Car insurance moving out of state can be a daunting task, especially when you’re unfamiliar with the new state’s insurance regulations. It’s crucial to understand how your current policy might change and what new options are available to you. Moving to a new state often means adjusting to different driving conditions, traffic laws, and insurance requirements, all of which can impact your insurance premiums.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the process of transferring your car insurance when moving to a new state. We’ll delve into state-specific insurance requirements, explore how moving affects your existing policy, and guide you through the process of finding the best insurance options in your new location. We’ll also address common FAQs and provide tips for a smooth transition.
Understanding State-Specific Insurance Requirements
Each state in the United States has its own set of car insurance laws and regulations. These laws can differ significantly, so it’s crucial to understand the requirements of your new state when you move. Failing to comply with these laws can lead to hefty fines and penalties.
Minimum Coverage Requirements
Each state mandates a minimum level of car insurance coverage to protect drivers and their passengers in case of accidents. These minimums are typically divided into different types of coverage, such as liability, collision, and comprehensive.
- Liability Coverage: This coverage protects you financially if you cause an accident that results in injuries or property damage to others. It is usually divided into two parts:
- Bodily Injury Liability: Covers medical expenses, lost wages, and other damages for injuries caused to others.
- Property Damage Liability: Covers repairs or replacement costs for damage to another person’s vehicle or property.
- Collision Coverage: This coverage pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle if it is damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. This is usually optional, but it is often recommended for newer vehicles or those with a significant loan balance.
- Comprehensive Coverage: This coverage pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle if it is damaged by events other than a collision, such as theft, vandalism, fire, or hail. This coverage is also typically optional, but it is often recommended for newer vehicles or those with a significant loan balance.
Coverage Requirements Based on Factors, Car insurance moving out of state
The specific car insurance requirements in a state can vary depending on several factors, including:
- Vehicle Type: The insurance requirements for a motorcycle, truck, or commercial vehicle may differ from those for a passenger car. For example, some states may require additional coverage for motorcycles, such as uninsured motorist coverage.
- Vehicle Age: States may have different requirements for older vehicles. For example, some states may not require collision or comprehensive coverage for older vehicles.
- Driving History: Your driving record can also affect your insurance requirements. For example, if you have a history of accidents or traffic violations, you may be required to carry higher levels of coverage or pay higher premiums.
Impact of Moving on Existing Insurance Policies

Moving to a new state can significantly impact your car insurance policy. It’s crucial to understand how your existing policy might change and what steps you need to take to ensure you have adequate coverage.
Notifying Your Insurer
It’s essential to inform your current insurance provider about your move as soon as possible. Failure to do so could lead to complications and potential coverage gaps. Most insurers have a grace period, typically 30 to 60 days, to update your policy. However, it’s best to notify them immediately to avoid any delays or issues.
You can notify your insurer by phone, email, or through their online portal. Be sure to provide your new address and the date you plan to move.
Consequences of Not Notifying Your Insurer
Failing to notify your insurer about your move can have serious consequences, including:
- Coverage Gaps: Your current policy may not cover you in your new state if you don’t update your address. This could leave you financially responsible for any accidents or damages.
- Policy Cancellation: If your insurer discovers you’ve moved without notifying them, they may cancel your policy, leaving you without coverage.
- Higher Premiums: Even if your policy isn’t canceled, failing to notify your insurer could lead to higher premiums later on.
Factors Affecting Premium Changes
Several factors can influence your insurance premium after moving:
- State Laws and Regulations: Each state has its own set of insurance laws and regulations, which can impact coverage requirements and premium costs.
- Driving History: Your driving record, including accidents and violations, plays a significant role in determining your premium.
- Vehicle Type: The type of vehicle you drive, including its make, model, and year, can affect your premium.
- Coverage Levels: The amount of coverage you choose, such as liability, collision, and comprehensive, will also impact your premium.
- Local Risk Factors: Factors like crime rates, traffic congestion, and weather conditions in your new location can influence your premium.
Exploring New Insurance Options in the New State
Moving to a new state requires you to adjust to a new environment, including your car insurance. You may find that your current insurance policy doesn’t meet the requirements of your new state or that you can get better coverage at a lower price.
Comparing Insurance Providers
It’s important to compare different insurance providers in your new state to find the best deal for your needs. You should consider factors like pricing, coverage options, and customer service.
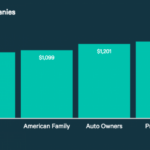
Here are some of the top insurance providers in the United States:
* Geico: Known for its affordable rates and simple online processes.
* Progressive: Offers a wide range of coverage options and discounts.
* State Farm: Offers excellent customer service and a variety of insurance products.
* Allstate: Provides a range of insurance options and discounts, including accident forgiveness.
* USAA: Exclusively for military members and their families, known for its competitive rates and excellent customer service.
Understanding Insurance Policy Features
Once you’ve identified a few potential insurance providers, it’s essential to understand the different types of coverage they offer. Here’s a table outlining the key features and benefits of various insurance policies:
| Policy Type | Coverage | Benefits |
|—|—|—|
| Liability Coverage | Protects you financially if you cause an accident that injures someone or damages their property. | Essential for all drivers. |
| Collision Coverage | Covers repairs or replacement of your vehicle if you’re involved in an accident, regardless of fault. | Recommended if you have a newer or financed vehicle. |
| Comprehensive Coverage | Covers damage to your vehicle from non-accident events like theft, vandalism, or natural disasters. | Recommended for newer or financed vehicles. |
| Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage | Protects you if you’re involved in an accident with a driver who doesn’t have insurance or doesn’t have enough coverage. | Essential for all drivers. |
| Personal Injury Protection (PIP) | Covers medical expenses and lost wages for you and your passengers, regardless of fault. | Required in some states. |
Getting Quotes and Comparing Them
You can obtain quotes from different insurers online, over the phone, or in person. Most insurance providers have online quote tools that allow you to get a personalized quote in minutes.
To compare quotes effectively, make sure you’re comparing the same coverage levels. You should also consider the insurer’s financial stability, customer satisfaction ratings, and the availability of discounts.
Tip: Consider getting quotes from multiple insurance providers to ensure you’re getting the best deal.
Factors Influencing Insurance Premiums in the New State
Your insurance premium in your new state will be influenced by a number of factors, including your driving history, age, vehicle type, and location. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your insurance coverage and potentially save money on your premiums.
Driving History
Your driving history is a significant factor in determining your insurance premiums. Insurance companies look at your driving record to assess your risk as a driver. Factors considered include:
- Accidents: The number and severity of accidents you’ve been involved in. A history of accidents, especially those where you were at fault, will likely increase your premiums.
- Traffic Violations: Speeding tickets, reckless driving citations, and other traffic violations can also raise your premiums.
- Driving Record in Previous States: Insurance companies may access your driving record from previous states to get a complete picture of your driving history.
Age
Your age can also influence your insurance premiums. Young drivers, especially those under 25, are statistically more likely to be involved in accidents. As a result, they often pay higher premiums. However, as you age, your premiums typically decrease because you are considered a lower risk. This is because older drivers have more experience and are statistically less likely to be involved in accidents.
Vehicle Type
The type of vehicle you drive also plays a role in your insurance premium. Sports cars, luxury vehicles, and vehicles with high horsepower are generally considered riskier to insure. This is because they are more expensive to repair and replace, and they are often associated with higher speeds and more aggressive driving. On the other hand, smaller, less expensive vehicles are typically cheaper to insure.
Location
Your location is a major factor in determining your insurance premiums. Insurance companies consider factors such as:
- Population Density: Areas with higher population density tend to have more traffic and a greater risk of accidents, which can lead to higher premiums.
- Crime Rates: Areas with higher crime rates may have a greater risk of vehicle theft or vandalism, which can increase insurance premiums.
- Local Traffic Patterns: Areas with heavy traffic congestion or complex road layouts can increase the risk of accidents, leading to higher premiums.
- Accident Statistics: Insurance companies analyze accident statistics for specific areas to determine the risk of accidents in those locations.
Strategies for Lowering Your Insurance Premium
Here are some strategies you can use to potentially lower your insurance premium in your new state:
- Shop Around: Compare quotes from multiple insurance companies to find the best rates.
- Consider Bundling: Bundling your car insurance with other types of insurance, such as homeowners or renters insurance, can often result in discounts.
- Increase Your Deductible: Choosing a higher deductible can lower your premium, but it means you will have to pay more out of pocket if you have an accident.
- Improve Your Driving Record: Avoid traffic violations and drive safely to keep your driving record clean.
- Ask About Discounts: Inquire about any available discounts, such as good student discounts, safe driver discounts, or discounts for anti-theft devices.
- Maintain a Good Credit Score: In some states, insurance companies may use your credit score to determine your premium. A good credit score can lead to lower premiums.
Tips for a Smooth Transition of Car Insurance: Car Insurance Moving Out Of State

Moving to a new state often involves a lot of adjustments, and your car insurance is no exception. Ensuring a smooth transition of your car insurance is crucial to maintain coverage and avoid any potential gaps in protection. This section provides practical tips and a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the process efficiently.
Transferring Your Existing Policy
Transferring your existing car insurance policy to your new state can often be the most straightforward option. This involves notifying your current insurer about your move and requesting a policy update.
- Contact your insurer: Reach out to your current insurer as soon as you know your move date. This will allow them to start the process of transferring your policy.
- Provide new address and other details: Be prepared to provide your new address, driver’s license information, and any other relevant details required by your insurer. They will need this information to update your policy and ensure accurate coverage.
- Review policy updates: Once your insurer has processed your move, review the updated policy documents carefully. Ensure that the coverage limits, deductibles, and other terms remain consistent with your needs.
- Confirm effective date: Confirm the effective date of the policy transfer with your insurer. This will help you avoid any gaps in coverage during the transition period.
Final Wrap-Up

Moving out of state can be a significant life event, and ensuring you have adequate car insurance is essential. By understanding the intricacies of state-specific insurance laws, exploring new options, and following our tips for a smooth transition, you can navigate the process with confidence. Remember, having the right insurance coverage can provide peace of mind and protect you financially in the event of an accident.
Q&A
Do I need to notify my current insurance provider about my move?
Yes, you should inform your current insurance provider about your move as soon as possible. Failing to do so could lead to coverage gaps or potential issues if you need to file a claim.
Will my insurance rates change after I move?
Yes, your insurance rates can change after you move. Factors like the new state’s insurance laws, driving history, vehicle type, and local accident statistics can all affect your premiums.
How do I compare insurance quotes from different providers in my new state?
You can obtain quotes from different insurers online, by phone, or through an insurance broker. Make sure to compare coverage options, deductibles, and premium costs before making a decision.
What documents do I need to transfer my car insurance to the new state?
You will typically need your driver’s license, proof of vehicle registration, and your current insurance policy information. Some states may require additional documentation.