States where car insurance is not mandatory offer a unique perspective on the American driving landscape. In these states, drivers have the option to forgo traditional car insurance, potentially saving money in the short term but exposing themselves to significant financial risks in the event of an accident. This exploration delves into the legal implications, financial burdens, and alternative insurance options available in these states.
The decision to drive uninsured is a personal one, often weighed against the perceived cost of insurance. However, the potential consequences of an accident can be devastating, leaving uninsured drivers facing substantial financial liabilities and legal repercussions. This article examines the arguments for and against mandatory car insurance, highlighting the importance of responsible driving practices and informed decision-making.
States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
While most states in the US mandate car insurance, there are a few exceptions. Driving without insurance in these states, although not a direct violation of the law, can have significant legal and financial consequences.
Legal Implications of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without insurance in states where it is not mandatory does not mean you are completely free from legal repercussions. If you are involved in an accident, you could face serious legal consequences, including:
* Civil Liability: You could be held personally liable for all damages and injuries caused by the accident, even if you were not at fault.
* License Suspension: Your driver’s license may be suspended if you are involved in an accident and do not have insurance.
* Financial Penalties: You may face fines or other penalties for driving without insurance, even if you are not involved in an accident.
* Imprisonment: In some cases, driving without insurance can lead to imprisonment, particularly if you are involved in a serious accident.
Financial Risks of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without insurance in states where it is not mandatory exposes you to significant financial risks. If you are involved in an accident, you could be responsible for:
* Medical Expenses: You could be held liable for the medical expenses of anyone injured in the accident, including yourself.
* Property Damage: You could be responsible for repairing or replacing any damaged property, including your own vehicle.
* Lost Wages: You could be held liable for the lost wages of anyone injured in the accident.
* Legal Fees: You could be responsible for the legal fees of the other party involved in the accident.
States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
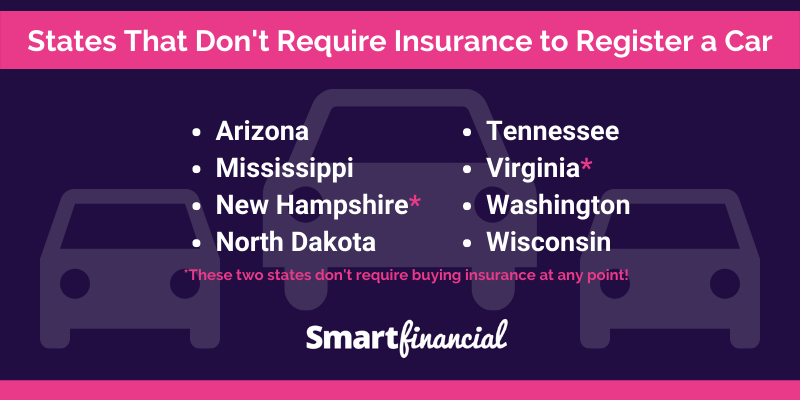
Currently, there are only a few states that do not require car insurance:
- New Hampshire
- Virginia (for drivers with proof of financial responsibility)
It is important to note that even in these states, it is highly recommended to have car insurance. The financial risks of driving without insurance far outweigh the potential savings.
Real-World Examples of Accidents Involving Uninsured Drivers
There have been numerous cases of accidents involving uninsured drivers in states where car insurance is not mandatory. These accidents have resulted in significant financial hardship for the victims, as the uninsured drivers were unable to cover the costs of their injuries and damages.
“In a recent case in New Hampshire, a driver without insurance caused a multi-car accident, leaving several people injured and with significant property damage. The uninsured driver was unable to cover the costs of the accident, leaving the victims to shoulder the financial burden.”
The Rationale Behind Non-Mandatory Insurance

In the United States, the requirement for car insurance varies by state. While many states mandate car insurance, a few have opted for a system that does not necessitate it. The decision to forgo mandatory car insurance is rooted in a complex interplay of economic, social, and philosophical considerations. This section explores the rationale behind this approach, examining the arguments for and against mandatory car insurance laws, comparing insurance regulations across different states, and analyzing the potential economic and social impacts of a non-mandatory system.
Arguments for and Against Mandatory Car Insurance
The debate surrounding mandatory car insurance centers on the balance between individual freedom and societal responsibility. Proponents of mandatory insurance argue that it protects vulnerable road users, ensures financial responsibility for accidents, and promotes a safer driving environment. They highlight the potential for catastrophic financial consequences for victims of uninsured drivers, as well as the burden on taxpayers and the healthcare system to cover the costs of uninsured accidents. Conversely, opponents of mandatory insurance emphasize the principle of individual liberty and the right to choose how to manage personal risks. They argue that forcing individuals to purchase insurance infringes on their autonomy and can lead to higher premiums for responsible drivers.
- Arguments for Mandatory Car Insurance:
- Protection for Victims: Mandatory car insurance ensures that victims of accidents have access to compensation for medical expenses, lost wages, and property damage, regardless of the driver’s financial status. This safeguard is particularly crucial for individuals who may be unable to afford legal representation or bear the financial burden of their injuries.
- Financial Responsibility: By requiring drivers to carry insurance, states ensure that individuals are financially responsible for the consequences of their actions on the road. This principle promotes accountability and discourages reckless driving.
- Safer Driving Environment: Research suggests that mandatory car insurance laws can contribute to a safer driving environment. Drivers who are aware of the potential financial consequences of an accident may be more likely to exercise caution and avoid risky behaviors.
- Reduced Burden on Taxpayers and Healthcare: The costs associated with uninsured accidents are often borne by taxpayers through government programs and by healthcare providers through uncompensated care. Mandatory car insurance helps to mitigate these costs by ensuring that drivers are financially responsible for their actions.
- Arguments Against Mandatory Car Insurance:
- Individual Liberty: Opponents of mandatory car insurance argue that it infringes on individual liberty by forcing people to purchase a product they may not need or desire. They believe that individuals should have the freedom to choose how to manage their own risks.
- Higher Premiums for Responsible Drivers: The presence of high-risk uninsured drivers in the pool of insured drivers can lead to higher premiums for responsible drivers who are forced to subsidize the costs of those who choose not to carry insurance.
- Government Overreach: Some argue that mandatory car insurance represents government overreach into personal affairs and that individuals should be free to make their own decisions about insurance coverage.
Consequences of Driving Uninsured

While states without mandatory car insurance might not require drivers to have coverage, there are significant consequences for those who choose to drive without it. These consequences can range from legal penalties to substantial financial burdens in the event of an accident.
Legal Penalties for Driving Without Insurance
Driving without insurance in states where it is not mandatory can lead to various legal penalties. These penalties can vary from state to state, but some common consequences include:
- Fines: Drivers caught driving without insurance can face hefty fines, which can range from hundreds to thousands of dollars. The specific amount of the fine can vary based on the state and the number of offenses.
- License Suspension: In some states, driving without insurance can lead to the suspension of your driver’s license. This suspension can make it difficult to legally operate a vehicle and could have further repercussions, such as difficulty finding employment or accessing essential services.
- Vehicle Impoundment: Your vehicle might be impounded until you provide proof of insurance. This can be an inconvenience and may result in additional fees for storage and release.
- Court Appearances: You might be required to appear in court to address the violation, which can involve additional time and costs.
Higher Insurance Premiums After Obtaining Insurance
Even if you manage to avoid legal penalties for driving uninsured, opting to obtain insurance later could lead to higher premiums. Insurance companies view drivers without a history of continuous coverage as higher risk. This is because they may have been involved in accidents or incidents that went unreported, increasing the likelihood of future claims.
Financial Burden of Accident-Related Expenses
The most significant consequence of driving uninsured is the financial burden you could face in the event of an accident. Without insurance coverage, you will be personally responsible for all accident-related expenses, including:
- Medical Expenses: If you or someone else is injured in an accident, you will be responsible for all medical bills, including hospital stays, surgeries, and rehabilitation.
- Property Damage: You will be responsible for repairing or replacing any damaged property, including your vehicle, the other driver’s vehicle, and any other property involved in the accident.
- Legal Fees: If you are sued by the other party involved in the accident, you will have to cover your own legal expenses, which can be significant.
- Lost Wages: If you are unable to work due to injuries sustained in the accident, you will not receive any compensation for lost wages.
Consequences of Serious Accidents
The consequences of driving uninsured can be particularly severe in the event of a serious accident. In such cases, the financial burden can be overwhelming, potentially leading to:
- Bankruptcy: The costs associated with a serious accident can quickly exceed your financial resources, potentially leading to bankruptcy.
- Legal Judgment: You could face a significant legal judgment that you may be unable to pay, potentially resulting in wage garnishment or the seizure of assets.
- Criminal Charges: In some cases, serious accidents involving uninsured drivers could result in criminal charges, such as reckless driving or vehicular manslaughter.
Alternatives to Traditional Car Insurance
In states without mandatory car insurance, drivers have the option to explore alternative insurance options or even choose to self-insure. These alternatives can offer cost savings or cater to specific needs, but they also come with inherent risks and require careful consideration.
Self-Insurance
Self-insurance, also known as going without insurance, involves assuming full financial responsibility for any accidents or damages you cause. It can be a cost-effective option for drivers with a clean driving record and a substantial financial cushion. However, the potential financial burden of a significant accident can be substantial.
- Pros:
- Lower costs compared to traditional insurance.
- Potential for greater financial control.
- Cons:
- Significant financial risk in the event of an accident.
- Potential legal repercussions if you cannot cover damages.
- Limited access to legal representation and claims assistance.
Liability Umbrella Policy
A personal liability umbrella policy provides additional coverage above and beyond your existing home, auto, and other liability insurance policies. While it’s not a replacement for car insurance, it can offer a financial safety net in case of a significant accident, helping to cover costs exceeding your primary policy limits.
- Pros:
- Provides additional coverage beyond primary policies.
- Can offer protection against lawsuits and judgments.
- Cons:
- Does not cover damage to your own vehicle.
- Requires a significant financial investment.
- May have deductibles and other limitations.
Other Financial Safety Nets
In addition to self-insurance and umbrella policies, drivers in states without mandatory car insurance can explore other financial safety nets to mitigate the risks of driving uninsured.
- Savings Accounts: Setting aside a dedicated emergency fund can provide financial cushion in case of an accident.
- Credit Lines: A readily available line of credit can offer short-term financing for unexpected expenses. However, using credit can come with high interest rates.
- Family and Friends: While not a formal financial safety net, relying on family and friends for financial assistance in the event of an accident is a possibility.
Safety Considerations and Best Practices
Driving without insurance in states where it’s not mandatory comes with significant risks. It’s crucial to prioritize safety and minimize potential liabilities.
Safe Driving Practices, States where car insurance is not mandatory
It’s essential to adopt safe driving habits to protect yourself and others on the road.
- Defensive Driving: Always be aware of your surroundings, anticipate potential hazards, and maintain a safe following distance. This proactive approach can help avoid accidents.
- Speed Limits: Adhere to posted speed limits and adjust your speed based on weather and road conditions.
- Distracted Driving: Avoid using your phone or engaging in other distracting activities while driving. Focus on the road and maintain situational awareness.
- Impaired Driving: Never drive under the influence of alcohol or drugs. Designate a sober driver or use alternative transportation options.
- Vehicle Maintenance: Regular vehicle maintenance is crucial for safe driving. Ensure your brakes, tires, lights, and other essential components are in good working order.
Maintaining a Clean Driving Record
A clean driving record is crucial for mitigating risks in states without mandatory insurance.
- Avoid Traffic Violations: Obeying traffic laws and avoiding violations such as speeding, reckless driving, and running red lights can significantly reduce your risk of accidents and insurance premiums.
- Defensive Driving Courses: Consider taking a defensive driving course to enhance your driving skills and learn strategies for avoiding accidents. These courses can also lead to discounts on your insurance premiums in some states.
- Safe Driving Habits: Maintain a consistent safe driving record to avoid accidents and potential liabilities. This can help you secure better insurance rates and avoid penalties.
Investing in Safety Features and Equipment
Upgrading your vehicle with safety features and equipment can enhance your safety on the road.
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): ABS helps prevent wheel lockup during braking, enhancing control and reducing the risk of skidding.
- Electronic Stability Control (ESC): ESC helps maintain vehicle stability during maneuvers, particularly in slippery conditions.
- Airbags: Airbags provide an extra layer of protection in case of an accident. Ensure your vehicle has a sufficient number of airbags for all occupants.
- Backup Camera: A backup camera can help prevent accidents when backing up, especially in areas with limited visibility.
- Blind Spot Monitoring: Blind spot monitoring systems alert you to vehicles in your blind spots, reducing the risk of collisions during lane changes.
Avoiding Potential Accidents and Minimizing Financial Liability
Taking precautions can help minimize the risk of accidents and financial liabilities.
- Avoid High-Risk Areas: Be aware of areas with high traffic volume or accident rates and avoid driving in those areas if possible.
- Proper Parking: Park your vehicle in well-lit, safe areas to reduce the risk of theft or vandalism.
- Secure Valuables: Don’t leave valuable items in plain sight in your vehicle, as this can attract thieves.
- Emergency Kit: Keep an emergency kit in your vehicle, including a first-aid kit, flashlight, jumper cables, and other essential supplies.
Final Thoughts: States Where Car Insurance Is Not Mandatory
Navigating the roads in states without mandatory car insurance requires a high level of awareness and responsibility. Drivers must carefully weigh the potential risks and costs associated with choosing not to carry insurance. While the freedom to choose is a significant aspect of these states’ approach to car insurance, the financial and legal consequences of an accident can be severe. Ultimately, understanding the potential consequences and exploring alternative insurance options are crucial for ensuring financial security and peace of mind on the road.
FAQ Compilation
What happens if I get into an accident in a state without mandatory car insurance?
You will be held personally liable for any damages or injuries you cause. You may face lawsuits, financial hardship, and potential legal penalties.
Are there any states that require car insurance even if it’s not mandatory?
Yes, some states require drivers to show proof of financial responsibility, which may include insurance or other forms of financial security.
What are some alternative insurance options available in states without mandatory car insurance?
Alternatives include self-insurance, liability umbrella policies, and specialized insurance plans designed for high-risk drivers.
Can I drive without insurance if I have a clean driving record?
While a clean driving record may reduce your risk, it does not eliminate the potential for accidents and the financial burden they can bring.