No fault auto insurance states – No-fault auto insurance states operate on a system where drivers are primarily responsible for covering their own injuries and damages after an accident, regardless of fault. This system, a departure from traditional fault-based insurance, has been implemented in several states across the US, aiming to streamline the claims process and reduce litigation.
This guide will explore the intricacies of no-fault auto insurance, delving into its history, advantages, disadvantages, and impact on the legal system and insurance industry. We will also examine the different types of no-fault insurance systems and the coverage options available in these states.
What is No-Fault Auto Insurance?: No Fault Auto Insurance States
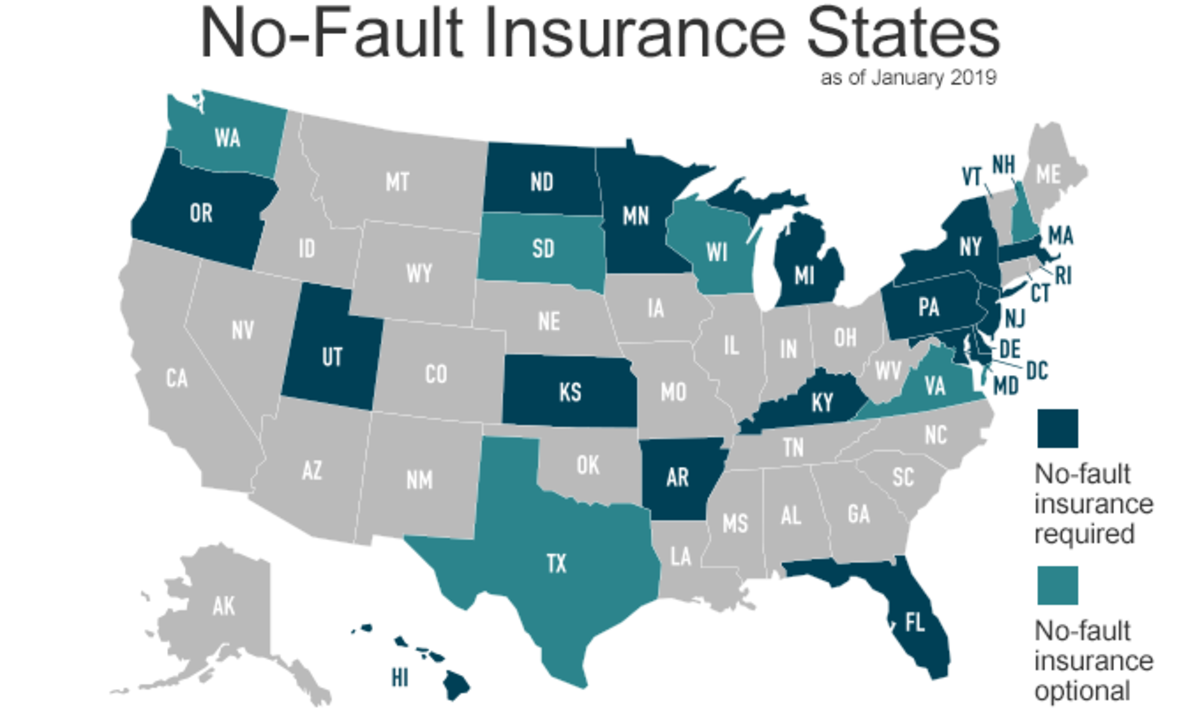
No-fault auto insurance is a system where drivers are compensated for their own injuries and damages, regardless of who caused the accident. It contrasts with traditional fault-based systems, where the at-fault driver’s insurance company is responsible for covering the other driver’s losses.
History of No-Fault Insurance
No-fault insurance emerged as a response to concerns about the complexities and delays associated with traditional fault-based systems. The concept gained traction in the 1960s and 1970s, driven by a desire to streamline the claims process and reduce litigation costs.
- 1960s: The first no-fault insurance laws were enacted in the United States, starting with Massachusetts in 1970. These early laws were relatively limited in scope and often included optional provisions.
- 1970s: No-fault insurance gained momentum, with more states adopting the system. However, the design and implementation varied widely across states, leading to a patchwork of regulations.
- 1980s and beyond: No-fault insurance continued to evolve, with some states making changes to their laws, while others continued to debate its merits. Today, a majority of U.S. states have some form of no-fault insurance, though the extent of its implementation varies significantly.
Key Features and Principles
No-fault insurance operates on the principle of “first-party coverage,” meaning that drivers are primarily responsible for covering their own losses. This contrasts with traditional fault-based systems, where “third-party coverage” is the norm, meaning the at-fault driver’s insurance company is responsible for covering the other driver’s losses.
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): This coverage pays for medical expenses, lost wages, and other related costs incurred by the insured driver and passengers, regardless of fault. PIP coverage is typically mandatory in no-fault states.
- Limited Tort Threshold: In many no-fault states, drivers are restricted from suing for pain and suffering unless their injuries meet a certain threshold, such as a serious injury or significant medical expenses. This threshold is intended to reduce frivolous lawsuits and keep costs down.
- No-Fault Benefits: These benefits typically cover medical expenses, lost wages, and other related costs, up to a certain limit. The limits vary by state and insurance policy.
- Direct Payment: In most no-fault systems, drivers file claims directly with their own insurance company, rather than having to pursue the other driver’s insurance. This simplifies the claims process and speeds up payment.
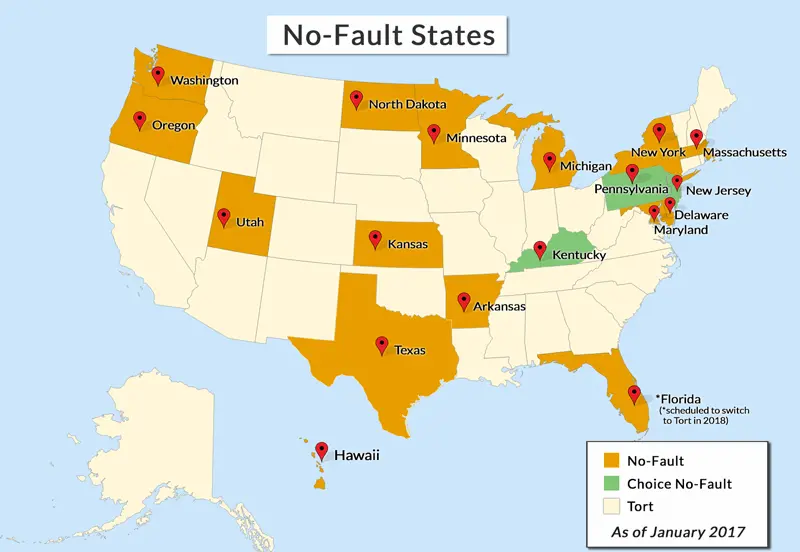
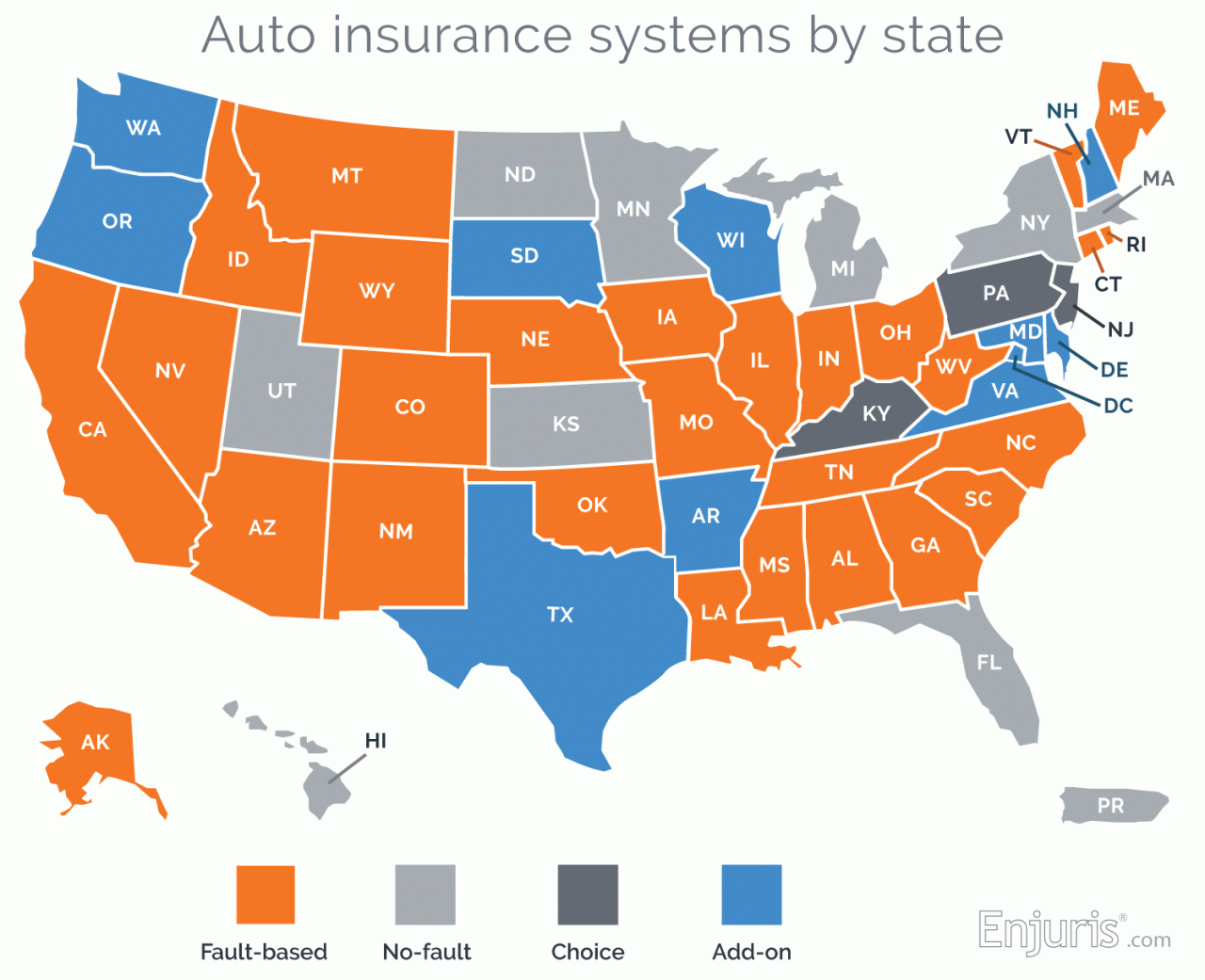
States with No-Fault Auto Insurance
No-fault auto insurance is a system where drivers are required to file claims with their own insurance companies, regardless of who is at fault in an accident. This system aims to streamline the claims process and reduce litigation. While it is not universally adopted, several states have implemented no-fault laws, each with its own unique approach.
States with No-Fault Auto Insurance Laws
This table lists states with no-fault auto insurance laws, including the year of implementation.
| State | Year Implemented |
|—|—|
| Florida | 1971 |
| Hawaii | 1974 |
| Kansas | 1974 |
| Kentucky | 1975 |
| Massachusetts | 1971 |
| Michigan | 1973 |
| Minnesota | 1974 |
| New Jersey | 1973 |
| New York | 1973 |
| North Dakota | 1975 |
| Pennsylvania | 1975 |
| Rhode Island | 1971 |
| Utah | 1973 |
| | |
Types of No-Fault Insurance Systems
This table compares the different types of no-fault insurance systems used in different states.
| Type | Description | States |
|—|—|—|
| Pure No-Fault | Drivers are required to file claims with their own insurance companies, regardless of who is at fault. They cannot sue for pain and suffering, regardless of the severity of the injuries. | Florida, Hawaii, Kansas, Kentucky, Michigan, North Dakota, Utah |
| Modified No-Fault | Drivers are required to file claims with their own insurance companies, but they can sue for pain and suffering if their injuries meet certain thresholds, such as exceeding a specific dollar amount or involving serious injuries. | Massachusetts, Minnesota, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island |
| Add-on No-Fault | This system allows drivers to choose to purchase no-fault coverage in addition to traditional liability insurance. | |
States with No-Fault Laws by Coverage Level
This list organizes states with no-fault laws by the level of coverage offered.
Personal Injury Protection (PIP)
PIP coverage pays for medical expenses, lost wages, and other expenses related to injuries sustained in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. States with PIP coverage include:
* Florida
* Hawaii
* Kansas
* Kentucky
* Massachusetts
* Michigan
* Minnesota
* New Jersey
* New York
* North Dakota
* Pennsylvania
* Rhode Island
* Utah
Medical Payments Coverage (Med Pay)
Med Pay coverage pays for medical expenses regardless of who is at fault, but it does not cover lost wages or other expenses. States with Med Pay coverage include:
* Florida
* Hawaii
* Kansas
* Kentucky
* Massachusetts
* Michigan
* Minnesota
* New Jersey
* New York
* North Dakota
* Pennsylvania
* Rhode Island
* Utah
Benefits of No-Fault Auto Insurance
No-fault auto insurance offers several advantages for both individuals and society as a whole. This system streamlines the claims process, reduces litigation, and potentially leads to lower insurance premiums.
Benefits for Individuals
No-fault insurance simplifies the claims process for individuals involved in car accidents. Instead of needing to determine fault, individuals can file claims directly with their own insurance company. This reduces the need for lengthy legal battles and associated expenses.
- Faster Claims Processing: Individuals can receive compensation for their injuries and vehicle damage more quickly, as they do not have to wait for the other party’s insurance company to investigate the accident. This can be crucial for individuals who are unable to work due to their injuries.
- Reduced Litigation: The emphasis on direct compensation through personal injury protection (PIP) coverage reduces the need for lawsuits. This can save individuals time, money, and emotional stress.
- Guaranteed Benefits: No-fault insurance typically guarantees coverage for medical expenses and lost wages, regardless of who is at fault. This provides greater peace of mind for individuals, knowing they will receive compensation for their injuries.
Benefits for Society
No-fault insurance benefits society by reducing court congestion and potentially lowering insurance premiums.
- Decreased Court Congestion: By reducing the number of lawsuits, no-fault insurance helps alleviate the burden on the court system. This allows courts to focus on more complex cases and improve efficiency.
- Lower Insurance Premiums: The potential cost savings associated with reduced litigation and administrative expenses can translate into lower insurance premiums for policyholders. This is particularly beneficial for individuals who are risk-averse and value financial stability.
Cost Savings
Studies have shown that no-fault insurance can lead to significant cost savings compared to fault-based systems.
“A 2010 study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) found that no-fault states had lower average insurance premiums than fault-based states.”
This is attributed to the reduced administrative costs associated with claims processing and litigation.
Drawbacks of No-Fault Auto Insurance
While no-fault insurance has its benefits, it also comes with certain drawbacks that are important to consider. These drawbacks can significantly impact the overall experience for individuals involved in car accidents, potentially affecting their financial well-being and access to justice.
Limitations on Recovery for Serious Injuries
No-fault insurance systems typically set limits on the amount of compensation available for certain types of injuries, especially for pain and suffering. This can be a significant issue for individuals who sustain serious injuries, such as permanent disabilities, that require extensive medical treatment and rehabilitation.
For example, in some no-fault states, the maximum amount that can be recovered for non-economic damages (like pain and suffering) is capped at a certain amount, regardless of the severity of the injuries. This means that even if someone suffers a severe injury that requires lifelong care, they may only be able to recover a limited amount of compensation.
Potential Impact on Safe Driving and Accident Prevention
Some argue that no-fault insurance can potentially reduce the incentive for drivers to be cautious and prevent accidents. This is because drivers are not directly responsible for the costs of accidents they cause.
The argument is that under a traditional fault-based system, drivers who are found at fault for accidents face the consequences of their actions through higher insurance premiums. This can encourage safer driving practices. In contrast, no-fault systems may lead to a situation where drivers are less concerned about the financial repercussions of their actions, potentially contributing to riskier driving behaviors.
Concerns Regarding Fairness and Accountability
No-fault insurance has also been criticized for its potential to create a system where individuals are not held accountable for their actions. This is particularly relevant in cases where drivers are clearly at fault for causing accidents, but the victims are limited in their ability to seek full compensation.
Critics argue that no-fault insurance can create a sense of unfairness and lack of accountability, as drivers who are negligent may not face the same consequences as they would in a fault-based system. This can lead to a situation where drivers are less incentivized to drive safely and avoid accidents, potentially increasing the overall number of accidents on the road.
Key Components of No-Fault Auto Insurance
No-fault auto insurance systems are designed to streamline the claims process and reduce litigation. They do this by establishing a system where drivers are primarily responsible for covering their own losses, regardless of fault. However, there are key components that define how these systems work and the coverage they provide.
Personal Injury Protection (PIP)
PIP is a critical component of no-fault insurance. It covers the medical expenses and lost wages of the insured person and their passengers, regardless of who caused the accident. This coverage is typically limited to a specific dollar amount or time period. For example, a policy might cover up to $10,000 in medical expenses and $5,000 in lost wages over a period of two years.
Medical Payments Coverage (MPC)
MPC is another type of coverage offered in no-fault states. It is designed to supplement PIP coverage and cover medical expenses for the insured and passengers, regardless of fault. However, MPC typically has a lower coverage limit than PIP and may only cover expenses incurred in the first few months after the accident.
Coverage Available Under No-Fault Policies
No-fault policies typically include several types of coverage, in addition to PIP and MPC:
- Collision Coverage: This coverage pays for repairs to your vehicle if it is damaged in an accident, regardless of fault.
- Comprehensive Coverage: This coverage pays for repairs to your vehicle if it is damaged by something other than a collision, such as theft, vandalism, or a natural disaster.
- Liability Coverage: This coverage protects you financially if you are at fault in an accident and cause injury or damage to another person or their property.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: This coverage protects you if you are injured in an accident caused by a driver who does not have insurance or does not have enough insurance to cover your losses.
No-Fault Insurance and the Legal System
No-fault insurance significantly alters the legal landscape of car accident claims, simplifying the process for some while creating new challenges for others. It eliminates the traditional fault-based system where drivers are held liable for their actions, replacing it with a system that focuses on prompt compensation for injuries and damages, regardless of who caused the accident. This shift in approach has both benefits and drawbacks, impacting how claims are filed, resolved, and disputed.
Comparison of Legal Procedures
The legal procedures for handling claims differ significantly between no-fault and fault-based systems. In fault-based systems, the process is typically more complex and involves establishing fault, negotiating settlements, and potentially pursuing litigation. In contrast, no-fault systems streamline the process by focusing on prompt compensation for covered losses, often through a direct payment system where the insurer pays the insured’s benefits regardless of fault.
- Fault-Based System:
- Involves determining fault for the accident.
- Requires negotiating a settlement with the at-fault driver’s insurer.
- May involve litigation if a settlement cannot be reached.
- No-Fault System:
- Focuses on prompt compensation for covered losses, regardless of fault.
- Typically involves a direct payment system where the insured’s insurer pays benefits.
- May involve arbitration or mediation for disputes.
Role of Arbitration and Mediation
In no-fault insurance disputes, arbitration and mediation play a crucial role in resolving disagreements between insurers and policyholders. These alternative dispute resolution methods offer a less formal and potentially more cost-effective way to reach a resolution compared to traditional litigation.
- Arbitration: Involves a neutral third party who reviews the evidence and makes a binding decision.
- Mediation: Involves a neutral third party who facilitates discussions between the parties to reach a mutually agreeable settlement.
Impact of No-Fault Insurance on the Insurance Industry
No-fault insurance has significantly impacted the insurance industry, leading to changes in pricing, coverage, and the overall operating landscape. This system has brought about both challenges and opportunities for insurance companies, while state regulators play a crucial role in overseeing these practices.
Changes in Pricing and Coverage, No fault auto insurance states
No-fault insurance has generally resulted in lower premiums for policyholders. This is because the system eliminates the need for extensive litigation and associated costs, which are often passed on to policyholders through higher premiums. However, the extent of premium reductions varies depending on the specific no-fault laws in each state.
- No-fault laws often limit the amount of coverage available for pain and suffering, which can reduce the overall cost of insurance.
- These laws also require policyholders to use their own insurance for medical expenses, regardless of fault, leading to lower claim costs for insurance companies.
- However, some no-fault states have experienced increased premium costs due to factors like higher medical expenses or increased fraud.
Challenges and Opportunities for Insurance Companies
No-fault insurance presents both challenges and opportunities for insurance companies.
- One of the biggest challenges is managing medical costs, as no-fault systems typically require insurers to pay for all medical expenses, regardless of fault. This can lead to higher claims costs if medical providers charge higher rates.
- Another challenge is preventing fraud, as the system can make it easier for individuals to file fraudulent claims.
- However, no-fault insurance also presents opportunities for insurance companies, such as the potential for lower operating costs due to reduced litigation and the ability to offer more competitive premiums.
- Insurance companies can also benefit from the streamlined claims process and the reduced burden of defending against lawsuits.
Role of State Regulators
State regulators play a critical role in overseeing no-fault insurance practices.
- They set minimum coverage requirements and ensure that insurance companies comply with state laws.
- Regulators also monitor insurance rates and investigate complaints against insurance companies.
- They work to balance the interests of consumers, insurance companies, and the overall stability of the insurance market.
The Future of No-Fault Auto Insurance
The landscape of auto insurance is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing societal needs, and the emergence of new driving models. As a result, the future of no-fault auto insurance systems is likely to be shaped by these transformative trends.
Impact of Telematics and Driverless Vehicles
Telematics, the use of technology to monitor and analyze driving behavior, is rapidly gaining traction in the auto insurance industry. Telematics devices, such as smartphone apps or in-car sensors, can collect data on driving habits, including speed, acceleration, braking, and location. This data can be used to create personalized insurance premiums based on individual driving risk, potentially leading to lower rates for safe drivers.
- Personalized Premiums: Telematics data allows insurers to assess individual driving risk more accurately, enabling them to offer personalized premiums based on actual driving behavior. This could lead to lower premiums for safe drivers and higher premiums for those with riskier driving habits.
- Incentives for Safe Driving: Telematics systems can be used to encourage safe driving by providing feedback on driving behavior and offering rewards for good driving habits. This could lead to a reduction in accidents and insurance claims.
- Real-Time Risk Assessment: Telematics data can provide real-time insights into driving conditions, such as traffic congestion and weather hazards. This information can be used to adjust premiums or provide warnings to drivers, enhancing safety and efficiency.
The rise of driverless vehicles presents both opportunities and challenges for no-fault insurance systems. While autonomous vehicles have the potential to significantly reduce accidents and injuries, the liability and insurance implications are still being debated.
- Liability Issues: Determining liability in an accident involving an autonomous vehicle can be complex, as the vehicle’s software and sensors may play a role. This raises questions about who is responsible for damages and how insurance claims should be handled.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Autonomous vehicles collect vast amounts of data about driving behavior and passengers, raising concerns about data privacy and security. This data could be used to assess driving risk or for other purposes, potentially leading to ethical and legal challenges.
- Insurance Coverage for Autonomous Vehicles: Existing no-fault insurance systems may need to be adapted to accommodate the unique features and risks associated with autonomous vehicles. This could involve developing new insurance policies specifically designed for driverless cars.
Future of No-Fault Laws and Regulations
The future of no-fault insurance laws and regulations will be influenced by the ongoing debate about the effectiveness and fairness of these systems. Some argue that no-fault insurance has contributed to higher insurance costs and limited access to justice for accident victims. Others believe that no-fault systems offer significant benefits, such as reducing litigation and promoting efficiency.
- Reforms and Amendments: Some states may consider reforms or amendments to their no-fault insurance laws to address concerns about rising insurance costs and limited access to justice. This could involve changes to the threshold for accessing tort litigation, adjustments to benefit levels, or modifications to the dispute resolution process.
- Shifting to a Hybrid System: Some states may move towards a hybrid system that combines elements of no-fault and tort-based systems. This could allow for greater flexibility in addressing different types of accidents and injuries.
- Increased Focus on Accident Prevention: As the emphasis on accident prevention grows, no-fault insurance systems may be modified to encourage safer driving practices and promote the adoption of advanced safety technologies. This could involve incentives for safe drivers or penalties for risky behavior.
Epilogue
Understanding the nuances of no-fault auto insurance is crucial for drivers in states where it’s mandated. This system offers benefits like faster claim processing and reduced litigation, but it also presents limitations and potential drawbacks. By weighing the pros and cons, drivers can make informed decisions about their coverage and navigate the complexities of the no-fault system effectively.
Clarifying Questions
What are the main differences between no-fault and fault-based insurance?
In no-fault insurance, drivers are primarily responsible for covering their own losses, regardless of who caused the accident. In fault-based insurance, the at-fault driver is responsible for covering the other driver’s losses.
Can I sue the other driver in a no-fault state?
In most no-fault states, you can only sue the other driver for serious injuries, like permanent disability or death. For minor injuries, you are typically limited to filing a claim with your own insurance company.
How does no-fault insurance affect my insurance premiums?
No-fault insurance is generally intended to lower insurance premiums by reducing litigation costs. However, the impact on premiums can vary depending on the specific no-fault system in place.







