Are there any states that don’t require auto insurance? This question sparks curiosity, especially for those who value financial security and peace of mind. Navigating the complex world of auto insurance regulations, we delve into the diverse landscape of state laws, uncovering the intricacies of mandatory insurance requirements and exploring the potential consequences of driving without coverage.
Understanding the rationale behind these laws, we analyze the various factors influencing state-specific requirements, such as public safety, financial responsibility, and the need to protect drivers and victims of accidents. We also examine the potential risks and challenges associated with driving without insurance, highlighting the importance of responsible driving practices and adherence to legal obligations.
States with Mandatory Auto Insurance: Are There Any States That Don’t Require Auto Insurance
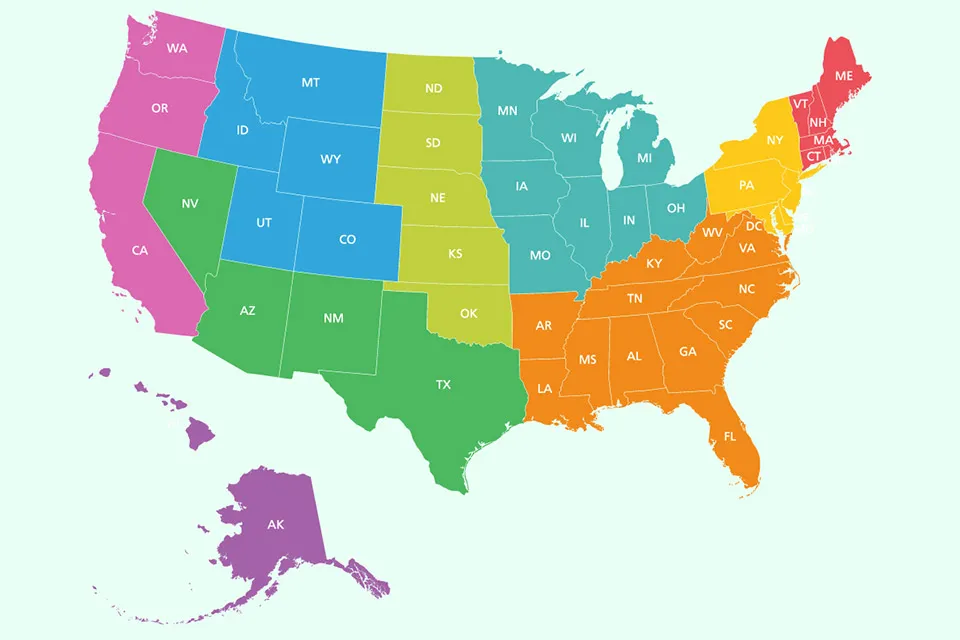
In the United States, all states except New Hampshire require drivers to carry auto insurance. This requirement is designed to protect both drivers and the public from financial hardship in the event of an accident.
Rationale for Mandatory Auto Insurance Laws
Mandatory auto insurance laws are designed to ensure that drivers have financial resources to cover the costs associated with accidents, including:
- Medical Expenses: Insurance covers the cost of medical treatment for injuries sustained in an accident, including hospitalization, surgery, and rehabilitation.
- Property Damage: Insurance covers the cost of repairs or replacement of damaged vehicles and other property involved in an accident.
- Liability Coverage: Insurance provides protection against lawsuits filed by individuals injured or whose property is damaged in an accident.
Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without insurance in a state that mandates it can result in severe consequences, including:
- Fines and Penalties: Drivers caught driving without insurance face substantial fines and penalties, which can vary significantly depending on the state and the number of offenses.
- License Suspension or Revocation: Driving without insurance can lead to the suspension or revocation of driving privileges, making it impossible to legally operate a vehicle.
- Impoundment of Vehicle: In some states, authorities may impound the vehicle of a driver caught operating without insurance.
- Financial Responsibility: Even if a driver is not directly at fault in an accident, they may be held financially responsible for all damages if they are uninsured.
- Jail Time: In some states, driving without insurance can be a criminal offense, leading to potential jail time.
States with Limited or No Mandatory Auto Insurance
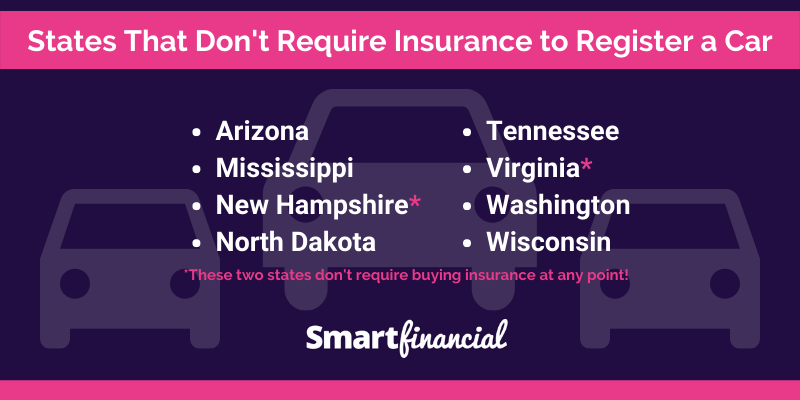
While most states in the U.S. mandate auto insurance, a few states have limited or no mandatory requirements. These states typically have alternative financial responsibility laws that require drivers to demonstrate proof of financial responsibility in case of an accident, even if they don’t have traditional insurance.
States with Limited or No Mandatory Auto Insurance
The following states have limited or no mandatory auto insurance requirements:
- New Hampshire: New Hampshire is the only state in the U.S. that does not require drivers to have auto insurance. However, drivers must demonstrate financial responsibility by posting a bond or surety, or by proving they have sufficient assets to cover potential liabilities. This option is known as “financial responsibility law.”
- Virginia: Virginia requires drivers to have liability insurance, but it allows drivers to opt out of collision and comprehensive coverage. This means drivers can choose to only have liability coverage, which protects others in case of an accident but does not cover damage to their own vehicle.
Conditions for Exemption from Insurance Requirements
In states with limited or no mandatory auto insurance, drivers may be exempt from insurance requirements under specific conditions. These conditions vary by state but typically include:
- Financial Responsibility: As mentioned above, drivers may be exempt from insurance requirements if they can demonstrate financial responsibility through alternative means, such as posting a bond or surety or proving they have sufficient assets to cover potential liabilities. This is often a requirement in states that have “financial responsibility laws.”
- Historical Driving Record: Some states may exempt drivers with a clean driving record for a certain period, typically a few years, from insurance requirements. This exemption may be available only for certain types of vehicles, such as classic cars or motorcycles.
- Membership in a Self-Insurance Plan: Some states may allow drivers to join self-insurance plans that provide financial protection in case of an accident. These plans typically require members to pay premiums and contribute to a pool of funds that is used to cover claims.
Risks and Challenges of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without insurance in states that do not require it presents several risks and challenges:
- Financial Ruin: In the event of an accident, drivers without insurance could be held personally liable for all damages, including medical bills, property damage, and legal fees. This could lead to significant financial hardship, including bankruptcy.
- License Suspension: Even in states that do not require insurance, drivers may face license suspension or other penalties if they are involved in an accident and cannot prove financial responsibility.
- Limited Access to Coverage: Drivers who choose not to have insurance may find it difficult to obtain coverage in the future, especially if they have a history of accidents or traffic violations.
- Increased Risk of Accidents: Studies have shown that drivers without insurance are more likely to be involved in accidents. This is likely due to a lack of financial responsibility and the potential for drivers to take more risks when they know they are not financially protected.
Financial Responsibility Laws

Financial responsibility laws are designed to ensure that drivers have the financial means to cover the costs of damages or injuries they may cause in an accident. These laws require drivers to prove they can pay for potential liabilities, usually through auto insurance, but can also include other financial means.
Types of Financial Responsibility Laws
Financial responsibility laws vary by state, with different requirements and enforcement mechanisms. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
- Financial Responsibility Requirement: These laws mandate drivers to prove their financial responsibility by providing proof of insurance, surety bonds, or other financial instruments. This ensures drivers have the means to cover potential liabilities.
- Compulsory Insurance Laws: These laws require all drivers to maintain a minimum level of liability insurance coverage. These laws are the most common, ensuring drivers are insured against potential financial losses resulting from accidents.
- No-Fault Insurance Laws: These laws require drivers to be insured for their own medical expenses and lost wages, regardless of who is at fault in an accident. This simplifies the claims process and reduces litigation.
- Unsatisfied Judgment Funds: These funds are established by states to compensate accident victims when the responsible driver is uninsured or financially insolvent. This provides a safety net for victims who might otherwise be left without compensation.
Exceptions to Auto Insurance Requirements
While most states mandate auto insurance, there are certain exceptions to these requirements. These exceptions are often tied to specific situations, vehicle types, or driving purposes. It’s important to understand these exceptions as driving without insurance can lead to severe consequences, including fines, license suspension, and even jail time.
Vehicles Exempt from Insurance Requirements
In some states, certain types of vehicles may be exempt from mandatory insurance requirements. This typically applies to vehicles that are not driven on public roads or used for specific purposes.
- Antique or Classic Cars: Many states have exemptions for vehicles classified as antique or classic cars that are primarily used for display or occasional driving in parades or special events. However, these exemptions often come with specific conditions, such as age and usage restrictions. For instance, some states might require antique cars to be insured for liability coverage while being transported on a trailer or towed by another vehicle.
- Farm Vehicles: Vehicles used solely for agricultural purposes on private property might be exempt from insurance requirements. These exemptions often apply to tractors, combines, and other farm equipment that are not driven on public roads.
- Construction Equipment: Heavy construction equipment, such as bulldozers, excavators, and cranes, may be exempt from insurance requirements if they are used solely on private construction sites and not driven on public roads. However, it’s important to note that even if exempt from insurance, owners might still be held liable for damages caused by their equipment.
Driving for Specific Purposes
In some states, drivers may be exempt from insurance requirements for specific driving purposes, such as driving to a mechanic or for a short distance.
- Driving to a Mechanic: Some states allow drivers to drive uninsured to a mechanic for repairs or maintenance. This exemption is often limited to a short distance and may require proof of an appointment with a licensed mechanic. The exemption may also require that the vehicle is driven directly to the mechanic and not for any other purpose.
- Driving for Short Distances: Some states allow drivers to drive uninsured for short distances, such as to a nearby store or for a brief errand. However, these exemptions are typically limited to very short distances and may require that the driver has valid insurance for their other vehicles.
The Impact of No-Fault Insurance Laws
No-fault insurance laws are a unique approach to handling auto insurance claims that shift the focus from fault determination to providing coverage for injured parties, regardless of who caused the accident. These laws aim to simplify the claims process, reduce litigation, and potentially lower insurance premiums.
The Concept of No-Fault Insurance Laws
No-fault insurance laws establish a system where drivers are required to carry personal injury protection (PIP) coverage, which pays for their own medical expenses, lost wages, and other related costs, regardless of who caused the accident. In a no-fault system, drivers file claims with their own insurance company, rather than pursuing a lawsuit against the other driver.
Benefits of No-Fault Insurance Laws
- Faster Claims Processing: No-fault systems typically streamline the claims process, as drivers file claims with their own insurer, eliminating the need for lengthy investigations and potential disputes over fault. This can lead to quicker payouts for medical expenses and other costs.
- Reduced Litigation: By shifting the focus from fault to coverage, no-fault laws can significantly reduce the number of lawsuits arising from auto accidents. This can save time, money, and resources for both individuals and the legal system.
- Lower Insurance Premiums: The potential for reduced litigation and administrative costs associated with no-fault systems can lead to lower insurance premiums for drivers.
Drawbacks of No-Fault Insurance Laws
- Limited Compensation: In some cases, no-fault laws may limit the amount of compensation available to drivers for certain types of damages, such as pain and suffering. This can be a concern for drivers who have sustained serious injuries.
- Increased Premiums for High-Risk Drivers: No-fault laws can incentivize high-risk drivers to file more claims, potentially leading to higher premiums for all drivers.
- Potential for Abuse: There is a potential for abuse in no-fault systems, as drivers may be tempted to inflate their claims or file fraudulent claims.
Impact on Auto Insurance Requirements in Different States
No-fault insurance laws have varying impacts on auto insurance requirements in different states. Some states have adopted a pure no-fault system, while others have implemented a modified no-fault system, which allows drivers to sue for damages in certain situations, such as when the injuries are severe. For example, in Michigan, a pure no-fault system is in place, while in Florida, a modified no-fault system is implemented. These variations reflect the different priorities and approaches to auto insurance regulation in different states.
Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without auto insurance is a serious offense in most states, and it can lead to a variety of consequences, including fines, penalties, and license suspension. In addition, driving without insurance can leave you financially vulnerable if you are involved in an accident.
Potential Consequences of Driving Without Insurance, Are there any states that don’t require auto insurance
Driving without insurance can have serious consequences, including:
- Fines: You can be fined for driving without insurance. The amount of the fine varies by state, but it can be substantial.
- Penalties: You may also face other penalties, such as having your license suspended or revoked.
- License Suspension: Driving without insurance can lead to your driver’s license being suspended or revoked, depending on the state.
- Financial Liabilities: If you are involved in an accident while driving without insurance, you will be personally liable for any damages or injuries caused. This can include medical bills, property damage, and legal fees.
- Legal Repercussions: Driving without insurance can also lead to legal repercussions, such as being sued by the other party involved in the accident.
Financial Liabilities and Legal Repercussions
Driving without insurance can result in significant financial liabilities and legal repercussions. If you are involved in an accident, you could be held responsible for:
- Medical Bills: If you injure someone in an accident, you will be responsible for their medical bills.
- Property Damage: You will also be responsible for any damage to the other person’s vehicle or property.
- Lost Wages: If the other person is unable to work due to injuries, you may be responsible for their lost wages.
- Pain and Suffering: In some cases, you may be held liable for the other person’s pain and suffering.
- Legal Fees: You will also be responsible for your own legal fees.
State-Specific Consequences
The consequences of driving without insurance vary by state. Here is a table showing the potential consequences in some states:
| State | Fine | Penalty | License Suspension |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | $1,000 | License suspension | Up to 6 months |
| Florida | $150 – $500 | License suspension | Up to 3 years |
| New York | $500 | License suspension | Up to 90 days |
| Texas | $175 – $350 | License suspension | Up to 6 months |
Concluding Remarks
While some states may offer exceptions or have limited mandatory insurance requirements, the general consensus remains clear: driving without insurance poses significant risks. It’s essential to understand the specific laws in your state and ensure you have adequate coverage to protect yourself and others.
FAQ Explained
What are the benefits of having auto insurance?
Auto insurance provides financial protection against potential costs associated with accidents, such as medical expenses, property damage, and legal fees. It also helps cover your own vehicle repairs or replacement.
What happens if I get into an accident without insurance?
You could face significant financial and legal repercussions, including fines, penalties, license suspension, and even jail time. You may also be held personally liable for any damages or injuries caused.
Can I get insurance if I have a poor driving record?
Yes, but you may have to pay higher premiums. Insurance companies assess your driving history and other factors to determine your risk level and adjust your rates accordingly.