A state insurance plays a crucial role in the economic landscape, providing a safety net for individuals and businesses. From health and auto to workers’ compensation and unemployment benefits, state-run programs offer essential protection against unforeseen circumstances.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of state insurance, exploring its regulation, market dynamics, consumer considerations, and future prospects. We’ll examine the diverse range of insurance products offered, the regulatory framework that governs them, and the factors that influence consumer choices. By understanding the complexities of state insurance, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions to safeguard their well-being and financial security.
What is State Insurance?

State insurance refers to insurance programs run and regulated by a state government. These programs are designed to provide essential insurance coverage to residents, often in areas where private insurers are unwilling or unable to offer coverage. State insurance plays a crucial role in a state’s economy by ensuring access to essential insurance products for its citizens, fostering stability in the insurance market, and protecting vulnerable populations.
Types of State-Run Insurance Programs
State insurance programs encompass a diverse range of insurance products, tailored to meet specific needs within a state’s population. Here are some common types:
- Health Insurance: State-run health insurance programs, such as Medicaid, provide health coverage to low-income individuals and families. These programs are funded through a combination of federal and state contributions, offering essential medical services to those who might otherwise lack access.
- Workers’ Compensation: State-run workers’ compensation programs offer benefits to employees who are injured or become ill due to work-related causes. These programs ensure that workers receive medical care, lost wages, and other benefits during their recovery period.
- Property and Casualty Insurance: Some states operate insurance programs for property and casualty coverage, particularly in areas where private insurers are reluctant to offer policies due to high risks, such as natural disasters or urban areas with high crime rates. These programs provide essential protection against financial losses caused by events like fires, floods, or theft.
- Auto Insurance: Certain states operate state-run auto insurance programs, particularly in regions with high rates of uninsured drivers. These programs offer affordable auto insurance options to residents, helping to ensure that all drivers are adequately insured.
Examples of State-Run Insurance Programs
Here are some examples of specific state-run insurance programs and their coverage:
- Medicaid: This federal-state partnership provides health coverage to low-income individuals and families, offering a wide range of medical services, including doctor visits, hospital care, prescription drugs, and mental health services. For example, in California, the state’s Medicaid program, known as Medi-Cal, covers over 13 million residents, providing access to essential healthcare services.
- Workers’ Compensation: In New York, the state’s Workers’ Compensation Board administers the workers’ compensation program, providing benefits to injured or ill workers, including medical care, lost wages, and disability payments. For instance, a construction worker who suffers a back injury while working on a construction site would be eligible for benefits under the New York Workers’ Compensation program.
- State-Run Property Insurance: Florida’s Citizens Property Insurance Corporation (CPIC) offers property insurance to homeowners who are unable to obtain coverage from private insurers, particularly in areas prone to hurricanes. CPIC provides coverage for damages caused by hurricanes, floods, and other natural disasters, offering essential protection to homeowners in high-risk regions.
State Insurance Regulation
State insurance regulators play a crucial role in ensuring a fair and stable insurance market. They are responsible for overseeing insurance companies, protecting consumers, and maintaining the solvency of the industry.
Insurance Product and Pricing Regulations, A state insurance
State regulators establish regulations that govern the products and pricing of insurance policies. These regulations aim to ensure that insurance products are fair, transparent, and meet the needs of consumers. Some key aspects of these regulations include:
- Product Approval: Before an insurance company can sell a new product in a state, it must be approved by the state insurance commissioner. This process ensures that the product meets minimum standards of fairness and consumer protection.
- Rate Filings: Insurance companies must file their rates with the state insurance commissioner for approval. The commissioner reviews these rates to ensure they are actuarially sound and not excessive. This process helps prevent companies from charging unreasonable premiums.
- Anti-Discrimination Laws: States have laws that prohibit insurance companies from discriminating against individuals based on factors like race, gender, or age. These laws ensure that all consumers have access to fair and affordable insurance.
Examples of State-Specific Insurance Regulations
Each state has its own unique set of insurance regulations. Some examples of state-specific regulations include:
- California: California has strict regulations regarding auto insurance, requiring all drivers to carry liability insurance. The state also has a “no-fault” system for personal injury protection (PIP), where drivers are covered for their own medical expenses regardless of who is at fault in an accident.
- New York: New York has a “shared responsibility” system for health insurance, where individuals who do not have employer-sponsored coverage must purchase health insurance from a private insurer or through the state’s health insurance exchange.
- Texas: Texas has a “free market” approach to insurance, with limited regulations on pricing and product offerings. This approach allows for greater competition but can also lead to higher premiums for some consumers.
State Insurance Market

The state insurance market is a dynamic and complex ecosystem where various insurance companies compete to offer a wide range of products to individuals and businesses. Understanding the competitive landscape and key players is crucial for both consumers seeking insurance and companies looking to enter or expand their presence in the state.
Key Players in the State Insurance Market
The state insurance market is characterized by a diverse range of players, including both private and public insurers. These entities play a significant role in shaping the market dynamics and offering a variety of insurance products to meet the diverse needs of the state’s population.
- Private Insurers: Private insurers are for-profit companies that offer insurance products to individuals and businesses. They operate in a competitive market and strive to generate profits by effectively managing risks and offering competitive pricing. Examples of private insurers in the state include [Name of insurance company], [Name of insurance company], and [Name of insurance company].
- Public Insurers: Public insurers are government-owned or operated entities that provide insurance products, often focusing on specific sectors or offering coverage that may not be readily available in the private market. Examples of public insurers in the state include [Name of insurance company] and [Name of insurance company].
Comparison of Insurance Products
The state insurance market offers a diverse range of insurance products to cater to various needs and risk profiles. These products can be categorized based on their coverage and target audience, allowing consumers to choose the most suitable option for their specific requirements.
- Life Insurance: Life insurance provides financial protection to beneficiaries in the event of the policyholder’s death. It can be categorized into term life insurance, which offers coverage for a specific period, and permanent life insurance, which provides lifelong coverage.
- Health Insurance: Health insurance covers medical expenses incurred due to illness or injury. It can be obtained through individual plans, employer-sponsored plans, or government programs like Medicare and Medicaid.
- Property and Casualty Insurance: This category includes insurance products that protect against losses related to property damage, liability, and other unforeseen events. Examples include homeowners insurance, renters insurance, auto insurance, and business insurance.
- Other Insurance Products: The state insurance market also offers a range of specialized insurance products, such as disability insurance, long-term care insurance, and travel insurance, to address specific needs and risks.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the state insurance market is characterized by factors such as the number of players, market share, product offerings, pricing strategies, and regulatory environment. Understanding these factors is essential for both insurers and consumers to make informed decisions.
- Market Concentration: The state insurance market can be characterized as either concentrated, with a few dominant players, or fragmented, with numerous smaller players. The level of concentration influences competition and pricing dynamics.
- Product Differentiation: Insurers differentiate themselves through their product offerings, coverage options, pricing strategies, and customer service. This competition drives innovation and provides consumers with a wider range of choices.
- Regulatory Environment: State insurance regulations play a crucial role in shaping the competitive landscape by setting standards for financial solvency, consumer protection, and market conduct.
Consumer Considerations for State Insurance
Choosing the right state insurance product can be a complex decision, especially with the diverse range of options available. This section explores key factors consumers should consider when selecting a state insurance plan, examining the benefits and drawbacks of various programs.
Benefits and Drawbacks of State Insurance Programs
The benefits and drawbacks of state insurance programs vary significantly depending on the specific program and the individual’s needs. Here’s a breakdown of some common factors to consider:
- Coverage: State insurance programs often offer essential coverage, such as health insurance, unemployment benefits, and disability insurance. However, the specific coverage may vary depending on the program and the state. It’s crucial to review the program details carefully to ensure it meets your individual needs.
- Eligibility: Eligibility requirements for state insurance programs can be complex. They often depend on factors like income, employment status, and residency. It’s essential to understand the eligibility criteria before applying to avoid disappointment.
- Premiums and Costs: State insurance programs often have lower premiums compared to private insurance plans. However, the cost of coverage can still be significant. It’s important to factor in the premium cost, deductibles, and co-pays when evaluating the overall affordability of a state insurance program.
- Customer Service: The quality of customer service can vary between state insurance programs. It’s essential to research the reputation of the program and read customer reviews to get a sense of the overall experience.
- Claim Filing Process: The process for filing claims with state insurance providers can vary depending on the program. It’s essential to understand the process and any required documentation before submitting a claim.
Process for Filing Claims with State Insurance Providers
Filing a claim with a state insurance provider generally involves the following steps:
- Contact the Provider: The first step is to contact the state insurance provider to report the claim. This can typically be done by phone, email, or online.
- Gather Required Documentation: The provider will likely request specific documentation to support your claim. This may include medical records, police reports, or other relevant documents. It’s essential to gather all required documentation promptly to avoid delays in processing your claim.
- Submit the Claim: Once you have gathered the necessary documentation, you can submit your claim to the provider. This can be done online, by mail, or in person.
- Claim Review: The provider will review your claim and verify the information provided. This process may take some time, depending on the complexity of the claim.
- Claim Decision: Once the provider has reviewed your claim, they will make a decision about whether to approve or deny it. If your claim is approved, you will receive payment for your covered expenses.
Future of State Insurance: A State Insurance
The landscape of state insurance is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, shifting demographics, and changing consumer expectations. Understanding these trends and challenges is crucial for ensuring the continued relevance and effectiveness of state insurance programs.
Emerging Technologies and their Impact
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and data analytics is transforming the insurance industry, including state insurance programs. These technologies can enhance efficiency, improve risk assessment, and personalize customer experiences. For instance, AI-powered chatbots can provide 24/7 customer support, while blockchain technology can streamline claims processing and reduce fraud. Data analytics can be used to identify risk factors and tailor insurance policies to specific demographics.
Challenges and Opportunities
State insurance programs face several challenges, including:
- Funding shortfalls: Rising healthcare costs and an aging population put pressure on state insurance programs, requiring innovative funding models and cost-containment strategies.
- Accessibility and affordability: Ensuring access to affordable insurance for all citizens, particularly low-income and vulnerable populations, remains a critical challenge.
- Cybersecurity threats: The increasing reliance on technology exposes state insurance programs to cyberattacks, necessitating robust cybersecurity measures.
Improving Effectiveness and Accessibility
To address these challenges and ensure the future success of state insurance programs, several strategies can be implemented:
- Leveraging technology: Implementing AI, blockchain, and data analytics can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer experiences.
- Promoting transparency and accountability: Clear communication about program benefits, eligibility criteria, and cost structures can increase trust and participation.
- Collaborating with stakeholders: Partnerships with healthcare providers, community organizations, and other government agencies can enhance program reach and effectiveness.
- Investing in workforce development: Training insurance professionals on emerging technologies and best practices is essential for adapting to the evolving landscape.
Last Word
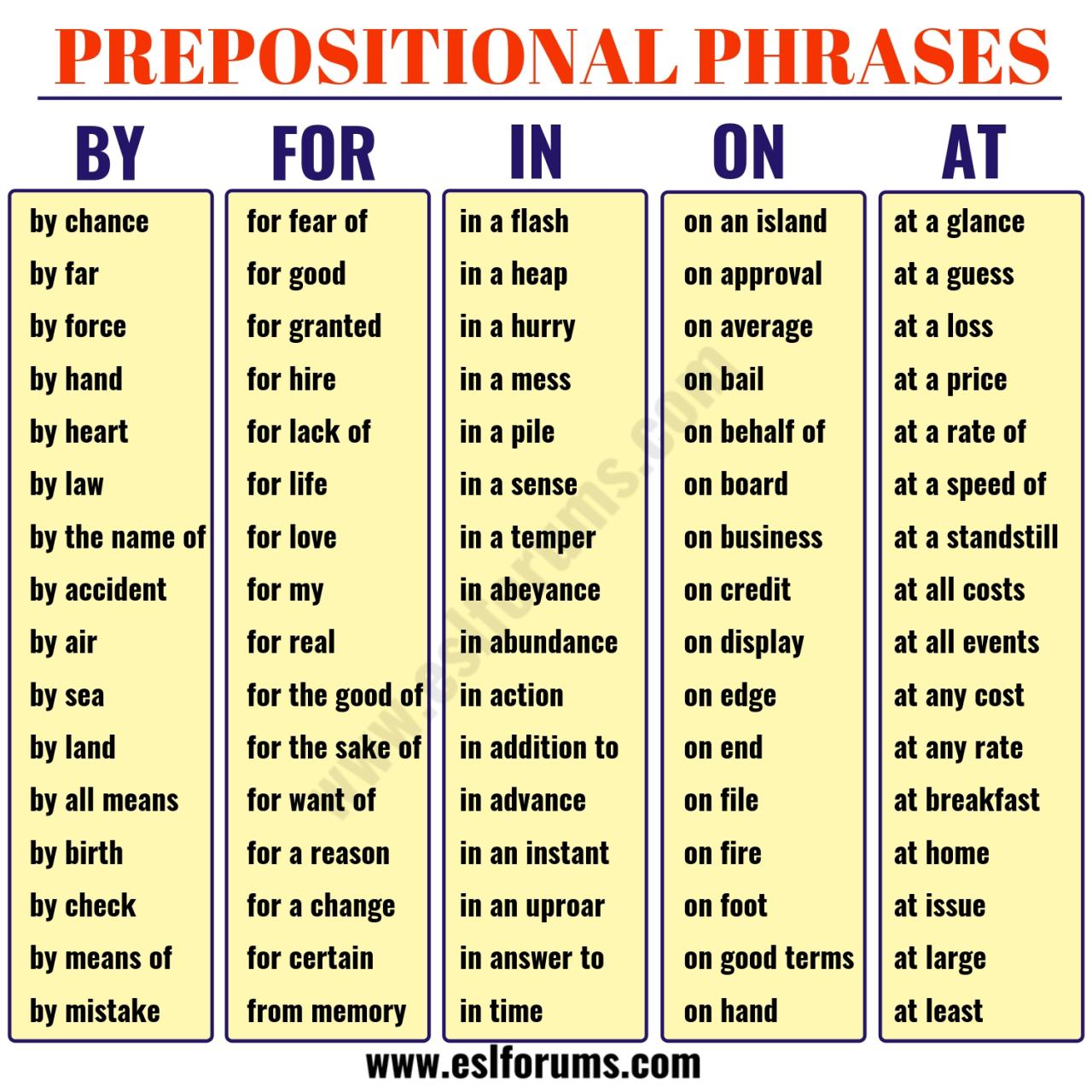
As we navigate an increasingly complex world, state insurance remains a vital pillar of social and economic stability. Understanding the intricacies of this system empowers individuals and businesses to make informed choices, ensuring they have the protection they need in a constantly evolving landscape. By staying informed about the latest trends, regulations, and consumer considerations, we can collectively work towards a future where state insurance effectively serves its purpose: to provide peace of mind and security for all.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the difference between state insurance and private insurance?
State insurance is provided by government programs, while private insurance is offered by commercial companies. State insurance typically focuses on providing essential coverage for specific needs, while private insurance offers a wider range of products and customization options.
How do I find out what state insurance programs are available in my area?
You can visit your state’s insurance department website or contact them directly for information about available programs. Many states also have online portals where you can search for specific insurance products based on your needs.
Are state insurance programs affordable?
State insurance programs are designed to be affordable and accessible to a wide range of individuals and families. However, premiums and coverage vary depending on the specific program and your individual circumstances.







