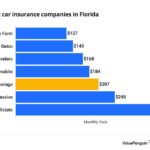
How much does state farm insurance agent make – How much do State Farm insurance agents make? It’s a question that often pops up for those considering a career in insurance. State Farm is a well-known and respected name in the industry, and its agents are known for their personalized service and financial expertise. But what exactly does their compensation look like?
State Farm agents earn income through a combination of base salary, commission on policies sold, and bonuses. Their earnings can be influenced by factors like experience, location, and the size of their client base. The potential for growth and earning potential within the company is significant, making it an attractive career option for many.
State Farm Insurance Agent Compensation Structure: How Much Does State Farm Insurance Agent Make

State Farm Insurance agents are independent contractors, which means they are responsible for their own income and expenses. However, State Farm provides a comprehensive compensation structure designed to reward agents for their performance and help them build successful businesses.
Base Salary
State Farm agents do not receive a traditional base salary. Instead, they earn income through a commission structure based on the policies they sell. This structure provides agents with the opportunity to earn a substantial income based on their efforts and sales success.
Commission Structure
The commission structure for State Farm agents is complex and varies based on the type of insurance policy sold. Generally, agents earn a percentage of the premium paid by policyholders.
For example, an agent might earn a 10% commission on a homeowner’s insurance policy or a 15% commission on an auto insurance policy.
The specific commission rates are determined by State Farm and can fluctuate based on market conditions and the agent’s performance.
Bonuses and Incentives, How much does state farm insurance agent make
State Farm offers a variety of bonuses and incentives to its agents, including:
- Production Bonuses: Agents can earn bonuses based on their overall sales volume and growth in their book of business.
- Performance Bonuses: State Farm may offer bonuses for achieving specific sales targets or exceeding performance benchmarks.
- Referral Bonuses: Agents can earn bonuses for referring new customers to State Farm.
- Leadership Bonuses: Agents who demonstrate strong leadership skills and mentor other agents may receive bonuses.
These bonuses can significantly supplement an agent’s income and provide additional financial rewards for their hard work and dedication.
Additional Benefits and Perks
In addition to the commission structure and bonuses, State Farm agents are eligible for various benefits and perks, including:
- Health Insurance: State Farm offers health insurance plans to its agents, providing coverage for medical, dental, and vision care.
- Retirement Plan: Agents can participate in State Farm’s 401(k) retirement plan, allowing them to save for their future and receive potential tax benefits.
- Training and Development: State Farm provides extensive training and development programs to its agents, equipping them with the skills and knowledge necessary to succeed in their roles.
- Marketing and Advertising Support: State Farm provides marketing and advertising support to its agents, helping them build their brand and attract new customers.
- Technology Resources: Agents have access to state-of-the-art technology resources, including online platforms, mobile apps, and CRM systems, to streamline their operations and enhance their efficiency.
These benefits and perks contribute to the overall compensation package for State Farm agents, providing them with financial security, professional development opportunities, and the resources needed to build a successful business.
Factors Influencing Earnings
A State Farm insurance agent’s income is influenced by a variety of factors, primarily their experience, location, and performance. These factors can significantly impact their earning potential, and understanding them is crucial for aspiring agents.
Book of Business Size
The size of an agent’s book of business, which refers to the number of clients they have and the total amount of insurance premiums they generate, is a significant factor influencing earnings. A larger book of business generally translates to higher income. This is because agents earn commissions on the premiums they generate, and a larger book of business means more premiums and, consequently, higher commissions.
Experience
Experience plays a vital role in an agent’s earning potential. New agents typically start with a smaller book of business and may have limited knowledge of the industry. As they gain experience, they develop stronger client relationships, expand their network, and become more proficient in selling insurance products. This leads to a larger book of business and higher earnings.
Location
The geographic location where an agent operates can also affect their income. Agents in high-population areas with a strong demand for insurance may have a greater opportunity to build a large book of business. Conversely, agents in rural areas with a smaller population may face more competition and have a lower earning potential.
Performance
An agent’s performance directly impacts their earnings. Agents who consistently meet or exceed their sales targets and maintain high customer satisfaction levels are likely to earn higher commissions. Performance is measured by factors such as the number of new policies sold, the retention rate of existing clients, and customer feedback.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Earnings | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experience | Years of experience in the insurance industry | Higher experience generally leads to a larger book of business and higher earnings | A seasoned agent with 10 years of experience may have a significantly larger book of business and earn more than a new agent. |
| Location | Geographic area where the agent operates | High-population areas with strong demand for insurance may offer higher earning potential | An agent in a major city with a large population and high insurance demand may earn more than an agent in a rural area. |
| Book of Business Size | Number of clients and total premiums generated | Larger book of business generally leads to higher earnings | An agent with 500 clients and $1 million in premiums may earn significantly more than an agent with 100 clients and $200,000 in premiums. |
| Performance | Sales performance, customer satisfaction, and retention rates | Strong performance leads to higher commissions | An agent who consistently meets or exceeds their sales targets and has a high customer satisfaction rating may receive bonuses and higher commissions. |
Career Path and Growth Opportunities
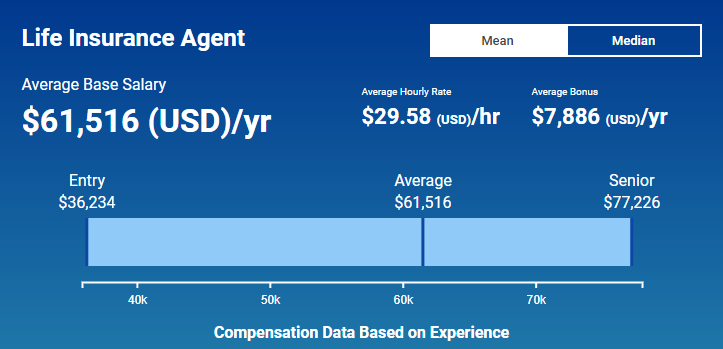
A career as a State Farm Insurance agent offers a clear path for professional growth and development. Agents can progress through various stages, gaining experience and expertise, ultimately leading to leadership roles within the company.
Career Progression
The typical career progression for a State Farm Insurance agent involves several stages:
- Agent Trainee: This initial stage focuses on acquiring the necessary skills and knowledge to become a successful agent. New agents receive comprehensive training on State Farm products, sales techniques, customer service, and agency management. They are also mentored by experienced agents to gain practical experience and learn best practices.
- Agent: Once an agent successfully completes the training program and meets the licensing requirements, they become a fully licensed agent. They are responsible for building their own clientele, managing their agency, and providing insurance solutions to customers.
- Senior Agent: Experienced agents who consistently exceed performance expectations and demonstrate strong leadership qualities can advance to Senior Agent. They may take on additional responsibilities, such as mentoring new agents or managing a larger team.
- District Manager: District Managers oversee a group of agents in a specific geographic area. They provide guidance, support, and leadership to agents in their district, ensuring they meet performance goals and maintain high standards of customer service.
- Regional Manager: Regional Managers are responsible for overseeing a larger group of agents and district managers across a wider geographic area. They focus on strategic planning, resource allocation, and driving overall performance within their region.
Leadership Roles
State Farm offers various leadership roles within its agency network. Agents who demonstrate strong leadership qualities, business acumen, and a commitment to customer service can progress to management positions, such as:
- Agency Manager: Agency Managers oversee the day-to-day operations of a State Farm agency. They are responsible for recruiting, training, and developing agents, as well as managing agency finances and ensuring compliance with company policies.
- Regional Director: Regional Directors oversee a group of agencies in a specific region. They are responsible for developing and implementing strategic plans to drive growth and performance within their region.
- Corporate Leadership: Highly successful agents and managers can progress to corporate leadership roles, such as Vice President of Sales or Chief Operating Officer. These positions involve strategic decision-making and oversight of the company’s overall operations.
Training and Development
State Farm is committed to providing its agents with ongoing training and development opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge. These programs may include:
- Initial Agent Training: This comprehensive program provides new agents with the foundation they need to succeed. It covers topics such as product knowledge, sales techniques, customer service, and agency management.
- Continuing Education: State Farm offers a variety of continuing education courses to help agents stay up-to-date on industry trends, new products, and best practices.
- Leadership Development Programs: State Farm provides leadership development programs to help agents develop the skills and knowledge they need to progress to management positions. These programs cover topics such as strategic planning, team building, and effective communication.
- Mentorship Programs: Experienced agents provide mentorship to new agents, helping them navigate the challenges of building a successful agency and developing their careers.
Comparison to Other Insurance Agencies
State Farm agents operate within a unique compensation structure that sets them apart from agents at other insurance companies. Understanding these differences is crucial for aspiring insurance professionals seeking to navigate the industry’s diverse compensation models.
Compensation Structure Comparison
Comparing the compensation structures of State Farm agents to those of other insurance agencies reveals distinct approaches to rewarding their sales force. While State Farm agents primarily earn through commissions on sold policies, other agencies may employ a mix of salary, bonuses, and commissions, offering different levels of financial security and earning potential.
- State Farm: State Farm agents typically receive a commission-based compensation structure. This means they earn a percentage of the premiums collected on the policies they sell. The commission rate varies depending on the type of insurance policy sold.
- Other Insurance Agencies: Many other insurance agencies employ a combination of salary, bonuses, and commissions. Some agencies may offer a base salary with additional commissions based on sales performance, while others may offer bonuses for exceeding sales targets or achieving specific milestones.
Unique Aspects of the State Farm Model
The State Farm model distinguishes itself through its emphasis on building a book of business and fostering long-term client relationships. This approach offers agents the potential for substantial income growth over time as they cultivate a loyal customer base.
- Focus on Building a Book of Business: State Farm agents are encouraged to develop long-term relationships with clients, building a sustainable book of business that generates recurring income. This emphasis on client retention and loyalty fosters a sense of ownership and rewards agents for their efforts in building strong client relationships.
- Emphasis on Client Service: State Farm’s focus on customer satisfaction and retention is reflected in its compensation structure. Agents are incentivized to provide exceptional service, leading to increased client loyalty and a steady stream of referrals.
Earning Potential and Career Paths
The earning potential and career paths for insurance agents can vary significantly across different companies. While State Farm agents have the potential to earn substantial income through commissions, other agencies may offer a more predictable salary-based structure.
- State Farm: State Farm agents with a strong book of business can achieve high earning potential. However, their income is directly tied to their sales performance, and they may face income fluctuations depending on market conditions and their ability to attract new clients.
- Other Insurance Agencies: Other agencies may offer a more stable income with a combination of salary and commissions. However, their earning potential may be capped compared to State Farm agents with a large book of business.
Compensation Feature Comparison Table
The table below summarizes key compensation features of State Farm and two other prominent insurance agencies:
| Feature | State Farm | Allstate | Farmers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compensation Structure | Commission-based | Salary + Commission | Commission-based |
| Base Salary | None | Yes | None |
| Commission Rates | Vary by policy type | Vary by policy type | Vary by policy type |
| Bonuses | Yes (for exceeding sales targets) | Yes (for exceeding sales targets) | Yes (for exceeding sales targets) |
Industry Trends and Future Outlook

The insurance industry is constantly evolving, influenced by technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, and changing economic landscapes. These factors have a direct impact on the compensation structure and career paths of insurance agents, including those at State Farm.
Emerging Technologies and Automation
The insurance industry is embracing technological advancements, leading to automation in various processes. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being used for tasks like risk assessment, claims processing, and customer service. These technologies are streamlining operations and reducing costs, potentially leading to changes in agent roles.
“AI and ML are revolutionizing the insurance industry, creating opportunities for agents to focus on higher-value activities like customer relationship management and personalized advice.”
- Automated underwriting: AI algorithms analyze data to assess risk and determine premiums, reducing the need for manual underwriting by agents.
- Chatbots and virtual assistants: These technologies are handling routine customer inquiries, freeing up agents to focus on more complex issues.
- Data analytics: Advanced analytics tools help agents identify customer needs and personalize their services, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Shifting Consumer Preferences
Consumers are increasingly demanding personalized experiences, convenience, and digital solutions. They are more likely to research insurance options online and interact with agents through digital channels. This shift in consumer behavior is influencing how insurance agents operate and interact with their clients.
- Digital insurance platforms: Consumers are increasingly using online platforms to compare insurance quotes, purchase policies, and manage their accounts.
- Mobile-first approach: Insurance agents need to adapt to the mobile-first approach, providing services and information through mobile apps and responsive websites.
- Personalized communication: Agents need to leverage data analytics to understand customer needs and tailor their communication strategies to individual preferences.
Future Landscape for State Farm Agents
Despite the industry trends, State Farm agents are expected to remain an integral part of the company’s success. The company’s focus on building strong customer relationships and providing personalized advice positions its agents to thrive in the evolving landscape.
- Focus on customer relationships: State Farm agents will continue to play a crucial role in building and nurturing relationships with customers, providing personalized advice and guidance.
- Leveraging technology: Agents will need to embrace technology to enhance their efficiency and provide a seamless digital experience for customers.
- Specialization and expertise: Agents who specialize in specific areas, such as commercial insurance or high-net-worth clients, will be highly valued.
Ultimate Conclusion
A career as a State Farm insurance agent can be both rewarding and lucrative. The opportunity to build a successful business, earn a competitive income, and make a difference in people’s lives is enticing. By understanding the compensation structure, factors influencing earnings, and career paths available, you can make an informed decision about whether this career path is right for you.
Quick FAQs
What is the typical base salary for a State Farm insurance agent?
The base salary for State Farm agents varies depending on factors such as experience and location. However, it’s generally a modest amount, with the majority of income coming from commissions and bonuses.
What are some common bonuses offered to State Farm agents?
State Farm offers various bonuses, including performance-based bonuses for meeting sales targets, referral bonuses for bringing in new clients, and leadership bonuses for those in management roles.
What are the career advancement opportunities for State Farm agents?
State Farm offers several career advancement opportunities, including becoming a senior agent, a district manager, or a regional manager. There are also opportunities to specialize in specific insurance areas like life insurance or commercial insurance.