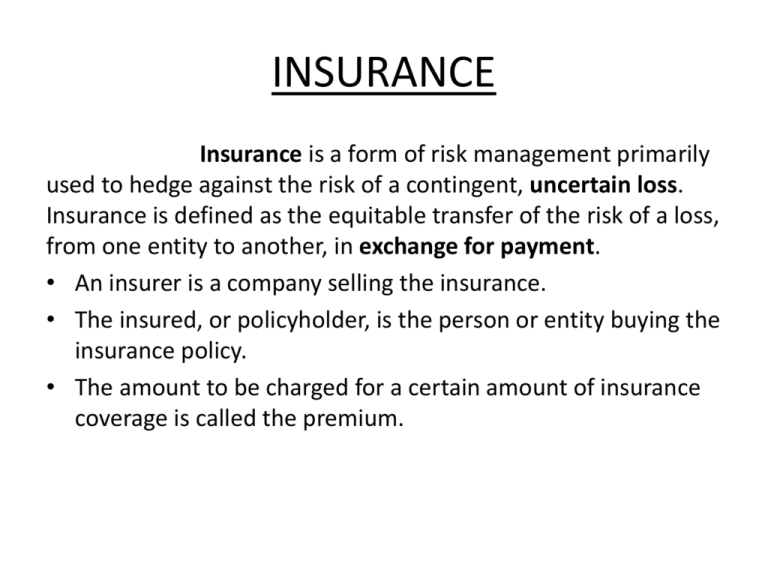
State of Insurance: Navigating a Transformative Industry explores the dynamic landscape of the insurance sector, where digital innovation, technological advancements, and evolving customer expectations are reshaping the way we think about risk and protection. The industry is experiencing a period of rapid transformation, driven by a confluence of forces that are fundamentally changing the way insurance is bought, sold, and delivered.
From the rise of insurtech startups to the adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain, the insurance landscape is becoming increasingly complex and competitive. Consumers are demanding more personalized and digital-first experiences, while insurers are striving to adapt their offerings and operations to meet these evolving needs.
The Evolving Landscape of Insurance
The insurance industry is undergoing a dramatic transformation, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and a growing awareness of emerging risks. This evolution is reshaping how insurance is bought, sold, and delivered, creating new opportunities and challenges for insurers and consumers alike.
Digital Transformation, State of insurance
Digital transformation is revolutionizing the insurance industry by making it more accessible, efficient, and customer-centric. Insurers are leveraging digital technologies to streamline operations, improve customer experiences, and develop innovative products and services.
- Online platforms and mobile apps: Consumers are increasingly turning to digital channels to research, compare, and purchase insurance policies. This trend has led to the emergence of online insurance platforms and mobile apps that offer a convenient and transparent way to access insurance services.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML): AI and ML are being used to automate tasks, personalize customer experiences, and improve risk assessment and pricing. Insurers are using these technologies to develop chatbots for customer service, automate claims processing, and identify fraud.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The widespread adoption of connected devices is creating new opportunities for insurers to monitor risks and provide personalized insurance solutions. For example, insurers can use data from smart home devices to offer discounts on home insurance policies or provide real-time alerts in case of emergencies.
Data Analytics
Data analytics is becoming increasingly important in the insurance industry, enabling insurers to make better decisions, improve risk assessment, and personalize customer experiences.
- Predictive modeling: Insurers are using data analytics to develop predictive models that can identify potential risks and predict future claims. This allows them to price policies more accurately and offer more tailored insurance solutions.
- Customer segmentation: Data analytics enables insurers to segment their customer base based on demographics, behavior, and risk profiles. This allows them to develop targeted marketing campaigns and offer more relevant products and services.
- Fraud detection: Data analytics can be used to identify suspicious claims and detect fraudulent activity. Insurers are using data analytics to build sophisticated fraud detection systems that can identify patterns and anomalies in claims data.
The Rise of Insurtech
Insurtech refers to the use of technology to disrupt and innovate the insurance industry. Insurtech startups are developing new insurance products, services, and business models that are challenging traditional insurance companies.
- Direct-to-consumer insurance: Insurtech startups are using technology to bypass traditional distribution channels and sell insurance directly to consumers. This allows them to offer more competitive pricing and personalized products.
- Micro-insurance: Insurtech startups are developing micro-insurance products that offer affordable coverage for specific risks, such as mobile phone insurance or travel insurance.
- On-demand insurance: Insurtech startups are offering on-demand insurance products that provide coverage for specific periods or events. This allows consumers to pay only for the insurance they need, reducing costs and increasing flexibility.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
The insurance industry is undergoing a significant transformation driven by technological advancements. Emerging technologies are reshaping the way insurers operate, interact with customers, and assess risks. This section explores the most impactful technologies influencing the insurance landscape and their applications in enhancing efficiency, personalizing customer experiences, and revolutionizing risk assessment.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is playing a pivotal role in automating tasks, improving decision-making, and enhancing customer service in the insurance industry.
- Underwriting: AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data, including historical claims, demographics, and driving records, to assess risk profiles and automate underwriting processes. This results in faster and more accurate risk assessments, leading to quicker policy issuance and improved pricing.
- Fraud Detection: AI-powered systems can detect fraudulent claims by analyzing patterns in claims data, identifying anomalies, and flagging suspicious activities. This helps insurers reduce fraudulent claims and protect their bottom line.
- Customer Service: Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by AI are becoming increasingly prevalent in insurance. They can handle routine inquiries, provide personalized recommendations, and assist customers with policy management tasks, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent platform for managing insurance data and processes.
- Claims Processing: Blockchain can streamline claims processing by providing a secure and immutable record of claims data, reducing fraud and disputes. This also allows for faster claim settlements, improving customer satisfaction.
- Smart Contracts: Blockchain-based smart contracts can automate insurance policy terms and conditions, ensuring that payments are made automatically upon the occurrence of specific events. This eliminates the need for manual processing and reduces the risk of errors.
- Data Sharing: Blockchain enables secure and transparent data sharing among insurers, reinsurers, and other stakeholders. This facilitates better risk assessment and allows for more efficient collaboration in the insurance ecosystem.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices are generating vast amounts of data that can be leveraged to improve risk assessment, personalize insurance products, and provide real-time insights into customer behavior.
- Telematics: Telematics devices installed in vehicles track driving behavior, providing insurers with data on speed, braking, and other factors. This data can be used to personalize premiums based on driving habits and provide incentives for safe driving.
- Home Monitoring: Smart home devices can monitor environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and smoke levels, providing valuable insights into potential risks. This data can be used to offer discounts on home insurance policies or provide early warnings about potential hazards.
- Health and Wellness: Wearable fitness trackers and other health monitoring devices can collect data on physical activity, sleep patterns, and other health metrics. This data can be used to develop personalized health insurance plans and incentivize healthy lifestyles.
Customer Expectations and Engagement: State Of Insurance
The digital age has fundamentally transformed the way consumers interact with businesses, and the insurance industry is no exception. Customers today demand personalized experiences, seamless digital interactions, and transparent communication, reflecting a shift in expectations that insurance providers must adapt to.
Personalized Experiences
Meeting the individual needs of each customer is crucial in today’s competitive landscape. Insurance providers can achieve this by leveraging data analytics to understand customer profiles, preferences, and risk factors. This enables them to offer tailored insurance products, pricing, and communication strategies that resonate with individual customers. For instance, a young, tech-savvy customer may prefer an online-only insurance experience with digital policy management and instant claims processing, while an older, risk-averse customer may value personalized advice and traditional communication channels.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance
The insurance industry is subject to a complex and ever-evolving regulatory landscape. This landscape encompasses a broad range of regulations, including those related to data privacy, cybersecurity, and consumer protection. These regulations are designed to ensure fair and transparent practices, protect consumer interests, and maintain the stability of the insurance market.
Impact of New Regulations on Insurance Providers
New regulations significantly impact insurance providers, requiring them to adapt their operations and invest in compliance initiatives. These impacts can be categorized as follows:
- Increased Compliance Costs: Implementing new regulations necessitates significant investments in technology, infrastructure, and personnel. This includes developing new systems, training employees, and conducting audits to ensure compliance.
- Operational Changes: Regulations often require insurers to modify their business processes, data management practices, and customer interactions. For example, regulations like GDPR require insurers to obtain explicit consent from customers for data processing and provide them with greater control over their personal information.
- Enhanced Risk Management: Regulatory changes often necessitate insurers to strengthen their risk management frameworks. This involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with data breaches, cyberattacks, and non-compliance.
- Potential for Fines and Penalties: Failure to comply with regulations can result in substantial fines, penalties, and reputational damage. Therefore, insurers must prioritize compliance to avoid these consequences.
Adapting to Evolving Regulations
Insurance companies are actively adapting to the evolving regulatory landscape by implementing various strategies:
- Investing in Technology: Insurers are investing in advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and cloud computing, to automate compliance processes, improve data security, and enhance customer experiences. For example, AI-powered tools can be used to automate data privacy audits and detect potential compliance violations.
- Building Strong Compliance Teams: Insurance companies are building dedicated compliance teams with expertise in data privacy, cybersecurity, and consumer protection. These teams are responsible for monitoring regulatory changes, implementing compliance programs, and providing guidance to employees.
- Developing Robust Risk Management Frameworks: Insurers are strengthening their risk management frameworks to proactively identify and mitigate regulatory risks. This involves conducting regular risk assessments, implementing appropriate controls, and establishing clear accountability mechanisms.
- Engaging with Regulators: Insurance companies are actively engaging with regulators to understand their expectations and provide feedback on proposed regulations. This collaboration helps ensure that regulations are practical and achievable for the industry.
Emerging Risks and Challenges
The insurance industry faces a dynamic and evolving landscape of risks and challenges. These threats stem from global trends, technological advancements, and changing societal needs. It is crucial for insurers to proactively adapt their offerings and strategies to effectively address these emerging risks and ensure the long-term sustainability of the industry.
Climate Change Impacts
Climate change poses a significant and multifaceted challenge to the insurance industry. Rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, and sea-level rise are increasing the frequency and severity of insured losses.
- Increased Frequency and Severity of Natural Disasters: Climate change is leading to an increase in the frequency and intensity of natural disasters such as hurricanes, wildfires, floods, and droughts. This results in higher claims payouts for insurers.
- Rising Insurance Premiums: To mitigate the increased risk, insurers are forced to raise premiums, which can make insurance unaffordable for some individuals and businesses.
- Underwriting Challenges: Predicting and assessing the risk associated with climate change is becoming increasingly complex. Insurers need to develop sophisticated models and data analysis techniques to accurately assess and underwrite policies.
Insurance providers are responding to climate change through various strategies, including:
- Developing Climate-Resilient Products: Insurers are creating new products and services that specifically address climate change risks, such as parametric insurance that provides payouts based on specific weather events.
- Investing in Climate-Smart Technologies: Insurers are leveraging technologies such as remote sensing, artificial intelligence, and predictive analytics to better assess climate risks and develop more effective risk management strategies.
- Promoting Climate Adaptation: Insurers are working with policyholders to encourage climate adaptation measures, such as building resilience to extreme weather events.
Cyber Threats and Data Security
Cyberattacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated and pose a major threat to insurance companies and their policyholders. Data breaches can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory fines.
- Data Breaches and Ransomware Attacks: Insurers are vulnerable to data breaches and ransomware attacks that can compromise sensitive customer information and disrupt business operations.
- Increased Regulatory Scrutiny: Data breaches and cybersecurity incidents are subject to increased regulatory scrutiny, leading to hefty fines and penalties for non-compliance.
- Evolving Threat Landscape: Cybercriminals are constantly developing new attack methods, making it challenging for insurers to stay ahead of the curve.
Insurers are adopting a range of measures to enhance their cybersecurity posture and mitigate cyber risks, including:
- Investing in Robust Cybersecurity Infrastructure: Insurers are investing in advanced security technologies, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption, to protect their systems and data.
- Implementing Strong Cybersecurity Policies: Insurers are establishing comprehensive cybersecurity policies and procedures to guide employees on best practices for data security.
- Cybersecurity Awareness Training: Regular cybersecurity awareness training for employees is essential to prevent human error and social engineering attacks.
Emerging Diseases and Pandemics
The emergence of new diseases and pandemics poses significant challenges to the insurance industry. These events can disrupt global economies, strain healthcare systems, and lead to widespread business interruptions.
- Business Interruption Insurance: Insurers need to adapt their business interruption insurance policies to cover the financial losses associated with pandemics and other emerging diseases.
- Pandemic Risk Modeling: Developing accurate pandemic risk models is crucial for insurers to assess the potential impact of future outbreaks and adjust their pricing and underwriting strategies.
- Public Health Collaboration: Insurers are collaborating with public health organizations to gain insights into emerging diseases and develop strategies for mitigating their impact.
Examples of innovative solutions for mitigating emerging risks include:
- Parametric Insurance: This type of insurance provides payouts based on pre-defined triggers, such as the intensity of a hurricane or the number of confirmed cases of a pandemic. It can help insurers provide faster and more predictable compensation to policyholders in the event of a disaster.
- Microinsurance: Microinsurance offers affordable insurance coverage to low-income individuals and communities, helping them to manage risks such as natural disasters and health emergencies.
- Insurtech Solutions: Insurtech companies are developing innovative technologies, such as artificial intelligence and blockchain, to improve risk assessment, claims processing, and customer engagement.
Future of Insurance

The insurance industry is on the cusp of a transformative era, driven by technological advancements, evolving customer expectations, and a changing risk landscape. The future of insurance promises to be a dynamic and innovative space, with a focus on personalization, digitalization, and data-driven insights.
Impact of Automation, Artificial Intelligence, and Predictive Analytics
Automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and predictive analytics are poised to revolutionize the insurance industry, streamlining processes, enhancing decision-making, and creating new opportunities for customer engagement.
- Automation: Automation is already transforming insurance operations, automating repetitive tasks such as claims processing, policy administration, and underwriting. This frees up human resources to focus on more complex and value-adding activities, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI is being used to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and predict risks, enabling insurers to personalize coverage, offer tailored pricing, and provide proactive risk management solutions. For example, AI-powered chatbots are being used to provide 24/7 customer support, while AI-driven fraud detection systems are helping to reduce fraudulent claims.
- Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics is used to forecast future events and trends, enabling insurers to anticipate risks, develop proactive strategies, and optimize pricing models. For example, predictive analytics can be used to identify individuals at high risk of certain health conditions, allowing insurers to offer tailored health insurance plans and preventive care services.
Closing Summary
As we navigate this evolving landscape, it’s clear that the future of insurance is bright. The industry is embracing innovation, leveraging technology to enhance customer experiences, and finding new ways to address emerging risks. By staying ahead of the curve, insurers can continue to provide valuable protection and build lasting relationships with their customers. The state of insurance is a testament to the industry’s ability to adapt and thrive in a rapidly changing world.
Essential Questionnaire
What are some of the biggest challenges facing the insurance industry today?
The insurance industry faces a number of challenges, including increasing regulatory scrutiny, rising costs, and the need to adapt to new technologies and customer expectations. Other challenges include climate change, cyber threats, and emerging diseases.
How is technology impacting the insurance industry?
Technology is having a profound impact on the insurance industry, enabling insurers to automate processes, personalize customer experiences, and develop new products and services. Technologies like AI, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are playing a key role in this transformation.
What are some of the emerging trends in insurance?
Some of the emerging trends in insurance include the rise of insurtech startups, the adoption of digital channels, and the increasing use of data analytics. Other trends include the growth of on-demand insurance and the development of new insurance products tailored to specific needs.







