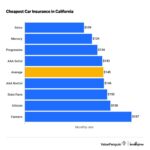
Can you get insurance in another state? It’s a question many people ask when they relocate or spend significant time away from their home state. While it may seem straightforward, the answer depends on various factors, including the type of insurance, state regulations, and your residency status.
This guide explores the complexities of obtaining insurance in a new state, covering everything from residency requirements and insurance types to reciprocity and factors that influence costs. We’ll delve into the regulations, challenges, and considerations you need to be aware of when navigating the world of interstate insurance.
State Residency Requirements
Insurance companies typically require you to be a resident of the state where you’re seeking coverage. This is to ensure that the insurer is operating within its authorized territory and that the policyholder is subject to the state’s insurance regulations.
Residency is a crucial factor in determining your eligibility for insurance. Insurance companies often use various criteria to establish residency, including your primary residence, driver’s license, and voter registration.
Determining Residency
Residency is not simply about where you live; it’s about your intention to make a particular state your permanent home. Here are some key factors insurance companies consider:
- Primary Residence: This is the address where you primarily reside, receive mail, and pay property taxes. Your lease or mortgage agreement can be used as evidence of residency.
- Driver’s License: Your driver’s license should reflect the address of your primary residence. It’s a strong indicator of your intention to establish residency in a particular state.
- Voter Registration: Registering to vote in a state is another way to demonstrate your intent to reside there. Your voter registration card serves as proof of residency.
- Other Factors: Insurance companies may also consider your employment, bank accounts, and other factors to determine your residency.
Situations that May Raise Residency Questions
In some cases, your residency may be questioned. For example:
- Temporary Relocation: If you move to a state temporarily for work or school, you might not meet the residency requirements for insurance. It’s essential to check with the insurance company about their specific guidelines.
- Dual Residency: Maintaining residency in multiple states can complicate insurance matters. Insurance companies may require you to designate a primary residence and demonstrate your intention to establish residency in that state.
Insurance Types and State Regulations

Insurance regulations vary significantly from state to state, impacting coverage, premiums, and eligibility for different insurance types. These regulations are put in place to protect consumers and ensure fair competition within the insurance industry.
State-Specific Regulations and Their Impact
State regulations can significantly impact the coverage, premiums, and eligibility of different insurance types.
| Insurance Type | State A Regulations | State B Regulations | State C Regulations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Auto Insurance | Minimum liability coverage requirements: $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident. No-fault insurance system. | Minimum liability coverage requirements: $15,000 per person/$30,000 per accident. Choice No-fault system. | Minimum liability coverage requirements: $10,000 per person/$20,000 per accident. Tort system. |
| Health Insurance | Mandates coverage for essential health benefits. Prohibits pre-existing condition exclusions. | Allows insurers to offer plans with limited coverage. May allow pre-existing condition exclusions. | Offers subsidies for low-income individuals. Prohibits insurers from denying coverage based on pre-existing conditions. |
| Homeowners Insurance | Mandates coverage for specific perils, such as fire, wind, and hail. May require coverage for specific hazards, such as earthquakes or floods. | Allows insurers to offer plans with limited coverage. May exclude coverage for specific perils. | Requires coverage for specific perils, including earthquakes and floods. May offer discounts for home security systems. |
For example, state regulations regarding minimum liability coverage in auto insurance can impact the cost of premiums. States with higher minimum coverage requirements typically have higher premiums, as insurers need to cover potential claims up to those limits.
Insurance Rate Determination
Insurance companies use a variety of factors to determine insurance rates, including state regulations and risk factors.
- State Regulations: Minimum coverage requirements, mandated benefits, and other regulations set by the state influence the base rate for insurance.
- Risk Factors: Individual risk factors, such as age, driving history, credit score, and location, can affect the individual premium.
For instance, insurers may charge higher premiums for drivers with a history of accidents or violations, reflecting the increased risk of future claims.
Obtaining Insurance in a New State
Moving to a new state often involves a lot of adjustments, and securing insurance is a crucial step in settling in. Whether you’re moving for work, school, or simply a change of scenery, understanding the process of obtaining insurance in your new state is essential.
Process of Obtaining Insurance in a New State
- Research Insurance Providers: Begin by researching insurance providers in your new state. Consider factors such as coverage options, pricing, customer reviews, and financial stability. Utilize online resources, compare insurance quotes, and consult with insurance brokers or agents.
- Gather Necessary Documentation: Prepare the necessary documentation for your insurance application. This typically includes your driver’s license, Social Security number, proof of residency, vehicle registration (for auto insurance), and details of your current insurance policy (if applicable).
- Contact Your Current Insurer: If you have existing insurance coverage, inform your current insurer about your move. They may be able to provide you with coverage in your new state, potentially with a seamless transition. However, be prepared for possible rate changes or coverage limitations based on the new state’s regulations.
- Apply for New Insurance: Once you’ve chosen an insurance provider, complete the application process. Provide accurate and complete information, including your contact details, driving history, and vehicle information (for auto insurance). Review the policy carefully before signing.
- Pay Premiums and Receive Policy: After your application is approved, you’ll need to pay your first premium. Your insurance provider will then issue you a policy document outlining your coverage details and terms.
Challenges of Switching Insurance Providers Across State Lines
Switching insurance providers across state lines can present some challenges.
- Coverage Differences: State regulations vary significantly, leading to differences in coverage requirements, limits, and exclusions. What’s standard in one state might not be available in another. For example, minimum liability coverage for auto insurance can differ substantially between states.
- Rate Variations: Insurance premiums can fluctuate based on state regulations, risk factors, and the insurer’s pricing models. You might encounter higher or lower rates in your new state compared to your previous location.
- Gaps in Coverage: There may be a brief period between the cancellation of your old policy and the activation of your new one, potentially leaving you without coverage. It’s crucial to coordinate the timing of these events to ensure continuous protection.
Flowchart for Obtaining Insurance in a New State
This flowchart provides a visual representation of the steps involved in obtaining insurance in a new state:
[Flowchart Illustration]
* Start: The process begins with the decision to move to a new state.
* Research: Investigate insurance providers in your new state.
* Gather Documentation: Collect the required documents for your application.
* Contact Current Insurer: Inform your current insurer about your move.
* Apply for New Insurance: Submit an application with a chosen provider.
* Pay Premiums: Make your initial premium payment.
* Receive Policy: Receive your new insurance policy.
* End: The process concludes with obtaining insurance coverage in your new state.
Reciprocity and Coverage: Can You Get Insurance In Another State
Insurance reciprocity is a concept that affects how your insurance coverage translates across state lines. It essentially means that certain aspects of your insurance policy might be recognized and honored in another state, even if you’re not a resident there.
This concept plays a significant role when it comes to accidents or claims that occur outside your home state.
Reciprocity in Practice
Reciprocity typically applies to certain types of insurance, such as auto insurance. However, it’s crucial to understand that not all states have reciprocity agreements with each other, and the extent of coverage that’s recognized can vary.
Here are some examples of how reciprocity might impact your coverage:
- If you’re driving in another state and get into an accident, your auto insurance from your home state might be honored, ensuring you have the necessary coverage for liability, medical expenses, and property damage.
- In some cases, your state’s minimum liability insurance requirements might be recognized in another state, even if that state has higher minimums. However, you might be required to purchase additional coverage to meet the higher requirements of the other state.
- Reciprocity may also extend to other types of insurance, such as workers’ compensation or unemployment benefits. However, the specific rules and regulations regarding these types of insurance can vary significantly from state to state.
Limitations of Reciprocity
While reciprocity can be beneficial, it’s important to remember that it has limitations:
- Not all states have reciprocity agreements with each other. For example, if you’re driving in a state that doesn’t have a reciprocity agreement with your home state, your insurance might not be recognized, and you could face legal consequences if you’re involved in an accident.
- Even if a state has a reciprocity agreement with your home state, the extent of coverage that’s recognized might be limited. For example, your home state’s minimum liability insurance requirements might be recognized, but you might still need to purchase additional coverage to meet the higher requirements of the other state.
- Reciprocity typically applies to certain types of insurance, such as auto insurance. It might not apply to other types of insurance, such as health insurance or life insurance.
Checking for Reciprocity
It’s always best to contact your insurance company or your state’s insurance department to confirm if your insurance policy has reciprocity in a particular state. This will help you understand the extent of your coverage and ensure you’re adequately protected while traveling or living in another state.
Factors Affecting Insurance Costs

Insurance premiums vary significantly across states due to a complex interplay of factors. These factors influence the risk assessment conducted by insurance companies, leading to variations in pricing. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your insurance needs and potentially find more affordable coverage.
Driving History
Your driving history is a major factor influencing insurance costs. A clean driving record with no accidents or traffic violations typically translates to lower premiums. Conversely, a history of accidents, speeding tickets, or DUI convictions will likely result in higher premiums.
- Accidents: Insurance companies view accidents as indicators of higher risk, as they suggest a higher likelihood of future claims. The severity of the accident and the driver’s fault also play a role in premium increases.
- Traffic Violations: Speeding tickets, reckless driving citations, and other traffic violations signal to insurers that you may be a riskier driver. These violations can lead to significant premium hikes, particularly for multiple offenses.
- DUI Convictions: DUI convictions are considered very serious offenses, demonstrating a disregard for traffic laws and potentially impaired judgment. These convictions often result in the highest premium increases, sometimes even leading to policy cancellations.
Credit Score
In many states, insurance companies use your credit score as a factor in determining your insurance premiums. While the relationship between credit score and driving behavior isn’t always clear, insurers argue that individuals with good credit scores are more likely to be financially responsible and less likely to file fraudulent claims.
- Credit Score Impact: Higher credit scores generally lead to lower insurance premiums, while lower credit scores can result in higher premiums. The impact of credit score on premiums varies by state and insurance company.
- Fairness Debate: The use of credit scores in insurance pricing has been controversial, with some arguing that it unfairly penalizes individuals with poor credit history who may be responsible drivers. However, insurers maintain that credit scores are a reliable indicator of risk.
Age
Age is a significant factor in insurance pricing, as it correlates with driving experience and risk. Younger drivers typically have less experience and may be more prone to accidents, leading to higher premiums. As drivers age and gain more experience, their premiums tend to decrease.
- Teenage Drivers: Insurance premiums for teenage drivers are generally the highest due to their lack of experience and higher risk of accidents. Some insurers offer discounts for good grades or driver’s education courses to incentivize responsible driving.
- Mature Drivers: Drivers over the age of 65 often experience lower premiums as they have a longer driving history and may have developed safer driving habits. However, some insurers may impose higher premiums for older drivers due to potential health concerns or reduced reaction times.
Other Factors, Can you get insurance in another state
Besides driving history, credit score, and age, several other factors can influence insurance premiums. These include:
- Vehicle Type: The make, model, and year of your vehicle can impact your insurance costs. Luxury cars or high-performance vehicles often have higher premiums due to their higher repair costs and potential for higher accident severity.
- Location: Your state and zip code can influence premiums due to variations in accident rates, crime rates, and other factors. Areas with higher accident rates or more congested traffic tend to have higher premiums.
- Driving Habits: Your driving habits, such as the number of miles you drive annually and whether you use your vehicle for work, can also impact your premiums. Higher mileage and commercial use can lead to higher premiums.
- Coverage Levels: The amount of coverage you choose, such as liability limits, collision coverage, and comprehensive coverage, will affect your premium. Higher coverage levels generally mean higher premiums.
- Discounts: Insurance companies offer various discounts to reduce premiums. These include discounts for good driving records, safety features, multiple policy discounts, and more.
End of Discussion
Navigating the world of interstate insurance can be a complex process, but with the right information and understanding, you can make informed decisions about your coverage. Remember to research state regulations, consider your residency status, and explore your options for obtaining insurance in your new location. By understanding the nuances of interstate insurance, you can ensure you have the coverage you need wherever you go.
General Inquiries
What if I’m only moving temporarily?
If you’re only moving temporarily, you may be able to keep your current insurance policy. However, you should contact your insurance company to confirm if your policy covers you in the new state and for how long.
Can I get insurance in another state if I’m not a resident?
It’s possible to get insurance in another state even if you’re not a resident, but it may be more difficult and expensive. Insurance companies may require you to provide additional documentation or proof of residency.
How do I know if my insurance is valid in another state?
The best way to determine if your insurance is valid in another state is to contact your insurance company directly. They can provide you with specific information about your policy’s coverage in different states.