State homeowners insurance plays a vital role in safeguarding your biggest investment – your home. This type of insurance provides financial protection against various perils that could damage or destroy your property, leaving you financially vulnerable. Understanding the intricacies of state homeowners insurance is crucial for every homeowner, as it empowers you to make informed decisions about your coverage and ensure peace of mind.
From understanding the basics of coverage to navigating the complexities of state-specific regulations, this guide delves into the world of homeowners insurance. We’ll explore the key elements of a standard policy, discuss factors influencing premiums, and provide insights on choosing the right coverage for your individual needs.
Understanding State Homeowners Insurance
State homeowners insurance is a crucial financial safety net that protects homeowners against various risks that could damage their property or lead to financial hardship. It provides financial compensation for covered losses, helping homeowners rebuild their lives after unforeseen events.
Types of Coverage, State homeowners insurance
State homeowners insurance policies typically offer a comprehensive range of coverage designed to protect your home and belongings. These coverages can be categorized into several key areas:
- Dwelling Coverage: This coverage protects the physical structure of your home, including the walls, roof, foundation, and attached structures like garages and porches. It covers damages caused by perils like fire, windstorms, hail, and vandalism.
- Other Structures Coverage: This coverage extends protection to detached structures on your property, such as sheds, fences, and detached garages. It covers damages similar to dwelling coverage.
- Personal Property Coverage: This coverage protects your belongings inside your home, including furniture, electronics, clothing, and other personal items. It covers damages caused by covered perils and can also include theft and vandalism.
- Loss of Use Coverage: This coverage provides financial assistance if you are unable to live in your home due to a covered loss. It helps cover expenses like temporary housing, food, and other essential living costs.
- Liability Coverage: This coverage protects you from financial liability if someone is injured on your property or if you are held responsible for damage to someone else’s property.
- Medical Payments Coverage: This coverage provides medical payments to individuals who are injured on your property, regardless of fault.
State-Specific Considerations

Homeowners insurance is regulated at the state level, which means there are significant variations in coverage, requirements, and pricing across the country. Understanding these state-specific nuances is crucial for securing the right policy and ensuring you’re adequately protected.
State Insurance Requirements
State regulations dictate the minimum coverage requirements for homeowners insurance. These requirements vary significantly from state to state. For instance, some states require coverage for specific perils like earthquakes or floods, while others do not. Understanding these requirements is crucial for complying with local laws and avoiding potential financial penalties.
- Flood Insurance: In flood-prone areas, states often require or strongly recommend flood insurance, which is typically separate from standard homeowners insurance. For example, in Florida, which is known for its coastal vulnerability, flood insurance is often a requirement for mortgage lenders.
- Earthquake Insurance: States in earthquake-prone regions, like California, may mandate earthquake insurance or encourage its purchase. It’s essential to research whether your state has specific requirements or recommendations for earthquake coverage.
- Windstorm Coverage: Coastal states, particularly those prone to hurricanes, may have specific regulations for windstorm coverage. For example, Florida has a “Hurricane Catastrophe Fund” that provides additional coverage in the event of a hurricane.
Coverage Options and Pricing Variations
State regulations influence the coverage options and pricing of homeowners insurance. Some states have more stringent regulations, which may lead to higher premiums but broader coverage. Others may have more flexible regulations, allowing for more customized policies but potentially lower coverage.
- Coverage Limits: States may have different regulations regarding the maximum coverage limits for various perils, such as fire, theft, or liability. It’s crucial to understand these limits to ensure your policy adequately protects your assets.
- Deductibles: The amount you pay out of pocket before your insurance kicks in, known as the deductible, can vary based on state regulations. Some states may have minimum deductible requirements, while others allow for more flexibility.
- Exclusions: State regulations can influence the exclusions, or specific events or situations not covered by your policy. For example, some states may exclude coverage for certain types of natural disasters, such as earthquakes or landslides.
State-Specific Considerations Table
Here’s a table highlighting some key differences in homeowners insurance across states:
| State | Minimum Coverage Requirements | Coverage Options | Pricing Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | Earthquake insurance may be required or strongly recommended | Wide range of coverage options, including earthquake and wildfire coverage | Higher premiums due to earthquake risk and wildfire potential |
| Florida | Flood insurance often required for mortgage lenders | Hurricane coverage is crucial, with additional coverage through the Hurricane Catastrophe Fund | High premiums due to hurricane risk and flood potential |
| Texas | Coverage for hail damage is common | Options for windstorm coverage and hail damage protection | Premiums can vary significantly depending on location and risk factors |
Factors Influencing Premiums
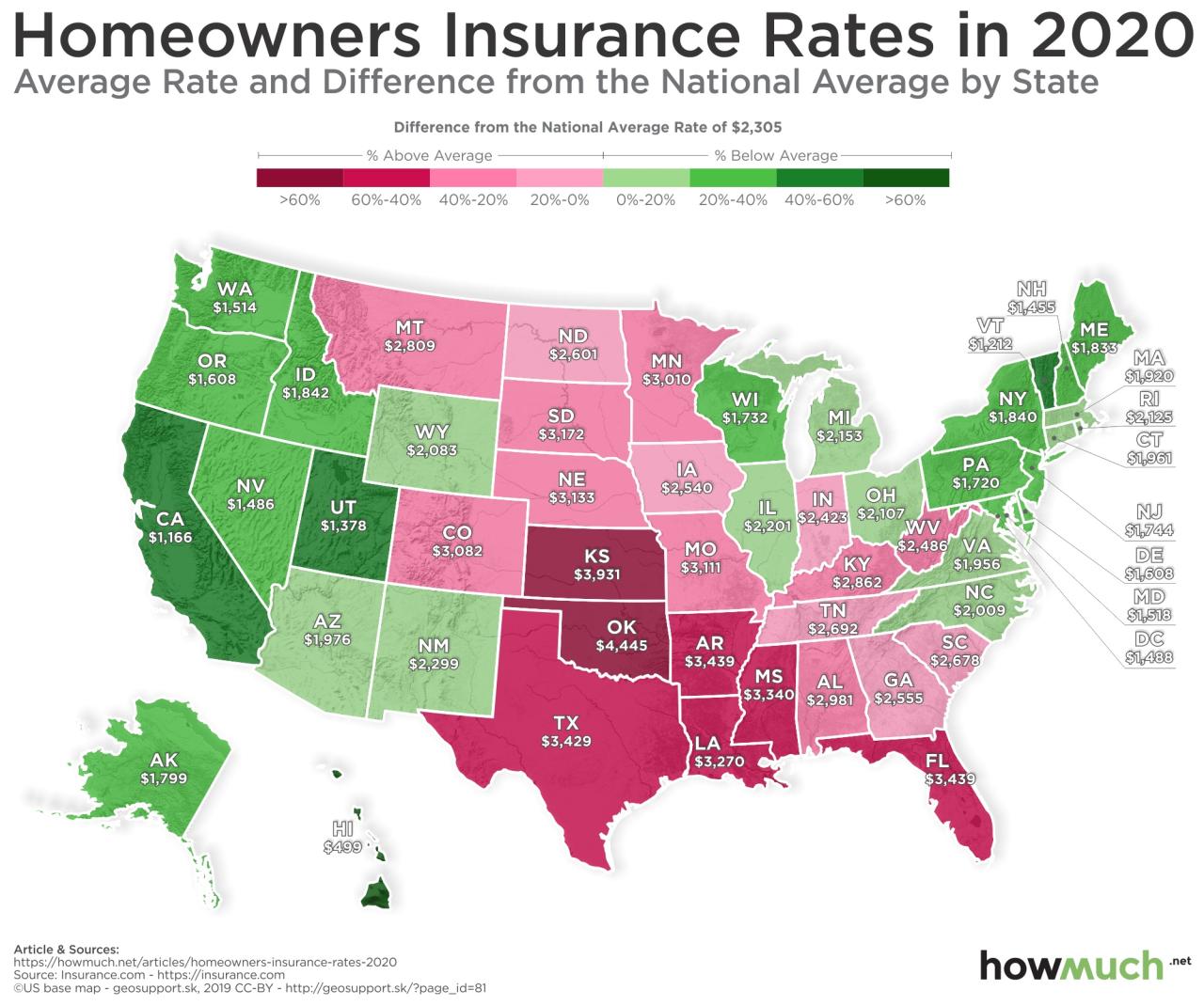
Homeowners insurance premiums are influenced by a variety of factors, including your location, the value of your property, the coverage limits you choose, and your individual risk profile. These factors can vary significantly from state to state, leading to wide differences in premium costs. Understanding how these factors influence your premiums can help you make informed decisions about your homeowners insurance coverage.
Impact of Location on Premiums
Your location plays a significant role in determining your homeowners insurance premium. Insurance companies consider factors such as:
- Natural disaster risk: Areas prone to hurricanes, earthquakes, wildfires, or floods typically have higher premiums due to the increased risk of damage. For instance, coastal areas with a history of hurricane activity will generally have higher premiums than inland areas.
- Crime rates: Areas with higher crime rates, particularly property crime, will generally have higher premiums due to the increased risk of theft or vandalism.
- Cost of living: Areas with a higher cost of living, such as those with expensive housing markets, tend to have higher premiums as the cost of rebuilding or repairing a damaged home is greater.
Impact of Property Value on Premiums
The value of your home is a primary factor in determining your premium. This is because the higher the value of your property, the more it will cost to rebuild or repair it in the event of damage.
The premium is often calculated as a percentage of the insured value of your home.
For example, a homeowner with a $500,000 home may pay a higher premium than a homeowner with a $250,000 home, even if they have the same coverage limits.
Impact of Coverage Limits on Premiums
The amount of coverage you choose will also affect your premium. Higher coverage limits generally result in higher premiums. This is because you are paying for more protection in the event of a loss.
It is important to choose coverage limits that adequately protect your property and your financial interests.
For example, if you choose a higher coverage limit for your dwelling, you will pay a higher premium, but you will be better protected in the event of a major disaster.
Impact of Risk Profiles on Premiums
Insurance companies use a variety of factors to assess your individual risk profile, which can influence your premium. These factors may include:
- Credit score: A higher credit score generally indicates a lower risk to insurers, which can lead to lower premiums.
- Claim history: If you have filed a homeowners insurance claim in the past, you may have a higher premium. This is because you are considered a higher risk to insurers.
- Safety features: Homes with security features, such as smoke detectors, burglar alarms, and fire sprinklers, may qualify for lower premiums as they reduce the risk of loss.
- Age of the home: Older homes may have a higher risk of damage, leading to higher premiums.
- Type of construction: Homes built with fire-resistant materials, such as brick or stone, may qualify for lower premiums.
Factors Influencing Premiums: A Summary
| Factor | Impact on Premium |
|---|---|
| Location | Higher risk areas (natural disasters, crime) lead to higher premiums. |
| Property Value | Higher value homes generally have higher premiums due to increased cost of rebuilding. |
| Coverage Limits | Higher coverage limits result in higher premiums due to increased protection. |
| Risk Profile | Factors like credit score, claim history, safety features, and home age influence risk assessment and premium calculation. |
Choosing the Right Coverage
Choosing the right homeowners insurance coverage is crucial to protecting your financial well-being in case of unexpected events. The level of coverage you need depends on your individual circumstances, property value, and potential risks. By carefully considering these factors, you can ensure you have adequate protection without paying for unnecessary coverage.
Determining Your Coverage Needs
It’s essential to understand your coverage needs before selecting a policy. This involves assessing the value of your home and belongings, considering potential risks, and evaluating your financial situation.
- Home Value: The most important factor in determining coverage is the value of your home. Your insurance policy should provide enough coverage to rebuild your home if it is damaged or destroyed. This includes the cost of materials, labor, and any necessary permits. You can use online tools, real estate agents, or appraisers to estimate your home’s market value.
- Personal Property: Your homeowners insurance policy should also cover your personal belongings, such as furniture, electronics, clothing, and jewelry. You’ll need to decide how much coverage you want for these items. You can choose to insure them for their actual cash value, which is their replacement cost minus depreciation, or for their replacement cost, which covers the full cost of replacing them with new items.
- Liability Coverage: Your policy should include liability coverage, which protects you from financial losses if someone is injured on your property or if you cause damage to someone else’s property. The amount of liability coverage you need will depend on your personal circumstances and the potential risks associated with your home.
- Additional Living Expenses: If your home is damaged and uninhabitable, your homeowners insurance policy can help cover the costs of living elsewhere, such as hotel expenses, food, and other necessities. This coverage is known as additional living expenses or loss of use coverage.
Maximizing Coverage and Optimizing Premiums
Once you understand your coverage needs, you can start shopping for a policy. Here are some tips to help you maximize your coverage while optimizing your premium costs:
- Compare Quotes: Obtain quotes from multiple insurance companies to find the best rates and coverage options.
- Consider Discounts: Ask about discounts you may be eligible for, such as those for safety features, home security systems, or bundling your insurance policies.
- Review Your Policy Regularly: It’s important to review your policy regularly to ensure it still meets your needs and that you are not paying for unnecessary coverage.
- Increase Your Deductible: Raising your deductible can lower your premium, but it means you will have to pay more out of pocket if you file a claim.
- Make Improvements: Making improvements to your home, such as installing smoke detectors, fire alarms, and security systems, can reduce your premium costs.
Understanding Claims and Disasters
When unfortunate events happen, knowing how to file a claim and what your homeowners insurance covers is crucial. This section explores the process of filing claims, common disaster types covered, and examples of scenarios where you might need to file a claim.
Filing a Claim
The process of filing a claim for homeowners insurance can vary slightly from state to state. However, the general steps are usually similar:
- Contact your insurance company: The first step is to inform your insurance company about the damage or loss. This can be done by phone, email, or through their online portal.
- Provide details of the incident: You will need to provide information about the date, time, and location of the incident, as well as a description of the damage.
- File a claim: Your insurance company will guide you through the claim filing process, which may involve completing forms and providing supporting documentation.
- Insurance company investigation: The insurance company will typically send an adjuster to inspect the damage and assess the extent of the loss.
- Negotiate a settlement: Once the insurance company has completed its investigation, you will receive a settlement offer. You can negotiate this offer if you believe it is too low.
- Receive payment: If you accept the settlement offer, you will receive payment for the covered damages.
Common Disasters Covered
Homeowners insurance policies typically cover a range of disasters, including:
- Fire: This includes damage caused by fires, explosions, and smoke.
- Windstorm and hail: Damage caused by strong winds, hailstorms, and tornadoes is generally covered.
- Lightning: Damage caused by lightning strikes, including electrical damage, is often covered.
- Theft: Most policies cover theft of belongings from your home, although there may be limits on the amount covered.
- Vandalism: Damage caused by vandalism is typically covered under homeowners insurance.
- Natural disasters: Depending on the specific policy and location, some policies may cover damage caused by earthquakes, floods, or landslides.
Examples of Claims
Here are a few examples of scenarios where you might need to file a claim:
- Fire damage: If your home is damaged by a fire, you would file a claim to cover the cost of repairs or replacement of damaged belongings.
- Hail damage: If a hailstorm damages your roof, you would file a claim to cover the cost of roof repairs.
- Theft of valuables: If your home is burglarized and valuables are stolen, you would file a claim to cover the loss of those items.
- Flood damage: If your home is damaged by a flood, you would need to file a claim if you have flood insurance.
Resources and Additional Information: State Homeowners Insurance

Seeking additional information or assistance with homeowners insurance can be helpful for making informed decisions. Numerous resources and organizations offer valuable insights and support for homeowners.
Reputable Resources and Organizations
These resources provide a wealth of information on homeowners insurance, including consumer guides, industry updates, and advocacy initiatives.
- National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC): This organization represents insurance regulators from all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and five U.S. territories. The NAIC website provides information on insurance regulations, consumer protection, and industry trends.
- Insurance Information Institute (III): The III is a non-profit organization that provides information on insurance issues, including homeowners insurance. Their website offers consumer guides, statistics, and research on insurance topics.
- Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA): FEMA provides resources and assistance for disaster preparedness and recovery, including information on flood insurance and other disaster-related insurance coverage.
- Consumer Reports: This organization provides independent reviews and ratings of various products and services, including homeowners insurance. They offer insights on insurance providers, coverage options, and customer satisfaction.
State Insurance Departments and Consumer Protection Agencies
State insurance departments are responsible for regulating insurance companies and protecting consumers within their respective states. These departments provide information on insurance regulations, consumer rights, and complaint resolution processes.
- State Insurance Departments: Each state has its own insurance department, which can be found through a simple online search.
- Consumer Protection Agencies: Many states also have consumer protection agencies that address consumer complaints and provide information on various consumer issues, including insurance.
Finding and Comparing Quotes
Comparing quotes from different insurance providers is essential to ensure you’re getting the best coverage at the most competitive price.
- Online Insurance Comparison Websites: Several websites allow you to compare quotes from multiple insurance providers simultaneously.
- Insurance Brokers: Brokers act as intermediaries between you and insurance companies. They can help you compare quotes from multiple providers and find the best coverage for your needs.
- Direct Contact with Insurance Companies: You can also contact insurance companies directly to request quotes.
Closing Summary
Navigating the landscape of state homeowners insurance can seem daunting, but with the right information and resources, you can make informed choices that protect your home and financial well-being. By understanding the intricacies of coverage, premiums, and claims processes, you can secure the peace of mind that comes with knowing your property is adequately insured.
FAQ Section
What are some common perils covered by state homeowners insurance?
State homeowners insurance typically covers perils such as fire, theft, vandalism, windstorms, and hail damage. Specific coverage may vary depending on the state and your chosen policy.
How often should I review my homeowners insurance policy?
It’s advisable to review your homeowners insurance policy annually, or whenever you experience significant life changes like a major renovation, purchase of new valuables, or changes in your risk profile.
What are some tips for getting a competitive homeowners insurance quote?
To get the best quote, compare rates from multiple insurance providers, consider increasing your deductible, and explore discounts for safety features, security systems, or bundling policies.







