State house insurance is a crucial aspect of owning a historical property. It provides financial protection against unforeseen events that could damage or destroy your valuable investment. From fire and water damage to theft and vandalism, state house insurance policies offer peace of mind knowing you’re covered in the event of an unexpected disaster.
Understanding the different types of coverage, the factors influencing costs, and the benefits of having insurance are essential for making informed decisions about your state house. This guide explores the intricacies of state house insurance, empowering you to protect your historic property and secure its future.
Understanding State House Insurance
State house insurance is a type of property insurance designed to protect homeowners from financial losses caused by unforeseen events that damage their homes. It provides financial coverage to rebuild or repair the house and its contents, offering peace of mind and financial security.
Types of Coverage
State house insurance policies typically include various types of coverage to address different risks. The most common types of coverage include:
- Building Coverage: This coverage protects the physical structure of the house, including the walls, roof, foundation, and other attached structures. It covers damage caused by events like fire, storms, vandalism, and other perils.
- Contents Coverage: This coverage protects the personal belongings inside the house, such as furniture, electronics, clothing, and other valuables. It provides financial assistance to replace or repair damaged or stolen items.
- Liability Coverage: This coverage protects homeowners from financial losses arising from injuries or property damage caused to others on their property. It covers legal expenses and compensation claims related to accidents.
- Additional Living Expenses: This coverage provides financial support for temporary accommodation and other expenses if the house becomes uninhabitable due to an insured event. It helps homeowners maintain their lifestyle while repairs are underway.
Common Risks Covered
State house insurance policies cover a wide range of risks that could damage a home. Some of the most common risks include:
- Natural Disasters: This includes events like hurricanes, tornadoes, earthquakes, floods, and wildfires.
- Fire: Accidental fires caused by faulty wiring, cooking accidents, or other factors.
- Theft: Coverage for stolen property, including jewelry, electronics, and other valuables.
- Vandalism: Damage caused by intentional acts of destruction.
- Liability: Accidents or injuries that occur on the property, resulting in legal claims against the homeowner.
Key Considerations for State House Insurance
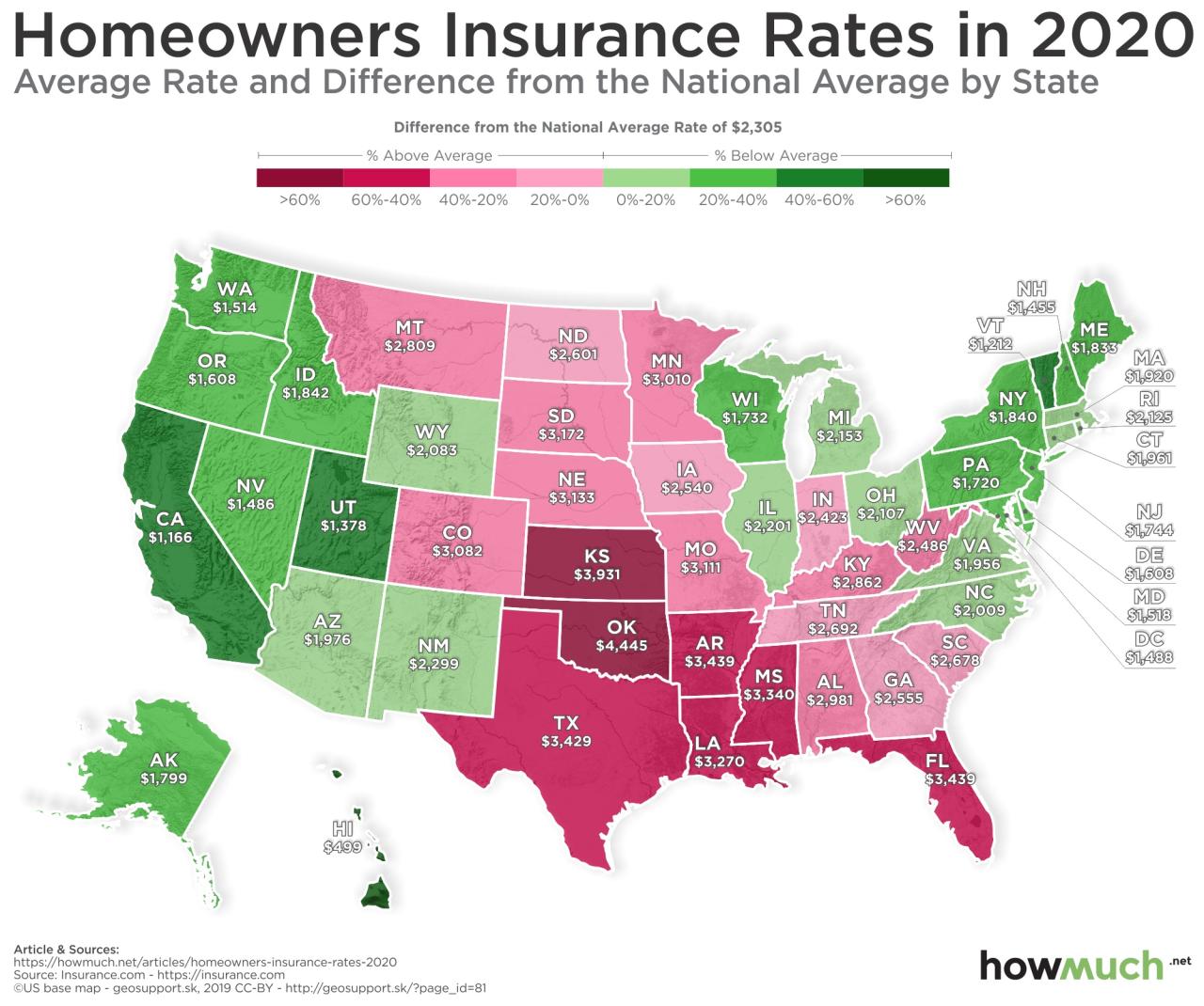
Choosing the right state house insurance policy can be a complex process, as it involves weighing various factors to ensure adequate coverage and affordability. This section delves into key considerations that can guide you towards making an informed decision.
Factors Influencing State House Insurance Costs
Several factors contribute to the cost of state house insurance, including:
- Location: The risk of natural disasters, crime rates, and other hazards in a specific location can significantly impact insurance premiums. Areas prone to earthquakes, hurricanes, or floods typically have higher insurance costs.
- Property Value: The higher the value of your state house, the more expensive the insurance will be. This is because the insurer is covering a greater financial risk.
- Building Materials: State houses constructed with fire-resistant materials like brick or stone generally have lower insurance premiums compared to those built with wood.
- Security Features: Installing security systems, fire alarms, and other safety features can reduce your insurance premiums by demonstrating a lower risk of loss.
- Deductible: A higher deductible, which is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before insurance coverage kicks in, typically results in lower premiums. Conversely, a lower deductible leads to higher premiums.
- Coverage Options: Choosing comprehensive coverage with additional protection against various risks, such as floods or earthquakes, will generally increase the insurance cost.
- Insurance History: Your past claims history can influence your insurance rates. Frequent claims may lead to higher premiums, while a clean record can result in discounts.
Comparing Insurance Providers and Coverage Options
When selecting state house insurance, it’s crucial to compare different providers and their coverage options. Key aspects to consider include:
- Coverage Limits: Ensure the chosen policy provides sufficient coverage for the value of your state house, including its contents and any potential liability risks.
- Deductibles: Carefully assess the deductible amount and its impact on your overall insurance cost. A higher deductible can significantly reduce premiums but may leave you with a larger out-of-pocket expense in case of a claim.
- Exclusions: Review the policy document to understand any exclusions or limitations in coverage. Some policies may not cover specific events, such as floods or earthquakes, which may require additional coverage.
- Customer Service: Evaluate the provider’s reputation for customer service, responsiveness to claims, and overall ease of doing business.
- Discounts: Explore available discounts for safety features, bundling multiple insurance policies, or being a long-term customer.
Benefits of State House Insurance
State house insurance offers several key benefits:
- Financial Protection: In case of damage or loss to your state house due to covered events, insurance provides financial protection to cover repair or replacement costs.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that your state house is insured against unforeseen events can provide peace of mind and reduce financial stress in the event of a disaster.
- Liability Coverage: Most state house insurance policies include liability coverage, protecting you from legal claims if someone is injured on your property.
- Protection for Contents: Your state house insurance policy may also cover the contents of your home, such as furniture, appliances, and personal belongings.
- Additional Coverage Options: Many insurance providers offer additional coverage options, such as flood insurance, earthquake insurance, or personal property coverage, to cater to specific needs.
State House Insurance Policies and Features
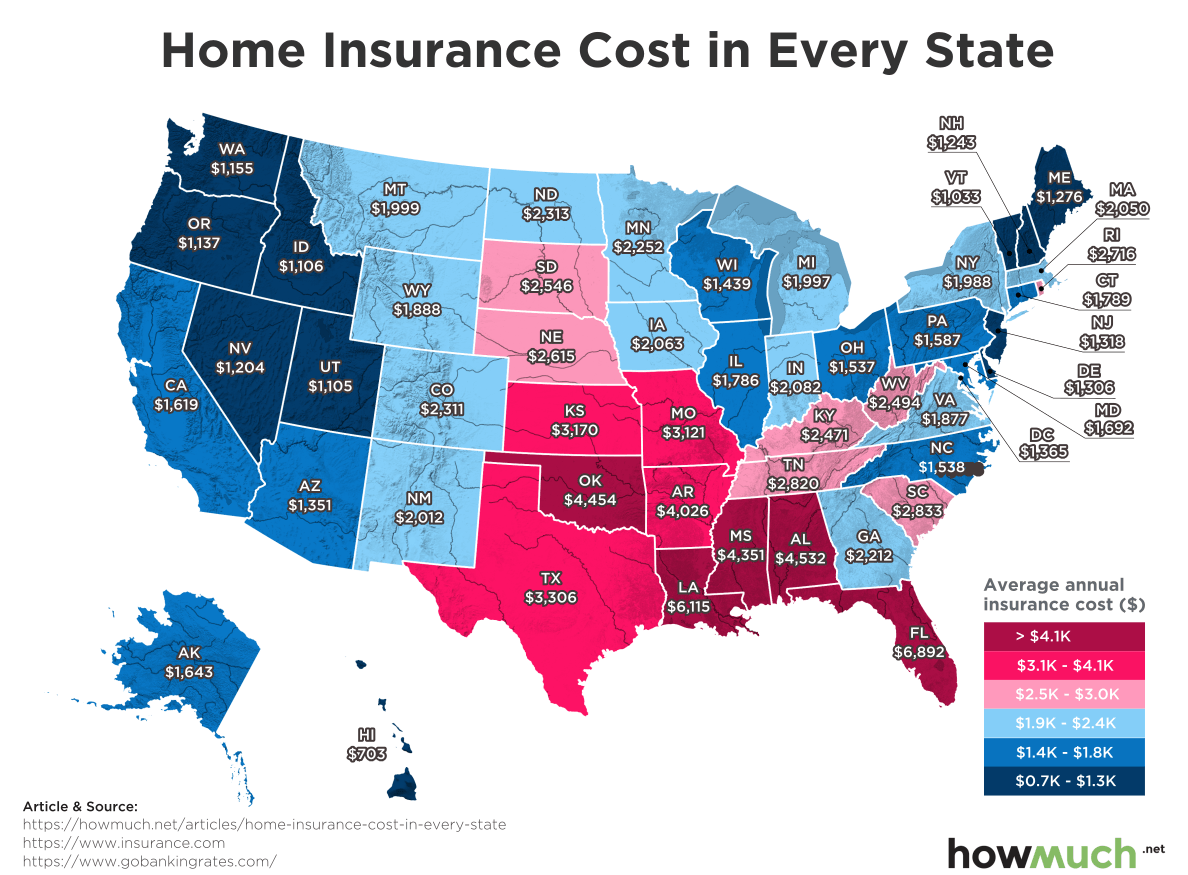
State house insurance policies offer financial protection against various risks associated with owning or renting a property. They are designed to cover losses caused by events like fire, theft, and natural disasters. Understanding the features and types of state house insurance policies is crucial for making informed decisions about your coverage.
Common Features of State House Insurance Policies
State house insurance policies typically share common features that help define the scope of coverage and financial responsibilities. These features include:
- Deductible: This is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. A higher deductible often translates to lower premiums.
- Coverage Limits: These are the maximum amounts your insurance company will pay for covered losses. The limits can vary depending on the type of policy and the specific coverage.
- Exclusions: These are specific events or circumstances that are not covered by the policy. Common exclusions include acts of war, intentional damage, and certain types of wear and tear.
Types of State House Insurance Policies
State house insurance policies are categorized based on the type of property they cover. The most common types include:
- Homeowners Insurance: This policy covers a wide range of risks associated with owning a house, including fire, theft, vandalism, and natural disasters.
- Renters Insurance: This policy protects your personal belongings and provides liability coverage for renters in case of accidents or injuries that occur in their rented space.
- Condo Insurance: This policy covers the interior of a condo unit and personal belongings, while the homeowner’s association (HOA) typically provides insurance for the building’s exterior and common areas.
Filing a Claim with a State House Insurance Provider
Filing a claim with your state house insurance provider involves a series of steps:
- Contact Your Insurance Company: Immediately notify your insurance company about the loss or damage. Provide them with the necessary details, such as the date and time of the incident, the extent of the damage, and any relevant documentation.
- File a Claim: Complete the claim form provided by your insurance company, providing accurate and detailed information about the incident.
- Provide Documentation: Gather any relevant documentation to support your claim, such as police reports, receipts for repairs, or photographs of the damage.
- Cooperate with the Insurance Company: Cooperate with the insurance company’s investigation process by providing them with access to the property and answering their questions.
- Review and Negotiate the Settlement: Once the insurance company completes its investigation, they will provide you with a settlement offer. Review the offer carefully and negotiate if necessary.
Protecting Your State House
Owning a state house is a significant investment, and protecting it from damage is crucial. By implementing preventive measures, you can minimize the risk of costly repairs and ensure the longevity of your property. This guide will provide a comprehensive understanding of common hazards, preventive measures, and the importance of regular maintenance for safeguarding your state house.
Common Hazards
A state house is susceptible to various hazards that can cause damage. Understanding these risks is the first step towards effective protection. Here are some common hazards that can impact state houses:
- Fire: Fires can be caused by electrical malfunctions, faulty appliances, or even careless actions. They can cause extensive damage to structures, belongings, and even result in loss of life.
- Water Damage: Leaks from plumbing, roof damage, or burst pipes can lead to significant water damage. This can cause mold growth, structural issues, and costly repairs.
- Theft: State houses are often targets for theft due to their valuable contents and remote locations. Security measures are crucial to deter burglars and protect your property.
- Natural Disasters: State houses can be vulnerable to natural disasters like hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods. These events can cause extensive damage and require significant restoration efforts.
Regular Maintenance and Inspections
Regular maintenance and inspections are essential for preventing damage and ensuring the safety of your state house. Here’s why:
- Early Detection of Issues: Regular inspections can help identify potential problems before they escalate into major issues. This can prevent costly repairs and minimize disruption to your property.
- Preventative Measures: Maintenance tasks like cleaning gutters, inspecting roofs, and checking electrical wiring can prevent potential hazards from developing.
- Extended Lifespan: Regular maintenance can extend the lifespan of your state house by addressing issues before they become major problems. This can save you money on repairs and replacements in the long run.
Preventive Measures
Implementing preventive measures is crucial for protecting your state house from damage. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Fire Safety:
- Install smoke detectors and carbon monoxide detectors throughout the house. Ensure they are regularly tested and batteries are replaced as needed.
- Create a fire escape plan and practice it with your family. This includes identifying multiple escape routes and a designated meeting point outside the house.
- Keep flammable materials away from heat sources and ensure proper ventilation in areas with appliances that generate heat.
- Water Damage Prevention:
- Regularly inspect plumbing fixtures and pipes for leaks. Repair any leaks promptly to prevent water damage.
- Ensure proper drainage around the house to prevent water from pooling and infiltrating the foundation.
- Inspect the roof regularly for damage and leaks. Repair any damage promptly to prevent water from entering the house.
- Theft Prevention:
- Install a robust security system with alarms, motion sensors, and security cameras. Consider a monitored system for added protection.
- Invest in strong doors and windows with high-quality locks. Ensure all entry points are secure and well-lit.
- Keep valuables out of sight and consider using a safe for storing important documents and jewelry.
- Natural Disaster Preparedness:
- Develop a disaster preparedness plan and practice it with your family. This includes identifying safe zones within the house and evacuation routes.
- Secure loose objects around the house to prevent them from becoming projectiles during strong winds or earthquakes.
- Store essential supplies like food, water, and medical supplies in a safe and accessible location.
State House Insurance and Legal Requirements

State house insurance is often a legal requirement, and failing to meet these requirements can lead to significant financial and legal repercussions. Understanding the legal landscape regarding state house insurance is crucial for property owners to avoid potential risks.
Legal Requirements for State House Insurance
The legal requirements for state house insurance vary depending on the jurisdiction. Some jurisdictions mandate specific types of insurance, while others focus on minimum coverage amounts. It is important to consult with local authorities or insurance professionals to determine the specific requirements in your area.
For instance, in some states, homeowners are required to maintain insurance that covers damage caused by natural disasters like hurricanes, earthquakes, or wildfires. These requirements are often tied to mortgage lending agreements, where lenders may insist on specific coverage levels to protect their investment.
Consequences of Inadequate State House Insurance
The consequences of not having adequate state house insurance can be severe, ranging from financial hardship to legal liability. If a covered event occurs, and the homeowner does not have sufficient insurance coverage, they may be responsible for covering the costs out of pocket.
- Financial Burden: Without adequate insurance, homeowners may face significant financial losses, potentially exceeding their financial capacity. This can lead to debt, financial instability, and even bankruptcy.
- Legal Liability: In some cases, inadequate insurance can lead to legal liability. For example, if a homeowner’s property damages a neighbor’s property due to a lack of sufficient coverage, they could be held liable for the damages.
- Mortgage Default: Many mortgage lenders require homeowners to maintain specific levels of insurance coverage as a condition of the loan. Failure to meet these requirements can result in mortgage default and potential foreclosure.
State Laws and Regulations
Each state has its own set of laws and regulations regarding state house insurance. These laws often specify minimum coverage requirements, acceptable insurance providers, and procedures for filing claims.
For example, some states may require homeowners to purchase flood insurance if their property is located in a flood-prone area. Others may have specific requirements for earthquake coverage in seismically active regions.
It is essential to research and understand the specific laws and regulations in your state to ensure you are adequately protected. Consulting with an insurance professional can provide valuable insights into your legal obligations and help you choose the appropriate coverage for your needs.
Closure
Investing in state house insurance is an investment in the preservation of your historical property. By understanding the nuances of coverage, comparing providers, and implementing preventive measures, you can safeguard your state house against the unexpected. Remember, having adequate insurance provides peace of mind and ensures that you have the financial resources to restore your home should the unthinkable occur.
Top FAQs
What are the common exclusions in state house insurance policies?
Common exclusions may include damage caused by earthquakes, floods, or acts of war. It’s important to review your policy carefully to understand the specific exclusions that apply.
How often should I review my state house insurance policy?
It’s advisable to review your policy annually, or whenever there are significant changes to your property or your risk profile.
What are the steps involved in filing a claim with a state house insurance provider?
Typically, you’ll need to report the claim immediately, gather documentation, and follow the insurer’s instructions for submitting the claim.







