Do all states require auto insurance? The answer, surprisingly, is no. While most states mandate auto insurance, a few exceptions exist, primarily for vehicles considered antique or those used solely on private property. This article delves into the nuances of auto insurance requirements, exploring the reasons behind them, the potential consequences of driving without insurance, and the various types of coverage available.
Understanding the complexities of auto insurance is crucial for responsible drivers. Whether you’re a seasoned motorist or a new driver, knowing the laws and regulations surrounding auto insurance can help you navigate the roads safely and avoid potential legal and financial pitfalls. This guide will provide valuable insights into the world of auto insurance, helping you make informed decisions and protect yourself on the road.
The Importance of Auto Insurance
Auto insurance is a crucial aspect of responsible driving, offering financial protection and legal safeguards in case of accidents, property damage, or injuries. It’s a legal requirement in most states, ensuring that drivers are held accountable for potential damages they may cause.
Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without insurance can lead to significant financial and legal consequences.
- Financial Penalties: Most states impose hefty fines on uninsured drivers, ranging from hundreds to thousands of dollars. These fines can significantly impact your finances, especially if you’re already facing financial difficulties.
- License Suspension: Driving without insurance can result in the suspension of your driver’s license, preventing you from driving legally. This can be a major inconvenience, impacting your ability to commute, work, or attend essential appointments.
- Vehicle Impoundment: Your vehicle could be impounded if you’re caught driving without insurance. This can be a costly inconvenience, requiring additional fees to retrieve your vehicle.
- Legal Repercussions: In the event of an accident, driving without insurance can lead to legal issues, potentially including lawsuits and criminal charges. This can result in substantial legal fees and even jail time, depending on the severity of the accident and the state laws.
Situations Where Auto Insurance is Crucial
Auto insurance is essential for protecting yourself and others from financial hardship in various situations:
- Accidents: If you’re involved in an accident, auto insurance covers damages to your vehicle and the other party’s vehicle, as well as medical expenses for yourself and any passengers. Without insurance, you’ll be responsible for all costs associated with the accident, which can be substantial, especially in cases of serious injuries or extensive property damage.
- Property Damage: If you’re responsible for damaging another person’s property, such as a fence, building, or parked vehicle, auto insurance will cover the costs of repair or replacement. Without insurance, you’ll be liable for the full cost of repairs, which can be significant, especially in cases of extensive damage.
- Medical Expenses: In the event of an accident resulting in injuries, auto insurance will cover your medical expenses, including hospital bills, doctor’s visits, and rehabilitation costs. Without insurance, you’ll be responsible for all medical bills, which can be overwhelming, especially in cases of serious injuries.
States That Require Auto Insurance
Every state in the United States requires drivers to have some form of auto insurance. This is to protect drivers and their passengers from financial losses in the event of an accident. The minimum insurance requirements vary from state to state.
Minimum Insurance Requirements
The minimum insurance requirements for each state are Artikeld in the table below. The table includes the minimum liability coverage, property damage coverage, and uninsured motorist coverage.
| State | Minimum Liability Coverage | Minimum Property Damage Coverage | Minimum Uninsured Motorist Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Alaska | $50,000 per person/$100,000 per accident | $25,000 | $50,000 per person/$100,000 per accident |
| Arizona | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $15,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Arkansas | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| California | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident | $5,000 | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident |
| Colorado | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $15,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Connecticut | $20,000 per person/$40,000 per accident | $10,000 | $20,000 per person/$40,000 per accident |
| Delaware | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident | $10,000 | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident |
| Florida | $10,000 per person/$20,000 per accident | $10,000 | $10,000 per person/$20,000 per accident |
| Georgia | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Hawaii | $20,000 per person/$40,000 per accident | $10,000 | $20,000 per person/$40,000 per accident |
| Idaho | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Illinois | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $20,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Indiana | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Iowa | $20,000 per person/$40,000 per accident | $10,000 | $20,000 per person/$40,000 per accident |
| Kansas | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Kentucky | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Louisiana | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident | $10,000 | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident |
| Maine | $50,000 per person/$100,000 per accident | $25,000 | $50,000 per person/$100,000 per accident |
| Maryland | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident | $15,000 | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident |
| Massachusetts | $20,000 per person/$40,000 per accident | $5,000 | $20,000 per person/$40,000 per accident |
| Michigan | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Minnesota | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident | $10,000 | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident |
| Mississippi | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Missouri | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Montana | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Nebraska | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Nevada | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $15,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| New Hampshire | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| New Jersey | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident | $5,000 | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident |
| New Mexico | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| New York | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| North Carolina | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident | $25,000 | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident |
| North Dakota | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Ohio | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Oklahoma | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Oregon | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $20,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Pennsylvania | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident | $5,000 | $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident |
| Rhode Island | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| South Carolina | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| South Dakota | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Tennessee | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $15,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Texas | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident | $25,000 | $30,000 per person/$60,000 per accident |
| Utah | $25,000 per person/$65,000 per accident | $15,000 | $25,000 per person/$65,000 per accident |
| Vermont | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Virginia | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $20,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Washington | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| West Virginia | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Wisconsin | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $10,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
| Wyoming | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident |
Exceptions to Auto Insurance Requirements: Do All States Require Auto Insurance
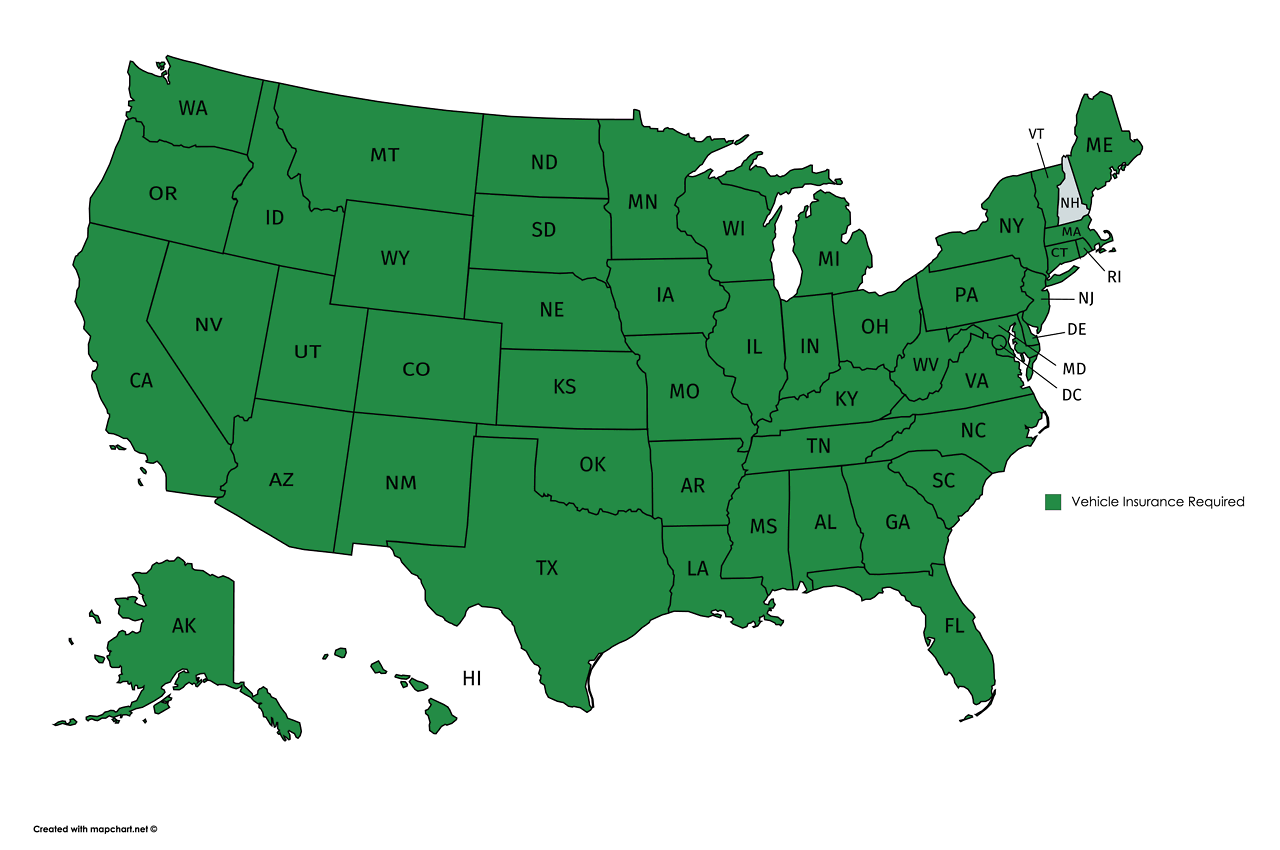
While most states mandate auto insurance, certain situations exempt individuals from this requirement. These exceptions often pertain to vehicles that are not typically used on public roads or are considered less of a risk.
Vehicles Exempt from Insurance Requirements
- Antique Vehicles: Many states exempt antique vehicles from insurance requirements if they are used solely for display purposes or for occasional trips to car shows or rallies. These vehicles are often defined as being at least 25 years old and in original condition, but the specific requirements can vary by state.
- Vehicles Used Solely on Private Property: Vehicles that are only used on private property, such as a farm or a closed course, may be exempt from insurance requirements. However, it’s crucial to check with your state’s regulations, as these exemptions may be limited to specific types of vehicles or activities.
- Vehicles Used for Specific Purposes: Certain vehicles used for specific purposes, such as construction equipment or farm machinery, may be exempt from insurance requirements. These exemptions often apply when the vehicles are not driven on public roads.
Potential Risks of Driving Without Insurance
It’s essential to understand that even if a vehicle is exempt from insurance requirements, driving without insurance can still pose significant risks.
- Financial Liability: In the event of an accident, even if the vehicle is exempt from insurance requirements, the driver could be held financially responsible for damages to other vehicles or injuries to other individuals.
- Legal Consequences: Driving without insurance can lead to legal consequences, including fines, license suspension, and even jail time, depending on the state and the circumstances.
- Increased Costs: If you are involved in an accident without insurance, you could face higher costs for repairs, medical bills, and legal fees.
Types of Auto Insurance Coverage
Auto insurance policies are designed to protect you financially in the event of an accident or other incident involving your vehicle. They offer various coverage options that can be tailored to your specific needs and circumstances.
Types of Auto Insurance Coverage
The different types of auto insurance coverage provide protection for various situations, from liability to damage to your vehicle.
| Coverage Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Liability Coverage | Liability coverage protects you financially if you are at fault in an accident that causes injury or damage to others. It covers the costs of medical expenses, property damage, and legal fees for the other party involved.
Liability coverage is typically divided into two parts: – Bodily injury liability: This covers medical expenses, lost wages, and pain and suffering for injuries caused to others. – Property damage liability: This covers damages to another person’s property, such as their vehicle or other possessions. |
| Collision Coverage | Collision coverage pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle if it is damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. This coverage is optional, but it is essential if you want to protect yourself financially in the event of an accident that damages your own vehicle. |
| Comprehensive Coverage | Comprehensive coverage protects your vehicle against damage from events other than accidents, such as theft, vandalism, fire, hail, and natural disasters. This coverage is also optional, but it is essential if you want to protect yourself financially against unexpected events that could damage your vehicle. |
| Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage | Uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage protects you if you are injured in an accident caused by a driver who is uninsured or underinsured. This coverage pays for your medical expenses, lost wages, and pain and suffering, even if the other driver is at fault and cannot afford to cover your losses. |
Factors Influencing Auto Insurance Rates
Auto insurance premiums are calculated based on various factors that assess the risk of an insured driver. These factors can significantly influence the cost of your insurance, making it crucial to understand how they work and how you can potentially lower your rates.
Driving History
Your driving history plays a significant role in determining your insurance premiums. A clean driving record with no accidents, violations, or claims will generally result in lower rates. Conversely, a history of accidents, speeding tickets, or DUI convictions will increase your risk profile, leading to higher premiums. Insurance companies use a system called a “risk score” to evaluate your driving history and assign a premium based on your risk level.
Age
Age is another significant factor in auto insurance rates. Younger drivers, particularly those under 25, are statistically more likely to be involved in accidents. This increased risk is reflected in higher insurance premiums. As drivers gain experience and age, their risk profile decreases, resulting in lower rates. However, older drivers, especially those over 75, may also face higher premiums due to potential health issues or reduced reaction times.
Location
The location where you live can significantly impact your auto insurance rates. Insurance companies consider factors such as population density, traffic congestion, crime rates, and the prevalence of accidents in specific areas. Urban areas with heavy traffic and high crime rates tend to have higher insurance premiums compared to rural areas with lower population densities and fewer accidents.
Vehicle Type
The type of vehicle you drive is also a crucial factor in determining your insurance premiums. Luxury vehicles, sports cars, and high-performance vehicles are often more expensive to repair and replace, leading to higher insurance costs. Conversely, smaller, less expensive vehicles tend to have lower insurance rates. Additionally, vehicles with advanced safety features, such as anti-lock brakes, airbags, and stability control, may qualify for discounts, lowering your overall premiums.
Credit Score
While it may seem surprising, your credit score can also affect your auto insurance rates. Insurance companies often use credit scores as an indicator of financial responsibility. Individuals with good credit scores are statistically less likely to file claims or default on payments, making them less risky to insure. Conversely, individuals with poor credit scores may face higher premiums.
Tips for Obtaining Lower Insurance Rates
- Maintain a Clean Driving Record: Avoid accidents, traffic violations, and DUI convictions to keep your premiums low.
- Shop Around for Quotes: Compare quotes from multiple insurance companies to find the best rates.
- Consider Bundling Policies: Combining your auto insurance with other policies, such as homeowners or renters insurance, can often lead to discounts.
- Increase Your Deductible: A higher deductible means you pay more out-of-pocket in case of an accident but can result in lower premiums.
- Ask About Discounts: Many insurance companies offer discounts for good students, safe drivers, and vehicles with safety features.
- Improve Your Credit Score: Pay your bills on time and manage your debt to improve your credit score and potentially lower your insurance premiums.
Consequences of Driving Without Insurance

Driving without insurance is a risky decision that can lead to severe financial and legal consequences. Not only is it illegal in most states, but it can also leave you vulnerable to significant financial burdens if you are involved in an accident.
Financial Penalties
The financial penalties for driving without insurance can vary depending on the state, but they can be substantial. In addition to fines, drivers without insurance may also face surcharges on their future insurance premiums. These surcharges can be significant and can make it difficult to obtain affordable insurance in the future.
Legal Consequences
Beyond financial penalties, driving without insurance can also result in serious legal consequences. These can include:
- License Suspension or Revocation: Many states will suspend or revoke the driver’s license of individuals who are caught driving without insurance. This can make it impossible to legally drive a vehicle until the license is reinstated.
- Imprisonment: In some states, driving without insurance can even lead to jail time, especially if the driver is involved in an accident that results in injuries or property damage.
Real-World Scenarios, Do all states require auto insurance
It is important to understand that driving without insurance can have devastating consequences. Consider these real-world scenarios:
“A driver without insurance was involved in an accident that resulted in significant property damage and injuries to the other driver. The uninsured driver was found liable for the accident and was ordered to pay tens of thousands of dollars in damages. Without insurance, the driver was unable to afford the legal fees and settlements, leading to financial ruin.”
“A driver without insurance was pulled over for a traffic violation. Upon discovering that the driver did not have insurance, the police officer issued a citation and suspended the driver’s license. The driver was unable to drive for several months, causing significant inconvenience and financial hardship.”
Last Word
Navigating the world of auto insurance can seem daunting, but understanding the basics is essential for responsible driving. Remember, while some states may have exceptions, most require auto insurance, emphasizing its importance for both personal and financial protection. By understanding the different types of coverage, the factors influencing premiums, and the potential consequences of driving without insurance, you can make informed decisions to ensure safe and responsible driving.
FAQ Guide
How much does auto insurance typically cost?
Auto insurance costs vary widely depending on factors like your driving history, age, location, vehicle type, and credit score. It’s best to get quotes from multiple insurers to compare prices.
What happens if I get into an accident without insurance?
Driving without insurance in a state that requires it can result in hefty fines, license suspension, and even jail time. You’ll also be responsible for covering all accident-related costs, including medical bills and property damage.
Can I get a discount on my auto insurance?
Yes, many insurers offer discounts for safe driving, good grades, multiple policies, and other factors. Be sure to ask about available discounts when you’re getting a quote.
What is uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage?
This coverage protects you if you’re involved in an accident with a driver who has no insurance or insufficient coverage. It helps cover your medical expenses and property damage.