States with no fault car insurance – States with no-fault car insurance operate under a system where drivers are primarily responsible for covering their own losses after an accident, regardless of fault. This approach aims to streamline the claims process and reduce litigation, offering a unique alternative to traditional fault-based insurance. While no-fault systems offer potential advantages like quicker claim resolution and lower premiums, they also come with specific considerations for drivers, such as coverage limitations and the “threshold” for filing lawsuits.
Understanding the nuances of no-fault insurance is crucial for drivers in these states, as it significantly impacts their rights and responsibilities following an accident. This guide explores the key aspects of no-fault insurance, including its core principles, the states that have adopted it, and the implications for drivers seeking coverage and filing claims.
Understanding No-Fault Insurance
No-fault insurance is a type of auto insurance that covers your own injuries and damages, regardless of who caused the accident. This means you file a claim with your own insurance company, regardless of whether you were at fault. It’s a different approach compared to traditional fault-based insurance, where you file a claim with the at-fault driver’s insurance company.
No-Fault Insurance Explained
No-fault insurance operates on the principle of “first-party coverage,” meaning your own insurance company covers your losses, regardless of who was at fault. This system aims to simplify the claims process and reduce the time and cost associated with resolving accidents.
Difference Between No-Fault and Fault-Based Insurance
- In no-fault insurance, you file a claim with your own insurance company, regardless of fault. Your insurance company covers your losses, such as medical expenses, lost wages, and property damage.
- In fault-based insurance, you file a claim with the at-fault driver’s insurance company. The at-fault driver’s insurance company is responsible for covering your losses.
Situations Where No-Fault Insurance Applies
No-fault insurance typically applies to situations involving:
- Medical expenses: Covers medical treatment, rehabilitation, and other related expenses for injuries sustained in an accident.
- Lost wages: Compensates for income lost due to inability to work following an accident.
- Property damage: Covers repairs or replacement of your vehicle or other property damaged in an accident.
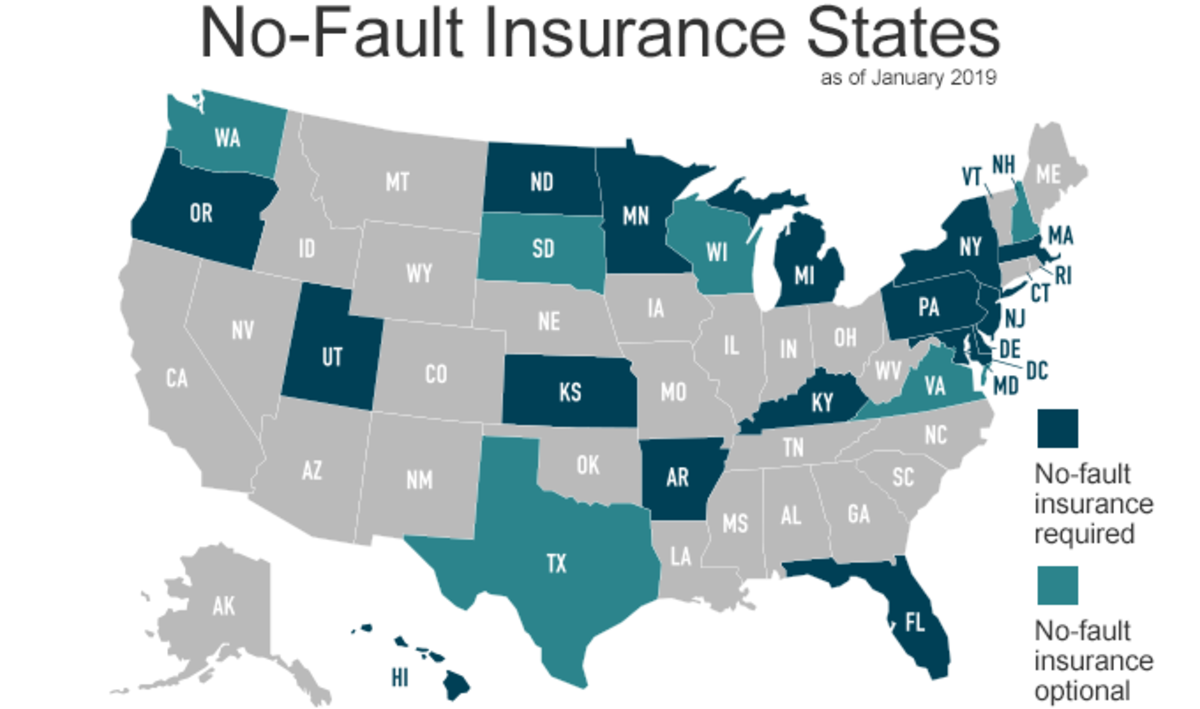
States with No-Fault Laws
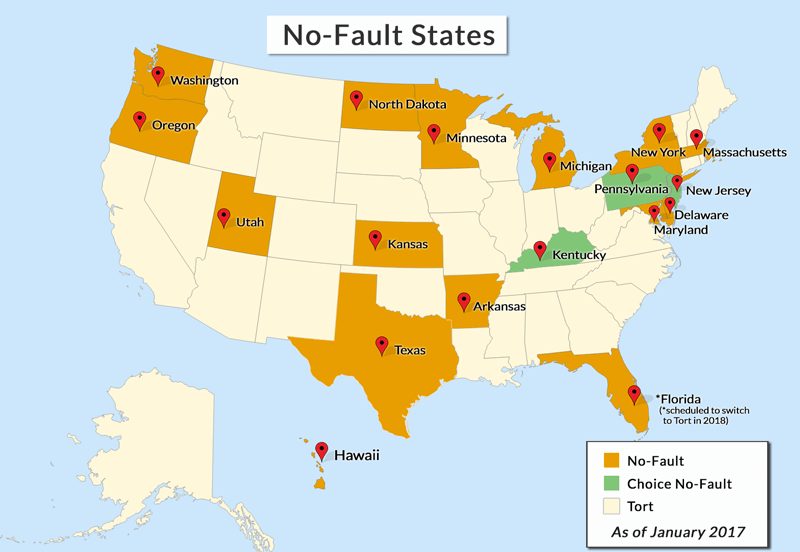
No-fault insurance, also known as personal injury protection (PIP), is a type of car insurance that covers your own medical expenses and lost wages after an accident, regardless of who is at fault. It is designed to simplify the claims process and reduce litigation. Some states have no-fault laws that require drivers to carry this type of coverage.
States with No-Fault Laws, States with no fault car insurance
The following table lists all states with no-fault car insurance laws, along with the effective date of the law and any specific features or exceptions.
| State | Effective Date | Features/Exceptions |
|—|—|—|
| Florida | 1971 | Pure no-fault; limited right to sue for pain and suffering |
| Hawaii | 1974 | Pure no-fault; limited right to sue for pain and suffering |
| Kansas | 1974 | Modified no-fault; right to sue for serious injuries |
| Kentucky | 1975 | Modified no-fault; right to sue for serious injuries |
| Michigan | 1973 | No-fault; right to sue for economic losses exceeding PIP benefits |
| Minnesota | 1975 | Modified no-fault; right to sue for serious injuries |
| New Jersey | 1973 | No-fault; right to sue for economic losses exceeding PIP benefits |
| New York | 1973 | No-fault; right to sue for serious injuries |
| North Dakota | 1975 | Modified no-fault; right to sue for serious injuries |
| Pennsylvania | 1975 | Modified no-fault; right to sue for serious injuries |
| | | |
Types of No-Fault Systems
There are three main types of no-fault systems:
* Pure no-fault: In a pure no-fault system, drivers are required to file claims with their own insurance company, regardless of who caused the accident. Drivers are generally prohibited from suing for pain and suffering, even if they have suffered a serious injury.
* Modified no-fault: In a modified no-fault system, drivers are required to file claims with their own insurance company, but they retain the right to sue for damages in certain circumstances, such as when their injuries are serious or when the other driver was at fault.
* Add-on no-fault: In an add-on no-fault system, drivers can choose to purchase no-fault coverage in addition to traditional liability coverage. This allows drivers to choose the level of coverage they want and to decide whether they want to retain the right to sue.
Advantages and Disadvantages of No-Fault Insurance
No-fault insurance has both advantages and disadvantages for drivers.
Advantages:
* Faster claims processing: Because drivers file claims with their own insurance company, the claims process is often faster and simpler than in traditional liability systems.
* Reduced litigation: No-fault systems are designed to reduce litigation, which can save drivers time and money.
* Lower insurance premiums: Some studies have shown that no-fault insurance can lead to lower insurance premiums, although this is not always the case.
Disadvantages:
* Limited compensation: In some cases, no-fault insurance may not provide enough compensation for serious injuries.
* Potential for abuse: Some drivers may abuse the system by filing false claims or exaggerating their injuries.
* Limited right to sue: In some states, drivers may be prohibited from suing for pain and suffering, even if they have suffered a serious injury.
Coverage Under No-Fault Insurance
No-fault insurance, as the name suggests, focuses on covering your own losses after a car accident, regardless of who caused it. It simplifies the claims process and aims to expedite compensation. Let’s delve into the specific types of coverage and how they work.
Types of Coverage
No-fault insurance policies typically include the following types of coverage:
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): This coverage pays for your medical expenses, lost wages, and other related costs resulting from injuries sustained in an accident, regardless of fault. It’s usually capped at a certain amount, and you may need to meet a deductible.
- Property Damage Coverage: This coverage helps pay for repairs or replacement of your vehicle if it’s damaged in an accident. It’s typically limited to the actual cash value of the vehicle, meaning the current market value, minus depreciation.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage (UM/UIM): This coverage protects you if you’re involved in an accident with a driver who doesn’t have insurance or doesn’t have enough coverage to cover your losses. It’s essential, as it can help cover medical expenses, lost wages, and property damage.
Determining and Paying Out Benefits
No-fault insurance benefits are typically determined and paid out based on the following factors:
- Policy Limits: Your policy will specify the maximum amount of coverage you have for each type of benefit, such as medical expenses, lost wages, and property damage.
- Deductible: You may need to pay a deductible before your insurance company starts paying benefits. This is a fixed amount that you pay out of pocket for each claim.
- Documentation: You’ll need to provide documentation to support your claim, such as medical bills, lost wage statements, and repair estimates.
- Time Limits: There may be time limits for filing claims and receiving benefits. For instance, you might have a limited time to seek medical treatment or file a claim for lost wages.
Common Limitations and Exclusions
While no-fault insurance aims to simplify the claims process, it does have limitations and exclusions:
- Thresholds for Filing a Lawsuit: In some no-fault states, you may not be able to sue the other driver for pain and suffering unless your injuries meet a certain severity threshold, such as a specific medical expense limit or a permanent disability.
- Exclusions for Certain Injuries: No-fault insurance may exclude coverage for certain types of injuries, such as those caused by intentional acts or while engaging in illegal activities.
- Limited Coverage for Passengers: The coverage for passengers in your vehicle may be limited or subject to different rules than your own coverage.
Impact of No-Fault on Claims Processes: States With No Fault Car Insurance
No-fault insurance significantly alters the claims process compared to traditional fault-based systems. The emphasis shifts from determining fault to expediting the process and providing swift compensation for covered losses.
Role of Personal Injury Protection (PIP)
Personal Injury Protection (PIP) coverage plays a crucial role in no-fault systems. It covers medical expenses, lost wages, and other related costs for the policyholder and their passengers, regardless of who caused the accident. This eliminates the need for lengthy investigations into fault and allows for quicker access to medical treatment and financial assistance.
Threshold for Filing a Lawsuit
No-fault laws typically include a “threshold” that determines when an injured party can file a lawsuit against the other driver. This threshold can be based on the severity of the injuries, the amount of medical expenses incurred, or a combination of factors. If the threshold is not met, the injured party is limited to recovering benefits under their own PIP coverage.
Considerations for Drivers in No-Fault States
Living in a no-fault state means navigating a unique insurance landscape. Understanding the intricacies of no-fault insurance is crucial for drivers to ensure they have adequate coverage and are prepared to handle potential accidents. This section explores key considerations for drivers in no-fault states, providing insights on choosing the right insurance policy, understanding coverage limits and deductibles, and navigating the claims process.
Choosing the Right Insurance Policy
Selecting the right insurance policy in a no-fault state involves carefully considering your individual needs and risk profile. Factors such as your driving history, vehicle type, and budget play a significant role in determining the optimal coverage. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Understand Your State’s Minimum Requirements: Each no-fault state has specific minimum coverage requirements that drivers must meet. These requirements typically include Personal Injury Protection (PIP) and Property Damage Liability (PDL). Make sure your chosen policy complies with these legal mandates.
- Evaluate Your Coverage Needs: While minimum requirements are essential, you may need additional coverage based on your individual circumstances. Consider factors like your health insurance coverage, the value of your vehicle, and your driving habits. If you frequently drive in high-traffic areas or have a history of accidents, higher coverage limits might be beneficial.
- Compare Quotes and Deductibles: Obtaining quotes from multiple insurers is crucial to finding the best value for your money. Compare coverage options, deductibles, and premiums to determine the most suitable policy. A higher deductible generally translates to lower premiums, but you’ll need to pay more out of pocket in case of an accident.
- Consider Additional Coverage: Beyond basic requirements, consider adding optional coverage such as collision and comprehensive insurance. Collision coverage covers damage to your vehicle in an accident, while comprehensive insurance covers damage from events like theft or vandalism. These additional layers of protection can provide peace of mind and financial security.
Understanding Coverage Limits and Deductibles
Coverage limits and deductibles are essential components of your no-fault insurance policy. They define the maximum amount your insurer will pay for covered expenses and the amount you’ll pay out of pocket before coverage kicks in.
- PIP Coverage Limits: This coverage typically has a limit on the total amount your insurer will pay for medical expenses, lost wages, and other related costs. It’s crucial to choose a limit that aligns with your potential medical expenses and income loss.
- Deductibles: This is the amount you pay out of pocket for each claim before your insurance coverage starts. Higher deductibles generally result in lower premiums, but you’ll need to pay more in case of an accident. Consider your financial situation and risk tolerance when selecting a deductible.
Navigating the Claims Process
Filing a claim under no-fault insurance involves specific steps and considerations. Here’s a guide to navigating the process:
- Report the Accident: Immediately report the accident to your insurer, providing details about the incident and any injuries sustained. This ensures prompt initiation of the claims process.
- Seek Medical Treatment: If you’ve been injured, seek medical attention promptly. Your insurer may require you to use specific healthcare providers within their network.
- Document Everything: Keep detailed records of all medical expenses, lost wages, and other related costs. These documents will be crucial for supporting your claim.
- Cooperate with Your Insurer: Provide your insurer with all necessary documentation and information to facilitate the claims process. Be responsive to their requests and inquiries.
- Understand Your Rights: Familiarize yourself with your rights under no-fault insurance laws. This includes the right to choose your own healthcare provider, the right to appeal denied claims, and the right to negotiate settlements.
Conclusive Thoughts
Navigating the world of no-fault car insurance can be complex, but by understanding its intricacies, drivers in these states can make informed decisions about their coverage and navigate the claims process effectively. Whether you’re considering a move to a no-fault state or simply seeking a deeper understanding of this unique insurance system, this guide provides valuable insights to empower you to make the best choices for your driving needs.
Detailed FAQs
What is the difference between no-fault and traditional fault-based insurance?
In traditional fault-based insurance, the at-fault driver is responsible for covering the other driver’s damages. In no-fault insurance, each driver is primarily responsible for their own losses, regardless of fault.
What are the main types of no-fault systems?
There are three main types: pure no-fault, modified no-fault, and add-on no-fault. Pure no-fault prohibits lawsuits for pain and suffering, while modified no-fault allows lawsuits under certain circumstances. Add-on no-fault is an optional add-on to traditional insurance.
How does the “threshold” work in no-fault states?
The “threshold” determines when you can sue the other driver. Some states have a “serious injury” threshold, meaning you can sue only if your injuries meet a certain severity level.