Car insurance no fault states – Car insurance no-fault states set the stage for a unique approach to car accident coverage, offering a departure from traditional fault-based systems. In these states, drivers are primarily responsible for covering their own medical expenses and other losses, regardless of who caused the accident. This system aims to streamline the claims process, potentially reducing insurance premiums and litigation, but it also comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
The no-fault system has been implemented in various forms across the United States, with states adopting different variations to address their specific needs and concerns. This article will delve into the intricacies of no-fault insurance, exploring its benefits, challenges, and impact on drivers.
What is No-Fault Car Insurance?
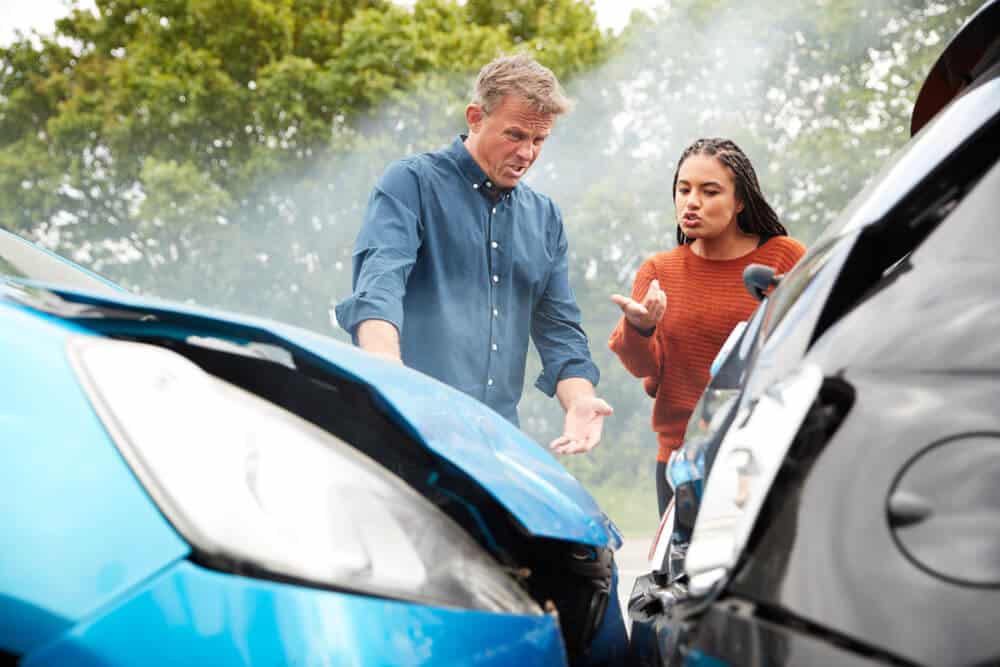

No-fault car insurance is a system where drivers are primarily responsible for covering their own losses after a car accident, regardless of who is at fault. This means that you file a claim with your own insurance company, regardless of who caused the accident. It’s a different approach compared to traditional fault-based insurance, where the at-fault driver’s insurance company is responsible for paying for the other driver’s damages.
How No-Fault Insurance Differs from Traditional Fault-Based Insurance
No-fault insurance differs significantly from traditional fault-based insurance. In traditional fault-based insurance, the at-fault driver’s insurance company is responsible for covering the other driver’s damages. This often involves lengthy investigations and legal battles to determine fault. In contrast, no-fault insurance eliminates the need for these processes. You file a claim with your own insurance company, regardless of who caused the accident.
Advantages of No-Fault Insurance
No-fault insurance systems offer several advantages.
Faster Claims Processing
No-fault insurance systems generally result in faster claims processing. Since you file a claim with your own insurance company, there’s no need to wait for a determination of fault. This can be particularly beneficial for minor accidents where liability is clear.
Reduced Legal Costs
No-fault insurance systems can reduce legal costs associated with car accidents. With no need to determine fault, there’s less litigation and fewer disputes between insurance companies. This can lead to lower insurance premiums for everyone.
Guaranteed Coverage
No-fault insurance provides guaranteed coverage for your own injuries and damages. Even if you are at fault for an accident, you’ll still be able to receive benefits for your losses. This can offer peace of mind knowing that you’ll be covered, regardless of the circumstances.
Disadvantages of No-Fault Insurance
While no-fault insurance has its benefits, it also comes with some drawbacks.
Limited Coverage for Serious Injuries
No-fault insurance systems typically have limits on the amount of coverage available for serious injuries. In some cases, you may need to pursue a separate lawsuit against the at-fault driver to recover additional compensation.
Higher Premiums
No-fault insurance systems can lead to higher premiums for some drivers. This is because insurance companies need to cover the costs of paying out benefits to all drivers, regardless of fault.
Potential for Abuse
There’s a potential for abuse in no-fault insurance systems. Some drivers may try to take advantage of the system by exaggerating their injuries or filing fraudulent claims.
No-Fault States in the United States
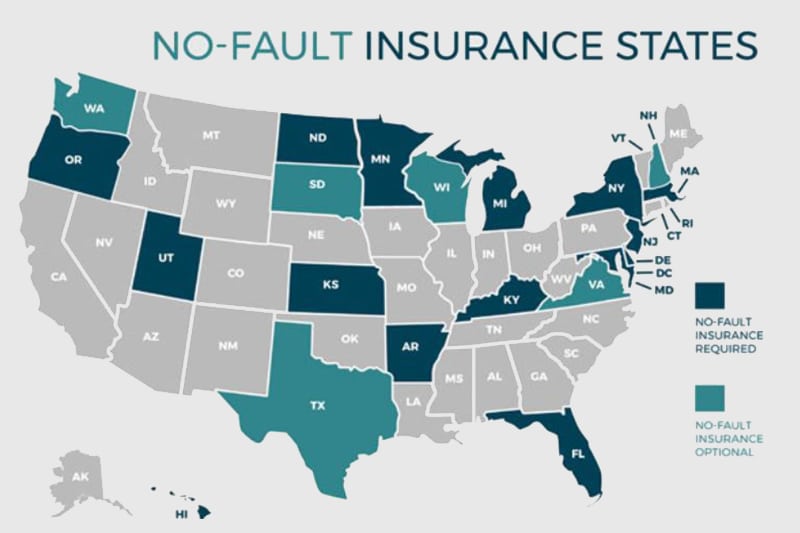
No-fault insurance systems are a unique approach to car insurance that varies significantly across different states. Understanding the types of no-fault systems and their implementation is crucial for anyone navigating the car insurance landscape.
Types of No-Fault Systems
The United States features three primary types of no-fault insurance systems: pure, modified, and add-on. Each system has its own set of rules and regulations that impact how claims are handled and the extent of coverage provided.
No-Fault System Types and States
| State | No-Fault System Type |
|---|---|
| Florida | Pure No-Fault |
| Michigan | Pure No-Fault |
| New Jersey | Modified No-Fault |
| New York | Modified No-Fault |
| Pennsylvania | Add-on No-Fault |
| Kentucky | Add-on No-Fault |
Benefits of No-Fault Car Insurance
No-fault car insurance offers several benefits for drivers, aiming to streamline the claims process, reduce insurance premiums, and promote fairness in the event of an accident.
Reduced Insurance Premiums
No-fault insurance systems are designed to reduce the number of lawsuits related to car accidents. By limiting the potential for costly litigation, insurance companies can potentially lower their overall costs, which can translate into lower premiums for policyholders. This is because no-fault insurance typically requires drivers to file claims with their own insurance companies, regardless of who caused the accident. This eliminates the need for extensive investigations and legal battles, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
Challenges of No-Fault Car Insurance
While no-fault insurance aims to simplify the claims process and reduce litigation, it’s not without its challenges. Some argue that it can lead to higher insurance premiums, limit compensation for injured drivers, and make it more difficult to recover for certain types of damages.
Higher Insurance Premiums
No-fault insurance can potentially lead to higher insurance premiums in some cases. This is because the system encourages more claims, as drivers are generally entitled to compensation for their own injuries regardless of fault. With more claims being filed, insurance companies may need to increase premiums to cover the increased costs. Additionally, the “no-fault” aspect can sometimes incentivize fraudulent claims, which can further drive up premiums for everyone.
Limited Compensation
No-fault insurance often sets limits on the amount of compensation available to injured drivers. These limits can vary by state but generally cover medical expenses, lost wages, and other related costs. However, they may not fully compensate drivers for all their losses, particularly for serious injuries that require extensive medical treatment or rehabilitation.
Difficulty in Recovering for Non-Economic Damages
No-fault insurance systems typically limit or exclude compensation for non-economic damages, such as pain and suffering, emotional distress, and loss of enjoyment of life. This is because these damages are subjective and difficult to quantify. While some states allow for recovery of non-economic damages under certain circumstances, such as when the injuries are severe, the process can be more complex and challenging than in traditional fault-based systems.
Threshold Requirements in Modified No-Fault Systems
Modified no-fault systems often include a “threshold” requirement, which determines when an injured driver can sue the at-fault party for additional damages. These thresholds typically involve factors like the severity of the injuries or the amount of medical expenses incurred. The challenge with these thresholds is that they can be difficult to interpret and apply consistently, leading to potential disputes and legal challenges. For example, if a driver suffers significant pain and suffering but does not meet the threshold for medical expenses, they may be denied the opportunity to seek compensation for their non-economic damages.
No-Fault Car Insurance and Personal Injury Protection (PIP)
Personal Injury Protection (PIP) is a crucial component of no-fault car insurance systems. It provides coverage for medical expenses and lost wages resulting from car accidents, regardless of who is at fault. PIP coverage is designed to help injured individuals recover from their injuries without having to engage in lengthy legal battles to determine fault.
How PIP Coverage Works
PIP coverage operates on a “no-fault” basis, meaning that injured individuals can seek compensation for their injuries from their own insurance company, regardless of who caused the accident. This eliminates the need for fault determination, which can be a time-consuming and complex process. PIP coverage typically covers medical expenses, including:
- Hospitalization
- Doctor’s visits
- Surgery
- Prescription drugs
- Physical therapy
- Other related medical expenses
It also often covers lost wages, up to a certain limit.
Limitations of PIP Coverage
While PIP coverage offers significant benefits, it also has limitations. One common limitation is the maximum amount of coverage available. Most states have a maximum dollar amount that PIP coverage will pay out for medical expenses and lost wages. Another limitation is the time limit for claiming PIP benefits. Many states have a time limit for filing claims, typically within a year of the accident. If a claim is not filed within the specified time frame, the injured individual may be barred from receiving benefits.
PIP Coverage Compared to Other Types of Insurance Coverage
PIP coverage differs from other types of insurance coverage, such as medical payments coverage (MedPay), in several key ways. MedPay is a supplemental coverage that pays for medical expenses regardless of fault, but it typically has a lower coverage limit than PIP. PIP coverage also differs from liability coverage, which covers the insured driver’s legal responsibility for injuries or damages caused to others.
No-Fault Car Insurance and Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage
While no-fault insurance focuses on covering your own losses after an accident, it’s crucial to remember that not all drivers are insured. This is where uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage (UM/UIM) plays a vital role in protecting you and your financial well-being in no-fault states.
Importance of UM/UIM Coverage in No-Fault States
UM/UIM coverage is an essential addition to your no-fault policy because it steps in when the other driver is either uninsured or their insurance coverage is insufficient to cover your damages. In no-fault states, your own insurance company will typically cover your medical expenses and lost wages, but it won’t cover damages caused by the other driver’s negligence. This is where UM/UIM coverage comes into play.
How UM/UIM Coverage Protects Drivers
In cases where the other driver is uninsured or underinsured, your UM/UIM coverage acts as a safety net. It helps compensate you for:
* Medical expenses: If your injuries are more extensive than your PIP coverage, UM/UIM coverage can cover the additional medical costs.
* Lost wages: If your injuries prevent you from working, UM/UIM coverage can help replace lost income.
* Property damage: If the other driver’s insurance is inadequate to cover the cost of repairing or replacing your vehicle, UM/UIM coverage can bridge the gap.
* Pain and suffering: In some cases, UM/UIM coverage may also cover non-economic damages, such as pain and suffering, emotional distress, and loss of consortium.
Scenarios Where UM/UIM Coverage is Essential
- Hit-and-run accidents: When the driver who caused the accident flees the scene, you have no way to pursue their insurance. UM/UIM coverage ensures you’re not left financially responsible for your own losses.
- Accidents with uninsured drivers: Many drivers operate vehicles without proper insurance, putting others at risk. UM/UIM coverage protects you in these situations.
- Accidents with underinsured drivers: Even if the other driver has insurance, their coverage limits may be insufficient to cover all your damages. UM/UIM coverage provides additional protection in such scenarios.
How UM/UIM Coverage Works
When you file a claim under your UM/UIM coverage, your own insurance company will act as if the at-fault driver was insured and had sufficient coverage. You will be treated as if you were injured by a fully insured driver.
“UM/UIM coverage is like having an extra layer of protection in case the other driver is uninsured or underinsured.”
The process of filing a claim under UM/UIM coverage is similar to filing a claim under your PIP coverage. You’ll need to provide your insurance company with all the necessary documentation, such as a police report, medical bills, and wage statements. Your insurance company will then investigate the claim and determine the extent of your damages.
Choosing Car Insurance in a No-Fault State
Navigating car insurance in a no-fault state can seem complex, but with the right information, you can make informed decisions that protect you financially. Here’s a breakdown of key factors to consider when choosing car insurance in a no-fault state.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Car Insurance
Understanding the unique aspects of no-fault insurance is crucial for making the right choice. These factors can help you select the coverage that best suits your needs and budget:
- Your State’s No-Fault Laws: Each no-fault state has specific regulations. Understanding the minimum coverage requirements, such as Personal Injury Protection (PIP), is essential.
- Your Driving History: A clean driving record can lead to lower premiums. Factors like accidents, traffic violations, and driving experience influence your rates.
- Your Vehicle’s Value: The value of your vehicle impacts the amount of coverage you need for collision and comprehensive insurance.
- Your Budget: Set a realistic budget for car insurance and explore options that fit your financial constraints.
Determining the Appropriate Level of PIP Coverage
Personal Injury Protection (PIP) is a crucial component of no-fault insurance. It covers medical expenses and lost wages for you and your passengers, regardless of who is at fault in an accident.
- Evaluate Your Needs: Consider your health, employment situation, and potential medical expenses. Higher PIP coverage provides greater financial protection in case of a serious injury.
- Balance Coverage and Cost: Higher PIP limits generally come with higher premiums. Determine the level of coverage that offers adequate protection without straining your budget.
- Consider Your State’s Minimum Requirements: Most no-fault states have minimum PIP coverage requirements. Ensure you meet these minimums to comply with the law.
Finding Affordable Car Insurance in a No-Fault State
While no-fault insurance can offer advantages, it’s essential to find affordable coverage. Here are some tips:
- Compare Quotes: Obtain quotes from multiple insurance companies to compare rates and coverage options.
- Explore Discounts: Ask about available discounts, such as good driver discounts, multi-car discounts, and safety feature discounts.
- Consider Bundling: Bundling your car insurance with other insurance policies, such as homeowners or renters insurance, can often result in lower premiums.
- Review Your Coverage Regularly: Your insurance needs may change over time. Periodically review your coverage to ensure it aligns with your current situation and budget.
Comparing Different Car Insurance Quotes, Car insurance no fault states
When comparing car insurance quotes, it’s essential to focus on more than just the price. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Gather Information: Collect details about your vehicle, driving history, and coverage needs.
- Request Quotes: Contact multiple insurance companies and request quotes for the same coverage options.
- Compare Coverage: Carefully examine the coverage details, including deductibles, limits, and exclusions.
- Evaluate Customer Service: Consider the reputation and customer service of each insurance company.
- Choose the Best Option: Select the insurance policy that offers the most comprehensive coverage at a price that fits your budget.
No-Fault Car Insurance and the Future
The no-fault insurance system, while aiming to streamline claims processing and reduce litigation, has sparked ongoing debate regarding its effectiveness and potential for reform. As technology advances and societal needs evolve, the future of no-fault insurance is subject to various considerations and potential changes.
Potential Changes to No-Fault Systems
The future of no-fault insurance is likely to be shaped by several factors, including technological advancements, changing societal expectations, and evolving legal landscapes.
- Increased Use of Technology: Emerging technologies, such as telematics and artificial intelligence (AI), could play a significant role in shaping no-fault systems. Telematics devices can track driving behavior, providing valuable data for risk assessment and premium calculation. AI-powered systems could automate claims processing, reducing administrative costs and processing times.
- Shifting Attitudes Towards Litigation: A growing preference for alternative dispute resolution (ADR) methods, such as mediation and arbitration, might influence the future of no-fault systems. ADR processes could provide faster and more cost-effective solutions compared to traditional litigation.
- Changes in Legislation: Legislative reforms could introduce modifications to no-fault systems, addressing concerns about rising insurance costs, limited coverage, and potential loopholes. These reforms could involve adjustments to thresholds for accessing benefits, expanding coverage options, or revising the balance between tort and no-fault systems.
Arguments for and Against No-Fault Insurance
The debate surrounding no-fault insurance revolves around its perceived benefits and drawbacks.
- Arguments for No-Fault Insurance:
- Reduced Litigation: No-fault systems aim to minimize lawsuits by eliminating the need to prove fault in minor accidents, leading to quicker settlements and reduced court backlogs.
- Faster Claims Processing: The absence of fault determination allows insurers to process claims more efficiently, leading to faster payment of benefits.
- Lower Insurance Premiums: Proponents argue that reduced litigation costs and streamlined claims processing can translate into lower insurance premiums for policyholders.
- Arguments Against No-Fault Insurance:
- Limited Coverage: Critics argue that no-fault systems can restrict coverage for certain types of injuries or damages, potentially leaving victims with insufficient compensation.
- Higher Premiums: Some studies suggest that no-fault systems can lead to higher insurance premiums, particularly for high-risk drivers, as insurers may have less incentive to incentivize safe driving.
- Potential for Abuse: There are concerns that no-fault systems could be abused by individuals filing fraudulent claims or exaggerating injuries to receive higher benefits.
Outcome Summary: Car Insurance No Fault States
Understanding the nuances of no-fault car insurance is crucial for drivers residing in these states. By navigating the system’s intricacies, drivers can make informed decisions regarding their coverage and ensure adequate protection in the event of an accident. As the landscape of car insurance continues to evolve, understanding the benefits and drawbacks of no-fault systems remains essential for drivers seeking comprehensive coverage and financial security.
Top FAQs
What are the main types of no-fault systems?
The three primary types of no-fault systems are pure, modified, and add-on. Pure no-fault systems prohibit lawsuits for pain and suffering, while modified systems allow lawsuits under certain circumstances. Add-on no-fault systems provide additional coverage options on top of traditional fault-based insurance.
How does no-fault insurance affect my ability to sue for damages?
In pure no-fault states, you generally cannot sue for pain and suffering unless your injuries meet a specific threshold, such as a serious injury. Modified no-fault states allow lawsuits for damages above a certain amount or for specific types of injuries.
What are the potential downsides of no-fault insurance?
Potential downsides include higher premiums in some cases, limitations on compensation for injured drivers, and challenges in recovering for non-economic damages. Additionally, the threshold requirement in modified no-fault systems can be difficult to meet, limiting access to legal remedies for some injured drivers.