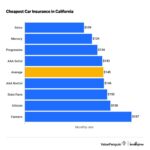
Cheapest insurance states are a beacon of hope for budget-conscious consumers seeking affordable coverage. This article delves into the factors that influence insurance premiums across different states, highlighting the states with the lowest average insurance costs for various types of coverage.
From understanding the intricate interplay of state regulations and individual choices to exploring the impact of demographics and emerging technologies, this exploration sheds light on the key drivers behind insurance pricing variations. We’ll examine the data, uncover the secrets behind low premiums, and equip you with practical tips to secure the best possible rates.
Understanding Insurance Premiums

Insurance premiums are the monthly or annual payments you make to an insurance company in exchange for coverage. These premiums are calculated based on various factors that assess the risk associated with insuring you. The higher the risk, the higher the premium.
Factors Influencing Insurance Premiums
Insurance premiums are determined by a complex set of factors that assess the likelihood of you filing a claim. Here are some of the most common factors:
- Demographics: Your age, gender, and marital status are considered, as they can influence your risk profile. For example, younger drivers tend to have higher premiums than older drivers, due to their inexperience.
- Driving History: Your driving record, including accidents, traffic violations, and DUI convictions, significantly impacts your premium. A clean driving record translates to lower premiums.
- Vehicle Type: The make, model, and year of your vehicle are important. Expensive cars or high-performance vehicles generally cost more to insure because they are more likely to be involved in accidents and more expensive to repair.
- Location: Your location is a key factor. Areas with higher crime rates, traffic congestion, or natural disaster risks will have higher premiums.
- Coverage Levels: The type and amount of coverage you choose directly affect your premium. Higher coverage limits, such as comprehensive or collision coverage, result in higher premiums.
- Credit Score: Your credit score can be a factor in determining your premium, as insurance companies use it to assess your financial responsibility. A higher credit score generally leads to lower premiums.
State Regulations Impacting Insurance Costs
State regulations play a crucial role in influencing insurance costs. Each state has its own set of laws governing insurance practices, including:
- Minimum Coverage Requirements: State laws specify the minimum levels of liability coverage that drivers must carry. These requirements can vary significantly from state to state, affecting the overall cost of insurance.
- Rate Regulation: Some states have strict regulations on how insurance companies can set rates, while others allow more flexibility. States with tighter regulations often have lower average premiums.
- Consumer Protection Laws: States may have laws that protect consumers from unfair insurance practices, such as discrimination or unreasonable rate increases.
Individual Choices Affecting Premium Rates
You have some control over your insurance premiums through your personal choices. Here are a few examples:
- Driving Habits: Safe driving habits, such as avoiding speeding, distracted driving, and driving under the influence, can reduce your risk of accidents and, therefore, lower your premiums.
- Vehicle Maintenance: Regular vehicle maintenance can help prevent breakdowns and accidents, potentially reducing your premium.
- Discounts: Many insurance companies offer discounts for good students, safe drivers, multi-car policies, and other factors. Taking advantage of these discounts can significantly lower your premium.
Data Analysis and Research
To determine the most affordable states for insurance, we need to delve into the data and analyze average insurance premiums across the nation. This analysis involves comparing premiums for various types of insurance, including car, home, and health, to identify states with the lowest average costs. By understanding the factors influencing these premiums, we can gain insights into the reasons behind lower costs in specific states.
Average Insurance Premiums Across States
Analyzing average insurance premiums across different states provides valuable insights into the cost of insurance nationwide. This analysis involves examining data from reputable sources, such as insurance companies, government agencies, and independent research organizations, to obtain accurate and comprehensive information. The data should be collected for different types of insurance, including car, home, and health, to ensure a holistic understanding of insurance costs across states.
- Car Insurance: States with lower car insurance premiums often have factors like lower traffic density, fewer accidents, and favorable weather conditions. Additionally, state regulations and insurance market competition can influence car insurance costs.
- Home Insurance: Factors influencing home insurance premiums include the risk of natural disasters, crime rates, and the value of homes in a particular state. States with lower risks and more affordable housing tend to have lower home insurance premiums.
- Health Insurance: Health insurance premiums are influenced by factors such as the cost of healthcare services, the prevalence of chronic diseases, and the state’s healthcare regulations. States with lower healthcare costs and healthier populations generally have lower health insurance premiums.
States with the Lowest Average Insurance Costs
Identifying states with the lowest average insurance costs for different types of coverage is essential for individuals seeking affordable insurance options. This analysis involves comparing average premiums across states and identifying those with consistently lower costs for car, home, and health insurance.
- Car Insurance: States like Maine, Idaho, and Vermont consistently rank among the states with the lowest average car insurance premiums. These states often have lower traffic density, fewer accidents, and favorable weather conditions, contributing to lower insurance costs.
- Home Insurance: States with lower average home insurance premiums include Idaho, Wyoming, and Utah. These states generally have lower risks of natural disasters, lower crime rates, and more affordable housing, resulting in lower insurance costs.
- Health Insurance: States with lower average health insurance premiums include Utah, Idaho, and Wyoming. These states often have lower healthcare costs, healthier populations, and more affordable healthcare services, leading to lower insurance premiums.
Factors Contributing to Lower Premiums
Understanding the factors contributing to lower insurance premiums in specific states is crucial for individuals seeking affordable insurance options. This analysis involves examining the factors influencing insurance costs, such as state regulations, market competition, and local risk factors.
- State Regulations: States with stricter regulations on insurance companies, such as those limiting the types of coverage exclusions or requiring specific coverage mandates, can result in lower premiums for consumers. This is because stricter regulations can prevent insurers from charging excessive premiums or denying coverage for certain risks.
- Market Competition: States with a more competitive insurance market, where multiple insurance companies operate, can lead to lower premiums. This is because competition forces insurance companies to offer lower premiums to attract and retain customers.
- Local Risk Factors: States with lower risks, such as those with lower traffic density, fewer accidents, and lower crime rates, tend to have lower insurance premiums. This is because insurers assess the likelihood of claims based on local risk factors and adjust premiums accordingly.
State-Specific Factors
Insurance premiums are influenced by a variety of factors, and understanding how these factors vary across states can help explain why insurance costs differ significantly. This section will explore key state-specific factors that contribute to the cost of insurance.
State-Specific Factors Affecting Insurance Costs
State-specific factors play a crucial role in determining insurance costs. These factors can be broadly categorized into population characteristics, driving conditions, and regulatory environments.
| Factor | Impact on Premiums | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Population Density | Higher density often leads to increased traffic congestion and accidents, resulting in higher premiums. | States like New York and California, with dense urban areas, tend to have higher insurance premiums compared to states with lower population density. |
| Driving Habits | States with higher rates of accidents, speeding violations, and drunk driving incidents tend to have higher premiums. | States with lax traffic laws or a culture of aggressive driving may experience higher premiums due to increased accident risks. |
| Healthcare Infrastructure | States with advanced healthcare systems and lower healthcare costs may have lower insurance premiums. | States with well-developed healthcare infrastructure, such as Massachusetts, may have lower healthcare costs, which can influence insurance premiums. |
| Climate and Weather Conditions | States with severe weather conditions, such as hurricanes or earthquakes, may have higher premiums due to increased risk of damage. | States like Florida and California, prone to hurricanes and earthquakes, respectively, may experience higher premiums to cover potential natural disaster-related claims. |
| State Regulations and Laws | States with strict regulations on insurance companies, such as mandated coverage or restrictions on rate increases, may have lower premiums. | States like Massachusetts and California have stringent regulations on insurance companies, which can lead to lower premiums for consumers. |
Examples of State-Specific Initiatives
Many states implement initiatives or policies to influence insurance costs. Some examples include:
- No-Fault Insurance Laws: Some states have no-fault insurance laws, which require drivers to file claims with their own insurance companies regardless of fault. This can lead to lower premiums as it reduces litigation costs. For example, Michigan has a no-fault system, which has been credited with reducing the number of lawsuits and lowering premiums.
- Driver Education Programs: States with mandatory driver education programs may have lower premiums as these programs can help reduce accidents. For instance, Texas has a mandatory driver education program for new drivers, which may contribute to lower accident rates and lower insurance premiums.
- Safety Inspection Programs: States with mandatory vehicle safety inspection programs may have lower premiums as these programs can help ensure vehicles are in safe operating condition. For example, Pennsylvania has a mandatory vehicle inspection program, which may help reduce accidents and lower insurance premiums.
- Discounts for Safety Features: States may offer discounts for vehicles with safety features like anti-lock brakes or airbags, which can help reduce accidents and lower premiums. For example, California offers discounts for vehicles with advanced safety features, encouraging drivers to purchase safer vehicles.
Impact of Demographics
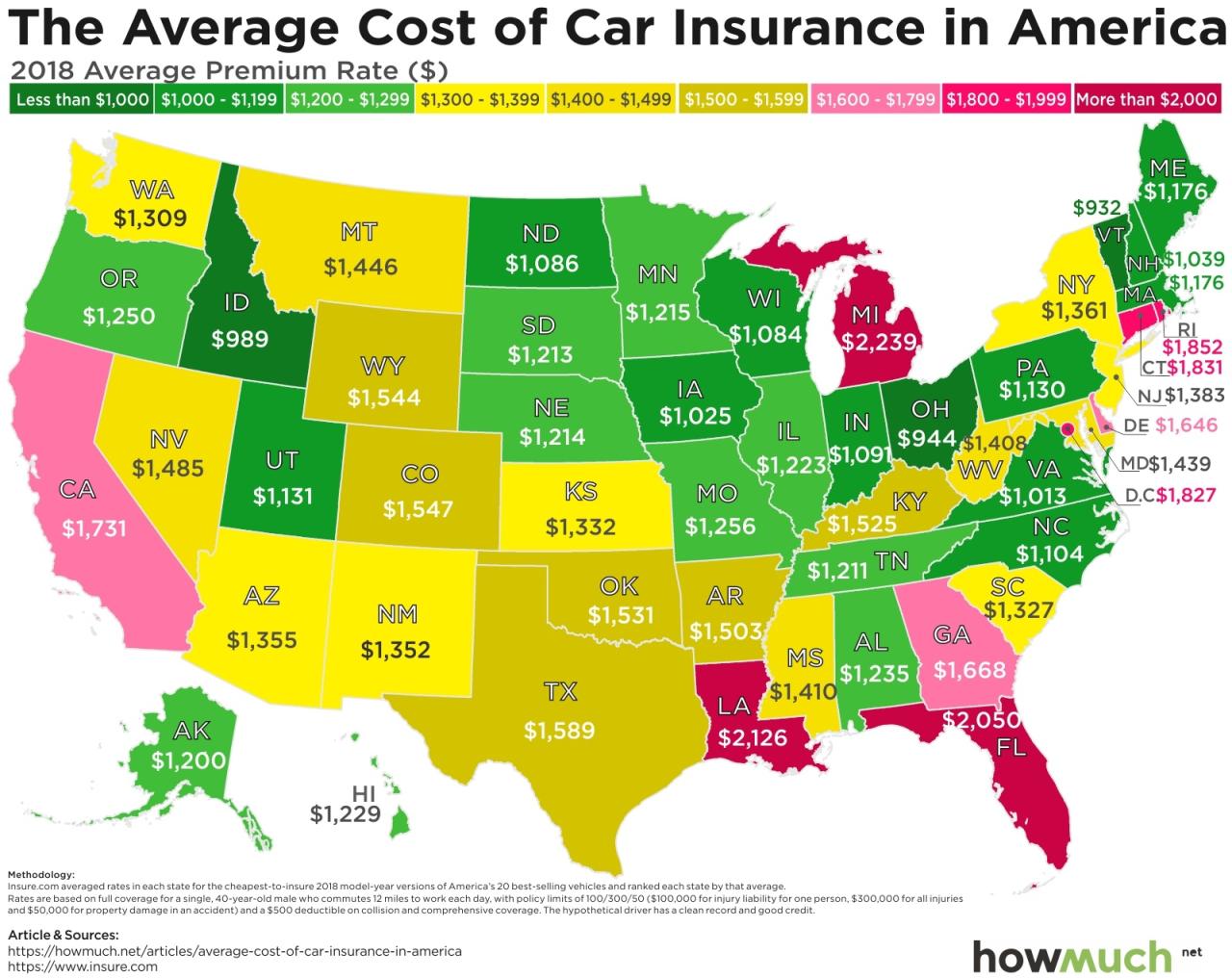
Demographics play a significant role in determining insurance premiums. Insurance companies use demographic data to assess risk and set premiums accordingly. These factors can vary across states, leading to differences in insurance costs.
Age
Age is a key factor in determining insurance premiums. Younger drivers are statistically more likely to be involved in accidents due to inexperience and risk-taking behavior. As drivers age, they gain more experience, and their risk profile decreases, resulting in lower premiums.
Insurance companies use actuarial tables to calculate the risk associated with different age groups. These tables are based on historical data and reflect the average accident rates for various age groups. For example, a 20-year-old driver might pay significantly higher premiums than a 50-year-old driver with the same driving record.
Consumer Considerations
Finding the most affordable insurance rates requires careful consideration and proactive steps from consumers. Understanding how insurance premiums are calculated and identifying factors that influence pricing is crucial to securing the best possible coverage at the most competitive price.
Comparing Insurance Quotes
Consumers have several options for comparing insurance quotes and finding the best rates.
- Online Comparison Websites: Websites like Policygenius, Insurance.com, and NerdWallet allow users to enter their information and receive quotes from multiple insurance providers simultaneously. This streamlines the comparison process and saves time.
- Directly Contacting Insurance Companies: Consumers can contact insurance companies directly to request quotes. This allows for more personalized interactions and the opportunity to ask specific questions about coverage options.
- Using an Insurance Broker: Brokers act as intermediaries between consumers and insurance companies. They can provide personalized advice and help consumers find the best coverage for their needs.
It is important to note that insurance companies use different algorithms and data points when calculating quotes. Therefore, comparing quotes from multiple providers is essential to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of available options.
Tips for Lowering Insurance Premiums
Consumers can take several proactive steps to reduce their insurance premiums.
- Maintain a Good Driving Record: A clean driving record with no accidents or traffic violations is a significant factor in determining insurance premiums. Avoiding reckless driving habits and adhering to traffic laws can significantly lower costs.
- Increase Your Deductible: A higher deductible means you pay more out-of-pocket in the event of an accident. However, it can lead to lower premiums. Consider increasing your deductible if you are comfortable with a higher out-of-pocket expense.
- Bundle Policies: Combining multiple insurance policies, such as home, auto, and life insurance, with the same provider can result in significant discounts.
- Shop Around Regularly: Insurance rates can fluctuate over time. It is advisable to shop around for new quotes every year or two to ensure you are getting the best possible rate.
- Consider Discounts: Insurance companies often offer discounts for good students, safe drivers, and homeowners with security systems. Inquire about available discounts and see if you qualify.
- Improve Your Credit Score: While not universally applicable, some insurance companies consider credit scores when determining premiums. Improving your credit score can potentially lead to lower rates.
These strategies can significantly impact your insurance costs and ensure you are getting the best value for your coverage.
Resources for Affordable Insurance
Consumers seeking affordable insurance options can leverage various resources.
- State Insurance Departments: Each state has an insurance department that regulates insurance companies and provides consumer protection. They can offer information on available insurance options and assist with complaints or disputes.
- Consumer Advocacy Groups: Organizations like the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) and the Consumer Federation of America (CFA) provide resources and advocacy for consumers seeking affordable insurance.
- Community Organizations: Local community organizations, such as faith-based groups or non-profit agencies, may offer assistance programs or resources for individuals struggling to afford insurance.
By exploring these resources, consumers can access valuable information and support in finding affordable insurance solutions.
Future Trends

The insurance industry is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and evolving risk landscapes. These factors are shaping the future of insurance pricing models and the overall cost of insurance.
Changes in Insurance Pricing Models
The traditional insurance pricing model, based on historical data and actuarial analysis, is facing significant challenges. New data sources, advanced analytics, and real-time risk assessment are driving the emergence of more dynamic and personalized pricing models.
- Usage-Based Insurance (UBI): UBI programs utilize telematics devices or smartphone apps to track driving behavior, such as speed, braking, and mileage. This data allows insurers to assess individual risk more accurately and offer personalized premiums based on actual driving habits. For example, drivers with good driving records and low mileage could receive lower premiums compared to those with more risky driving patterns.
- Risk-Based Pricing: This model leverages data from various sources, including credit scores, social media activity, and even wearable devices, to create a more comprehensive risk profile for individuals. This allows insurers to tailor premiums based on individual risk factors, potentially leading to more accurate and equitable pricing. However, it raises concerns about privacy and data security, requiring careful consideration of ethical implications and regulatory frameworks.
- Dynamic Pricing: This approach utilizes real-time data, such as weather conditions, traffic patterns, and even social media sentiment, to adjust premiums dynamically. For example, insurers could offer lower premiums during periods of low risk or adjust premiums based on the risk associated with specific driving routes. This approach allows for greater flexibility and responsiveness to changing risk factors but requires robust data infrastructure and sophisticated algorithms.
Emerging Technologies Impacting Insurance Costs
Advancements in technology are revolutionizing the insurance industry, impacting both the cost and delivery of insurance products.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered algorithms are being used to automate tasks, improve risk assessment, and enhance customer service. AI can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential risks, leading to more accurate pricing and risk management. For example, AI-powered chatbots can provide instant customer support, reducing operational costs and improving customer satisfaction.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices, such as smart home sensors and connected vehicles, generate real-time data that can be used to monitor risks and optimize insurance policies. For example, smart home sensors can detect potential hazards like water leaks or fire, allowing insurers to provide timely intervention and reduce claims costs. This data can also be used to develop personalized insurance products tailored to specific needs and risks.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain can enhance transparency, security, and efficiency in insurance operations. It allows for secure and tamper-proof record-keeping, streamlining claims processing and reducing fraud. Blockchain can also facilitate peer-to-peer insurance models, where individuals can share risks and costs directly, potentially leading to lower premiums.
Future Outlook for Insurance Premiums, Cheapest insurance states
The future of insurance premiums is likely to be influenced by a combination of factors, including technological advancements, regulatory changes, and economic conditions.
- Increased Competition: The emergence of new insurance models and technologies is expected to increase competition within the industry. This could lead to more competitive pricing and innovative products designed to meet evolving consumer needs.
- Growing Risk: Climate change, natural disasters, and cyber threats are increasing the frequency and severity of insurance claims. Insurers may need to adjust premiums to reflect these growing risks, potentially leading to higher costs for consumers.
- Personalized Pricing: As technology enables more personalized risk assessment, premiums are likely to become more tailored to individual needs and behaviors. This could lead to both higher and lower premiums depending on individual risk factors and how effectively insurers can manage and mitigate risks.
Epilogue
By understanding the factors that shape insurance costs and utilizing the resources available, consumers can make informed decisions and find the most affordable coverage options. Whether you’re looking for car insurance, home insurance, or health insurance, this guide provides valuable insights to navigate the complex world of insurance pricing and secure the best possible rates.
Essential Questionnaire: Cheapest Insurance States
What is the cheapest state for car insurance?
The cheapest state for car insurance can vary depending on factors like your driving record and vehicle type. However, states like Idaho, Maine, and Vermont consistently rank among the most affordable for car insurance.
How can I lower my insurance premiums?
There are several ways to lower your insurance premiums, including maintaining a good driving record, increasing your deductible, bundling multiple policies, and choosing a higher coverage level.
What are the biggest factors that affect insurance premiums?
Some of the biggest factors that affect insurance premiums include your age, driving history, credit score, location, vehicle type, and coverage level.