What states require car insurance? This question is crucial for any driver, as it determines your legal obligation and potential consequences for failing to comply. The United States has a patchwork of regulations regarding car insurance, with some states mandating coverage while others leave it to individual discretion. Understanding these requirements is vital to ensure you’re protected on the road and avoid costly penalties.
Across the country, states have different minimum liability coverage requirements, meaning the minimum amount of financial protection you must have in case you cause an accident. Factors like driving history, age, vehicle type, and location can also significantly impact your insurance premiums. This guide explores the nuances of car insurance regulations, the different types of coverage available, and how to find the best policy for your needs.
States with Mandatory Car Insurance
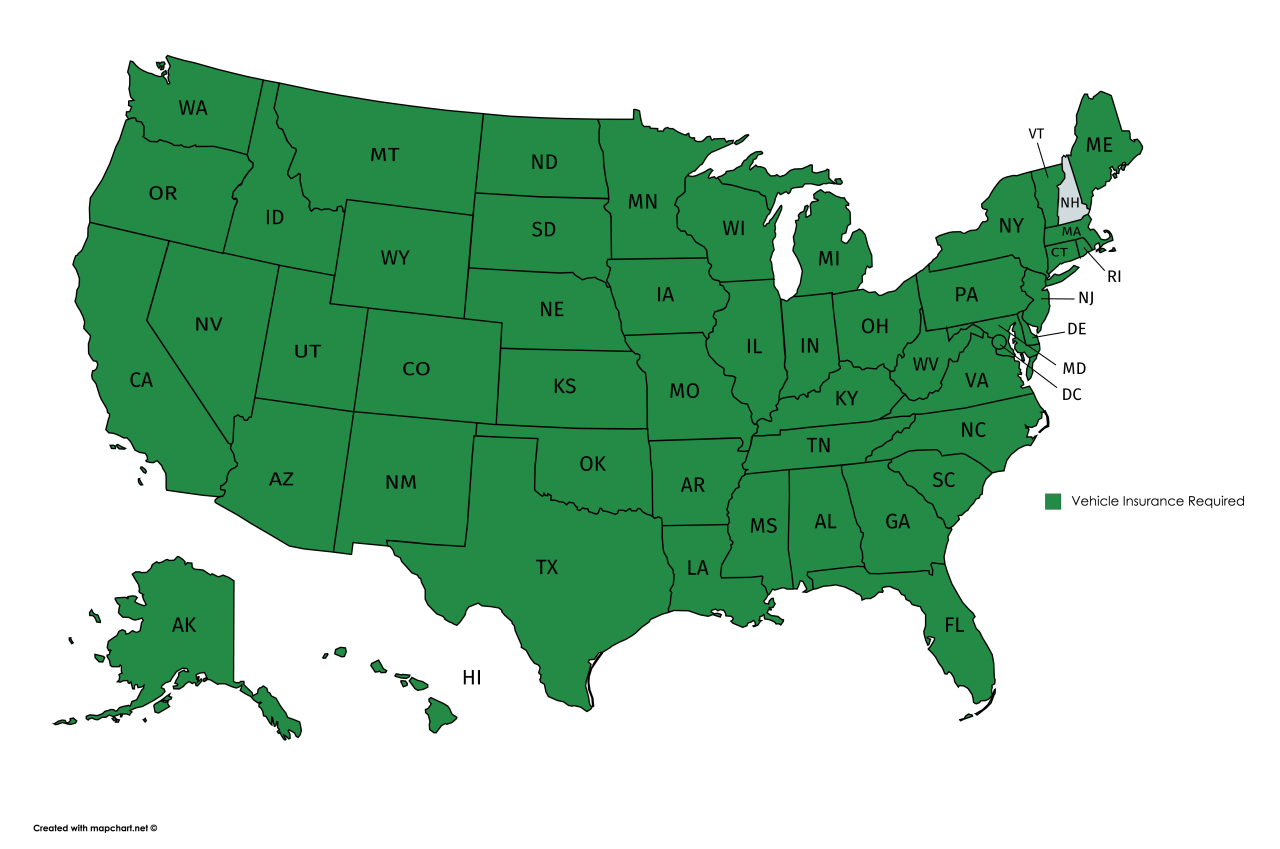
Driving without car insurance is illegal in all 50 states and the District of Columbia. These laws are in place to protect drivers and pedestrians from financial ruin in the event of an accident.
Minimum Liability Coverage Requirements
Each state sets its own minimum liability coverage requirements, which specify the minimum amount of financial protection drivers must have in case they cause an accident. These requirements are typically divided into three categories:
- Bodily Injury Liability: This coverage pays for medical expenses, lost wages, and other damages to people injured in an accident that you caused.
- Property Damage Liability: This coverage pays for damage to another person’s property, such as their car or a fence, that you caused in an accident.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: This coverage protects you if you are involved in an accident with a driver who has no insurance or insufficient insurance to cover your losses.
Here is a table outlining the minimum liability coverage requirements for each state:
| State | Bodily Injury Liability (per person) | Bodily Injury Liability (per accident) | Property Damage Liability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Alaska | $50,000 | $100,000 | $25,000 |
| Arizona | $25,000 | $50,000 | $15,000 |
| Arkansas | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| California | $15,000 | $30,000 | $5,000 |
| Colorado | $25,000 | $50,000 | $15,000 |
| Connecticut | $20,000 | $40,000 | $10,000 |
| Delaware | $30,000 | $60,000 | $10,000 |
| Florida | $10,000 | $20,000 | $10,000 |
| Georgia | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Hawaii | $20,000 | $40,000 | $10,000 |
| Idaho | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Illinois | $20,000 | $40,000 | $15,000 |
| Indiana | $25,000 | $50,000 | $10,000 |
| Iowa | $20,000 | $40,000 | $15,000 |
| Kansas | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Kentucky | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Louisiana | $15,000 | $30,000 | $10,000 |
| Maine | $50,000 | $100,000 | $25,000 |
| Maryland | $30,000 | $60,000 | $15,000 |
| Massachusetts | $20,000 | $40,000 | $5,000 |
| Michigan | $20,000 | $40,000 | $10,000 |
| Minnesota | $30,000 | $60,000 | $10,000 |
| Mississippi | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Missouri | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Montana | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Nebraska | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Nevada | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| New Hampshire | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| New Jersey | $15,000 | $30,000 | $5,000 |
| New Mexico | $25,000 | $50,000 | $10,000 |
| New York | $25,000 | $50,000 | $10,000 |
| North Carolina | $30,000 | $60,000 | $25,000 |
| North Dakota | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Ohio | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Oklahoma | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Oregon | $25,000 | $50,000 | $20,000 |
| Pennsylvania | $15,000 | $30,000 | $5,000 |
| Rhode Island | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| South Carolina | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| South Dakota | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Tennessee | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Texas | $30,000 | $60,000 | $25,000 |
| Utah | $25,000 | $65,000 | $25,000 |
| Vermont | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Virginia | $25,000 | $50,000 | $20,000 |
| Washington | $25,000 | $50,000 | $10,000 |
| West Virginia | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| Wisconsin | $25,000 | $50,000 | $10,000 |
| Wyoming | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
| District of Columbia | $25,000 | $50,000 | $25,000 |
Consequences of Driving Without Car Insurance
Driving without car insurance is a serious offense that can result in significant penalties. Here are some common consequences:
- Fines and Penalties: You can face hefty fines, suspension of your driver’s license, and even jail time for driving without car insurance.
- Increased Insurance Rates: Once you obtain insurance after being caught driving without it, your rates will likely be significantly higher than they would have been if you had maintained continuous coverage.
- Financial Responsibility: If you cause an accident without insurance, you will be personally liable for all damages, including medical expenses, property damage, and lost wages. This can lead to financial ruin.
- Difficulty Registering Your Vehicle: In some states, you may not be able to register your vehicle without proof of insurance.
It is important to note that the specific consequences of driving without car insurance can vary depending on the state and the circumstances of the offense. However, the penalties are generally severe and can have a significant impact on your driving privileges and finances.
Types of Car Insurance Coverage
Car insurance is a vital financial protection for vehicle owners, offering coverage against various risks. Understanding the different types of coverage available is crucial to making informed decisions and ensuring adequate protection for yourself and others.
Liability Coverage
Liability coverage is the most basic and often mandatory type of car insurance. It protects you financially if you are found liable for causing an accident that results in damage to another person’s property or injuries to another person.
Liability coverage typically covers bodily injury liability and property damage liability.
- Bodily Injury Liability covers medical expenses, lost wages, and pain and suffering for the other party involved in the accident.
- Property Damage Liability covers repairs or replacement costs for the other party’s vehicle or property.
For example, if you accidentally rear-end another car and cause damage to their vehicle and injuries to the driver, your liability coverage would pay for their medical bills and vehicle repairs.
Collision Coverage
Collision coverage protects you financially if your vehicle is damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. This coverage pays for repairs or replacement costs for your vehicle, minus any deductible you have chosen.
Collision coverage is optional, but it is highly recommended for drivers who want comprehensive protection.
For example, if you hit a tree or another vehicle, your collision coverage will help pay for repairs or replacement of your vehicle.
Comprehensive Coverage
Comprehensive coverage protects you financially against damage to your vehicle caused by events other than collisions, such as theft, vandalism, fire, hail, or natural disasters. This coverage also pays for repairs or replacement costs for your vehicle, minus any deductible you have chosen.
Comprehensive coverage is optional, but it is a good idea to consider it if your vehicle is new or has a high value.
For example, if your car is stolen or damaged by a hailstorm, your comprehensive coverage will help pay for repairs or replacement of your vehicle.
Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage
Uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage protects you financially if you are injured in an accident caused by a driver who has no insurance or insufficient insurance to cover your damages. This coverage can help pay for your medical bills, lost wages, and other expenses.
Uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage is optional, but it is highly recommended as it provides a safety net in the event of an accident with an uninsured or underinsured driver.
For example, if you are involved in an accident with a driver who has no insurance and you sustain injuries, your uninsured motorist coverage can help pay for your medical bills and other expenses.
Factors Affecting Car Insurance Rates: What States Require Car Insurance
Car insurance premiums are calculated based on various factors that insurers use to assess the risk of insuring a particular driver. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions to potentially lower your insurance costs.
Driving History
Your driving history is a major factor in determining your insurance rates. Insurers analyze your past driving behavior, including accidents, traffic violations, and claims history.
- A clean driving record with no accidents or violations will generally result in lower premiums.
- Accidents and traffic violations, such as speeding tickets or DUI convictions, increase your risk profile, leading to higher premiums.
- Multiple claims in a short period can significantly raise your rates, as insurers perceive you as a higher risk.
Age
Age is a significant factor in car insurance rates, as younger and older drivers are statistically more likely to be involved in accidents.
- Younger drivers, particularly those under 25, are often considered higher risk due to their lack of experience and tendency to engage in risky driving behaviors.
- Older drivers, particularly those over 65, may also face higher rates due to potential health issues and slower reaction times.
- However, drivers in their mid-30s to mid-50s often enjoy the lowest rates, as they have gained experience and have a lower risk profile.
Vehicle Type
The type of vehicle you drive plays a crucial role in your insurance rates. Insurers consider factors such as the vehicle’s value, safety features, and repair costs.
- Luxury cars, sports cars, and high-performance vehicles are generally more expensive to insure due to their higher repair costs and greater risk of theft.
- Vehicles with advanced safety features, such as anti-lock brakes, airbags, and stability control, may qualify for discounts, as they reduce the likelihood of accidents and severity of injuries.
- Older vehicles may have lower insurance rates, but they may lack modern safety features and could cost more to repair.
Location
Your location, including the state, city, and even neighborhood, can significantly influence your insurance rates. Insurers consider factors such as traffic density, crime rates, and the frequency of accidents in a particular area.
- Urban areas with high traffic congestion and higher crime rates often have higher insurance rates due to increased risk of accidents and theft.
- Rural areas with lower traffic density and fewer accidents typically have lower insurance rates.
Other Factors
Besides the primary factors discussed above, other factors can affect your car insurance rates, such as:
- Credit Score: In many states, insurers use credit scores as a proxy for risk, with those having lower credit scores often facing higher premiums.
- Driving Habits: Your driving habits, such as mileage driven, time of day you drive, and whether you commute or drive for work, can also influence your rates.
- Marital Status: Statistically, married individuals tend to have lower insurance rates than single individuals, as they may have a more stable lifestyle and drive less frequently.
Finding and Choosing Car Insurance

Finding the right car insurance policy can feel overwhelming with so many options available. But by taking a systematic approach and understanding your needs, you can find a policy that provides adequate coverage at a competitive price.
Comparing Car Insurance Quotes
Comparing quotes from different insurance providers is essential to finding the best deal. Several resources are available to help you do this:
- Online comparison websites: Websites like NerdWallet, Policygenius, and The Zebra allow you to enter your information once and receive quotes from multiple insurers. This can save you time and effort.
- Insurance company websites: You can also get quotes directly from insurance company websites. This allows you to explore their specific offerings and compare them side-by-side.
- Insurance brokers: Brokers work with multiple insurance companies and can help you find the best policy for your needs. They can also assist you with the application process.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Provider
When choosing a car insurance provider, consider these factors:
- Coverage: Make sure the policy provides the coverage you need, such as liability, collision, comprehensive, and uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage. Consider your driving habits, the value of your car, and your financial situation when determining the appropriate coverage levels.
- Price: Compare quotes from multiple providers to find the most competitive price. Don’t just focus on the lowest price, but also consider the value you’re getting for the price. Look for companies with good customer service and financial stability.
- Customer service: Read online reviews and ask friends and family for recommendations. Consider how easy it is to contact the insurer, how quickly they respond to claims, and how satisfied other customers are with their service.
- Financial stability: Look for companies with a strong financial rating, which indicates their ability to pay claims. You can check ratings from organizations like AM Best or Standard & Poor’s.
- Discounts: Many insurers offer discounts for safe driving, good grades, multiple policies, and other factors. Inquire about available discounts and see if you qualify.
Negotiating Car Insurance Rates
While you can’t always negotiate the base price of car insurance, there are still ways to lower your premium:
- Shop around: Get quotes from multiple providers and compare prices. Don’t be afraid to switch providers if you find a better deal.
- Increase your deductible: A higher deductible means you’ll pay more out-of-pocket in the event of an accident, but you’ll also pay a lower premium. Consider your financial situation and risk tolerance when deciding on a deductible amount.
- Bundle your policies: Many insurers offer discounts for bundling multiple policies, such as car insurance and homeowners insurance. Ask your insurer about bundling options.
- Improve your credit score: Your credit score can affect your car insurance rates in some states. Improving your credit score can lead to lower premiums.
- Ask about discounts: Many insurers offer discounts for safe driving, good grades, multiple policies, and other factors. Inquire about available discounts and see if you qualify.
Understanding Insurance Policies
Car insurance policies are legal contracts between you and your insurance company. They Artikel the terms and conditions of your coverage, including what is covered, what is excluded, and how much you’ll pay in premiums. Understanding the key terms and conditions in your policy is essential for making informed decisions about your coverage and ensuring you’re adequately protected in case of an accident.
Key Terms and Conditions
A standard car insurance policy includes several key terms and conditions.
- Policyholder: The individual or entity named in the policy who is insured.
- Insured: Any person authorized to drive the insured vehicle, as specified in the policy.
- Premium: The regular payment made by the policyholder to maintain coverage.
- Deductible: The amount you pay out-of-pocket for covered losses before your insurance kicks in.
- Coverage Limits: The maximum amount your insurance company will pay for covered losses.
- Exclusions: Specific events or situations not covered by the policy, such as intentional acts or driving under the influence.
Coverage Limits and Exclusions
Car insurance policies typically offer different types of coverage with specific limits and exclusions.
- Liability Coverage: Covers damages to other people’s property or injuries you cause in an accident. This is usually required by law and has specific limits for bodily injury and property damage.
- Collision Coverage: Covers damages to your vehicle if it’s involved in an accident, regardless of fault. You’ll need to pay your deductible before your insurance covers the remaining costs.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Covers damages to your vehicle from non-collision events like theft, vandalism, or natural disasters. You’ll also need to pay your deductible for these claims.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: Protects you if you’re involved in an accident with a driver who doesn’t have insurance or has insufficient coverage. It covers your medical expenses and property damage.
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): Covers your medical expenses and lost wages if you’re injured in an accident, regardless of fault. It’s often required in no-fault states.
Filing a Car Insurance Claim
If you need to file a car insurance claim, it’s important to follow the steps Artikeld in your policy.
- Report the Accident: Contact your insurance company immediately to report the accident. Provide them with the details of the incident, including the date, time, location, and any injuries or damages.
- Gather Evidence: Take photos or videos of the accident scene, any damage to your vehicle, and any injuries. Get contact information from other drivers and witnesses.
- File a Claim: Follow your insurance company’s instructions for filing a claim. You’ll typically need to provide them with a police report, medical records, and repair estimates.
- Cooperate with Your Insurance Company: Be honest and provide all necessary information to your insurance company. Respond to any requests for documentation promptly.
Consequences of Driving Without Insurance

Driving without car insurance is a serious offense in most states, and it can lead to significant legal and financial repercussions. Even if you believe you’re a safe driver, an accident can happen in an instant, leaving you facing potentially overwhelming costs. This section explores the various consequences you might face for driving without insurance.
Legal Penalties
Driving without insurance is illegal in all 50 states and the District of Columbia. The consequences can vary by state, but they generally include fines, license suspension, and even jail time.
- Fines: Fines for driving without insurance can range from a few hundred dollars to thousands of dollars, depending on the state and the number of offenses.
- License Suspension: Your driver’s license can be suspended for a certain period, preventing you from driving legally. The duration of the suspension varies by state and the severity of the offense.
- Jail Time: In some states, driving without insurance can result in jail time, especially if it’s a repeat offense or if an accident occurs.
Financial Repercussions
Driving without insurance can lead to significant financial problems, particularly if you’re involved in an accident.
- Medical Bills: If you’re injured in an accident, you’ll be responsible for paying all medical bills, which can be extremely expensive.
- Property Damage: If you damage another person’s property, you’ll be liable for the repair or replacement costs.
- Lawsuits: The other driver or their passengers could sue you for damages, leading to substantial legal fees and potential judgments.
- Higher Insurance Premiums: If you eventually obtain insurance, you’ll likely face significantly higher premiums due to your prior driving record.
Real-Life Scenarios, What states require car insurance
Here are some real-life examples of how driving without insurance can lead to significant problems:
- Scenario 1: A driver without insurance is involved in a minor fender bender. The other driver’s car is damaged, and the driver suffers minor injuries. Even though the accident was minor, the driver without insurance is now responsible for all repair costs, medical bills, and potential legal fees.
- Scenario 2: A driver without insurance is involved in a serious accident, resulting in severe injuries to themselves and others. The driver faces substantial medical bills, legal fees, and potential lawsuits. They may even lose their license and be forced to sell their car to cover the costs.
- Scenario 3: A driver without insurance is pulled over for a traffic violation. The police officer discovers that the driver is uninsured and issues a ticket. The driver now faces fines, license suspension, and potentially higher insurance premiums if they eventually obtain coverage.
Resources for Car Insurance Information
Navigating the world of car insurance can be overwhelming, but there are numerous resources available to help you make informed decisions. These resources provide valuable information, tools, and guidance to ensure you find the best coverage at the most affordable price.
Government Websites
Government websites offer a wealth of information about car insurance requirements, regulations, and consumer protection. These websites are reliable sources of accurate and up-to-date information.
- National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC): The NAIC is a non-profit organization that represents insurance commissioners from all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and five U.S. territories. Their website provides information on insurance regulations, consumer protection, and resources for filing complaints. You can find information on state-specific insurance requirements and consumer rights. [Link: https://www.naic.org/]
- Your State’s Department of Insurance: Each state has a Department of Insurance that regulates insurance companies and protects consumers. These websites offer information on insurance requirements, complaints procedures, and consumer education materials. You can find contact information for your state’s Department of Insurance on the NAIC website. [Link: https://www.naic.org/state_web_sites.htm]
Consumer Advocacy Groups
Consumer advocacy groups play a vital role in protecting consumers’ rights and advocating for fair insurance practices. They provide information, resources, and support to consumers facing insurance-related issues.
- Consumer Reports: Consumer Reports is a non-profit organization that conducts independent testing and research on a wide range of products and services, including car insurance. Their website provides car insurance ratings, comparisons, and consumer advice. [Link: https://www.consumerreports.org/]
- National Consumer Law Center (NCLC): The NCLC is a non-profit organization that advocates for consumer rights in areas such as insurance, banking, and debt collection. Their website provides resources and information on consumer protection laws and how to file complaints. [Link: https://www.nclc.org/]
Insurance Comparison Websites
Insurance comparison websites allow you to quickly and easily compare quotes from multiple insurance companies. They streamline the process of finding the best coverage at the most affordable price.
- Insurify: Insurify is an online insurance marketplace that allows you to compare quotes from multiple insurance companies in minutes. They provide personalized recommendations and insights to help you find the best coverage for your needs. [Link: https://www.insurify.com/]
- Policygenius: Policygenius is another popular insurance comparison website that offers a wide range of insurance products, including car insurance. They provide a user-friendly platform to compare quotes, review coverage options, and purchase insurance online. [Link: https://www.policygenius.com/]
Insurance Brokers and Agents
Insurance brokers and agents can provide valuable guidance and support in finding the right car insurance policy. They have expertise in the insurance industry and can help you understand your options and make informed decisions.
- Independent Insurance Brokers: Independent brokers represent multiple insurance companies and can provide you with a wider range of options to compare. They work on your behalf to find the best coverage at the most competitive price.
- Insurance Agents: Insurance agents represent a single insurance company and can provide you with information about that company’s products and services. They can help you understand your coverage options and answer your questions.
Closing Notes
Navigating the complex world of car insurance can be daunting, but understanding your state’s requirements and the various coverage options available is essential for responsible driving. By researching your options, comparing quotes, and carefully reviewing your policy, you can ensure you have the right protection for yourself and others on the road. Remember, driving without insurance can lead to severe consequences, so prioritize securing the necessary coverage to safeguard your financial well-being and protect yourself from potential liabilities.
Questions Often Asked
What happens if I get into an accident without car insurance?
If you cause an accident without insurance, you could face serious financial consequences, including hefty fines, license suspension, and even jail time. You’ll also be responsible for covering all damages to other vehicles and injuries to other people involved in the accident.
Can I get car insurance even if I have a poor driving record?
Yes, but it may be more expensive. Insurance companies assess your driving history, and a poor record can lead to higher premiums. However, you can still find insurance, though you may need to shop around for the best rates.
What are the different types of car insurance coverage?
Common types of coverage include liability, collision, comprehensive, and uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage. Liability coverage protects you financially if you cause an accident, collision coverage covers damage to your vehicle in an accident, comprehensive coverage protects against damage from non-collision events like theft or natural disasters, and uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage safeguards you if you’re hit by someone without or with insufficient insurance.







