Car insurance state comparison is a crucial aspect of securing the right coverage at an affordable price. The cost of car insurance varies significantly across states due to factors like traffic density, accident rates, and state regulations. This guide will explore the key differences in car insurance across the United States, helping you navigate the complexities and find the best policy for your needs.
Understanding how these factors impact insurance rates in different states can empower you to make informed decisions about your coverage. We’ll delve into the nuances of mandatory coverage requirements, optional coverage options, and the factors that influence rates, such as your age, driving history, and the type of vehicle you drive. By comparing rates from different insurance companies and exploring state-specific resources, you can find the most suitable and cost-effective car insurance policy.
Understanding Car Insurance State Variations
Car insurance rates are not uniform across the United States. Many factors influence the cost of car insurance, and these factors can vary significantly from state to state. Understanding these variations is crucial for making informed decisions about your insurance coverage.
Factors Influencing State-Specific Car Insurance Rates
Several factors contribute to the differences in car insurance rates across states. These include:
- Cost of Living: States with higher costs of living, including medical expenses, tend to have higher insurance premiums. For example, the cost of repairing a car in a state with a high cost of living is likely to be higher than in a state with a lower cost of living.
- Traffic Density and Accident Rates: States with high traffic density and frequent accidents generally have higher insurance premiums. This is because insurance companies have to pay out more claims in these areas, leading to higher premiums to cover these costs.
- State Laws and Regulations: State laws and regulations can significantly impact insurance premiums. For example, states with mandatory minimum coverage requirements tend to have higher average premiums than states with lower minimum coverage requirements.
- Number of Insurance Companies: States with a limited number of insurance companies may have higher premiums due to less competition. When there are fewer insurance companies, they can potentially charge higher rates because consumers have fewer options.
Key Differences in Insurance Regulations
State regulations play a significant role in determining car insurance rates. Here are some key differences in insurance regulations across states:
- Minimum Coverage Requirements: States have varying minimum coverage requirements for car insurance. Some states mandate higher coverage levels, which can lead to higher premiums. For example, a state requiring higher liability coverage will likely have higher average premiums than a state with lower liability coverage requirements.
- No-Fault Laws: Some states have no-fault insurance laws, which dictate that drivers involved in accidents can file claims with their own insurance companies, regardless of fault. These states typically have lower average premiums than states with fault-based insurance systems, where drivers are responsible for paying for the other party’s damages if they are found at fault.
- Usage-Based Insurance: Some states allow insurance companies to use telematics devices to track driving habits and offer discounts based on safe driving behavior. These programs can lead to lower premiums for drivers who demonstrate safe driving practices.
Examples of States with Significantly Higher or Lower Average Premiums
States with higher average premiums often have higher costs of living, traffic density, and accident rates. For instance, states like New Jersey and New York consistently rank among the states with the highest average car insurance premiums.
States with lower average premiums often have lower costs of living, lower traffic density, and more relaxed insurance regulations. For example, states like Idaho and Wyoming typically have lower average car insurance premiums compared to other states.
Comparing Coverage Options
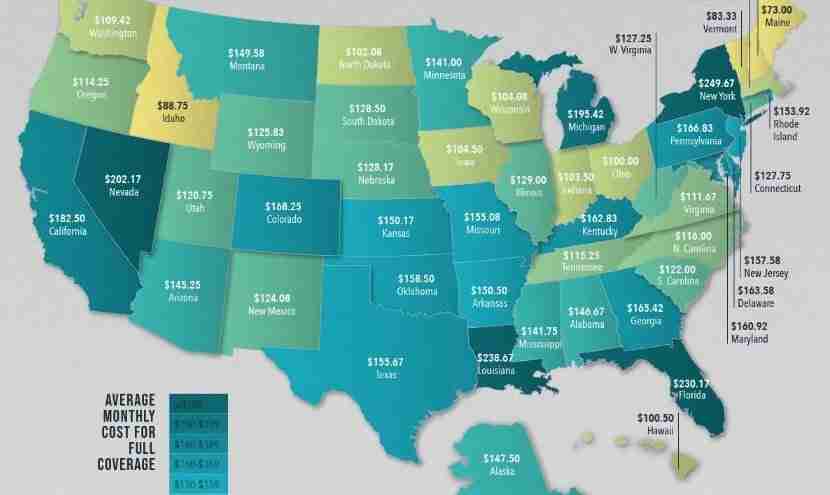
Car insurance coverage requirements and options vary significantly across states. Understanding these differences is crucial for drivers to make informed decisions about their coverage and ensure they have adequate protection. This section explores the diverse coverage options available, highlighting the differences in mandatory requirements, optional coverage choices, and the impact on coverage limits and deductibles.
Mandatory Coverage Requirements
Each state mandates certain minimum car insurance coverage levels to protect drivers and other parties involved in accidents. These requirements typically include:
- Liability Coverage: This covers the other driver’s medical expenses, property damage, and lost wages if you are at fault in an accident. States have different minimum liability limits, which determine the maximum amount your insurance company will pay for these expenses.
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): Some states require PIP coverage, which covers your own medical expenses, lost wages, and other related costs, regardless of who is at fault in an accident. PIP coverage limits vary by state.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist (UM/UIM) Coverage: This coverage protects you and your passengers if you are involved in an accident with an uninsured or underinsured driver. It covers your medical expenses, lost wages, and property damage. States have varying requirements for UM/UIM coverage, with some mandating it and others making it optional.
Optional Coverage Options
In addition to mandatory coverage, several optional coverage options are available to provide comprehensive protection for your vehicle and financial well-being. These include:
- Collision Coverage: This covers repairs or replacement costs for your vehicle if it is damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. Collision coverage is often optional, but it is recommended for newer vehicles or those with significant loan balances.
- Comprehensive Coverage: This covers damages to your vehicle caused by events other than collisions, such as theft, vandalism, fire, or natural disasters. Like collision coverage, comprehensive coverage is typically optional but valuable for protecting your vehicle against unforeseen events.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist (UM/UIM) Coverage: While some states mandate UM/UIM coverage, many offer it as an optional add-on. This coverage is crucial for protecting yourself and your passengers in case of an accident with a driver who has insufficient or no insurance.
Coverage Limits and Deductibles
Coverage limits and deductibles are essential components of car insurance policies that influence your out-of-pocket expenses in case of an accident.
- Coverage Limits: Coverage limits refer to the maximum amount your insurance company will pay for covered expenses, such as medical bills, property damage, or lost wages. States often set minimum coverage limits for mandatory coverage, but you can choose higher limits for greater protection. For example, a state might require a minimum liability limit of $25,000 per person and $50,000 per accident, but you can opt for higher limits, such as $100,000 per person and $300,000 per accident.
- Deductibles: A deductible is the amount you pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. For instance, if you have a $500 deductible for collision coverage and your vehicle sustains $2,000 worth of damage in an accident, you would pay the first $500, and your insurance company would cover the remaining $1,500. Deductibles are often customizable, with higher deductibles typically resulting in lower premiums and vice versa.
Analyzing Insurance Rates and Factors
Car insurance rates can vary significantly depending on various factors, and understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions. This section delves into the key elements that influence car insurance costs, exploring how they differ across states and offering insights on how drivers can potentially reduce their premiums.
Factors Influencing Insurance Rates
Numerous factors contribute to the calculation of car insurance premiums. These factors can be broadly categorized into:
- Driver-related factors: These factors relate directly to the individual driver’s characteristics and driving history. Examples include:
- Age: Younger drivers, particularly those under 25, generally face higher premiums due to their higher risk profile. As drivers gain experience and age, their premiums tend to decrease.
- Driving history: Drivers with a clean driving record, free from accidents or traffic violations, typically enjoy lower rates. Conversely, those with a history of accidents or violations can expect higher premiums.
- Credit history: In some states, insurers may consider credit history as a factor in determining rates. This is based on the assumption that individuals with good credit history tend to be more responsible and financially stable, potentially leading to fewer claims.
- Driving habits: Insurers may offer discounts for safe driving habits, such as avoiding driving at night or during peak traffic hours. Telematics devices, which track driving behavior, can also provide insights into driving habits and potentially lead to lower premiums.
- Vehicle-related factors: The type of vehicle driven can also significantly impact insurance rates. Key considerations include:
- Make and model: Certain car models are known for their safety features and performance, which can influence insurance rates. Cars with advanced safety features, such as anti-lock brakes and airbags, may attract lower premiums.
- Vehicle value: The cost of replacing or repairing a vehicle in case of an accident is a major factor in determining insurance premiums. More expensive vehicles typically require higher coverage, resulting in higher premiums.
- Vehicle usage: The frequency and purpose of vehicle usage can influence rates. For example, individuals who commute long distances or use their vehicle for business purposes may face higher premiums than those who primarily use their vehicle for personal errands.
- Location-related factors: Where a vehicle is driven and parked can significantly impact insurance rates. Factors considered include:
- State: Insurance rates vary significantly across states due to differences in regulations, claim frequency, and other factors. States with higher population density, more traffic congestion, and higher claim rates tend to have higher insurance premiums.
- Zip code: Even within a state, insurance rates can vary depending on the specific zip code. Areas with higher crime rates, more accidents, or higher vehicle theft rates may face higher premiums.
- Climate: Areas with extreme weather conditions, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, or hailstorms, may have higher insurance rates due to the increased risk of damage to vehicles.
- Consumer Reports: Provides independent ratings and reviews of insurance companies, as well as guidance on choosing the right coverage and negotiating rates.
- National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC): A non-profit organization that represents state insurance regulators. It provides information on insurance issues and consumer protection, and also offers resources for resolving insurance complaints.
- National Consumer Law Center (NCLC): A non-profit organization that advocates for consumer rights in various areas, including insurance. They offer resources and publications on insurance issues, as well as legal assistance to consumers.
- United States Public Interest Research Group (PIRG): A non-profit organization that advocates for consumer protection and public interest issues. They conduct research on insurance issues and provide information to consumers.
- Check Licensing and Credentials: Ensure that the agent is licensed to sell insurance in your state. You can verify their credentials through your state’s insurance department website.
- Seek Recommendations: Ask friends, family, and colleagues for recommendations. You can also check online reviews and ratings websites to see what others have to say about specific agents.
- Inquire About Expertise: Look for agents who specialize in car insurance and have experience in your state. They will have a better understanding of local regulations and pricing factors.
- Compare Quotes and Services: Obtain quotes from multiple agents to compare prices and coverage options. Also, inquire about their services, such as policy review, claims assistance, and customer support.
- Regional Insurers: These companies operate within specific geographic areas, often focusing on local communities. They may offer competitive rates and personalized service due to their familiarity with local driving conditions and customer needs.
- National Insurers: These companies operate nationwide, providing a wider reach and often a broader range of coverage options. They may have a larger customer base and greater financial stability, but their rates may not always be as competitive as regional insurers.
- Online Insurers: These companies operate solely online, offering convenient and efficient services through digital platforms. They often have lower overhead costs, which can translate into more competitive rates. However, they may lack the personal touch of traditional insurers.
- Regional Insurers:
- Advantages: Local expertise, personalized service, potentially lower rates.
- Disadvantages: Limited geographic coverage, may not offer as many coverage options as national insurers.
- National Insurers:
- Advantages: Wide geographic coverage, extensive coverage options, greater financial stability.
- Disadvantages: Rates may not be as competitive as regional insurers, less personalized service.
- Online Insurers:
- Advantages: Convenient and efficient, potentially lower rates, transparent pricing.
- Disadvantages: May lack the personal touch of traditional insurers, limited customer service options.
- Gather Information: Before requesting quotes, gather your personal information, including your driving history, vehicle details, and desired coverage levels.
- Use Online Comparison Tools: Many websites and apps allow you to compare quotes from multiple insurers simultaneously, saving time and effort.
- Contact Insurance Companies Directly: You can also contact insurance companies directly to obtain quotes. This allows for more personalized interactions and potential discounts.
- Review and Compare Quotes: Carefully review the quotes, paying attention to coverage details, deductibles, and premiums.
- Consider Additional Factors: Besides price, consider factors like customer service, claims handling processes, and financial stability when choosing an insurance company.
- Reporting the accident: You’ll need to provide details about the accident, including the date, time, location, and any injuries.
- Providing documentation: You’ll need to provide supporting documentation, such as a police report, photographs of the damage, and medical records.
- Submitting a claim form: Your insurance company will provide you with a claim form to complete.
- State regulations: Different states have varying regulations regarding claim processing times and settlement procedures.
- Insurance company practices: Each insurance company has its own internal procedures and timelines for processing claims.
- Complexity of the claim: Complex claims involving multiple parties or significant damage may take longer to process.
- Be prepared: Keep your insurance policy information readily available, including your policy number, coverage details, and contact information.
- Document everything: Take detailed notes about the accident, including the date, time, location, and any injuries.
- Take photographs: Take photographs of the damage to your vehicle, the other vehicle involved, and the accident scene.
- Get medical attention: If you are injured, seek medical attention immediately.
- Be patient: The insurance claims process can take time. Be patient and persistent in following up with your insurance company.
- Seek professional advice: If you are having difficulty navigating the claims process, consider seeking advice from a qualified insurance professional or attorney.
Exploring State-Specific Resources
Navigating the complexities of car insurance across different states can be daunting. Understanding the nuances of each state’s regulations, coverage options, and pricing factors is crucial to making informed decisions. This section will guide you to valuable resources that can help you find the information you need to secure the best car insurance coverage for your needs.
State Insurance Departments
State insurance departments are your primary resource for information about car insurance regulations and consumer protection in your state. These departments are responsible for overseeing the insurance industry, investigating consumer complaints, and ensuring that insurers comply with state laws. You can access their websites for information on:
| State | Department Website |
|---|---|
| Alabama | https://www.aldoi.gov/ |
| Alaska | https://www.insurance.alaska.gov/ |
| Arizona | https://www.azinsurance.gov/ |
| Arkansas | https://www.insurance.arkansas.gov/ |
| California | https://www.insurance.ca.gov/ |
| Colorado | https://www.colorado.gov/pacific/dora/insurance |
| Connecticut | https://portal.ct.gov/cid |
| Delaware | https://dfi.delaware.gov/insurance/ |
| Florida | https://www.fldfs.com/ |
| Georgia | https://www.oci.ga.gov/ |
| Hawaii | https://cca.hawaii.gov/ |
| Idaho | https://www.doi.idaho.gov/ |
| Illinois | https://www.insurance.illinois.gov/ |
| Indiana | https://www.idoi.in.gov/ |
| Iowa | https://www.iid.iowa.gov/ |
| Kansas | https://www.ksinsurance.org/ |
| Kentucky | https://www.kfi.ky.gov/ |
| Louisiana | https://www.ldi.la.gov/ |
| Maine | https://www.maine.gov/insurance/ |
| Maryland | https://www.marylandinsurance.gov/ |
| Massachusetts | https://www.mass.gov/orgs/division-of-insurance |
| Michigan | https://www.michigan.gov/lara/0,4563,7-154-3603_3606—,00.html |
| Minnesota | https://mn.gov/commerce/ |
| Mississippi | https://www.mid.ms.gov/ |
| Missouri | https://www.insurance.mo.gov/ |
| Montana | https://doi.mt.gov/ |
| Nebraska | https://www.nol.ne.gov/ |
| Nevada | https://www.insurance.nv.gov/ |
| New Hampshire | https://www.nh.gov/insurance/ |
| New Jersey | https://www.nj.gov/dobi/ |
| New Mexico | https://www.rrd.state.nm.us/insurance/ |
| New York | https://www.dfs.ny.gov/ |
| North Carolina | https://www.ncdoi.com/ |
| North Dakota | https://www.nd.gov/dmr/insurance/ |
| Ohio | https://insurance.ohio.gov/ |
| Oklahoma | https://www.oid.ok.gov/ |
| Oregon | https://www.oregon.gov/oic/Pages/index.aspx |
| Pennsylvania | https://www.insurance.pa.gov/ |
| Rhode Island | https://dbi.ri.gov/ |
| South Carolina | https://www.doi.sc.gov/ |
| South Dakota | https://www.sdsic.com/ |
| Tennessee | https://www.tn.gov/commerce/insurance.html |
| Texas | https://www.tdi.texas.gov/ |
| Utah | https://insurance.utah.gov/ |
| Vermont | https://www.insurance.vermont.gov/ |
| Virginia | https://www.scc.virginia.gov/ |
| Washington | https://www.insurance.wa.gov/ |
| West Virginia | https://www.wvinsurance.gov/ |
| Wisconsin | https://www.oci.wi.gov/ |
| Wyoming | https://www.wyominginsurance.gov/ |
Consumer Advocacy Organizations
Consumer advocacy organizations are valuable resources for unbiased information and assistance with insurance-related issues. They can help you understand your rights as a policyholder, file complaints against insurers, and negotiate with insurers to resolve disputes. Some notable consumer advocacy organizations include:
Finding Reputable Insurance Agents
Working with a reputable and licensed insurance agent can streamline the process of finding the right car insurance policy for your needs. Here are some tips for finding a reliable agent:
Navigating the Insurance Market
The car insurance market is diverse, with various insurance companies catering to different needs and preferences. Understanding the different types of insurance providers and their strengths and weaknesses is crucial for making an informed decision.
Types of Car Insurance Companies
The car insurance market offers a variety of companies, each with its own characteristics and offerings.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Insurance Providers
Choosing the right insurance provider involves weighing the pros and cons of each type.
Obtaining Quotes and Comparing Rates, Car insurance state comparison
To find the best car insurance rates, it’s essential to compare quotes from multiple insurance companies.
Tip: Don’t be afraid to negotiate with insurance companies. They may be willing to adjust their rates based on your individual needs and circumstances.
Understanding Insurance Claims and Processes: Car Insurance State Comparison
Navigating the insurance claims process can be a stressful experience, especially when you’re dealing with the aftermath of a car accident. However, understanding the general steps involved and potential state-specific variations can help you navigate the process more smoothly.
Claim Filing Procedures
The initial steps involved in filing a car insurance claim are generally similar across states. You’ll typically need to contact your insurance company as soon as possible after an accident. They will guide you through the process, including:
Claim Processing Times and Settlement Procedures
While the general process of filing a claim is similar, the time it takes to process a claim and the settlement procedures can vary significantly depending on the state. Some factors that can influence these variations include:
Tips for Navigating the Insurance Claims Process
Here are some tips for navigating the insurance claims process effectively:
Final Wrap-Up
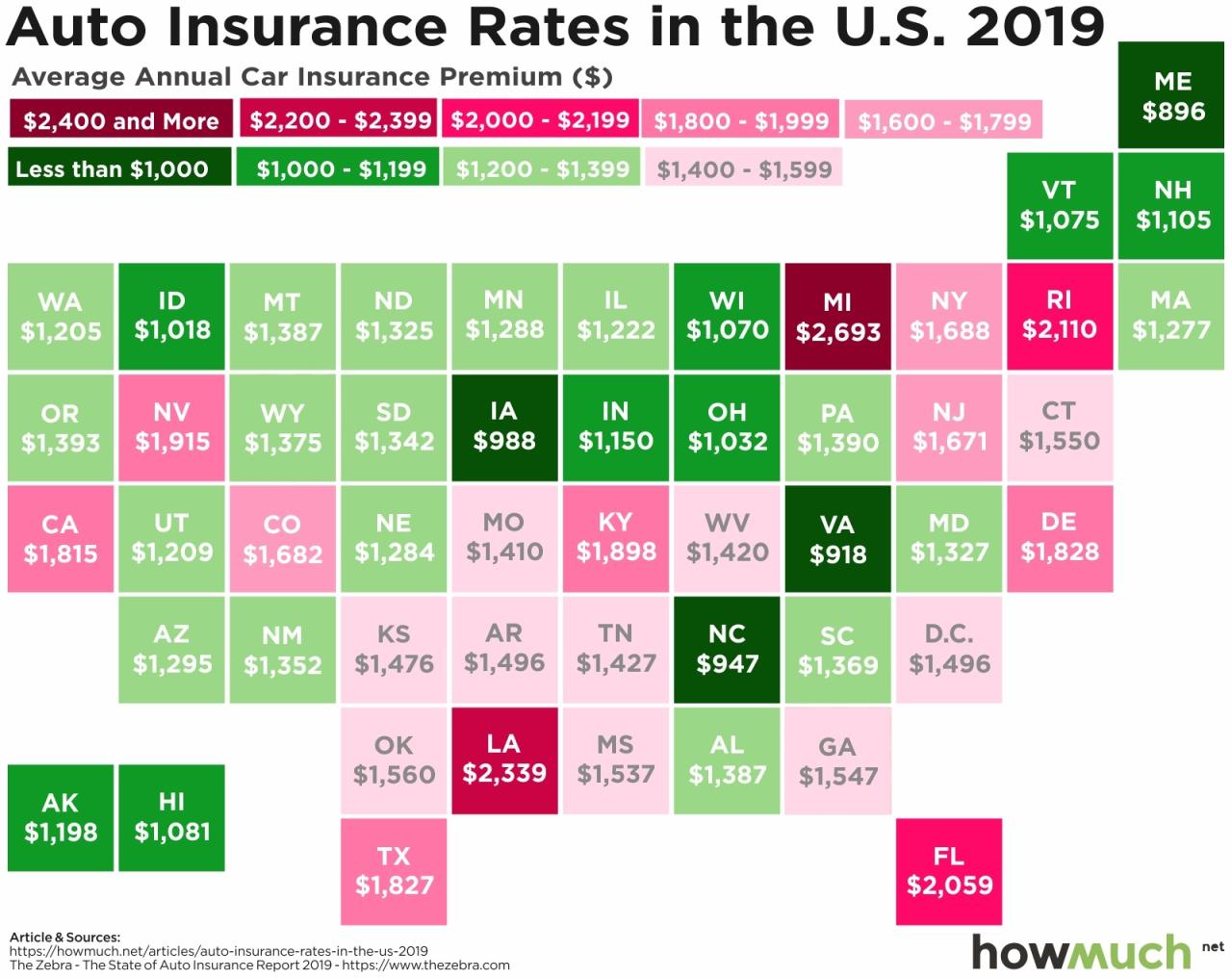
Navigating the car insurance market can feel overwhelming, but by understanding the factors that influence rates and comparing options across different states, you can secure the best coverage at a competitive price. Remember to consider your individual needs, driving habits, and budget when choosing a policy. With careful research and planning, you can find the car insurance that provides the peace of mind you deserve.
Q&A
What is the cheapest state for car insurance?
The cheapest states for car insurance often have lower accident rates, less traffic congestion, and more lenient regulations. However, it’s important to remember that rates can vary within a state based on individual factors.
How often should I review my car insurance policy?
It’s generally recommended to review your car insurance policy annually to ensure that your coverage is still adequate and that you’re getting the best rate. Your insurance needs may change over time due to factors such as changes in your driving habits, vehicle ownership, or financial situation.
What are the benefits of using an insurance broker?
Insurance brokers can provide valuable assistance by comparing quotes from multiple insurance companies and helping you find the best policy for your needs. They can also offer expert advice on coverage options and claim processes.