Auto insurance moving to another state is a common scenario for many individuals and families, but it can also be a confusing and overwhelming process. Navigating the complexities of state-specific insurance regulations, coverage options, and potential cost changes can be daunting. This comprehensive guide will provide you with the information and insights you need to ensure a smooth transition and secure the right auto insurance coverage in your new location.
From understanding the differences in state-specific auto insurance laws to finding the best possible rates in your destination state, we’ll cover all the essential aspects of moving your auto insurance. We’ll also address common mistakes to avoid and provide valuable resources to help you navigate this process with confidence.
Understanding State-Specific Auto Insurance Laws
Moving to a new state often means adjusting to different rules and regulations, and auto insurance is no exception. Every state has its own set of requirements and laws governing auto insurance, which can significantly impact the type of coverage you need and the cost of your premiums. It’s crucial to understand these differences to ensure you’re adequately protected on the road.
State-Specific Auto Insurance Requirements
Each state mandates certain types of auto insurance coverage, referred to as “minimum coverage.” These requirements are designed to protect you and other drivers in case of an accident. The specific types of coverage and their minimum limits vary widely from state to state. Here’s a comparison of mandatory coverage types in different states:
- Liability Coverage: This coverage protects you financially if you cause an accident that injures someone or damages their property. Liability coverage typically includes two parts:
- Bodily Injury Liability: Covers medical expenses, lost wages, and pain and suffering for injuries caused to others.
- Property Damage Liability: Covers repairs or replacement costs for damage to another person’s vehicle or property.
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): This coverage, also known as “no-fault insurance,” pays for your medical expenses and lost wages, regardless of who caused the accident. PIP coverage is mandatory in some states, while others offer it as an optional add-on.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage (UM/UIM): This coverage protects you if you’re involved in an accident with a driver who doesn’t have insurance or has insufficient coverage. It helps cover your medical expenses and lost wages, as well as damages to your vehicle.
- Collision Coverage: This coverage pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle if it’s damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. Collision coverage is often optional, but it’s usually a good idea to have it, especially if you have a newer vehicle.
- Comprehensive Coverage: This coverage pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle if it’s damaged by something other than a collision, such as theft, vandalism, fire, or natural disasters. Like collision coverage, comprehensive coverage is typically optional.
Examples of State-Specific Insurance Laws
Here are some examples of state-specific insurance laws that can impact your coverage:
- No-Fault Laws: Some states have “no-fault” insurance laws, which mean that you file a claim with your own insurance company, regardless of who caused the accident. These laws are designed to speed up the claims process and reduce litigation. For example, Florida, Michigan, and New York have no-fault insurance systems.
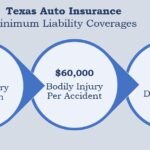
- Financial Responsibility Laws: Most states have financial responsibility laws that require drivers to prove they can pay for damages they cause in an accident. This can be done by carrying auto insurance or providing a certificate of self-insurance. The specific requirements vary by state. For example, in Texas, drivers must carry a minimum of $30,000 in liability coverage per person and $60,000 per accident.
- Deductible Requirements: Some states have specific deductible requirements for certain types of coverage, such as collision or comprehensive. A deductible is the amount you pay out of pocket before your insurance company starts covering the costs. For example, in California, drivers must have a deductible of no more than $1,000 for collision coverage.
- Insurance Rate Regulations: States also have different regulations regarding how insurance companies can set their rates. Some states have strict rate regulations, while others allow insurers more flexibility. For example, in Massachusetts, insurance companies must use a “merit rating” system, which means that drivers with good driving records pay lower premiums. In other states, insurers can use a wider range of factors to determine rates, such as age, gender, and credit score.
The Impact of Moving on Existing Policies
Moving to a new state can significantly impact your existing auto insurance policy. Understanding how your policy will be affected is crucial to ensure you have the right coverage and avoid any unexpected surprises.
Notifying Your Insurance Provider
It’s essential to inform your current insurance provider about your move as soon as possible. This will allow them to assess the new state’s requirements and adjust your policy accordingly. You can typically notify them by phone, email, or through their online portal.
Most insurance companies require you to notify them within 30 days of your move.
Potential Changes to Your Policy
Your move could lead to changes in your existing policy, including:
Coverage
- Minimum Coverage Requirements: Each state has different minimum coverage requirements for auto insurance. Your current policy might not meet the new state’s requirements, requiring you to increase your coverage. For example, some states require higher liability limits than others.
- Available Coverage Options: The types of coverage available in your new state might differ from your current state. For instance, your new state might offer additional coverage options like personal injury protection (PIP) or uninsured motorist coverage (UM) that weren’t available in your previous state.
Premium
- Risk Factors: Your premium might change based on factors like the new state’s accident rates, the cost of living, and the availability of repair shops. For example, if your new state has a higher cost of living, you might see an increase in your premium.
- Driving History: Your driving history is a significant factor in determining your premium. While your driving record remains the same, the new state’s insurance companies might use different rating systems or assign different weights to specific violations, potentially affecting your premium.
- Vehicle Value: The value of your vehicle can also influence your premium. If your vehicle is worth more in your new state, you might see an increase in your premium.
Finding New Auto Insurance in Your Destination State
Once you’ve moved to your new state, you’ll need to find a new auto insurance policy that meets your needs and budget. This can seem daunting, but it’s a crucial step in ensuring you’re properly protected on the road.
Factors Influencing Auto Insurance Premiums
The cost of auto insurance varies significantly from state to state. Several factors contribute to this variation, and understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your insurance coverage.
- State Laws and Regulations: Each state has its own set of laws and regulations governing auto insurance, including minimum coverage requirements and how insurers are allowed to calculate premiums. States with stricter laws or higher minimum coverage requirements generally have higher average premiums.
- Driving Habits and Risks: The number of accidents, traffic violations, and claims in a particular state can influence insurance rates. States with higher rates of accidents or risky driving behaviors tend to have higher premiums.
- Cost of Living and Vehicle Repair: The cost of living, including the cost of vehicle repair and replacement parts, can affect insurance premiums. States with higher costs of living and vehicle repair expenses generally have higher premiums.
- Competition in the Insurance Market: The level of competition among insurance companies in a state can influence premiums. States with a more competitive market may have lower premiums due to insurers vying for customers.
Comparing Auto Insurance Providers
Comparing quotes from different insurers is crucial to finding the best rates and coverage for your needs. Here’s how to approach the process:
- Use Online Comparison Tools: Many websites and apps allow you to compare quotes from multiple insurers simultaneously. These tools can save you time and effort. Make sure you’re comparing quotes based on the same coverage levels and deductibles for a fair comparison.
- Contact Insurers Directly: While online comparison tools are helpful, it’s also beneficial to contact insurers directly to discuss your specific needs and ask questions. This allows you to get personalized quotes and gain a better understanding of each insurer’s policies and services.
- Review Coverage Options Carefully: Don’t just focus on the cheapest option. Ensure you’re getting adequate coverage for your needs, considering factors like the value of your vehicle, your driving history, and your personal financial situation. Remember that inadequate coverage can lead to significant financial hardship in case of an accident.
Tips for Getting the Best Possible Rates
There are several strategies you can use to potentially lower your auto insurance premiums:
- Maintain a Good Driving Record: Avoid traffic violations and accidents, as these can significantly increase your premiums. A clean driving record can earn you discounts.
- Increase Your Deductible: A higher deductible means you’ll pay more out of pocket in case of an accident, but it can lower your premium. Choose a deductible that you can comfortably afford while balancing the potential cost savings.
- Bundle Your Policies: Many insurers offer discounts if you bundle your auto insurance with other policies, such as homeowners or renters insurance. Combining policies can save you money in the long run.
- Shop Around Regularly: Insurance rates can fluctuate, so it’s essential to shop around for new quotes regularly, even if you’re happy with your current insurer. This can help you ensure you’re getting the best possible rates.
- Ask About Discounts: Insurers often offer discounts for various factors, such as good student status, safe driver courses, and anti-theft devices. Make sure to inquire about any discounts you might qualify for.
Understanding Coverage Options in the New State

When you move to a new state, it’s essential to understand the auto insurance coverage options available and how they differ from your current policy. State laws vary significantly, and your existing policy may not meet the new state’s minimum requirements or offer the level of protection you need.
Comparing Coverage Options
It’s crucial to compare the coverage options available in your new state with your current policy. Some common coverage types include:
- Liability Coverage: This covers damages to other people and their property if you’re at fault in an accident. The minimum liability limits required by each state vary, so make sure your new policy meets the new state’s requirements.
- Collision Coverage: This covers damage to your vehicle in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. You’ll have to pay a deductible, but the insurance company will cover the remaining costs. If you’re financing your vehicle, your lender may require you to have collision coverage.
- Comprehensive Coverage: This covers damage to your vehicle from events other than accidents, such as theft, vandalism, or natural disasters. It’s usually optional, but it can be helpful if you live in an area prone to these events.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: This protects you if you’re involved in an accident with a driver who doesn’t have insurance or doesn’t have enough insurance to cover your damages. It’s a good idea to have this coverage, especially in states with a high number of uninsured drivers.
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): This coverage helps pay for medical expenses, lost wages, and other expenses if you’re injured in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. Some states require PIP coverage, while others offer it as an option.
Adjusting Your Coverage
Review your current policy and compare it to the coverage options available in your new state. You may need to adjust your coverage to meet the new state’s minimum requirements or to get the level of protection you need. For example, if you move to a state with higher minimum liability limits, you’ll need to increase your liability coverage. If you move to an area with a high risk of theft, you may want to consider adding comprehensive coverage.
Additional Coverage Options
Some states offer additional coverage options that may be relevant in your new location. For example:
- Rental Reimbursement: This coverage helps pay for a rental car if your vehicle is damaged in an accident or is being repaired.
- Roadside Assistance: This coverage provides assistance with services like towing, flat tire changes, and jump starts.
- Gap Insurance: This coverage helps pay the difference between the actual cash value of your vehicle and the amount you owe on your loan if your vehicle is totaled.
Potential Savings and Cost Considerations
Moving to a new state can significantly impact your auto insurance premiums. While you might be excited about a fresh start, it’s important to understand how your insurance costs could change. Let’s explore the factors that influence your premiums and how you can potentially save money.
Factors Affecting Insurance Costs
Your auto insurance premiums in your new state will be influenced by a variety of factors, including:
- Driving History: Your driving record is a major factor. A clean record with no accidents or violations will likely result in lower premiums. However, if you have a history of accidents or traffic tickets, you might face higher premiums.
- Vehicle Type: The type of vehicle you drive also plays a role. High-performance vehicles, luxury cars, or expensive SUVs tend to have higher insurance premiums due to their repair costs and potential for theft.
- Location: Where you live in your new state can significantly impact your insurance costs. Areas with high crime rates, traffic congestion, or a higher frequency of accidents often have higher premiums.
- Age and Gender: Your age and gender can also influence your premiums. Younger drivers, especially those under 25, generally have higher premiums due to their higher risk profile.
- Coverage Options: The type and amount of coverage you choose will impact your premiums. Higher coverage limits, such as comprehensive and collision, will generally lead to higher premiums.
Tips for Minimizing Insurance Costs
While you can’t always control factors like your driving history or vehicle type, there are strategies you can implement to potentially lower your insurance premiums in your new state:
- Shop Around: Don’t settle for the first insurance quote you receive. Compare quotes from multiple insurers to find the best rates. Use online comparison tools or contact insurance agents directly.
- Bundle Your Policies: If you have other insurance policies, such as homeowners or renters insurance, consider bundling them with your auto insurance. Many insurers offer discounts for bundling multiple policies.
- Ask About Discounts: Inquire about potential discounts that may be available to you, such as good driver discounts, safe driver discounts, or discounts for having safety features in your vehicle.
- Maintain a Clean Driving Record: Avoid traffic violations and accidents to keep your premiums low.
- Consider Higher Deductibles: Choosing a higher deductible can help reduce your monthly premiums. However, make sure you can afford to pay the deductible if you have an accident.
- Review Your Coverage Regularly: As your needs change, review your coverage to ensure you have the right amount of protection. You may be able to reduce your coverage and save money if your needs have changed.
Important Documents and Procedures: Auto Insurance Moving To Another State
Moving to a new state involves more than just packing your belongings. It also requires you to update your auto insurance policy to comply with the new state’s regulations. This process involves gathering essential documents, canceling your existing policy, and obtaining new coverage.
Essential Documents
To ensure a smooth transition, you’ll need to gather specific documents.
- Driver’s License: Your driver’s license must be valid in your new state. If it’s not, you’ll need to obtain a new one.
- Vehicle Registration: Your vehicle registration should also be updated to reflect your new address.
- Proof of Insurance: You’ll need proof of insurance from your previous insurer to show your new insurance provider.
- Previous Insurance Policy Details: This includes your policy number, coverage details, and any claims history.
Canceling Your Existing Policy, Auto insurance moving to another state
Once you have your new insurance policy in place, you need to cancel your existing policy.
- Contact Your Current Insurer: Inform your current insurer about your move and the date you’ll be leaving your old state. Be sure to provide them with your new address.
- Request a Cancellation Confirmation: Ask for a written confirmation of your policy cancellation and any potential refunds due to you.
Obtaining New Coverage
Finding new auto insurance in your destination state is essential for legal driving.
- Research Insurance Providers: Compare quotes from different insurance providers in your new state to find the best rates and coverage options.
- Provide Accurate Information: When applying for new insurance, be honest and accurate with the new provider. This includes details about your driving history, vehicle, and any other relevant information.
- Obtain Proof of Insurance: Once your new policy is in place, request a copy of your proof of insurance. This is essential for legal driving in your new state.
Common Mistakes to Avoid

Moving to a new state can be exciting, but it’s crucial to avoid common mistakes when dealing with auto insurance. Failing to properly address your insurance needs can lead to unexpected costs, gaps in coverage, and legal complications. This section will highlight common pitfalls and offer solutions to ensure a smooth transition.
Forgetting to Notify Your Current Insurer
It’s essential to inform your current insurer about your move. Failing to do so could lead to policy cancellation or coverage gaps. Your existing insurer might not be able to provide coverage in your new state, requiring you to find a new provider.
Failing to notify your insurer about your move can result in your policy being canceled, leaving you without coverage.
Delaying the Search for New Insurance
Procrastinating on finding new insurance in your destination state can result in a lapse in coverage, leaving you vulnerable. This could lead to fines or penalties if you’re involved in an accident during this period.
It’s advisable to start researching insurance options in your new state well in advance of your move to ensure a seamless transition.
Not Understanding New State Laws
Every state has unique auto insurance requirements. Ignoring these differences can lead to legal complications, fines, or inadequate coverage. For example, some states require higher minimum liability coverage than others.
Familiarizing yourself with the specific auto insurance laws in your new state is crucial to avoid legal issues and ensure adequate coverage.
Not Comparing Quotes from Multiple Insurers
Sticking with your current insurer without exploring other options might mean missing out on better rates and coverage. Comparing quotes from multiple insurers allows you to find the best value for your needs.
Comparing quotes from various insurers in your new state can help you secure the most competitive rates and coverage options.
Failing to Consider All Coverage Options
Auto insurance policies offer a variety of coverage options, and not considering all of them might leave you underinsured. For example, you might need additional coverage for comprehensive or collision damage, especially if you’re driving a newer vehicle.
Carefully review all coverage options offered by insurers in your new state to ensure you have adequate protection for your vehicle and financial well-being.
Overlooking Discounts
Insurers often offer discounts for various factors, such as good driving records, safety features in your vehicle, and multiple policy bundling. Failing to inquire about available discounts could lead to paying higher premiums.
Don’t hesitate to ask about potential discounts when obtaining quotes from insurers.
Not Reviewing Your Policy Regularly
Once you’ve settled in your new state, it’s crucial to review your policy periodically to ensure it still meets your needs. Your insurance needs might change over time, requiring adjustments to your coverage.
Regularly review your auto insurance policy to make sure it’s still adequate for your current situation and consider adjusting coverage if necessary.
Additional Resources and Information

Navigating the world of auto insurance can be complex, especially when moving to a new state. To help you find the right coverage and make informed decisions, we’ve compiled a list of resources and information.
State-Specific Insurance Regulatory Websites
These websites offer valuable information about auto insurance requirements, regulations, and consumer protection in your new state.
- Alabama: Alabama Department of Insurance: [Link to Alabama Department of Insurance website]
- Alaska: Alaska Division of Insurance: [Link to Alaska Division of Insurance website]
- Arizona: Arizona Department of Insurance: [Link to Arizona Department of Insurance website]
- Arkansas: Arkansas Department of Insurance: [Link to Arkansas Department of Insurance website]
- California: California Department of Insurance: [Link to California Department of Insurance website]
- Colorado: Colorado Division of Insurance: [Link to Colorado Division of Insurance website]
- Connecticut: Connecticut Insurance Department: [Link to Connecticut Insurance Department website]
- Delaware: Delaware Department of Insurance: [Link to Delaware Department of Insurance website]
- Florida: Florida Office of Insurance Regulation: [Link to Florida Office of Insurance Regulation website]
- Georgia: Georgia Department of Insurance: [Link to Georgia Department of Insurance website]
- Hawaii: Hawaii Department of Commerce and Consumer Affairs, Insurance Division: [Link to Hawaii Department of Commerce and Consumer Affairs, Insurance Division website]
- Idaho: Idaho Department of Insurance: [Link to Idaho Department of Insurance website]
- Illinois: Illinois Department of Insurance: [Link to Illinois Department of Insurance website]
- Indiana: Indiana Department of Insurance: [Link to Indiana Department of Insurance website]
- Iowa: Iowa Insurance Division: [Link to Iowa Insurance Division website]
- Kansas: Kansas Insurance Department: [Link to Kansas Insurance Department website]
- Kentucky: Kentucky Department of Insurance: [Link to Kentucky Department of Insurance website]
- Louisiana: Louisiana Department of Insurance: [Link to Louisiana Department of Insurance website]
- Maine: Maine Bureau of Insurance: [Link to Maine Bureau of Insurance website]
- Maryland: Maryland Insurance Administration: [Link to Maryland Insurance Administration website]
- Massachusetts: Massachusetts Division of Insurance: [Link to Massachusetts Division of Insurance website]
- Michigan: Michigan Department of Insurance and Financial Services: [Link to Michigan Department of Insurance and Financial Services website]
- Minnesota: Minnesota Department of Commerce, Insurance Division: [Link to Minnesota Department of Commerce, Insurance Division website]
- Mississippi: Mississippi Department of Insurance: [Link to Mississippi Department of Insurance website]
- Missouri: Missouri Department of Commerce and Insurance: [Link to Missouri Department of Commerce and Insurance website]
- Montana: Montana Department of Insurance: [Link to Montana Department of Insurance website]
- Nebraska: Nebraska Department of Insurance: [Link to Nebraska Department of Insurance website]
- Nevada: Nevada Division of Insurance: [Link to Nevada Division of Insurance website]
- New Hampshire: New Hampshire Insurance Department: [Link to New Hampshire Insurance Department website]
- New Jersey: New Jersey Department of Banking and Insurance: [Link to New Jersey Department of Banking and Insurance website]
- New Mexico: New Mexico Superintendent of Insurance: [Link to New Mexico Superintendent of Insurance website]
- New York: New York State Department of Financial Services: [Link to New York State Department of Financial Services website]
- North Carolina: North Carolina Department of Insurance: [Link to North Carolina Department of Insurance website]
- North Dakota: North Dakota Insurance Department: [Link to North Dakota Insurance Department website]
- Ohio: Ohio Department of Insurance: [Link to Ohio Department of Insurance website]
- Oklahoma: Oklahoma Insurance Department: [Link to Oklahoma Insurance Department website]
- Oregon: Oregon Department of Consumer and Business Services, Insurance Division: [Link to Oregon Department of Consumer and Business Services, Insurance Division website]
- Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania Insurance Department: [Link to Pennsylvania Insurance Department website]
- Rhode Island: Rhode Island Department of Business Regulation, Division of Insurance: [Link to Rhode Island Department of Business Regulation, Division of Insurance website]
- South Carolina: South Carolina Department of Insurance: [Link to South Carolina Department of Insurance website]
- South Dakota: South Dakota Department of Insurance: [Link to South Dakota Department of Insurance website]
- Tennessee: Tennessee Department of Commerce & Insurance: [Link to Tennessee Department of Commerce & Insurance website]
- Texas: Texas Department of Insurance: [Link to Texas Department of Insurance website]
- Utah: Utah Insurance Department: [Link to Utah Insurance Department website]
- Vermont: Vermont Department of Financial Regulation: [Link to Vermont Department of Financial Regulation website]
- Virginia: Virginia Bureau of Insurance: [Link to Virginia Bureau of Insurance website]
- Washington: Washington Insurance Commissioner: [Link to Washington Insurance Commissioner website]
- West Virginia: West Virginia Department of Insurance: [Link to West Virginia Department of Insurance website]
- Wisconsin: Wisconsin Office of the Commissioner of Insurance: [Link to Wisconsin Office of the Commissioner of Insurance website]
- Wyoming: Wyoming Insurance Department: [Link to Wyoming Insurance Department website]
Auto Insurance Comparison Websites
These websites allow you to compare quotes from multiple insurance providers, helping you find the best rates and coverage options.
- Insurance.com: [Link to Insurance.com website]
- The Zebra: [Link to The Zebra website]
- QuoteWizard: [Link to QuoteWizard website]
- Policygenius: [Link to Policygenius website]
- Bankrate: [Link to Bankrate website]
Consumer Protection Agencies
If you encounter any issues with your auto insurance, these agencies can provide assistance and guidance.
- National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC): [Link to NAIC website]
- Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB): [Link to CFPB website]
- Your State’s Department of Insurance: [Link to your state’s Department of Insurance website]
Final Conclusion
Moving your auto insurance to another state doesn’t have to be a stressful experience. By following the tips and advice Artikeld in this guide, you can ensure a smooth transition and secure the best possible coverage for your needs. Remember to research and compare different providers, understand your state’s specific requirements, and prioritize accurate communication with both your current and new insurance companies. With careful planning and preparation, you can confidently navigate the process and enjoy peace of mind on the road.
Answers to Common Questions
What happens to my current auto insurance policy when I move?
Your current policy will likely remain in effect until its expiration date, but you’ll need to notify your insurer about your move to ensure continuous coverage. You may need to update your policy based on the new state’s requirements.
How do I find the best auto insurance rates in my new state?
Use online comparison tools, contact multiple insurance providers directly, and consider factors like driving history, vehicle type, and coverage options. It’s also a good idea to shop around and compare quotes before making a decision.
What documents do I need to switch auto insurance providers?
You’ll typically need your driver’s license, vehicle registration, proof of insurance, and any other documentation requested by the new insurer. Be sure to gather all necessary paperwork before contacting the new provider.
Can I keep my current auto insurance policy after moving?
In some cases, your current insurer may offer coverage in your new state. However, it’s important to check with your insurer to confirm if they operate in your new location and whether your current policy meets the new state’s requirements.