Can I have insurance on a car in another state? This question often arises when people move or travel, and the answer isn’t always straightforward. Car insurance is typically tied to your residency, meaning your coverage might not extend to another state without adjustments. This can lead to complications, especially if you’re driving in a new state without proper insurance. Understanding the nuances of insurance and residency is crucial for ensuring you have adequate coverage wherever you drive.
The process of obtaining car insurance in a new state can vary depending on the specific requirements and regulations of that state. Factors like driving history, age, vehicle type, and even your credit score can influence the cost of your insurance premiums. However, with careful planning and research, you can navigate the process smoothly and secure the coverage you need.
Understanding Insurance and Residency

Car insurance is generally tied to your residency. This means your insurance policy is usually based on the state where you live. This principle ensures that you are covered by the laws and regulations of the state where you are driving.
State Laws and Insurance Coverage
State laws play a significant role in determining insurance coverage. Each state has its own regulations regarding:
- Minimum insurance requirements: These laws specify the minimum liability coverage you must have to legally drive in that state. The minimum requirements vary widely from state to state.
- Coverage options: Some states offer additional coverage options, such as uninsured motorist coverage, that may not be available in other states.
- Insurance rates: Factors like accident rates, population density, and other state-specific factors can influence insurance premiums.
Potential Issues When Insurance Doesn’t Match Residency
If your insurance policy doesn’t match your residency, you might face several issues:
- Invalid insurance: Your insurance policy may be deemed invalid if you are driving in a state where you are not a resident. This means you may not be covered in the event of an accident.
- Legal consequences: Driving without valid insurance can result in fines, license suspension, and other legal penalties.
- Higher premiums: Even if you can get coverage, you may be charged higher premiums because the insurer may consider you a higher risk.
Moving to a New State

Imagine you’re moving from California to Texas for a new job. You’ve got your boxes packed, your new apartment secured, and you’re ready for a fresh start. But what about your car insurance? You’ll need to make sure your car is covered in your new state.
This scenario highlights the common situation many people face when relocating. Getting car insurance in a new state involves several steps and considerations.
Steps to Obtain Insurance in a New State
It’s crucial to understand the process of getting car insurance in your new state. This ensures you’re properly covered and avoid any legal complications. Here are the key steps:
- Notify your current insurer: Inform your current insurer about your move and the date you’ll be leaving your old state. They might be able to provide coverage in your new state, or they might recommend an insurer in your new location.
- Research insurance providers in your new state: Explore different insurance companies in your new state to compare rates, coverage options, and customer service. Websites like Insurance.com or NerdWallet can help you compare quotes.
- Gather necessary information: Prepare your driver’s license, vehicle registration, and proof of address to provide to potential insurers. This information will help them assess your risk and provide accurate quotes.
- Get quotes and compare: Contact several insurance companies in your new state to get quotes. Compare the rates, coverage options, and discounts offered by each company.
- Choose a policy and pay your premium: Once you’ve selected the best option, you’ll need to sign up for the policy and pay your first premium. You might need to provide additional documentation, such as a copy of your lease or mortgage statement.
Challenges and Solutions
While obtaining car insurance in a new state is generally straightforward, some challenges might arise.
- Higher premiums: Depending on your new state’s insurance regulations, driving history, and the type of vehicle you own, your premiums might be higher than in your previous state. To address this, consider shopping around for quotes, exploring discounts offered by insurers, and opting for a higher deductible.
- Limited coverage options: Some insurers might not offer all the coverage options you had in your previous state. Research and compare coverage options offered by different insurers to ensure you have adequate protection.
- New state laws: Each state has its own set of car insurance laws, including minimum coverage requirements. Familiarize yourself with these laws to avoid any legal complications. You can find this information on your state’s Department of Motor Vehicles website.
Factors Influencing Insurance Costs: Can I Have Insurance On A Car In Another State
Car insurance premiums can vary significantly across different states. This is because insurance companies consider several factors when determining your rates. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your insurance coverage and potentially save money.
Factors Influencing Insurance Costs
Here are some key factors that can influence your car insurance premiums in different states:
| Factor | Description | Impact on Cost | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| State Laws and Regulations | Each state has its own laws and regulations regarding minimum insurance requirements, coverage limits, and other factors. | States with higher minimum insurance requirements or stricter regulations may have higher premiums. | For example, states with mandatory no-fault insurance laws, where drivers are responsible for their own injuries regardless of fault, may have higher premiums compared to states with tort liability systems. |
| Cost of Living | The cost of living in a particular state, including factors like housing costs, healthcare expenses, and wages, can influence insurance premiums. | States with a higher cost of living generally have higher insurance premiums due to higher repair costs and medical expenses. | For example, major metropolitan areas with high housing costs and traffic congestion tend to have higher insurance premiums than rural areas. |
| Driving Risk | Insurance companies assess the driving risk in a particular state based on factors like accident rates, traffic density, and the prevalence of uninsured drivers. | States with higher driving risk tend to have higher insurance premiums. | For example, states with high rates of drunk driving or distracted driving accidents may have higher premiums. |
| Demographics | Factors like age, gender, and driving history can influence insurance premiums. | Young drivers, especially those under 25, generally have higher premiums due to their higher risk of accidents. | For example, a state with a higher proportion of young drivers may have higher overall insurance premiums. |
| Competition | The level of competition among insurance companies in a particular state can impact premiums. | States with a more competitive insurance market may have lower premiums as companies compete for customers. | For example, states with a large number of insurance companies operating within their borders may have lower premiums. |
| Natural Disasters | States prone to natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, or floods, may have higher insurance premiums. | Insurance companies factor in the risk of natural disasters when setting premiums. | For example, states located along hurricane-prone coastlines may have higher premiums due to the risk of storm damage. |
| Vehicle Theft Rates | States with higher vehicle theft rates may have higher insurance premiums. | Insurance companies factor in the risk of theft when determining premiums. | For example, states with high concentrations of luxury vehicles or areas with high crime rates may have higher premiums. |
Navigating Insurance Transfer
Transferring your existing car insurance to a new state can seem daunting, but it’s a necessary step when relocating. This process involves informing your current insurer of your move and potentially adjusting your coverage to comply with the new state’s requirements.
Understanding the Transfer Process
The process of transferring your car insurance to a new state typically involves notifying your current insurer of your move and requesting a policy update. This might involve adjusting your coverage to comply with the new state’s minimum insurance requirements or making changes to your policy based on the new state’s driving laws.
Potential Complications During Transfer
Several factors can complicate the transfer process, including:
- State-Specific Requirements: Each state has unique insurance regulations, including minimum coverage levels, required coverage types, and policy terms. You may need to add or remove certain coverages to comply with your new state’s requirements.
- Insurance Company Coverage Areas: Not all insurance companies operate in every state. If your current insurer doesn’t have coverage in your new state, you’ll need to find a new insurer.
- Driving Record and Risk Factors: Your driving history, age, vehicle type, and other factors can influence your insurance rates in your new state. You might experience a rate increase or decrease depending on these factors.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Transferring Insurance
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the transfer process:
- Inform Your Current Insurer: Contact your current insurer as soon as you know your move date. Provide them with your new address and any other relevant details.
- Review Your Coverage: Your insurer will review your current coverage to ensure it meets the requirements of your new state. They may recommend changes or adjustments to your policy.
- Obtain a New Policy: Once your insurer has assessed your coverage needs, they will issue a new policy that reflects the requirements of your new state.
- Update Your Vehicle Registration: You’ll need to update your vehicle registration with your new state’s Department of Motor Vehicles. This typically involves providing proof of insurance and paying any applicable fees.
Insurance Options for Out-of-State Drivers

If you’re driving in a state where you don’t reside, you might need temporary insurance coverage. While your home state’s insurance policy might not cover you fully in another state, several temporary insurance options can provide the necessary protection. Let’s explore these options and their pros and cons.
Temporary Insurance Options, Can i have insurance on a car in another state
Temporary insurance options are designed for short-term needs, such as visiting another state for a vacation or business trip. They offer varying levels of coverage and can be purchased for a specific period, typically a few days, weeks, or months. Here’s a comparison of common temporary insurance options:
Non-Resident Insurance
Non-resident insurance is specifically designed for individuals who are not residents of the state but need to drive there. It typically covers liability and property damage, similar to a standard auto insurance policy.
- Pros: Offers comprehensive coverage for the duration of your stay, potentially including personal injury protection (PIP) and uninsured/underinsured motorist (UM/UIM) coverage.
- Cons: Can be more expensive than other temporary options, especially for longer durations. May require proof of residency in your home state.
Short-Term Insurance
Short-term insurance policies are often offered by insurance companies as a temporary solution for specific periods. They are typically available for a few days, weeks, or months.
- Pros: More affordable than non-resident insurance, especially for shorter durations. Can be purchased online or through an insurance agent.
- Cons: May have limited coverage compared to non-resident insurance. Not always available for longer durations.
Rental Car Insurance
Rental car insurance is often included with a rental car agreement, providing temporary coverage for the duration of your rental.
- Pros: Convenient and usually included with a rental car. Offers basic liability coverage.
- Cons: Limited coverage compared to non-resident insurance. May not cover personal injury or property damage.
Adding a Named Driver to an Existing Policy
If you have a family member or friend who lives in the state you’re visiting, you might be able to add yourself as a named driver to their existing insurance policy.
- Pros: Can be the most cost-effective option, especially for short visits. You’ll benefit from the coverage of the existing policy.
- Cons: Requires the cooperation of the policyholder and may not be possible for all situations.
Table Comparing Temporary Insurance Options
| Option | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Resident Insurance | Comprehensive coverage, potential for PIP and UM/UIM | More expensive, requires proof of residency |
| Short-Term Insurance | Affordable, convenient online purchase | Limited coverage, not available for long durations |
| Rental Car Insurance | Convenient, included with rental | Limited coverage, may not cover personal injury or property damage |
| Adding a Named Driver | Cost-effective, benefits from existing policy | Requires cooperation of policyholder, may not be possible for all situations |
Impact of Out-of-State Driving on Coverage
While your insurance policy covers you in your home state, driving in another state can potentially impact your coverage. Understanding how your policy operates in other states is crucial to ensure you’re adequately protected.
Potential Coverage Gaps
It’s important to understand that your insurance policy might not provide the same level of coverage in another state as it does in your home state. This is because each state has its own set of insurance regulations, which can differ significantly.
- Minimum Liability Coverage Requirements: States have different minimum liability insurance requirements. If you’re involved in an accident in a state with higher minimum requirements than your home state, your policy might not cover the full amount of damages. This means you could be personally liable for the difference.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: This coverage protects you in case you’re involved in an accident with a driver who doesn’t have insurance or has inadequate insurance. The limits of this coverage might vary between states, leaving you with potential gaps in protection.
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): PIP coverage helps pay for medical expenses and lost wages after an accident, regardless of fault. The availability and limits of PIP coverage can differ significantly between states.
Legal Implications
Driving without proper insurance in any state can have serious legal consequences. These consequences can range from fines and penalties to suspension of your driving privileges, and in some cases, even jail time.
Penalties and Fines
Understanding the potential penalties and fines associated with driving without insurance is crucial. The severity of these consequences can vary depending on the state, the specific violation, and the driver’s prior history. Here are some common penalties:
- Fines: These can range from a few hundred dollars to thousands of dollars, depending on the state and the severity of the violation.
- Suspension of Driving Privileges: Driving without insurance can lead to the suspension of your driver’s license, making it illegal to drive.
- Court Costs: You may also have to pay court costs, which can include fees for filing, processing, and court appearances.
- Vehicle Impoundment: In some cases, your vehicle may be impounded until you can provide proof of insurance.
- Jail Time: In certain situations, driving without insurance can result in jail time, especially if you are involved in an accident.
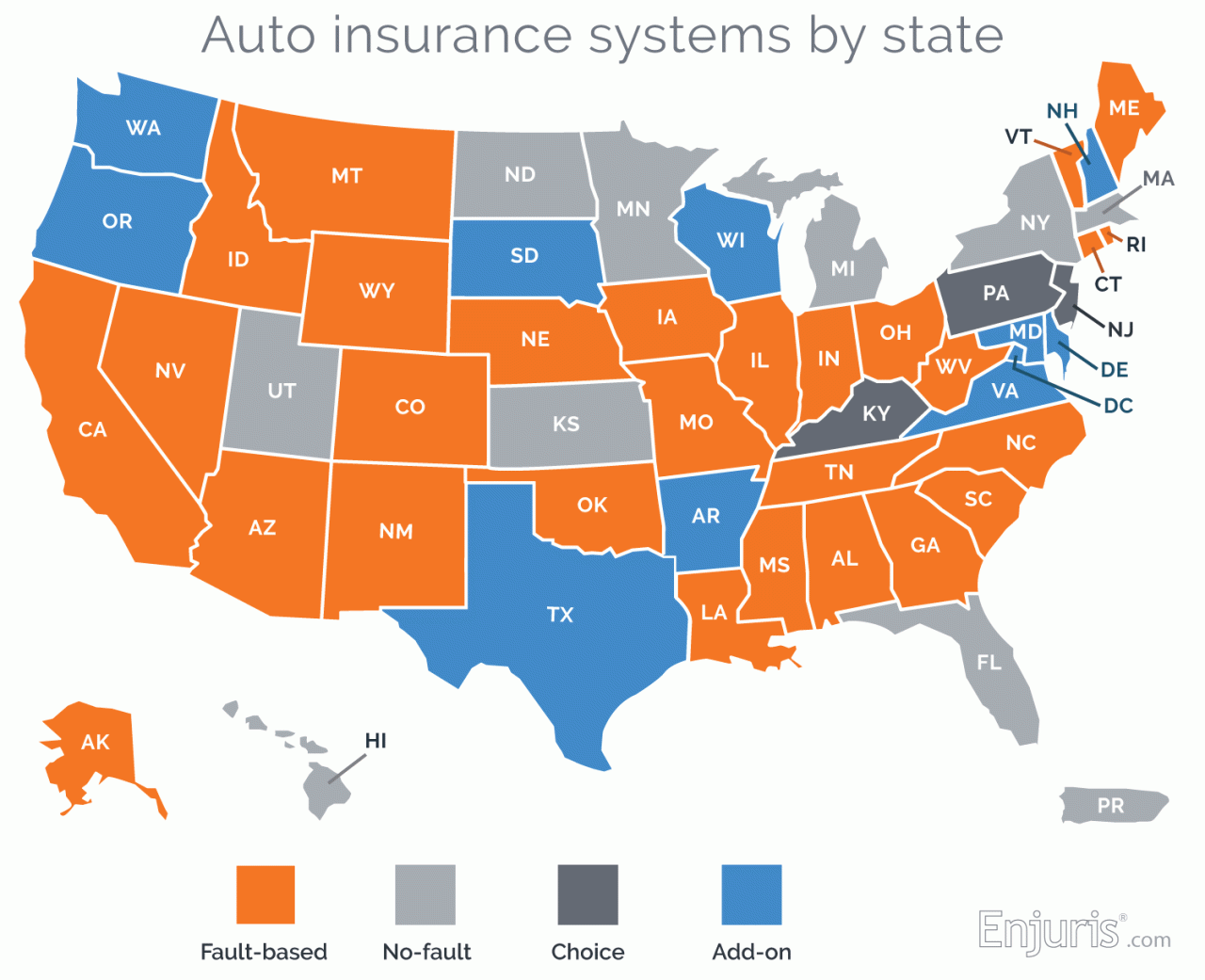
State-Specific Insurance Laws
Insurance laws vary significantly from state to state. Each state has its own minimum insurance requirements, which specify the minimum amount of coverage that drivers must have. Some states require drivers to carry liability insurance, while others require additional coverage, such as collision and comprehensive insurance. It’s important to understand the specific insurance requirements of the state you are driving in.
Last Point
Navigating car insurance across state lines can seem complex, but with a clear understanding of your options and the steps involved, it becomes manageable. Remember to consult with your insurance provider and research the specific regulations of the state you’re driving in. By taking the necessary precautions, you can ensure you have the appropriate coverage and avoid any legal consequences. Whether you’re moving, traveling, or simply driving through another state, knowing the ins and outs of car insurance can help you stay safe and protected on the road.
FAQ Compilation
What if I’m only driving through another state for a short period?
You may be covered under your existing policy for a limited time, but it’s crucial to check your policy terms and conditions. Some policies offer temporary coverage for out-of-state driving, while others may require additional coverage.
What if I’m moving to a new state and need to change my insurance?
Contact your current insurer and inform them about your move. They may be able to transfer your policy to the new state, or they may recommend a different insurer with better coverage options in your new location.
What documents do I need to provide when applying for car insurance in a new state?
You’ll likely need your driver’s license, proof of residency, vehicle registration, and your previous insurance information. Specific requirements can vary by state.