Do all states require car insurance? The answer is a resounding “almost.” While the vast majority of states mandate car insurance for drivers, there are a few exceptions. This article explores the reasons behind mandatory car insurance, the consequences of driving without it, and the types of coverage available to drivers.
Understanding the intricacies of car insurance is crucial for every driver. This guide will delve into the essential aspects of car insurance, from the different types of coverage to the factors that affect your premiums. We will also discuss the process of obtaining car insurance, ensuring you have the right coverage for your needs.
The Importance of Car Insurance
Car insurance is a crucial aspect of responsible vehicle ownership, offering financial protection against potential risks associated with driving. While it may seem like an added expense, the consequences of driving without insurance can be severe, making it a mandatory requirement in most states.
Reasons for Mandatory Car Insurance
The decision to make car insurance mandatory in most states stems from a combination of factors aimed at protecting both drivers and society as a whole.
- Financial Protection for Accident Victims: In the unfortunate event of an accident, car insurance provides financial compensation to individuals who have been injured or whose property has been damaged. This ensures that victims are not burdened with significant financial losses due to someone else’s negligence.
- Road Safety: By making car insurance mandatory, states encourage drivers to be more responsible on the roads. Knowing they are financially protected in case of an accident, drivers are more likely to exercise caution and follow traffic rules.
- Stability in the Insurance Market: Mandatory car insurance helps stabilize the insurance market by ensuring a consistent pool of insured drivers. This allows insurance companies to spread the risk of accidents more evenly, leading to more affordable premiums for everyone.
- Social Responsibility: Driving a vehicle comes with inherent risks, and car insurance is a way to share the responsibility for those risks among all drivers. It promotes a sense of fairness and social responsibility, ensuring that those who cause accidents are held accountable for their actions.
Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without car insurance is a serious offense that can lead to a range of consequences, including:
- Fines and Penalties: Driving without insurance is a violation of state law, and violators face hefty fines and penalties, which can vary depending on the state and the severity of the offense.
- License Suspension or Revocation: If you are caught driving without insurance, your license may be suspended or revoked, making it impossible for you to legally operate a vehicle.
- Vehicle Impoundment: In some cases, your vehicle may be impounded until you provide proof of insurance.
- Financial Ruin: If you are involved in an accident without insurance, you could be held personally liable for all damages and injuries, potentially leading to significant financial ruin.
- Criminal Charges: In some states, driving without insurance can even lead to criminal charges, especially if you are involved in an accident that results in injuries or fatalities.
Situations Where Car Insurance is Crucial
Car insurance is not just a legal requirement but also a vital financial safety net in various situations. Here are some examples:
- Accidents: In the event of an accident, car insurance covers the costs of repairs, medical expenses, and legal fees, protecting you from financial ruin. For example, if you are involved in a collision with another vehicle, your insurance will cover the cost of repairing your car and any medical expenses for you and your passengers. It will also cover the other driver’s damages and medical expenses if you are at fault.
- Natural Disasters: Car insurance can provide financial assistance for damage caused by natural disasters such as floods, earthquakes, or tornadoes. If your car is damaged or destroyed by a natural disaster, your insurance will cover the cost of repairs or replacement.
- Theft or Vandalism: If your car is stolen or vandalized, car insurance will cover the cost of replacing or repairing your vehicle.
- Liability Coverage: Car insurance includes liability coverage, which protects you from financial responsibility if you cause an accident that injures someone or damages their property. For example, if you hit a pedestrian while driving, your liability coverage will pay for their medical expenses and any other damages.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorists Coverage: This coverage protects you if you are involved in an accident with a driver who does not have insurance or does not have enough insurance to cover your damages. For example, if you are hit by a driver who has no insurance, your uninsured motorist coverage will pay for your medical expenses and damages.
States That Require Car Insurance
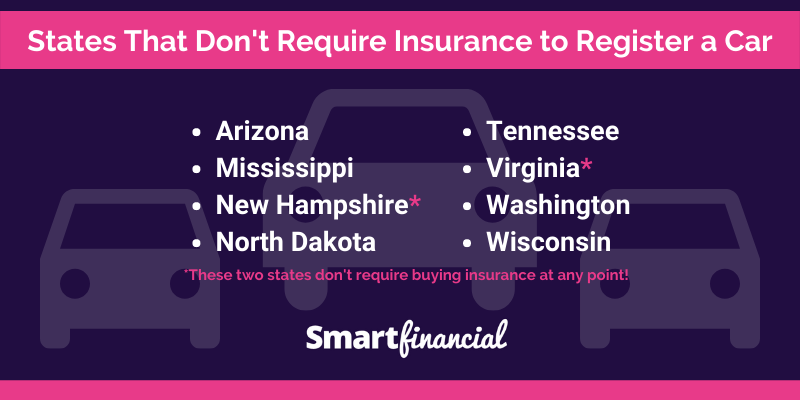
All states in the United States, except New Hampshire, require drivers to have car insurance. This is because car insurance is essential for protecting yourself and others financially in the event of an accident.
Minimum Coverage Requirements
The minimum car insurance requirements vary from state to state. These minimums are often referred to as “liability coverage,” which means that they only cover damages caused to others in an accident. They typically include:
| State | Bodily Injury Liability per Person | Bodily Injury Liability per Accident | Property Damage Liability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Alaska | $50,000 | $100,000 | $25,000 |
| Arizona | $25,000 | $50,000 | $15,000 |
| Arkansas | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| California | $15,000 | $30,000 | $5,000 |
| Colorado | $25,000 | $50,000 | $15,000 |
| Connecticut | $20,000 | $40,000 | $10,000 |
| Delaware | $30,000 | $60,000 | $10,000 |
| Florida | $10,000 | $20,000 | $10,000 |
| Georgia | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Hawaii | $20,000 | $40,000 | $10,000 |
| Idaho | $25,000 | $50,000 | $15,000 |
| Illinois | $20,000 | $40,000 | $15,000 |
| Indiana | $25,000 | $50,000 | $10,000 |
| Iowa | $20,000 | $40,000 | $15,000 |
| Kansas | $25,000 | $50,000 | $10,000 |
| Kentucky | $25,000 | $50,000 | $10,000 |
| Louisiana | $15,000 | $30,000 | $10,000 |
| Maine | $50,000 | $100,000 | $25,000 |
| Maryland | $30,000 | $60,000 | $15,000 |
| Massachusetts | $20,000 | $40,000 | $5,000 |
| Michigan | $20,000 | $40,000 | $10,000 |
| Minnesota | $30,000 | $60,000 | $10,000 |
| Mississippi | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Missouri | $25,000 | $50,000 | $10,000 |
| Montana | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Nebraska | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Nevada | $25,000 | $50,000 | $15,000 |
| New Hampshire | Not required | Not required | Not required |
| New Jersey | $15,000 | $30,000 | $5,000 |
| New Mexico | $25,000 | $50,000 | $10,000 |
| New York | $25,000 | $50,000 | $10,000 |
| North Carolina | $30,000 | $60,000 | $25,000 |
| North Dakota | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Ohio | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Oklahoma | $25,000 | $50,000 | $10,000 |
| Oregon | $25,000 | $50,000 | $20,000 |
| Pennsylvania | $15,000 | $30,000 | $5,000 |
| Rhode Island | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| South Carolina | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| South Dakota | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Tennessee | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Texas | $30,000 | $60,000 | $25,000 |
| Utah | $25,000 | $65,000 | $15,000 |
| Vermont | $25,000 | $50,000 | $10,000 |
| Virginia | $25,000 | $50,000 | $20,000 |
| Washington | $25,000 | $50,000 | $10,000 |
| West Virginia | $25,000 | $50,000 | $10,000 |
| Wisconsin | $25,000 | $50,000 | $10,000 |
| Wyoming | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
States That Do Not Require Car Insurance
Only one state in the US does not require car insurance: New Hampshire. However, New Hampshire drivers are still required to demonstrate financial responsibility, which can be done through a surety bond, self-insurance, or a deposit of cash or securities with the state.
Exceptions and Exemptions
While most states require car insurance, there are some exceptions and exemptions. These can include:
- Vehicles not driven on public roads: This includes vehicles that are used solely for private use, such as golf carts or farm vehicles.
- Vehicles owned by the government: This includes vehicles owned by the federal, state, or local government.
- Antique or classic vehicles: Some states allow antique or classic vehicles to be exempt from car insurance requirements if they are not driven regularly.
- Vehicles that are insured under a different policy: For example, if a vehicle is being transported on a trailer, it may be covered under the insurance policy for the towing vehicle.
- Vehicles that are not used for transportation: This includes vehicles that are used for storage or display.
It’s important to note that even if a vehicle is exempt from car insurance requirements, it may still be required to have liability insurance if it is involved in an accident.
Types of Car Insurance Coverage
Car insurance is a complex subject with various types of coverage designed to protect you and your vehicle in different situations. Understanding the different types of coverage is crucial to ensuring you have adequate protection.
Liability Coverage
Liability coverage is a crucial component of car insurance. It safeguards you financially if you cause an accident that injures another person or damages their property. This coverage pays for the other driver’s medical expenses, lost wages, property repairs, and legal fees. Liability coverage is typically expressed as a limit, such as 100/300/100, which means:
- $100,000: Maximum amount paid per person for bodily injury in an accident.
- $300,000: Maximum amount paid for all bodily injuries in a single accident.
- $100,000: Maximum amount paid for property damage in an accident.
The specific limits of your liability coverage will depend on your state’s minimum requirements and your individual needs.
Collision Coverage
Collision coverage protects you financially if your vehicle is damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. This coverage pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle, minus your deductible. For example, if you collide with another vehicle and cause damage to your car, collision coverage would help pay for the repairs.
Comprehensive Coverage
Comprehensive coverage protects you financially if your vehicle is damaged by something other than an accident, such as theft, vandalism, natural disasters, or falling objects. This coverage also pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle, minus your deductible. For instance, if your car is stolen and recovered damaged, comprehensive coverage would help pay for the repairs.
Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage
Uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage protects you financially if you are injured in an accident caused by a driver who is uninsured or has insufficient insurance. This coverage pays for your medical expenses, lost wages, and other related costs. For example, if you are hit by an uninsured driver and suffer injuries, this coverage would help pay for your medical bills.
Factors Affecting Insurance Rates
Car insurance premiums are not one-size-fits-all. Several factors influence the cost of your insurance, and understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions to potentially lower your rates.
Driving History
Your driving history is a major factor in determining your insurance rates. A clean driving record with no accidents or violations will generally result in lower premiums. However, if you have a history of accidents, traffic violations, or even DUI convictions, your rates will likely be higher.
Age
Age plays a significant role in car insurance rates. Younger drivers, especially those under 25, are statistically more likely to be involved in accidents. Insurance companies often consider young drivers to be higher risk and charge them higher premiums. On the other hand, older drivers, typically those over 65, tend to have more experience and safer driving habits, leading to lower rates.
Vehicle Type, Do all states require car insurance
The type of vehicle you drive also impacts your insurance premiums. Sports cars, luxury vehicles, and high-performance vehicles are generally considered more expensive to repair or replace, so insurance companies may charge higher rates for these types of cars. Conversely, older, less expensive vehicles with lower repair costs will typically have lower insurance premiums.
Location
Where you live can significantly affect your car insurance rates. Insurance companies consider factors such as the density of traffic, crime rates, and the frequency of accidents in your area when determining premiums. Urban areas with high traffic volume and more accidents tend to have higher insurance rates compared to rural areas with lower traffic and fewer accidents.
Credit Score
You might be surprised to learn that your credit score can also influence your car insurance rates. Insurance companies believe that individuals with good credit are more likely to be responsible and reliable, which translates to a lower risk of filing claims. Therefore, those with higher credit scores may qualify for lower premiums.
Getting Car Insurance
Navigating the process of getting car insurance can seem daunting, but it’s a crucial step in responsible vehicle ownership. Understanding the process and making informed decisions can help you secure the best possible coverage at a reasonable price.
Finding a Suitable Policy
Finding a suitable car insurance policy involves several steps, each contributing to securing the right coverage for your needs.
- Assess your needs: Begin by evaluating your individual circumstances and determining the type and amount of coverage you require. Consider factors like your driving history, the age and value of your vehicle, and your financial situation.
- Gather quotes from multiple insurance companies: Obtaining quotes from several insurers allows you to compare prices, coverage options, and discounts. This helps you identify the best value for your specific requirements.
- Review policy details: Carefully examine each quote, paying attention to the coverage limits, deductibles, and any exclusions. Understand the specific terms and conditions of each policy to ensure it meets your needs.
- Consider discounts and additional features: Many insurers offer discounts for safe driving, bundling policies, or having safety features in your vehicle. Explore these options to potentially lower your premiums.
Choosing a Reputable Insurance Provider
Selecting a reputable insurance provider is crucial for ensuring reliable coverage and efficient claims handling.
- Research company ratings: Consult independent rating agencies like AM Best or J.D. Power to assess an insurer’s financial stability and customer satisfaction.
- Read customer reviews: Online reviews from other policyholders can provide insights into an insurer’s reputation for claims handling, customer service, and overall experience.
- Check for licensing and certifications: Ensure the insurance company is licensed and certified to operate in your state.
- Consider company size and resources: Larger insurance companies may offer greater financial stability and resources for handling claims, while smaller companies might provide more personalized service.
Comparing Quotes from Multiple Insurance Companies
Comparing quotes from multiple insurance companies is a fundamental step in securing the best possible car insurance.
- Use online comparison tools: Several websites and apps allow you to enter your information once and receive quotes from multiple insurers simultaneously. This streamlines the comparison process and saves time.
- Contact insurers directly: Reach out to insurers directly to discuss your specific needs and obtain personalized quotes.
- Don’t just focus on price: While price is a significant factor, consider the coverage offered, the insurer’s reputation, and customer service when making your decision.
- Negotiate: Once you’ve chosen a policy, don’t hesitate to negotiate with the insurer to potentially lower your premium or add desired coverage.
Understanding Insurance Policies

Your car insurance policy is a legally binding contract that Artikels the terms and conditions of your coverage. Understanding its key elements is crucial for ensuring you have the right protection and can navigate potential claims smoothly.
Coverage Limits
Coverage limits define the maximum amount your insurer will pay for specific types of losses. These limits are usually stated in dollar amounts and can vary based on the type of coverage and your chosen policy. For example, your liability coverage might have a limit of $100,000 per person and $300,000 per accident. Understanding these limits is vital to ensure you have sufficient protection in case of a major accident.
Deductibles
A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. It’s a fixed amount that you’re responsible for, regardless of the total cost of the claim. For example, if your deductible is $500 and your car repairs cost $2,000, you’ll pay the first $500 and your insurer will cover the remaining $1,500. Choosing a higher deductible can often lead to lower premiums, but you’ll have to pay more upfront in case of a claim.
Exclusions
Exclusions are specific events or circumstances that are not covered by your policy. These can include things like intentional acts, wear and tear, or damage caused by certain natural disasters. It’s essential to carefully review your policy to understand what’s not covered, as this can help you avoid surprises during a claim.
Common Policy Terms and Conditions
Your car insurance policy will include various terms and conditions that define the scope of your coverage and your responsibilities as the policyholder. Some common examples include:
- Named Insured: This refers to the person or entity named on the policy who is primarily covered by the insurance.
- Covered Vehicles: This lists the specific vehicles covered under the policy, including their make, model, and year.
- Premium Payment Schedule: This Artikels the payment frequency and amount you are required to pay for your coverage.
- Cancellation and Non-Renewal: This section explains the conditions under which your policy can be canceled or not renewed.
- Claims Procedures: This details the steps you need to take to file a claim and the required documentation.
Importance of Reading and Understanding Your Policy
Reading and understanding your car insurance policy is crucial for several reasons:
- Knowing Your Coverage: This ensures you are aware of the specific types of coverage you have and their limits.
- Avoiding Surprises: It helps you understand what is and is not covered by your policy, preventing unexpected expenses.
- Making Informed Decisions: Understanding your policy can help you make informed decisions about your coverage, such as whether to increase your limits or change your deductible.
- Protecting Your Rights: Familiarizing yourself with your policy ensures you understand your rights and obligations during a claim.
Remember: If you have any questions about your policy, don’t hesitate to contact your insurance agent or company representative for clarification.
Filing a Claim
Filing a car insurance claim is a necessary process when you’re involved in an accident or experience damage to your vehicle. Understanding the steps involved and the different types of claims can help you navigate this process smoothly and ensure you receive the appropriate compensation.
The Claim Filing Process
The process of filing a car insurance claim typically involves the following steps:
- Report the Accident: Contact your insurance company as soon as possible after the accident. Provide them with the necessary details, including the date, time, location, and any injuries involved.
- Gather Documentation: Collect all relevant documentation, such as police reports, witness statements, photos of the damage, and medical records if applicable. These documents will support your claim.
- File the Claim: Submit your claim to your insurance company, either online, over the phone, or in person. You’ll need to provide information about the accident and the damage to your vehicle.
- Insurance Company Investigation: Your insurance company will investigate the claim to verify the details and determine the extent of the damage. This may involve an inspection of your vehicle.
- Negotiate a Settlement: Once the investigation is complete, your insurance company will offer a settlement amount. You can negotiate this amount if you believe it’s insufficient.
- Receive Payment: If you agree to the settlement, you’ll receive payment for the damage to your vehicle or for your medical expenses.
Types of Car Insurance Claims
There are several types of car insurance claims, each covering different types of damage or losses:
- Collision Claims: These claims cover damage to your vehicle resulting from a collision with another vehicle or object. This type of coverage is usually required by law in most states.
- Comprehensive Claims: This coverage protects you against damage to your vehicle caused by events other than collisions, such as theft, vandalism, fire, or natural disasters.
- Liability Claims: This coverage pays for damages or injuries you cause to other people or their property in an accident. It’s important to have liability coverage to protect yourself from financial ruin in case of an accident.
Tips for Maximizing Your Chances of a Successful Claim
Here are some tips to improve your chances of a successful claim:
- Report the Accident Promptly: Contact your insurance company as soon as possible after the accident. This will help ensure you receive timely assistance and avoid any delays in the claim process.
- Gather Evidence: Collect all relevant documentation and evidence, such as photos, witness statements, and police reports. This will help support your claim and demonstrate the extent of the damage.
- Be Honest and Accurate: Provide your insurance company with honest and accurate information about the accident. Any discrepancies or inaccuracies can delay or even jeopardize your claim.
- Cooperate with the Insurance Company: Be responsive to your insurance company’s requests for information and cooperate with their investigation. This will help expedite the claim process.
- Consult with a Lawyer: If you’re unsure about your rights or if you have a complex claim, consider consulting with an experienced car accident lawyer. They can help you navigate the legal complexities and ensure you receive fair compensation.
Maintaining Coverage

Maintaining continuous car insurance coverage is crucial for several reasons. It ensures you are financially protected in case of an accident or other covered event. Furthermore, it can save you money in the long run and prevent potential legal complications.
Consequences of Lapsed Coverage
Letting your car insurance lapse can have serious consequences.
- Financial Risk: You will be personally liable for any damages or injuries caused in an accident, even if you are not at fault. This could result in significant financial losses, including medical bills, property damage, and legal fees.
- Legal Penalties: Many states impose fines and penalties for driving without insurance. These penalties can vary depending on the state and the number of offenses.
- Increased Insurance Rates: Once you reinstate your coverage, you may face higher premiums because of the lapse in coverage. Insurance companies view lapses as a sign of increased risk and may charge higher rates to compensate for the potential losses.
- Difficulty Obtaining Coverage: If you let your coverage lapse for an extended period, you may find it challenging to obtain insurance again. Some insurance companies may be hesitant to provide coverage to drivers with a history of lapses.
Managing Your Insurance Policy
Here are some tips to ensure your car insurance coverage remains active:
- Set Reminders: Set reminders on your calendar or use a mobile app to alert you about upcoming renewal dates. This will help you avoid unintentional lapses.
- Pay Premiums on Time: Make sure you pay your insurance premiums on time to avoid cancellation. You can set up automatic payments to ensure that your premiums are paid without any delays.
- Review Your Policy Regularly: Periodically review your policy to ensure it still meets your needs and that you are not paying for coverage you no longer require. You may also find opportunities to reduce your premiums by adjusting your coverage or making changes to your driving habits.
- Communicate with Your Insurer: If you experience any changes in your circumstances, such as a change in address, a new driver in your household, or a new car, inform your insurance company immediately. Failing to update your policy could lead to coverage gaps.
End of Discussion: Do All States Require Car Insurance
In conclusion, car insurance plays a vital role in protecting drivers and their finances. While most states require it, understanding the nuances of coverage, factors affecting premiums, and the process of obtaining insurance is essential. By navigating these aspects, drivers can ensure they have adequate protection on the road.
Essential Questionnaire
What happens if I get into an accident without car insurance?
Driving without insurance can lead to severe consequences, including fines, license suspension, and even jail time. In addition, you will be responsible for all costs associated with the accident, including repairs, medical bills, and legal fees.
How can I find the best car insurance rates?
To find the best rates, compare quotes from multiple insurance companies. Consider factors like your driving history, vehicle type, location, and credit score. You can use online comparison tools or contact insurance brokers for assistance.
What is the difference between liability and collision coverage?
Liability coverage protects you from financial responsibility if you cause an accident, while collision coverage covers damages to your own vehicle in an accident, regardless of fault.