Florida State Insurance Requirements are a vital part of life in the Sunshine State, ensuring residents and businesses are protected against unexpected events. These regulations, enforced by various agencies, aim to provide financial security and peace of mind, safeguarding individuals and businesses from potential losses.
From mandatory auto insurance to homeowner’s coverage and specialized policies for businesses, Florida’s insurance landscape is comprehensive. Understanding these requirements is crucial for navigating the state’s unique environment, whether you’re a long-time resident or a newcomer.
Florida Insurance Requirements Overview
Florida’s insurance requirements are a set of rules and regulations designed to ensure that individuals and businesses have adequate financial protection against potential risks. These requirements play a crucial role in protecting residents and businesses from financial hardship in the event of unexpected events like accidents, natural disasters, or property damage.
Purpose and Significance
The purpose of Florida’s insurance requirements is to provide financial security and stability for residents and businesses by minimizing the impact of unforeseen events. These requirements ensure that individuals and businesses have access to insurance coverage that can help them recover from losses and rebuild their lives or businesses. The significance of these requirements lies in their ability to protect against significant financial burdens and promote a sense of security within the state.
Regulatory Bodies and Roles
Several regulatory bodies are responsible for enforcing and overseeing insurance regulations in Florida. These bodies play a vital role in ensuring that insurance companies operate fairly and responsibly, protecting consumers’ interests.
- Florida Office of Insurance Regulation (OIR): The OIR is the primary regulatory body for the insurance industry in Florida. It sets and enforces insurance regulations, licenses insurance companies and agents, and investigates consumer complaints.
- Florida Department of Financial Services (DFS): The DFS oversees the insurance industry, including insurance companies, agents, and brokers. It also investigates fraud and consumer complaints related to insurance.
- Florida Insurance Guaranty Association (FIGA): FIGA provides financial protection to policyholders in the event that an insurance company becomes insolvent. It covers unpaid claims up to certain limits, ensuring that policyholders are not left without coverage.
Types of Insurance Required in Florida: Florida State Insurance Requirements
Florida has a comprehensive set of insurance requirements for individuals and businesses to ensure financial protection in case of unexpected events. These requirements are designed to safeguard residents and visitors, promoting responsible ownership and minimizing potential financial burdens.
Florida’s Mandatory Insurance Types
Florida mandates specific types of insurance for different situations. These requirements are designed to protect individuals and businesses from financial hardship in the event of accidents, natural disasters, or other unforeseen circumstances.
| Insurance Type | Coverage | Minimum Requirements | Penalties for Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Auto Insurance | Protects against financial losses resulting from accidents involving a vehicle, covering damages to the insured vehicle, injuries to the insured or others, and property damage. | Florida requires drivers to have at least:
|
|
| Homeowners Insurance | Covers damage or loss to the insured’s home and personal property due to perils such as fire, theft, vandalism, and natural disasters like hurricanes and floods. | Florida requires homeowners to have insurance that covers at least:
|
|
| Flood Insurance | Provides coverage for damages caused by flooding, a peril not typically covered by standard homeowners insurance. | While not mandatory in all areas, flood insurance is highly recommended in flood-prone regions of Florida. |
|
| Workers’ Compensation Insurance | Provides coverage for employees injured or disabled on the job, covering medical expenses, lost wages, and other related costs. | Florida requires employers to have workers’ compensation insurance for their employees, with coverage varying based on the nature of the business and the number of employees. |
|
| Liability Insurance | Protects individuals and businesses from financial losses resulting from claims of negligence or wrongdoing, covering legal defense costs and potential settlements. | Florida requires certain businesses, such as those operating in specific industries or with high-risk activities, to have liability insurance. |
|
Vehicle Insurance Requirements
In Florida, driving without the proper insurance coverage can lead to serious legal and financial consequences. Therefore, understanding the state’s mandatory insurance requirements is crucial for all vehicle owners and drivers.
Minimum Coverage Amounts
Florida law requires all drivers to carry a minimum amount of liability insurance. These coverages protect you financially if you are found at fault in an accident.
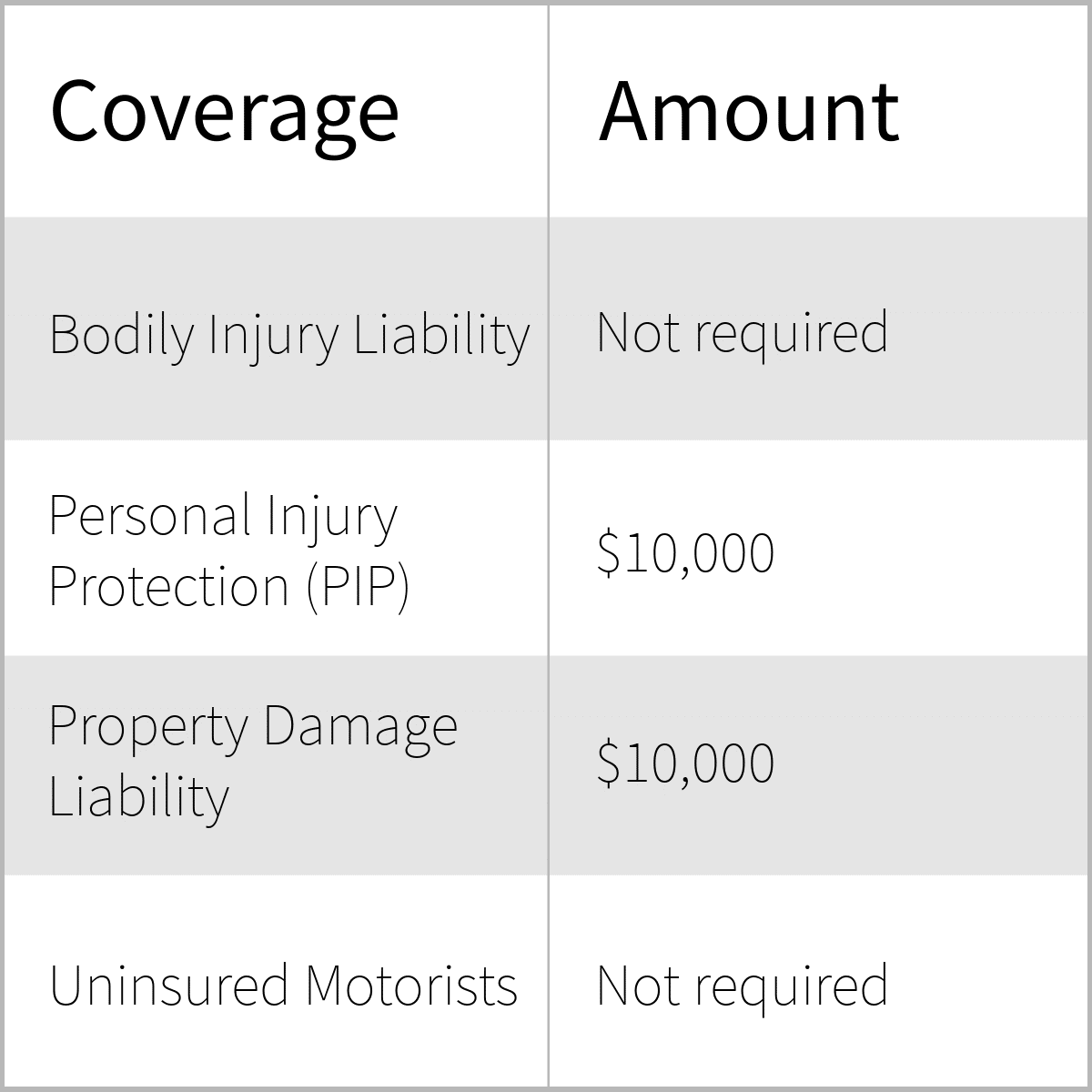
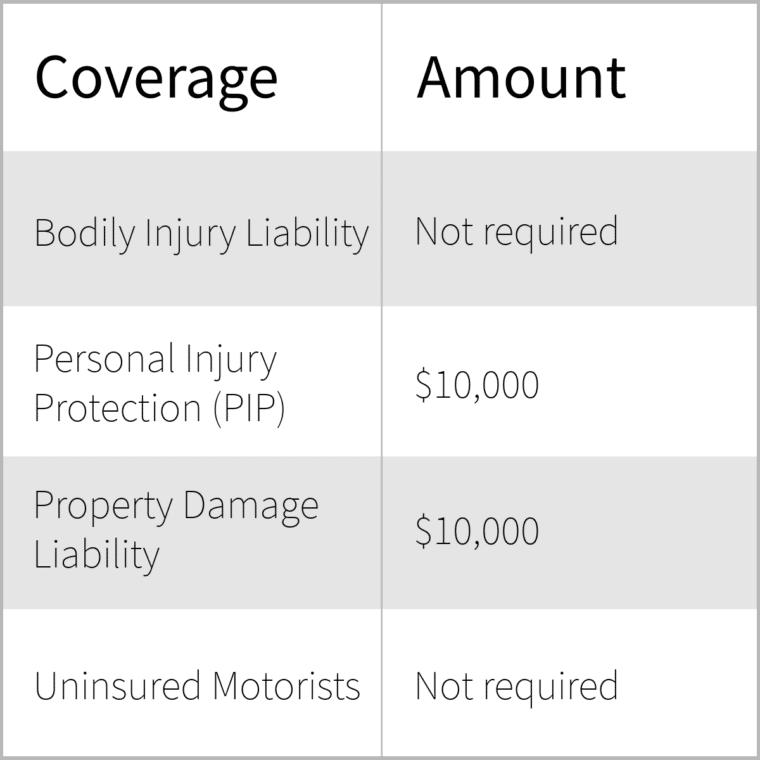
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): This coverage pays for medical expenses, lost wages, and other related costs for you and your passengers, regardless of who is at fault. The minimum required PIP coverage is $10,000.
- Property Damage Liability (PDL): This coverage pays for damages to another person’s property if you are at fault in an accident. The minimum required PDL coverage is $10,000.
Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without the required minimum insurance in Florida can result in various penalties, including:
- Fines and Penalties: You may face fines ranging from $150 to $500 for driving without insurance.
- License Suspension: Your driver’s license can be suspended for up to three years if you are caught driving without insurance.
- Vehicle Impoundment: Your vehicle may be impounded until you provide proof of insurance.
- Financial Responsibility: You may be held personally liable for all damages and injuries caused in an accident, even if you were not at fault.
Homeowner’s Insurance Requirements

Homeowner’s insurance is a crucial aspect of property ownership in Florida, offering financial protection against various risks. Understanding the essential coverage elements and factors influencing premiums is vital for securing adequate insurance.
Coverage Elements of Homeowner’s Insurance
Homeowner’s insurance policies in Florida typically include several essential coverage elements, providing financial protection against various perils. These coverages include:
- Dwelling Coverage: This coverage protects the physical structure of your home, including the attached structures, against damages caused by covered perils such as fire, windstorm, hail, and lightning.
- Other Structures Coverage: This coverage extends protection to detached structures on your property, such as garages, sheds, and fences, against covered perils.
- Personal Property Coverage: This coverage protects your belongings, including furniture, electronics, clothing, and personal items, against damages caused by covered perils. This coverage typically includes a limit on the amount of coverage for specific items, such as jewelry and art.
- Liability Coverage: This coverage provides financial protection against claims made against you for injuries or property damage caused by you or members of your household. It also covers legal defense costs in case of a lawsuit.
- Medical Payments Coverage: This coverage pays for medical expenses for individuals injured on your property, regardless of fault.
- Loss of Use Coverage: This coverage provides financial assistance for additional living expenses, such as hotel accommodations, if your home becomes uninhabitable due to a covered peril.
Factors Influencing Homeowner’s Insurance Premiums
Several factors can influence the cost of homeowner’s insurance premiums in Florida. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions to potentially reduce your premiums.
- Location: Your home’s location plays a significant role in determining your premiums. Areas prone to hurricanes, floods, or other natural disasters generally have higher premiums due to the increased risk.
- Age and Condition of the Home: Older homes with outdated plumbing, electrical systems, or roofing may have higher premiums due to increased risk of damage or repairs. Homes with recent upgrades or renovations may qualify for lower premiums.
- Property Value: The market value of your home is a major factor influencing your premiums. Higher-valued homes generally have higher premiums due to the greater potential financial loss in case of damage.
- Credit Score: Your credit score can impact your insurance premiums. Individuals with good credit scores may qualify for lower premiums than those with poor credit scores.
- Deductible: The deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket for covered losses before your insurance coverage kicks in. A higher deductible generally leads to lower premiums, while a lower deductible results in higher premiums.
- Coverage Limits: The amount of coverage you choose for different aspects of your policy, such as dwelling coverage and personal property coverage, can influence your premiums. Higher coverage limits generally lead to higher premiums.
Types of Homeowner’s Insurance Policies
Homeowner’s insurance policies in Florida are typically categorized into different types, each offering specific coverage levels and benefits.
| Policy Type | Coverage |
|---|---|
| HO-3 (Special Form) | Provides open perils coverage for the dwelling and other structures, meaning it covers all perils except those specifically excluded in the policy. Personal property is covered on a named perils basis, meaning it is only covered for perils listed in the policy. |
| HO-5 (Comprehensive Form) | Provides open perils coverage for both the dwelling and personal property, meaning it covers all perils except those specifically excluded in the policy. This is the most comprehensive type of homeowner’s insurance policy. |
| HO-8 (Modified Coverage Form) | Designed for older homes, this policy provides coverage on a named perils basis for both the dwelling and personal property. It is typically used when the replacement cost of the home is significantly lower than its market value. |
| HO-6 (Condominium Unit Owners Form) | Specifically designed for condominium owners, this policy covers the interior of the unit, personal property, and liability. It does not cover the building itself, which is typically insured by the condominium association. |
Business Insurance Requirements
Operating a business in Florida comes with various legal and financial obligations, including the need to secure adequate insurance coverage. These requirements are designed to protect both the business owner and the public from potential risks.
Florida Business Insurance Requirements, Florida state insurance requirements
Florida law mandates that businesses obtain specific types of insurance to operate legally. These requirements vary depending on the nature of the business and the industry it operates in. Here’s a breakdown of common business insurance types in Florida, along with their rationale and coverage details:
| Business Type | Required Insurance | Coverage Details | Exemptions |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Liability Insurance | Most businesses | Covers third-party bodily injury and property damage arising from business operations. This includes premises liability, product liability, and advertising injury. | Small businesses with limited public interaction and low risk profiles may be exempt. |
| Workers’ Compensation Insurance | Businesses with employees | Covers medical expenses, lost wages, and disability benefits for employees injured on the job. It also protects businesses from lawsuits arising from workplace injuries. | Sole proprietorships and independent contractors who are not considered employees are typically exempt. |
| Commercial Property Insurance | Businesses that own or lease property | Covers damage or loss to business property, including buildings, equipment, inventory, and other assets, caused by perils such as fire, theft, vandalism, and natural disasters. | Businesses that operate exclusively from rented office space without any owned or leased property may be exempt. |
| Professional Liability Insurance (E&O) | Professional service providers | Protects professionals against claims of negligence, errors, or omissions in their professional services. This is essential for businesses like accountants, lawyers, doctors, and consultants. | Businesses that do not provide professional services, such as retail stores or manufacturing companies, are typically exempt. |
| Commercial Auto Insurance | Businesses that operate vehicles | Covers damage to business vehicles and liability for accidents involving those vehicles. It may include coverage for property damage, bodily injury, and uninsured/underinsured motorist protection. | Businesses that do not use vehicles for business operations, such as online retailers or consulting firms, are exempt. |
Insurance Exemptions and Waivers
In Florida, specific situations exist where individuals or businesses may be exempt from certain insurance requirements. These exemptions are typically granted based on factors such as the nature of the property, the type of business, or the individual’s financial circumstances. Understanding these exemptions and the process for obtaining them can be beneficial for individuals and businesses looking to minimize their insurance costs.
Exemption Eligibility Criteria
Individuals or businesses may be eligible for exemptions from certain insurance requirements based on specific criteria. These criteria can vary depending on the type of insurance and the specific exemption being sought.
- Financial Hardship: Individuals or businesses experiencing significant financial hardship may be eligible for exemptions or waivers from certain insurance requirements. This typically involves demonstrating a lack of financial resources to afford the required insurance.
- Property Type: The type of property may also influence exemption eligibility. For instance, certain types of properties, such as historic buildings or those located in remote areas, may qualify for exemptions from certain insurance requirements.
- Business Type: The type of business can also play a role in determining exemption eligibility. Some businesses, such as those operating in specific industries or those with limited financial resources, may qualify for exemptions from certain insurance requirements.
Process for Obtaining Exemptions or Waivers
The process for obtaining exemptions or waivers from insurance requirements in Florida can vary depending on the specific exemption being sought. Generally, individuals or businesses must submit a formal application to the relevant regulatory authority.
- Application Submission: The application should typically include detailed information about the applicant, the property or business in question, and the reasons for seeking an exemption.
- Supporting Documentation: The applicant may be required to provide supporting documentation, such as financial statements, property appraisals, or business licenses, to support their claim for exemption.
- Review and Approval: The regulatory authority will review the application and supporting documentation. If the applicant meets the eligibility criteria, the exemption will be granted.
Common Exemption Scenarios
Several common exemption scenarios exist in Florida, where individuals or businesses may be eligible for exemptions from certain insurance requirements.
- Homeowner’s Insurance: In some cases, homeowners may be eligible for exemptions from certain homeowner’s insurance requirements, such as the requirement for windstorm coverage, if their home is located in a low-risk area.
- Vehicle Insurance: Individuals who own certain types of vehicles, such as antique cars or vehicles used solely for agricultural purposes, may be eligible for exemptions from certain vehicle insurance requirements.
- Business Insurance: Certain businesses, such as those operating in specific industries or those with limited financial resources, may be eligible for exemptions from certain business insurance requirements.
Insurance Dispute Resolution
Navigating insurance disputes can be challenging, but Florida provides a framework for resolving them fairly. This section Artikels the procedures for resolving insurance disputes, the role of the Florida Department of Financial Services (DFS), and the available dispute resolution options.
Role of the Florida Department of Financial Services
The DFS plays a crucial role in resolving insurance disputes in Florida. It acts as a mediator between policyholders and insurance companies, aiming to facilitate fair and timely claim settlements. The DFS offers several resources to assist policyholders, including:
- Consumer Assistance Hotline: The DFS operates a hotline for policyholders to report complaints and seek assistance. They can provide guidance, answer questions, and help navigate the dispute resolution process.
- Online Complaint Filing: Policyholders can file complaints with the DFS online, detailing the nature of the dispute and their desired outcome. The DFS will then investigate the complaint and attempt to reach a resolution.
- Mediation Services: The DFS offers mediation services to help policyholders and insurance companies reach a mutually agreeable settlement. A neutral mediator will facilitate discussions and assist in identifying potential solutions.
Dispute Resolution Options
Policyholders have several options for resolving insurance disputes, depending on the nature of the dispute and their desired outcome. These options include:
- Negotiation: The first step in resolving a dispute is often direct negotiation with the insurance company. Policyholders can try to reach a settlement through communication and compromise.
- Mediation: Mediation is a non-binding process where a neutral third party helps the parties involved reach a mutually agreeable settlement. It offers a structured and confidential setting for resolving disputes.
- Arbitration: Arbitration is a binding process where a neutral third party (the arbitrator) hears evidence and makes a decision that is legally binding on both parties. It is a more formal process than mediation and is often used when parties cannot reach a settlement through negotiation or mediation.
- Litigation: In cases where other dispute resolution options have failed, policyholders may choose to file a lawsuit in court. This is the most formal and costly option and should be considered as a last resort.
Insurance Industry Trends and Developments
The Florida insurance industry is constantly evolving, driven by factors such as climate change, economic conditions, and regulatory changes. Understanding these trends is crucial for both consumers and insurance companies to navigate the complexities of insurance coverage and pricing.
Impact of Climate Change on Insurance Requirements
Climate change is significantly impacting the Florida insurance industry, leading to increased insurance costs and availability challenges. The state’s vulnerability to hurricanes and other natural disasters has resulted in higher premiums and stricter underwriting standards.
- Increased Hurricane Frequency and Intensity: Hurricanes are becoming more frequent and intense, leading to greater property damage and higher insurance claims. This has caused insurers to raise premiums and limit coverage in high-risk areas.
- Rising Sea Levels and Coastal Flooding: Rising sea levels are increasing the risk of coastal flooding, posing significant challenges for property insurance. Insurers are increasingly reluctant to cover properties in flood-prone areas, leading to limited availability and higher premiums.
- Climate Change Litigation: Lawsuits related to climate change are on the rise, potentially impacting insurance companies’ financial stability. Insurers are facing increased costs associated with defending these lawsuits and paying claims related to climate-related events.
Impact of Economic Conditions on Consumer Costs
Economic factors play a significant role in shaping insurance costs. Inflation, reinsurance costs, and investment returns all influence premium pricing.
- Inflation: Rising inflation increases the cost of repairs and replacements, leading to higher insurance premiums. As the cost of materials and labor increases, insurers must adjust their rates to cover these expenses.
- Reinsurance Costs: Reinsurance, which protects insurance companies from catastrophic losses, is becoming more expensive. This is due to factors such as increased natural disasters and the growing financial burden on reinsurers. Higher reinsurance costs are passed on to consumers through increased premiums.
- Investment Returns: Insurance companies rely on investment returns to offset claims costs. Low interest rates and volatile market conditions can reduce investment returns, potentially leading to higher premiums.
Regulatory Changes and their Impact on Insurance Coverage
The Florida Legislature and the Office of Insurance Regulation (OIR) have implemented various reforms and regulations to address insurance challenges.
- Insurance Rate Regulation: The OIR has implemented rate regulations to ensure fair and reasonable premiums. These regulations aim to balance the needs of consumers with the financial stability of insurance companies.
- Hurricane Catastrophe Fund: The state-funded Hurricane Catastrophe Fund provides financial assistance to insurance companies in the event of a major hurricane. This fund helps stabilize the insurance market and prevent widespread price increases.
- Assignment of Benefits (AOB) Reform: The Legislature has passed reforms to address the issue of AOB abuse, which has contributed to rising insurance costs. These reforms aim to reduce fraudulent claims and limit the involvement of third-party vendors.
Closing Summary
Navigating Florida’s insurance requirements can be complex, but understanding the basics is essential for protecting your assets and securing your future. By complying with these regulations, you contribute to a safer and more stable community while ensuring peace of mind in the face of life’s uncertainties. Remember to consult with insurance professionals for personalized advice and guidance.
Q&A
What happens if I don’t have the required insurance?
Failing to meet Florida’s insurance requirements can result in fines, license suspension, or even legal action. The severity of the consequences depends on the type of insurance and the extent of non-compliance.
Are there any discounts available for Florida insurance?
Yes, many insurance companies offer discounts for factors like good driving records, safety features, multiple policy bundling, and home security systems. It’s always beneficial to inquire about available discounts.
How can I file a claim if I need to?
Contact your insurance company immediately to report the incident and follow their claim filing procedures. Provide all necessary documentation and cooperate with the investigation process.