Change state insurance, a critical aspect of moving to a new state, involves ensuring your existing insurance policies remain valid and adequate in your new location. Whether it’s auto, health, or homeowners insurance, understanding the nuances of state-specific regulations and coverage is crucial for a smooth transition.
This process encompasses notifying your insurance providers, understanding potential changes to coverage and premiums, and navigating the complexities of state-specific laws and regulations. It’s essential to be proactive and well-informed to avoid gaps in coverage or unexpected financial burdens.
Understanding Change of State Insurance
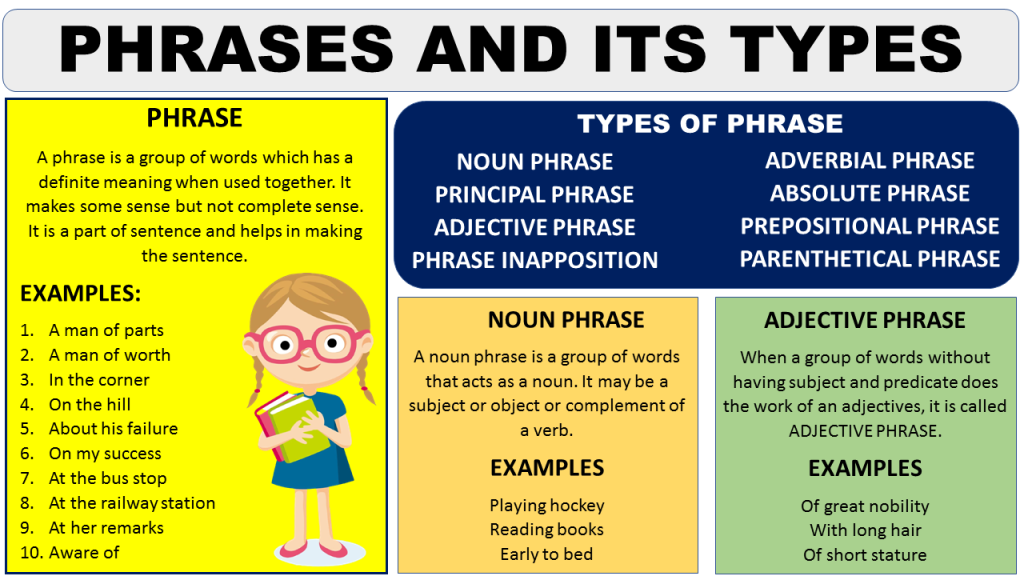
Moving to a new state can be an exciting adventure, but it also comes with some practical considerations, including insurance. Change of state insurance refers to the process of updating your insurance policies when you relocate to a new state. This is essential because insurance regulations and coverage vary from state to state.
Types of Insurance Policies Affected by Change of State
Many types of insurance policies are affected by a change of state. The most common ones include:
- Auto Insurance: State laws regarding minimum coverage requirements, fault systems (no-fault vs. at-fault), and other factors can significantly impact your auto insurance premiums and coverage. For example, some states have mandatory coverage for uninsured motorist protection, while others do not.
- Homeowners or Renters Insurance: Similar to auto insurance, homeowners and renters insurance policies are subject to state-specific regulations. These can include coverage for natural disasters, personal property limits, and liability limits. For instance, in some states, earthquake coverage is mandatory, while in others, it is optional or not available at all.
- Health Insurance: While the Affordable Care Act (ACA) provides some national standards for health insurance, states can have their own regulations and programs. You may need to adjust your health insurance plan when you move to a new state, especially if you are enrolled in a state-specific program like Medicaid or the state health insurance marketplace.
- Life Insurance: Life insurance policies are typically governed by the state where the policyholder resides. If you move to a new state, your policy may need to be reviewed and updated to ensure it complies with the new state’s regulations. This could involve changes to the death benefit amount, beneficiary designations, or policy provisions.
Examples of Situations Involving Change of State Insurance
Here are some examples of situations where change of state insurance becomes relevant:
- Relocating for a Job: When you move for a new job, you may need to update your auto insurance policy to reflect your new address and driving commute. If you are moving to a state with different insurance regulations, you may need to make further adjustments to your coverage.
- Retirement: If you are retiring and moving to a new state, you may need to update your homeowners or renters insurance policy to reflect your new property and living situation. For instance, you may need to increase your coverage if you are moving to a state with higher property values or more frequent natural disasters.
- Family Expansion: If you are expanding your family by welcoming a new child, you may need to update your health insurance policy to ensure your child is covered. You may also need to adjust your auto insurance policy to account for the addition of a new driver to your household.
Legal Requirements and Regulations

Navigating the world of insurance across state lines requires understanding the legal framework governing change of state insurance. State insurance departments, with their own unique regulations, govern this process. These regulations are crucial to ensure consumer protection and maintain the integrity of the insurance market.
Notification Process
Notifying your insurance company about a change of state is a vital step in maintaining coverage. This process involves providing the insurer with your new address and other relevant information. Failure to notify the insurer could lead to coverage lapses, policy cancellations, or other complications.
- Contacting the Insurer: The first step involves contacting your insurance company. This can be done via phone, email, or through their online portal. You should inform them of your upcoming move and the date of your relocation.
- Providing Necessary Documentation: You may be required to provide documentation to verify your change of address, such as a driver’s license or utility bill.
- Policy Review: The insurer may review your existing policy to ensure it’s compatible with the laws of your new state. They may need to adjust your coverage or premium based on your new location.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failing to comply with change of state insurance regulations can have serious consequences, including:
- Coverage Lapses: If you fail to notify your insurer, your coverage may lapse, leaving you without protection in your new state. This could have severe financial implications if you experience an accident or other covered event.
- Policy Cancellation: Your insurer may cancel your policy if they are not informed of your move. This could lead to difficulty obtaining new insurance in your new state, especially if you have a history of claims.
- Legal Penalties: Depending on the state, you may face legal penalties for failing to comply with change of state insurance regulations. This could include fines or other sanctions.
Impact on Coverage and Premiums
Moving to a new state can significantly impact your insurance coverage and premiums. Insurance regulations, risk factors, and market competition vary widely across states, leading to substantial differences in policy offerings and costs.
Coverage Variations Across States
Understanding how insurance coverage can differ across states is crucial. For instance, auto insurance requirements vary significantly. Some states mandate specific coverage, such as personal injury protection (PIP) or uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage (UM/UIM), while others do not.
- Auto Insurance: States may have different minimum liability coverage requirements, including bodily injury liability, property damage liability, and uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage. Some states also mandate personal injury protection (PIP) coverage, which covers medical expenses and lost wages for the insured and passengers, regardless of fault.
- Health Insurance: The availability and cost of health insurance plans can vary greatly depending on the state. States may have different regulations regarding individual health insurance markets, such as the availability of plans through state-based marketplaces or the types of plans offered. States also have varying regulations regarding Medicaid eligibility and coverage.
- Homeowners Insurance: Coverage for natural disasters can differ significantly across states. For example, states prone to earthquakes or hurricanes may require specific coverage or have higher premiums for homeowners insurance.
Factors Influencing Insurance Rates, Change state insurance
Several factors contribute to the variation in insurance rates across states. These include:
- Cost of Living: States with higher costs of living, including healthcare, housing, and auto repair, generally have higher insurance premiums. This is because insurers need to account for these increased costs when calculating premiums.
- Risk Factors: The frequency and severity of accidents, natural disasters, and other risk factors can impact insurance rates. For example, states with high rates of car accidents or natural disasters may have higher auto insurance premiums.
- Competition: The level of competition in the insurance market can influence premiums. States with a large number of insurers may have more competitive pricing, while states with fewer insurers may have higher premiums.
- State Regulations: State regulations can also impact insurance rates. For example, some states may have regulations that require insurers to offer certain coverage or limit the factors they can consider when setting premiums.
Navigating the Change of State Process: Change State Insurance
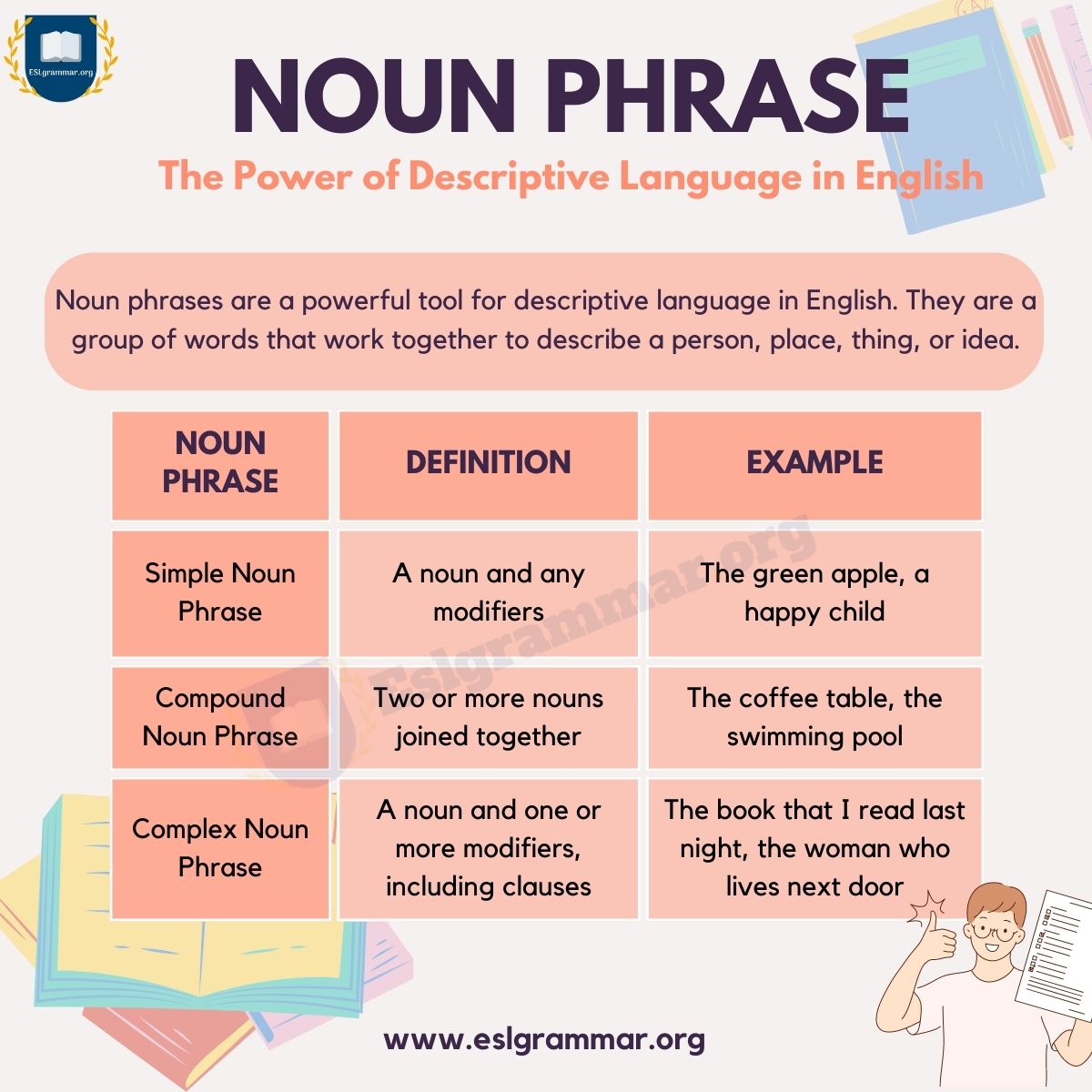
Moving to a new state can be an exciting experience, but it also involves navigating a variety of administrative tasks, including managing your insurance policies. Understanding the process of transferring your insurance coverage is crucial to ensure a smooth transition and avoid any potential disruptions in your protection.
Steps to Take When Changing States
It’s essential to start the process of updating your insurance policies as soon as you know you’re moving. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure a smooth transition:
- Notify Your Current Insurer: Inform your current insurance company about your move as soon as possible. This usually involves contacting them by phone or email and providing your new address and the date of your move.
- Check State Requirements: Each state has its own set of insurance regulations. It’s crucial to research the specific requirements for your new state to ensure your existing coverage meets the minimum standards. You can find this information on the state’s insurance department website or by consulting an insurance agent.
- Obtain New Insurance Quotes: Once you understand the insurance requirements in your new state, contact insurance companies in your new location to get quotes for coverage. This allows you to compare different options and choose the best plan for your needs.
- Consider New Coverage Options: Your new state may offer different types of insurance coverage, such as specific types of car insurance or additional health insurance options. It’s worth exploring these new options to ensure you have adequate protection.
- Finalize Your Policy: Once you’ve chosen a new insurance provider, complete the application process and finalize your policy. Make sure you understand the terms and conditions of the new policy before signing.
- Cancel Old Policy: After your new policy is in effect, cancel your old policy with your previous insurance company. Ensure you receive confirmation of cancellation and that there are no outstanding payments or obligations.
Case Studies and Examples
Understanding the practical implications of change of state insurance can be easier with real-world examples. This section will explore various scenarios where individuals and businesses have encountered change of state insurance situations, highlighting the challenges they faced and the solutions they implemented.
Individual Moving for Employment
Imagine Sarah, a young professional working in California, gets a dream job offer in New York. Excited about this new opportunity, she decides to relocate. However, Sarah realizes she needs to consider her auto insurance policy. As she moves to New York, her California-issued policy may no longer be valid. She faces the challenge of finding a new insurance policy that meets New York’s requirements while ensuring her coverage needs are met. Sarah’s situation highlights the importance of understanding the legal requirements and regulations of each state and how they can impact coverage and premiums.
Business Expanding Operations
A growing company, “Tech Solutions,” based in Texas, decides to open a new branch in Florida. This expansion requires them to obtain business insurance in Florida. The company must ensure their new policy meets the specific requirements for operating in Florida, including coverage for potential risks specific to the new location. They may also need to consider the impact of Florida’s regulations on their premiums. This case study illustrates how businesses need to adapt their insurance policies to accommodate their expanded operations and ensure they have adequate coverage in their new location.
Family Relocating for Retirement
John and Mary, a retired couple, decide to move from their home in Michigan to Arizona to enjoy the warmer climate. They need to consider their health insurance coverage, as Medicare plans vary by state. They may also need to update their auto and homeowners insurance policies to reflect their new location. This example demonstrates how change of state insurance considerations extend beyond employment or business operations and impact individuals in various life stages.
Last Word
Navigating change state insurance can seem daunting, but with careful planning and understanding, the process can be manageable. By proactively notifying your insurance providers, researching state-specific requirements, and comparing coverage options, you can ensure a seamless transition of your insurance policies and maintain the necessary protection in your new home.
FAQ
What happens to my insurance if I move to a different state?
Your existing insurance policies may not be valid in your new state. You’ll need to notify your insurance providers about your move and explore state-specific coverage options.
How do I find out about insurance requirements in my new state?
You can contact your state’s Department of Insurance or consult online resources to learn about specific insurance regulations and requirements.
Do I need to get new insurance when I move?
In most cases, you’ll need to obtain new insurance policies that meet the requirements of your new state. However, some insurance providers may offer coverage across multiple states.
How can I ensure a smooth transition of my insurance?
Notify your insurance providers well in advance of your move, research state-specific requirements, compare coverage options, and keep all relevant documentation organized.







