities and challenges. By understanding the complexities of coverage, costs, and legal frameworks, individuals can make informed decisions to ensure adequate protection while navigating the intricacies of interstate travel and relocation. This guide has provided a framework for understanding out-of-state insurance, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed choices and navigate this critical aspect of your insurance needs.
Helpful Answers
What happens if I get into an accident with out-of-state insurance?
Your out-of-state insurance policy should cover you in most accidents, but it’s crucial to understand the specific terms and conditions of your policy. You should also be aware of any reciprocity agreements between states that might affect your coverage.
How do I find out if my state has reciprocity agreements with other states?
You can usually find information about reciprocity agreements on your state’s insurance department website. Alternatively, you can contact your insurance agent or broker for assistance.
Can I get out-of-state insurance if I’m not a resident of that state?
Yes, you can often obtain out-of-state insurance even if you’re not a resident, but there may be specific requirements or restrictions depending on the state and the type of insurance.







