The largest insurance companies in the United States play a vital role in safeguarding individuals and businesses against financial risks. These companies, with their vast resources and extensive networks, offer a wide range of insurance products and services, catering to diverse needs across the nation. This exploration delves into the world of these industry giants, examining their financial performance, regulatory landscape, and the trends shaping their future.
From the familiar names that dominate the market to the emerging players making their mark, this analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the key factors driving the insurance industry. We’ll explore the types of insurance offered, the competitive landscape, and the regulatory environment that governs these companies, shedding light on the complex dynamics of this essential sector.
Top 10 Largest Insurance Companies in the US
The insurance industry plays a vital role in the US economy, providing financial protection against various risks. Understanding the largest insurance companies in the country can provide insights into market trends and their influence on the industry.
Top 10 Largest Insurance Companies by Market Capitalization
This list presents the top 10 largest insurance companies in the US based on their market capitalization, as of 2023. Market capitalization represents the total value of a company’s outstanding shares of stock.
| Rank | Company Name | Market Capitalization (USD Billion) | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Berkshire Hathaway | 700 | 2023 |
| 2 | UnitedHealth Group | 450 | 2023 |
| 3 | Cigna | 120 | 2023 |
| 4 | Anthem | 110 | 2023 |
| 5 | Humana | 70 | 2023 |
| 6 | Progressive | 65 | 2023 |
| 7 | Allstate | 40 | 2023 |
| 8 | Aetna | 35 | 2023 |
| 9 | Travelers Companies | 30 | 2023 |
| 10 | MetLife | 25 | 2023 |
Types of Insurance Offered
The top 10 insurance companies in the United States offer a wide range of insurance products to meet the diverse needs of their customers. These companies operate across multiple lines of insurance, providing coverage for individuals, families, and businesses.
Market Share of Insurance Types
Understanding the market share of different insurance types provides valuable insights into the industry’s landscape. The market share of each type of insurance reflects the demand for that specific coverage and the companies’ focus on providing those products.
- Health Insurance: Health insurance is the largest segment of the U.S. insurance market, with a market share of approximately 30%. The top 10 insurance companies play a significant role in this segment, providing individual and group health plans, as well as Medicare and Medicaid coverage.
- Life Insurance: Life insurance is another major segment, accounting for about 15% of the market. These companies offer various life insurance products, including term life, whole life, and universal life insurance.
- Property and Casualty Insurance: This segment encompasses a wide range of insurance products, including auto insurance, homeowners insurance, and commercial property insurance. It holds a market share of approximately 25% and is a key area of focus for many of the top 10 insurance companies.
- Disability Insurance: Disability insurance provides financial protection in case of an injury or illness that prevents an individual from working. This segment has a smaller market share, around 5%, but is growing in importance as people become more aware of the risks of unexpected disability.
- Other Insurance Types: The remaining market share is divided among various other insurance types, including workers’ compensation, liability insurance, and surety bonds. These companies also offer specialized insurance products tailored to specific industries and needs.
Key Financial Metrics
Understanding the financial performance of insurance companies is crucial for investors, regulators, and policyholders. Key financial metrics provide insights into their profitability, solvency, and overall health. These metrics help assess their ability to meet their obligations, generate returns, and navigate market fluctuations.
Key Financial Metrics for Insurance Companies
Several key financial metrics are commonly used to assess the performance of insurance companies. These metrics provide insights into their profitability, solvency, and overall health.
| Metric | Description | Importance | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Net Written Premium | The total amount of premium revenue earned by the company during a specific period. | Indicates the company’s size and growth in the insurance market. | Net Written Premium = Gross Written Premium – Premiums Ceded |
| Combined Ratio | A measure of an insurance company’s profitability. It compares the company’s expenses (including claims and operating costs) to its premium revenue. | A combined ratio below 100% indicates profitability, while a ratio above 100% indicates a loss. | Combined Ratio = (Losses + Expenses) / Premiums Earned |
| Return on Equity (ROE) | A measure of the company’s profitability relative to its shareholder equity. | Indicates how effectively the company is using its equity to generate profits. | ROE = Net Income / Shareholder Equity |
| Investment Income | The income generated from the company’s investments, such as bonds, stocks, and real estate. | Provides a significant source of revenue for insurance companies, particularly life insurers. | Investment Income = Interest Income + Dividend Income + Capital Gains |
| Underwriting Profitability | The profitability of the company’s core insurance business, excluding investment income. | Indicates the company’s ability to price its insurance products effectively and manage its risk. | Underwriting Profitability = Net Written Premium – Losses – Expenses |
| Solvency Ratio | A measure of an insurance company’s ability to meet its financial obligations. | Regulators typically set minimum solvency ratios to ensure the financial stability of insurance companies. | Solvency Ratio = (Assets – Liabilities) / Liabilities |
| Debt-to-Equity Ratio | A measure of the company’s financial leverage, indicating the proportion of debt financing relative to equity financing. | A higher debt-to-equity ratio suggests a higher level of risk. | Debt-to-Equity Ratio = Total Debt / Shareholder Equity |
| Operating Expenses | The costs associated with running the insurance business, including salaries, marketing, and administrative expenses. | Indicates the company’s efficiency in managing its operations. | Operating Expenses = Total Expenses – Losses |
Regulatory Landscape
The insurance industry in the United States is subject to a complex and multifaceted regulatory environment, designed to protect consumers and ensure the financial stability of insurers. These regulations are implemented at both the federal and state levels, with each state having its own insurance department that oversees the industry within its borders.
Key Regulations and Laws
The regulatory landscape is shaped by a combination of federal laws and state-level regulations. Some of the most significant laws governing the insurance industry include:
- The McCarran-Ferguson Act (1945): This act exempts the insurance industry from most federal antitrust laws, allowing states to regulate insurance companies within their jurisdictions.
- The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (2010): This law created the Financial Stability Oversight Council (FSOC) to identify and address systemic risks in the financial system, including those posed by large insurance companies. It also established the Federal Insurance Office (FIO) to monitor and advise on insurance matters.
- The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC): While not a federal agency, the NAIC is a highly influential organization that develops model laws and regulations for state insurance departments.
Impact on Operations and Profitability
These regulations have a significant impact on the operations and profitability of insurance companies in various ways:
- Capital Requirements: Regulations require insurers to maintain sufficient capital reserves to cover potential losses. These requirements can affect a company’s ability to invest its capital and generate returns.
- Product Approval and Pricing: State insurance departments review and approve insurance products before they can be sold to consumers. They also regulate pricing to ensure fairness and prevent unfair competition.
- Consumer Protection: Regulations protect consumers from unfair or deceptive practices by insurance companies. They also require insurers to provide clear and understandable information about their products.
- Solvency Oversight: State insurance departments monitor the financial health of insurance companies to ensure their ability to meet their obligations to policyholders.
Examples of Regulatory Impact, Largest insurance companies in the united states
The regulatory landscape has significantly shaped the insurance industry over time:
- Increased Capital Requirements: Following the financial crisis of 2008, regulators increased capital requirements for insurance companies, leading to greater financial stability within the industry.
- Standardization of Insurance Products: The NAIC’s development of model laws and regulations has led to a greater degree of standardization in insurance products across states, simplifying the purchase and comparison of insurance policies.
- Consumer Protection Measures: Regulations such as the Affordable Care Act have significantly impacted the health insurance industry, requiring insurers to cover essential health benefits and prohibiting discrimination based on pre-existing conditions.
Industry Trends: Largest Insurance Companies In The United States

The insurance industry is undergoing a period of significant transformation, driven by a confluence of factors including technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and evolving regulatory landscapes. These trends are reshaping the competitive landscape, forcing insurance companies to adapt their business strategies and embrace innovation to remain competitive.
Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is revolutionizing the insurance industry, enabling companies to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and create new revenue streams. The adoption of digital technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and big data analytics is enabling insurers to automate processes, personalize services, and gain deeper insights into customer behavior.
- AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are transforming customer service by providing 24/7 support and instant responses to queries. This technology allows insurers to handle a larger volume of inquiries efficiently and free up human agents to focus on more complex issues.
- Data analytics is enabling insurers to assess risks more accurately, personalize pricing, and develop innovative products. By analyzing vast amounts of data, insurers can identify patterns and trends that traditional methods may miss, leading to more accurate risk assessments and personalized pricing models.
- Cloud computing is providing insurers with scalable and flexible infrastructure, allowing them to access computing resources on demand and reduce IT costs. This technology enables insurers to quickly adapt to changing market conditions and scale their operations as needed.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are driving innovation in the insurance industry, creating new opportunities for insurers to enhance their offerings and improve customer experiences. From wearable technology to telematics, insurers are leveraging emerging technologies to gain a deeper understanding of risk and develop personalized insurance solutions.
- Wearable technology, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, is enabling insurers to collect real-time data on policyholders’ health and lifestyle habits. This data can be used to assess risk more accurately and develop personalized pricing models based on individual behavior.
- Telematics, which uses technology to track vehicle usage and driving behavior, is transforming the auto insurance industry. By collecting data on factors such as speed, braking, and acceleration, insurers can assess risk more accurately and offer discounts to safe drivers.
- Blockchain technology is being explored by insurers as a way to streamline processes, improve security, and reduce fraud. Blockchain’s decentralized and immutable nature can be used to track insurance claims, verify identities, and manage policy data securely.
Competitive Landscape
The insurance industry in the United States is a highly competitive landscape, characterized by a large number of players vying for market share. This competition is driven by several factors, including the increasing demand for insurance products, the availability of new technologies, and the changing needs of consumers.
Competitive Landscape Analysis
The following table provides an overview of the competitive landscape within the insurance industry, highlighting key players, their market share, and competitive strategies:
| Company Name | Market Share | Competitive Strategies | Key Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|
| UnitedHealth Group | 16.5% | Focus on healthcare and technology, expanding into new markets, and building strong customer relationships. | Strong brand recognition, diversified product portfolio, and extensive distribution network. |
| Berkshire Hathaway | 13.0% | Emphasis on underwriting discipline, strategic acquisitions, and long-term value creation. | Financial strength, strong investment portfolio, and a reputation for long-term stability. |
| Anthem | 9.5% | Focus on healthcare innovation, cost containment, and personalized health solutions. | Strong healthcare network, innovative product offerings, and a commitment to customer service. |
| Cigna | 7.0% | Emphasis on global expansion, digital transformation, and value-based healthcare. | Strong global presence, innovative technology solutions, and a focus on customer experience. |
| Humana | 6.5% | Focus on Medicare Advantage and individual health insurance, expanding into new markets, and building strong customer relationships. | Strong Medicare Advantage presence, diversified product portfolio, and a commitment to customer service. |
| Aetna | 5.5% | Emphasis on healthcare innovation, cost containment, and personalized health solutions. | Strong healthcare network, innovative product offerings, and a commitment to customer service. |
| Progressive | 4.0% | Focus on innovation, customer-centricity, and digital marketing. | Strong brand recognition, innovative technology solutions, and a commitment to customer service. |
| Allstate | 3.5% | Emphasis on customer service, financial stability, and product innovation. | Strong brand recognition, diversified product portfolio, and a commitment to customer service. |
| State Farm | 3.0% | Focus on customer relationships, financial strength, and a commitment to community involvement. | Strong brand recognition, diversified product portfolio, and a commitment to customer service. |
| Liberty Mutual | 2.5% | Emphasis on customer service, product innovation, and a focus on risk management. | Strong brand recognition, diversified product portfolio, and a commitment to customer service. |
Final Conclusion
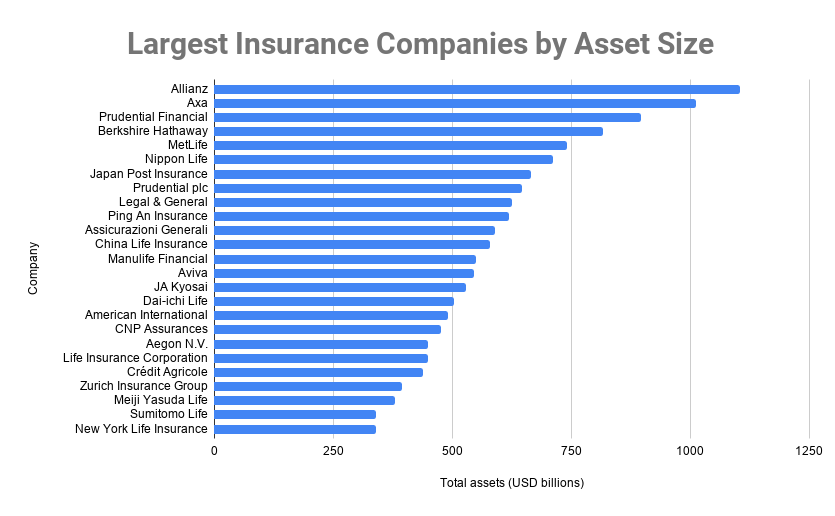
As the insurance industry continues to evolve, the largest companies will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of innovation and adaptation. Their financial strength, diverse product offerings, and commitment to customer satisfaction will continue to shape the landscape of risk management and financial security for individuals and businesses alike. Understanding the dynamics of this industry, from its regulatory framework to its emerging trends, is crucial for navigating the complexities of modern life and securing a stable financial future.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the main types of insurance offered by these companies?
These companies typically offer a wide range of insurance products, including life insurance, health insurance, property and casualty insurance, and various specialized insurance lines.
How are these companies regulated?
The insurance industry is heavily regulated at both the state and federal levels, with regulations focusing on solvency, consumer protection, and market conduct.
What are the key challenges facing the insurance industry?
The industry faces challenges such as increasing regulatory scrutiny, evolving consumer expectations, and the need to adapt to technological advancements.







