State minimum coverage auto insurance is a crucial aspect of responsible driving, ensuring financial protection in case of accidents. Every state mandates minimum coverage levels, designed to cover basic liabilities arising from accidents. While these minimums provide a baseline, understanding their limitations and exploring alternative options is essential for comprehensive protection.
This guide delves into the intricacies of state minimum coverage auto insurance, exploring its purpose, requirements, and potential implications. We’ll examine the different types of coverage included in minimum requirements, factors influencing these levels, and the benefits and drawbacks of relying solely on state minimums. Additionally, we’ll discuss alternative coverage options and cost considerations, empowering you to make informed decisions about your auto insurance needs.
State Minimum Coverage Auto Insurance Requirements
State minimum coverage auto insurance requirements are designed to protect drivers and their passengers in the event of an accident. These requirements ensure that drivers have sufficient financial resources to cover damages caused to others, as well as their own medical expenses.
State Minimum Coverage Requirements
Every state in the U.S. mandates minimum auto insurance coverage, but these requirements vary significantly. The table below provides a comparison of minimum coverage requirements across different states:
| State | Bodily Injury Liability | Property Damage Liability | Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | $25,000 per person / $50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person / $50,000 per accident |
| Alaska | $50,000 per person / $100,000 per accident | $25,000 | $50,000 per person / $100,000 per accident |
| Arizona | $25,000 per person / $50,000 per accident | $15,000 | $25,000 per person / $50,000 per accident |
| Arkansas | $25,000 per person / $50,000 per accident | $25,000 | $25,000 per person / $50,000 per accident |
| California | $15,000 per person / $30,000 per accident | $5,000 | $15,000 per person / $30,000 per accident |
Consequences of Driving Without Minimum Coverage
Driving without minimum coverage can have serious consequences. These consequences may include:
– Financial ruin: If you are involved in an accident and do not have adequate insurance coverage, you could be held personally liable for all damages, including medical expenses, property damage, and lost wages.
– License suspension: Most states will suspend your driver’s license if you are caught driving without minimum coverage.
– Fines and penalties: You could face significant fines and penalties, including jail time in some cases.
– Inability to register your vehicle: You may not be able to register your vehicle without proof of insurance.
– Difficulty obtaining insurance in the future: Having a lapse in coverage can make it difficult to obtain affordable insurance in the future.
Types of Coverage Included in State Minimums
State minimum auto insurance requirements typically include several types of coverage designed to protect you and others in the event of an accident. These coverages are mandatory in most states and are intended to provide basic financial protection for injuries, damages, and other liabilities arising from a car accident.
Liability Coverage
Liability coverage is a fundamental component of state minimum auto insurance requirements. It protects you financially if you are found at fault for causing an accident that results in injuries or property damage to others. Liability coverage typically consists of two parts: bodily injury liability and property damage liability.
Bodily Injury Liability
Bodily injury liability coverage covers medical expenses, lost wages, and other damages incurred by the other driver and passengers in the event of an accident where you are at fault. It is usually expressed as a per-person limit and a per-accident limit. For example, a 25/50 bodily injury liability limit means you have coverage for up to $25,000 per person and up to $50,000 per accident.
Property Damage Liability
Property damage liability coverage protects you from financial responsibility for damages to the other driver’s vehicle or other property involved in the accident. It covers repairs or replacement costs for the other driver’s car, as well as any damage to fences, buildings, or other property. Similar to bodily injury liability, property damage liability is expressed as a per-accident limit, such as a $25,000 limit.
Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage
Uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage (UM/UIM) provides financial protection if you are involved in an accident with a driver who is uninsured or underinsured. Uninsured motorist coverage protects you if the at-fault driver has no insurance, while underinsured motorist coverage comes into play if the at-fault driver’s insurance coverage is insufficient to cover your losses.
Uninsured Motorist Coverage
Uninsured motorist coverage is crucial because it can help cover your medical expenses, lost wages, and other damages if you are injured by an uninsured driver. It provides coverage for your own injuries and damages, regardless of who is at fault in the accident.
Underinsured Motorist Coverage
Underinsured motorist coverage protects you if the at-fault driver has insufficient insurance to cover your injuries and damages. For instance, if you are involved in an accident with a driver who has $25,000 in liability coverage, and your injuries exceed that amount, underinsured motorist coverage can help cover the difference.
Personal Injury Protection (PIP)
Personal injury protection (PIP) coverage, also known as no-fault insurance, covers your medical expenses, lost wages, and other damages regardless of who is at fault in an accident. This type of coverage is mandatory in some states, and it can be a valuable asset in helping you recover from an accident.
Collision Coverage
Collision coverage pays for repairs or replacement costs for your vehicle if it is damaged in an accident with another vehicle or object. It is optional in most states, but it is often a good idea to have it, especially if you have a car loan or lease.
Example
Imagine you are driving your car and you hit a parked car. If you have collision coverage, your insurance company will pay for the repairs to your vehicle, regardless of who is at fault. However, collision coverage does not cover damage caused by events like hail, theft, or vandalism.
Comprehensive Coverage
Comprehensive coverage provides protection for your vehicle against damages caused by events other than accidents, such as theft, vandalism, fire, hail, and floods. It covers the cost of repairs or replacement for your vehicle if it is damaged by these perils.
Example
If your car is stolen or damaged by a hailstorm, comprehensive coverage will help pay for repairs or replacement costs. Like collision coverage, comprehensive coverage is optional in most states.
Factors Influencing Minimum Coverage Requirements: State Minimum Coverage Auto Insurance
State minimum coverage requirements are not arbitrary numbers; they are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, reflecting the balance between providing basic protection and keeping insurance affordable.
Several key factors play a crucial role in determining the minimum coverage levels. These factors include:
Economic Considerations
Economic factors are central to determining minimum coverage requirements. These factors aim to balance the cost of insurance with the need to provide adequate protection for drivers and their property.
- Cost of Living: States with higher costs of living often have higher minimum coverage requirements to ensure adequate compensation for injuries and property damage. This is because medical expenses, vehicle repair costs, and other expenses associated with accidents tend to be higher in these areas.
- Insurance Market Competition: A competitive insurance market can influence minimum coverage levels. When there is more competition, insurance companies may offer lower premiums, potentially leading to lower minimum coverage requirements. Conversely, a less competitive market may result in higher premiums and potentially higher minimum coverage levels.
- State Budget and Revenue: States may consider their budget and revenue when setting minimum coverage levels. A state with a robust budget might be more inclined to set higher minimum coverage requirements, as it can afford to provide more extensive coverage for accidents.
Demographic Factors
Demographic factors also play a role in shaping minimum coverage requirements. These factors reflect the characteristics of the population, such as age, income, and driving habits.
- Population Density: Urban areas with higher population densities tend to have higher minimum coverage requirements due to the increased risk of accidents and potential for more significant damages.
- Age Distribution: States with a larger proportion of young drivers may have higher minimum coverage requirements, as younger drivers are statistically more likely to be involved in accidents.
- Income Levels: States with higher income levels might have higher minimum coverage requirements because drivers in these states are more likely to be able to afford higher premiums.
Traffic Safety and Accident Rates
States with higher traffic safety concerns and accident rates tend to have higher minimum coverage requirements to ensure adequate protection for victims.
- Accident Frequency: States with a higher frequency of accidents often have higher minimum coverage requirements to compensate for the increased likelihood of claims.
- Severity of Accidents: States with a higher severity of accidents, such as those with a higher proportion of fatal accidents, may also have higher minimum coverage requirements to ensure sufficient compensation for families of victims.
- Road Infrastructure: States with well-maintained road infrastructure may have lower minimum coverage requirements compared to states with less developed or poorly maintained roads, where the risk of accidents is higher.
Political Considerations
Political considerations can also influence minimum coverage requirements.
- Public Opinion: Public sentiment regarding insurance coverage can influence policy decisions. If there is strong public support for higher minimum coverage requirements, lawmakers may be more likely to enact such legislation.
- Lobbying Efforts: Lobbying groups representing various stakeholders, such as insurance companies, consumer advocacy groups, and victims’ rights organizations, can influence minimum coverage requirements.
- Legislative Priorities: Lawmakers may prioritize certain issues, such as traffic safety or consumer protection, which can influence minimum coverage requirements.
Benefits and Drawbacks of State Minimum Coverage

State minimum coverage, while fulfilling the legal requirements for driving, might not offer adequate protection in the event of an accident. Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of this level of coverage is crucial before making a decision about your auto insurance policy.
Benefits of State Minimum Coverage
State minimum coverage provides the basic legal protection required to drive legally. This means you can avoid penalties and legal repercussions for not having insurance.
Drawbacks of State Minimum Coverage
The primary drawback of state minimum coverage is its limited financial protection. In the event of an accident, the coverage might not be enough to cover the costs of damages, medical expenses, or lost wages.
- Insufficient Coverage for Damages: If you cause an accident, the liability coverage might not be enough to cover the other driver’s vehicle repairs, especially in a severe accident. This could leave you responsible for significant out-of-pocket expenses.
- Limited Medical Coverage: The personal injury protection (PIP) coverage provided by state minimum might not cover all your medical expenses. This could result in substantial medical bills that you need to pay out of pocket.
- No Coverage for Uninsured Motorists: If you are involved in an accident with an uninsured driver, state minimum coverage might not offer any protection for your damages or injuries.
Importance of Considering Individual Needs and Circumstances
Choosing the right auto insurance coverage is crucial and should be based on your individual needs and circumstances. It’s vital to consider factors such as:
- Driving Habits: If you frequently drive in high-traffic areas or have a history of accidents, you might need higher coverage.
- Value of Your Vehicle: If you own a newer or more expensive vehicle, you’ll need more comprehensive and collision coverage to protect your investment.
- Financial Situation: If you have a limited budget, you might opt for state minimum coverage. However, it’s important to weigh the risks and potential costs of insufficient coverage.
Alternatives to State Minimum Coverage
While state minimum coverage provides the bare minimum protection required by law, it may not be sufficient to cover all potential financial losses in the event of an accident. Consider these alternatives to ensure adequate financial protection.
Different Coverage Options
Beyond state minimums, several other coverage options can be considered to provide more comprehensive protection. These options offer varying levels of coverage and cost, allowing you to tailor your insurance policy to your specific needs and budget.
Comparison of Coverage Options
| Coverage Type | Description | Cost | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liability Coverage | Covers damages to others’ property and injuries sustained by others in an accident you cause. | Higher than state minimums | Provides greater financial protection for others in case of an accident you cause. |
| Collision Coverage | Covers damage to your vehicle in a collision, regardless of fault. | Higher than state minimums | Protects you from significant repair or replacement costs for your vehicle in a collision. |
| Comprehensive Coverage | Covers damage to your vehicle due to events other than collisions, such as theft, vandalism, or natural disasters. | Higher than state minimums | Protects your vehicle from damage caused by non-collision events. |
| Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage | Covers damages to you and your vehicle if you are involved in an accident with an uninsured or underinsured driver. | Higher than state minimums | Protects you from financial losses if the other driver does not have sufficient insurance. |
| Medical Payments Coverage | Covers medical expenses for you and your passengers, regardless of fault. | Higher than state minimums | Provides financial assistance for medical bills following an accident, regardless of who is at fault. |
| Personal Injury Protection (PIP) | Covers medical expenses, lost wages, and other expenses for you and your passengers, regardless of fault. | Higher than state minimums | Provides comprehensive financial assistance for injuries and related expenses following an accident. |
| Rental Reimbursement Coverage | Covers the cost of renting a vehicle while yours is being repaired. | Higher than state minimums | Provides transportation while your vehicle is unavailable due to repairs. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Choosing Different Coverage Options
Choosing the right coverage options involves considering your individual needs, budget, and risk tolerance. For example, if you drive an older vehicle with a lower value, collision and comprehensive coverage may not be as essential. However, if you drive a newer vehicle with a higher value, these coverages can provide valuable protection.
Important Note: It’s crucial to consult with an insurance agent to determine the best coverage options for your specific circumstances. They can help you assess your needs and recommend appropriate coverage levels to ensure you have adequate protection.
Cost Considerations for State Minimum Coverage
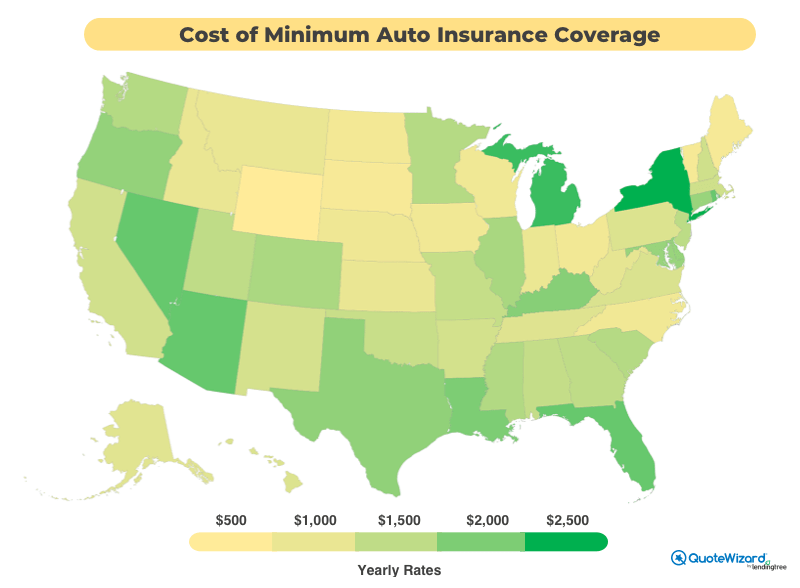
The cost of state minimum coverage auto insurance can vary significantly depending on several factors. Understanding these factors can help you determine the most affordable option for your needs.
Factors Affecting the Cost of State Minimum Coverage
The cost of state minimum coverage is influenced by various factors, including your age, driving history, and the type of vehicle you drive.
- Age: Younger drivers are statistically more likely to be involved in accidents, making their insurance premiums higher. As you age and gain experience, your premiums tend to decrease.
- Driving History: Your driving record plays a crucial role in determining your insurance rates. Drivers with a clean driving record, without accidents or traffic violations, typically enjoy lower premiums. However, accidents, speeding tickets, and DUI convictions can significantly increase your insurance costs.
- Vehicle Type: The type of vehicle you drive also affects your insurance premiums. High-performance cars, luxury vehicles, and expensive SUVs often have higher insurance costs due to their higher repair and replacement expenses.
Comparison of State Minimum Coverage Costs with Other Coverage Options, State minimum coverage auto insurance
State minimum coverage is generally the most affordable option, but it offers the least amount of protection. Other coverage options, such as full coverage or comprehensive and collision coverage, provide more protection but come at a higher cost.
- Full Coverage: Full coverage insurance includes comprehensive and collision coverage, which can protect you from financial losses in case of accidents or damage to your vehicle. It also covers theft and other risks.
- Comprehensive and Collision Coverage: These coverages provide protection for damage to your vehicle caused by events like accidents, theft, vandalism, or natural disasters.
Tips for Finding Affordable State Minimum Coverage
Finding affordable state minimum coverage requires careful comparison and research.
- Shop Around: Get quotes from multiple insurance companies to compare prices and coverage options.
- Consider Bundling: If you have other insurance policies, such as homeowners or renters insurance, bundling them with your auto insurance can often lead to discounts.
- Maintain a Clean Driving Record: Avoiding accidents and traffic violations can significantly reduce your insurance premiums.
- Ask About Discounts: Many insurance companies offer discounts for good students, safe drivers, and those who have installed safety features in their vehicles.
Final Summary

Navigating the world of auto insurance can be complex, but understanding state minimum coverage requirements is a vital step toward responsible driving. By recognizing the limitations of minimum coverage and exploring alternative options, you can tailor your insurance policy to meet your individual needs and ensure adequate financial protection in the event of an accident. Remember, choosing the right coverage goes beyond simply meeting minimum requirements; it’s about securing peace of mind and financial stability on the road.
FAQ Guide
What happens if I drive without minimum coverage?
Driving without the minimum required auto insurance coverage can result in fines, license suspension, or even the impounding of your vehicle. In the event of an accident, you could be held personally liable for damages, potentially leading to significant financial hardship.
Can I choose a higher coverage level than the state minimum?
Absolutely! You can choose higher coverage limits than the state minimums, providing greater financial protection in case of an accident. This is generally recommended, as state minimums may not be sufficient to cover all potential expenses.
How do I find affordable state minimum coverage?
Several factors influence the cost of auto insurance, including age, driving history, and vehicle type. You can find affordable state minimum coverage by comparing quotes from multiple insurers, taking advantage of discounts, and considering factors like your driving habits and vehicle usage.