Compare auto insurance by state and discover how rates vary across the country. Your location plays a significant role in determining your insurance premiums, influenced by factors like state laws, demographics, and even your driving habits. Understanding these differences can help you find the best coverage at the most affordable price.
Auto insurance premiums are influenced by a complex interplay of factors. State laws and regulations, such as minimum coverage requirements and no-fault laws, directly impact insurance costs. Additionally, demographics like population density and driving habits contribute to variations in premiums. For example, states with high population density may have higher insurance rates due to increased traffic congestion and the likelihood of accidents.
Understanding Auto Insurance Variations Across States
Auto insurance premiums can vary significantly from state to state, and understanding the factors that contribute to these differences is crucial for finding the best coverage at the most affordable price.
State Laws and Regulations
State laws and regulations play a significant role in shaping auto insurance costs. These regulations dictate minimum coverage requirements, no-fault laws, and other factors that directly impact insurance premiums.
- Minimum Coverage Requirements: States have varying minimum coverage requirements for liability, personal injury protection (PIP), and uninsured/underinsured motorist (UM/UIM) coverage. States with higher minimum coverage requirements generally have higher average insurance premiums because drivers are required to carry more insurance. For example, states with higher minimum liability coverage limits often have higher average premiums, as drivers are required to carry more insurance to cover potential damages in accidents.
- No-Fault Laws: No-fault laws determine how accident claims are handled. In no-fault states, drivers are required to file claims with their own insurance company, regardless of who caused the accident. This can reduce the number of lawsuits and lower insurance costs. However, no-fault states may have higher premiums for PIP coverage, as drivers are required to carry more insurance to cover their own medical expenses.
Demographics and Driving Habits
Demographics and driving habits also influence auto insurance rates. States with higher population density, more congested roads, and higher rates of accidents tend to have higher average premiums.
- Population Density: States with higher population density, such as New York and California, tend to have higher average insurance premiums. This is because more cars on the road increase the risk of accidents.
- Driving Habits: States with higher rates of accidents, such as Florida and Texas, often have higher average premiums. This is due to factors such as driving habits, weather conditions, and road infrastructure.
Key Factors Affecting Auto Insurance Costs
Auto insurance premiums are influenced by a multitude of factors, and these factors can vary significantly from state to state. Understanding these factors is crucial for consumers to make informed decisions and secure the most suitable coverage at a competitive price.
Vehicle Type
The type of vehicle you drive plays a significant role in determining your auto insurance premium. This is because different vehicles are associated with varying risks of accidents, repairs, and theft.
- Luxury or High-Performance Vehicles: These vehicles are often more expensive to repair or replace, leading to higher insurance premiums.
- Older Vehicles: Older vehicles may have a higher risk of mechanical failures and may be less safe in accidents, which can result in increased insurance costs.
- Sports Utility Vehicles (SUVs): SUVs generally have higher insurance premiums compared to sedans due to their size, weight, and increased risk of rollover accidents.
Driving History
Your driving record is a critical factor in determining your insurance rates. Insurance companies carefully evaluate your driving history to assess your risk of future accidents.
- Accidents: Having a history of accidents, particularly at-fault accidents, will significantly increase your insurance premiums.
- Traffic Violations: Speeding tickets, DUI convictions, and other traffic violations can also lead to higher insurance rates.
- Clean Driving Record: Maintaining a clean driving record with no accidents or violations can result in lower insurance premiums and discounts.
Age
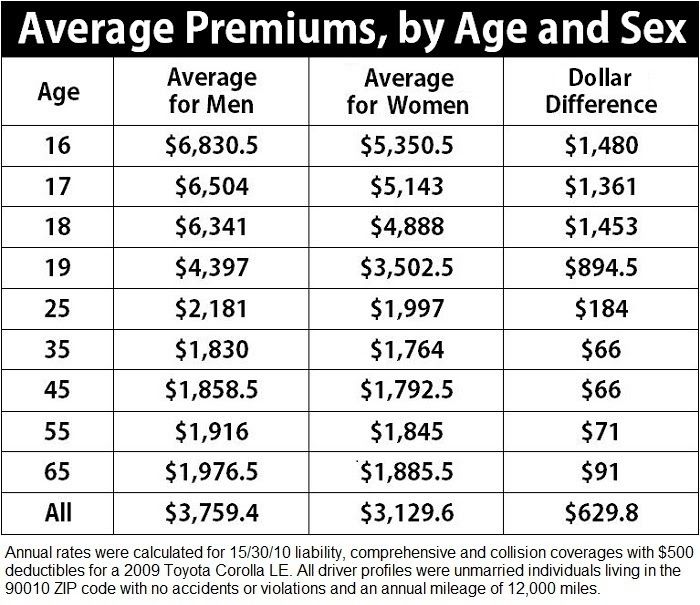
Age is a significant factor in determining auto insurance rates, as younger and older drivers are statistically associated with higher risk.
- Young Drivers: Young drivers, especially those under 25, are often considered higher risk due to their lack of experience and tendency to engage in riskier driving behaviors.
- Older Drivers: Older drivers, particularly those over 70, may also face higher premiums due to potential health issues or reduced reaction times.
- Experienced Drivers: Drivers in their mid-30s to mid-50s often have lower insurance rates due to their years of experience and generally safer driving habits.
Credit Score
While not universally applicable, some states allow insurance companies to consider your credit score as a factor in determining your auto insurance rates. The rationale behind this practice is that individuals with good credit scores are often seen as more responsible and financially stable, which may translate to a lower risk of insurance claims.
- Good Credit Score: A good credit score can potentially lead to lower insurance premiums in states that allow this practice.
- Poor Credit Score: A poor credit score may result in higher insurance premiums in states where this practice is permitted.
Other Factors
Several other factors can also influence your auto insurance premiums, including:
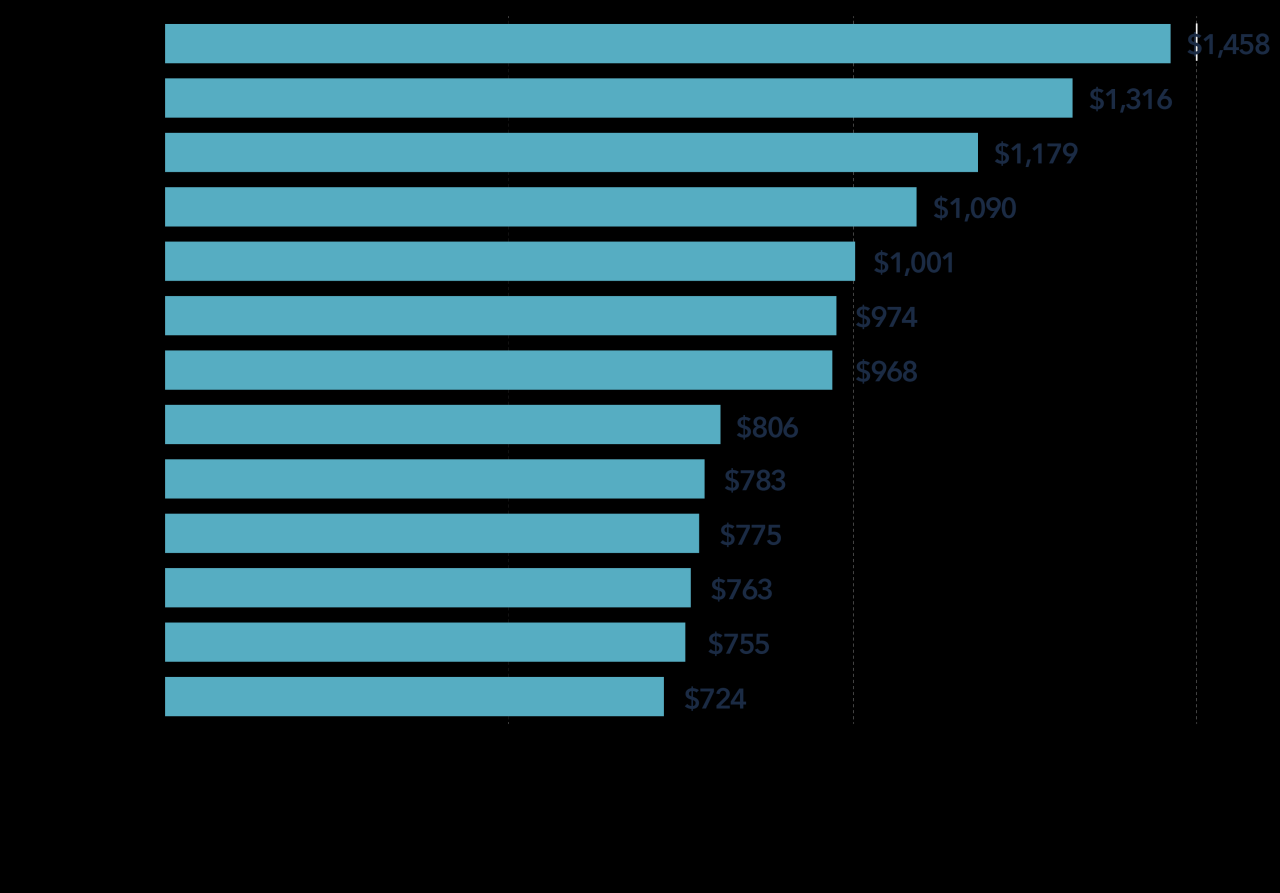
- Location: Insurance rates can vary significantly based on your location due to factors such as traffic density, crime rates, and the cost of repairs.
- Coverage Levels: The type and amount of coverage you choose, such as liability limits, collision coverage, and comprehensive coverage, will directly affect your premium.
- Deductible: A higher deductible (the amount you pay out of pocket before your insurance kicks in) generally results in lower premiums.
- Safety Features: Vehicles equipped with safety features such as anti-lock brakes, airbags, and stability control may qualify for discounts.
Impact of Factors
The impact of these factors on your insurance premiums can vary depending on your specific circumstances and the insurance company. For instance, a young driver with a poor driving record living in a high-risk area will likely face significantly higher premiums compared to an experienced driver with a clean record living in a low-risk area.
| Factor | Impact on Premium | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Vehicle Type | Higher for luxury or high-performance vehicles | A new Tesla Model S may have a higher premium than a used Honda Civic. |
| Driving History | Higher for accidents and traffic violations | A driver with two at-fault accidents may pay more than a driver with a clean record. |
| Age | Higher for young and older drivers | A 20-year-old driver may pay more than a 40-year-old driver. |
| Credit Score | Higher for poor credit score (in states that allow it) | A driver with a credit score of 500 may pay more than a driver with a score of 750. |
| Location | Higher in high-risk areas | A driver in New York City may pay more than a driver in a rural area. |
State-Specific Auto Insurance Requirements
Each state has its own unique set of auto insurance requirements, which can vary significantly. These requirements are designed to ensure that drivers have sufficient financial protection in case of an accident.
Minimum Auto Insurance Coverage Requirements
Understanding the minimum auto insurance requirements in each state is crucial for drivers. These requirements dictate the minimum levels of coverage that drivers must maintain to legally operate a vehicle.
| State | Liability Coverage | Collision Coverage | Comprehensive Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 25/50/25 | Optional | Optional |
| Alaska | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Arizona | 15/30/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Arkansas | 25/50/25 | Optional | Optional |
| California | 15/30/5 | Optional | Optional |
| Colorado | 25/50/15 | Optional | Optional |
| Connecticut | 20/40/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Delaware | 30/60/20 | Optional | Optional |
| Florida | 10/20/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Georgia | 25/50/25 | Optional | Optional |
| Hawaii | 20/40/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Idaho | 25/50/15 | Optional | Optional |
| Illinois | 20/40/15 | Optional | Optional |
| Indiana | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Iowa | 20/40/15 | Optional | Optional |
| Kansas | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Kentucky | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Louisiana | 10/20/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Maine | 50/100/25 | Optional | Optional |
| Maryland | 30/60/15 | Optional | Optional |
| Massachusetts | 20/40/5 | Optional | Optional |
| Michigan | 20/40/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Minnesota | 30/60/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Mississippi | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Missouri | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Montana | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Nebraska | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Nevada | 15/30/10 | Optional | Optional |
| New Hampshire | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| New Jersey | 15/30/5 | Optional | Optional |
| New Mexico | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| New York | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| North Carolina | 30/60/25 | Optional | Optional |
| North Dakota | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Ohio | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Oklahoma | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Oregon | 25/50/20 | Optional | Optional |
| Pennsylvania | 15/30/5 | Optional | Optional |
| Rhode Island | 25/50/25 | Optional | Optional |
| South Carolina | 25/50/25 | Optional | Optional |
| South Dakota | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Tennessee | 25/50/15 | Optional | Optional |
| Texas | 30/60/25 | Optional | Optional |
| Utah | 25/65/15 | Optional | Optional |
| Vermont | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Virginia | 25/50/20 | Optional | Optional |
| Washington | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| West Virginia | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Wisconsin | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
| Wyoming | 25/50/10 | Optional | Optional |
Financial Responsibility Laws and Penalties
States have financial responsibility laws that require drivers to demonstrate their ability to pay for damages caused in an accident. These laws often include penalties for driving without insurance.
- Penalties: Penalties for driving without insurance can vary significantly from state to state. They can include fines, license suspension, and even jail time.
- Financial Responsibility Proof: States typically require drivers to provide proof of financial responsibility, which can be in the form of auto insurance or a surety bond. This proof demonstrates that the driver has the means to cover potential damages.
- Exceptions: Some states may have exceptions to their financial responsibility laws, such as for drivers who have a valid reason for not having insurance. However, it is crucial to be aware of the specific requirements and exceptions in each state.
Tips for Finding Affordable Auto Insurance

Finding the right auto insurance policy can be a challenge, especially when you’re trying to balance affordability with coverage. But with some smart strategies, you can find a policy that fits your budget and protects you on the road.
Shopping Around and Comparing Quotes, Compare auto insurance by state
Comparing quotes from multiple insurance providers is crucial for securing the best deal.
- Use online comparison tools: Websites like Policygenius, NerdWallet, and Insurance.com allow you to enter your information once and receive quotes from multiple insurers, saving you time and effort.
- Contact insurers directly: Don’t hesitate to reach out to insurers directly to discuss your specific needs and obtain personalized quotes. Some insurers may offer discounts or special promotions that aren’t available through online comparison tools.
- Consider local insurers: Local insurance companies may offer competitive rates and personalized service, especially if you’re looking for a smaller, more community-oriented insurer.
Leveraging Discounts
Many insurance companies offer discounts to policyholders who meet certain criteria.
- Safe driving record: A clean driving record with no accidents or violations can significantly lower your premiums.
- Good credit score: Insurance companies often use credit scores as a proxy for risk assessment. Maintaining a good credit score can lead to lower insurance rates.
- Bundling policies: Combining your auto insurance with other policies, such as homeowners or renters insurance, can result in substantial savings.
- Other discounts: Some insurers offer discounts for things like completing a defensive driving course, being a good student, or having anti-theft devices installed in your vehicle. Be sure to inquire about all available discounts.
State-Specific Auto Insurance Resources
Navigating the complexities of auto insurance can be challenging, especially when factoring in state-specific regulations and requirements. Fortunately, each state provides a range of resources and websites to help individuals understand their auto insurance obligations, find affordable coverage, and resolve any disputes.
State Insurance Departments
State insurance departments serve as primary sources of information and guidance for auto insurance matters. They regulate insurance companies operating within their respective states, ensuring compliance with consumer protection laws.
Consumer Protection Organizations
Consumer protection organizations play a vital role in advocating for the rights of insurance consumers. They provide resources, information, and assistance to individuals facing issues with their insurance policies or claims.
- National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC): The NAIC is a non-profit organization representing insurance commissioners from all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and five U.S. territories. It develops model laws and regulations for the insurance industry, promotes uniformity in insurance regulation, and advocates for consumer protection. https://www.naic.org/
- Consumer Federation of America (CFA): The CFA is a non-profit consumer advocacy group that advocates for consumer protection in various sectors, including insurance. It provides information and resources on insurance issues and works to ensure fair and transparent insurance practices. https://www.consumerfed.org/
- National Consumer Law Center (NCLC): The NCLC is a non-profit organization that advocates for consumer rights and provides legal assistance to low-income consumers. It publishes resources and guides on insurance issues, including auto insurance, and provides legal representation to consumers facing insurance disputes. https://www.nclc.org/
Final Wrap-Up: Compare Auto Insurance By State
By understanding the factors that influence auto insurance rates and taking advantage of available resources, you can navigate the complexities of finding affordable coverage. Remember to shop around, compare quotes, and leverage discounts to secure the best possible rates. With careful research and comparison, you can find the right auto insurance policy that meets your needs and budget.
Detailed FAQs
How often should I review my auto insurance rates?
It’s generally recommended to review your auto insurance rates annually, or even more frequently if you experience significant life changes, such as a move, a new car, or a change in your driving record.
What are some common discounts available for auto insurance?
Common discounts include safe driver discounts, good student discounts, multi-car discounts, and bundling discounts for combining auto and home insurance.
What are the consequences of driving without insurance?
Driving without insurance can result in hefty fines, license suspension, and even jail time in some states. It’s crucial to maintain adequate insurance coverage to protect yourself financially in case of an accident.







