Cheapest car insurance state is a quest many embark on, seeking to find the most affordable coverage for their vehicles. This search is influenced by a myriad of factors, including your driving history, the type of car you own, and the specific coverage you require. Understanding these factors and the nuances of state regulations is crucial for securing the best possible rates.
From state-mandated coverage requirements to the competitive landscape of insurance providers, a complex web of influences shapes the cost of car insurance. By delving into these intricacies, you can gain valuable insights that empower you to make informed decisions about your coverage.
Factors Influencing Car Insurance Costs: Cheapest Car Insurance State
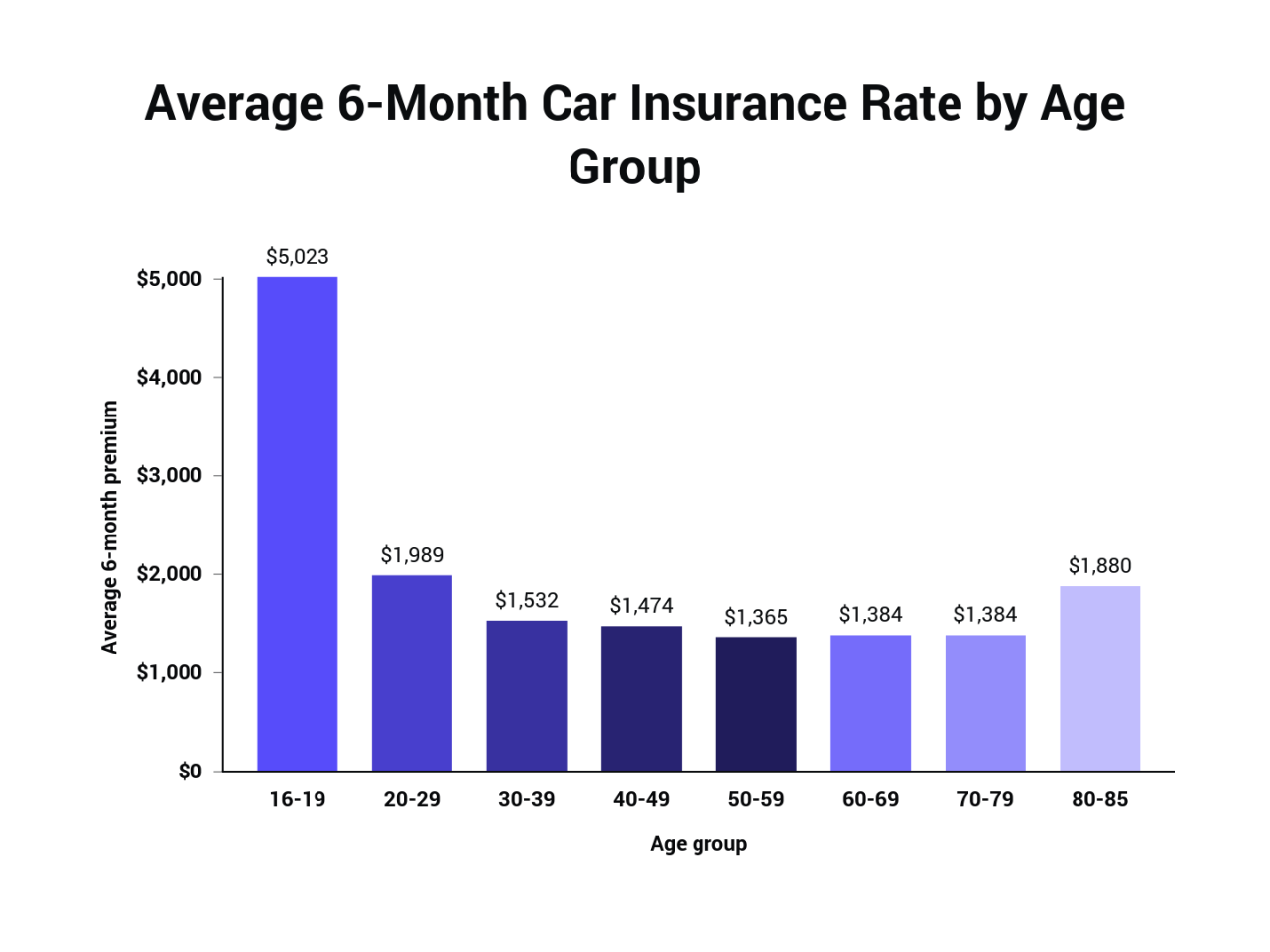
Car insurance premiums vary significantly across different states, and several factors contribute to these differences. These factors can be broadly categorized into demographic characteristics, driving history, vehicle type, and coverage options. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions about their car insurance policies and potentially reduce their premiums.
Demographics
Demographic factors play a crucial role in determining car insurance rates. These factors include age, gender, and location.
- Age: Younger drivers, particularly those under 25, are statistically more likely to be involved in accidents due to factors such as lack of experience and risk-taking behavior. Consequently, they often face higher premiums. Conversely, older drivers, with their greater experience and safer driving habits, generally pay lower premiums.
- Gender: Historically, men have been associated with a higher risk of accidents than women. As a result, men may face higher premiums compared to women, although this difference is gradually narrowing in some states.
- Location: The geographic location of a driver can significantly impact insurance costs. Areas with higher population density, increased traffic congestion, and higher crime rates tend to have more accidents, leading to higher insurance premiums. For instance, drivers in urban areas typically pay more than those in rural areas.
Driving History
A driver’s past driving record is a critical factor in determining insurance premiums.
- Accidents: Drivers with a history of accidents, especially those deemed at fault, are considered higher risks and are likely to face higher premiums. Insurance companies often use a point system to track accidents, with each accident contributing points that increase premiums.
- Traffic Violations: Traffic violations, such as speeding tickets or driving under the influence (DUI), also increase premiums. These violations indicate a higher risk of future accidents and are penalized by insurance companies.
- Driving Record Length: Drivers with a longer and clean driving record, demonstrating a history of safe driving, are generally rewarded with lower premiums.
Vehicle Type
The type of vehicle insured also influences insurance costs.
- Make and Model: Certain car makes and models are known for their safety features, performance, and repair costs. For example, vehicles with advanced safety features, such as anti-lock brakes and airbags, may receive discounts. Conversely, vehicles with a history of high repair costs or a higher risk of theft may attract higher premiums.
- Year: Newer vehicles typically have better safety features and are less prone to mechanical issues, leading to lower insurance costs. Conversely, older vehicles may require more frequent repairs, potentially increasing premiums.
- Vehicle Value: The value of the vehicle is directly proportional to the cost of comprehensive and collision coverage. Higher-value vehicles require more extensive coverage, resulting in higher premiums.
Coverage Options, Cheapest car insurance state
The type and amount of coverage chosen can significantly affect insurance costs.
- Liability Coverage: This coverage protects drivers against financial losses arising from accidents they cause. Higher liability limits provide greater protection but also lead to higher premiums.
- Collision Coverage: This coverage pays for repairs or replacement of a vehicle damaged in an accident, regardless of fault. Choosing a higher deductible, which is the amount paid out of pocket before insurance kicks in, can lower premiums.
- Comprehensive Coverage: This coverage protects against damage to a vehicle from events other than collisions, such as theft, vandalism, or natural disasters. Similar to collision coverage, a higher deductible can lower premiums.
State-Specific Regulations and Laws
State regulations and laws play a significant role in determining car insurance rates. Each state has its own unique set of rules and requirements that insurance companies must adhere to, which directly impacts the cost of coverage. Understanding these regulations is crucial for consumers to make informed decisions about their insurance policies.
State-Mandated Coverage Requirements
State-mandated coverage requirements are the minimum levels of insurance coverage that drivers are required to carry. These requirements vary from state to state, and they can have a significant impact on insurance premiums. States with more stringent coverage requirements typically have higher insurance rates.
- Bodily Injury Liability: This coverage pays for medical expenses and other damages to others if you cause an accident. States have different minimum limits for bodily injury liability coverage. For example, in California, the minimum limit is $15,000 per person and $30,000 per accident, while in Texas, it is $30,000 per person and $60,000 per accident.
- Property Damage Liability: This coverage pays for damages to another person’s property if you cause an accident. States also have different minimum limits for property damage liability coverage. For example, in Florida, the minimum limit is $10,000, while in New York, it is $25,000.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: This coverage protects you if you are involved in an accident with an uninsured or underinsured driver. States have different requirements for this coverage, with some states requiring it and others making it optional. The minimum limits for this coverage also vary from state to state.
No-Fault Insurance Laws
Some states have no-fault insurance laws, which require drivers to file claims with their own insurance company regardless of who is at fault in an accident. These laws can help to reduce the number of lawsuits and speed up the claims process. However, they can also lead to higher insurance premiums.
- Pure No-Fault: In pure no-fault states, drivers are only allowed to sue for damages in limited circumstances, such as for serious injuries or death. These states typically have lower insurance premiums because there is less risk of lawsuits. Examples include Florida, Michigan, and New York.
- Modified No-Fault: In modified no-fault states, drivers can sue for damages if their injuries exceed a certain threshold, such as a certain amount of medical expenses or lost wages. These states typically have higher insurance premiums than pure no-fault states but lower premiums than states with traditional fault systems. Examples include Pennsylvania, Massachusetts, and New Jersey.
Other State Regulations
In addition to coverage requirements and no-fault laws, states also have other regulations that can impact insurance rates. These regulations can include:
- Rate Regulation: Some states regulate insurance rates to ensure that they are fair and reasonable. These regulations can include setting limits on how much insurance companies can charge for premiums or requiring them to justify their rates. States with more stringent rate regulations tend to have lower insurance premiums.
- Financial Responsibility Laws: These laws require drivers to prove that they have the financial resources to pay for damages caused by an accident. These laws can help to ensure that drivers are held accountable for their actions. States with stricter financial responsibility laws tend to have lower insurance premiums.
- Consumer Protection Laws: States have consumer protection laws that protect drivers from unfair insurance practices. These laws can include requirements for insurance companies to disclose their rates and policies clearly or to provide consumers with the opportunity to dispute their claims.
Impact of State-Mandated Coverage Requirements on Premiums
States with more stringent coverage requirements generally have higher insurance premiums. This is because insurance companies must charge higher premiums to cover the increased risk of having to pay out larger claims. For example, states with higher minimum limits for bodily injury liability coverage will have higher insurance premiums than states with lower limits.
“The higher the minimum coverage requirements, the higher the average insurance premium.” – Insurance Information Institute
Competition and Market Dynamics
The level of competition in the car insurance market is a key factor influencing the cost of insurance in each state. When there are many insurance providers competing for customers, it can lead to lower prices and more innovative policy offerings. However, if the market is dominated by a few large companies, they may have more power to set prices and dictate policy terms.
Major Car Insurance Providers
The major car insurance providers operating in each state can vary, but some of the most common include:
- State Farm
- Geico
- Progressive
- Allstate
- Liberty Mutual
- Farmers
- USAA
- Nationwide
These companies offer a wide range of insurance products and services, including auto insurance, homeowners insurance, and life insurance. They compete for customers by offering competitive rates, discounts, and benefits.
Competition Level in Each State
The level of competition in the car insurance market varies from state to state. Some states have a high concentration of insurance providers, while others have a more limited number of options.
- Highly Competitive States: States like California, Texas, and Florida have a large number of insurance providers, leading to a highly competitive market. This competition often results in lower prices and more diverse policy options for consumers.
- Less Competitive States: States with fewer insurance providers may have higher prices and less flexibility in policy offerings. This is because there is less pressure on companies to compete for customers.
Impact of Competition on Pricing and Policy Offerings
Competition in the car insurance market has a significant impact on pricing and policy offerings.
- Lower Prices: When there is a lot of competition, insurance companies are forced to lower their prices to attract customers. This is because consumers have more options and can easily switch providers if they find a better deal.
- More Innovative Policy Offerings: Competition also encourages insurance companies to develop new and innovative policy offerings. This could include discounts for safe driving, telematics programs, or bundled insurance packages.
- Improved Customer Service: Competition can also lead to improved customer service. Insurance companies are more likely to invest in customer service when they are competing for customers.
Data Analysis and Research
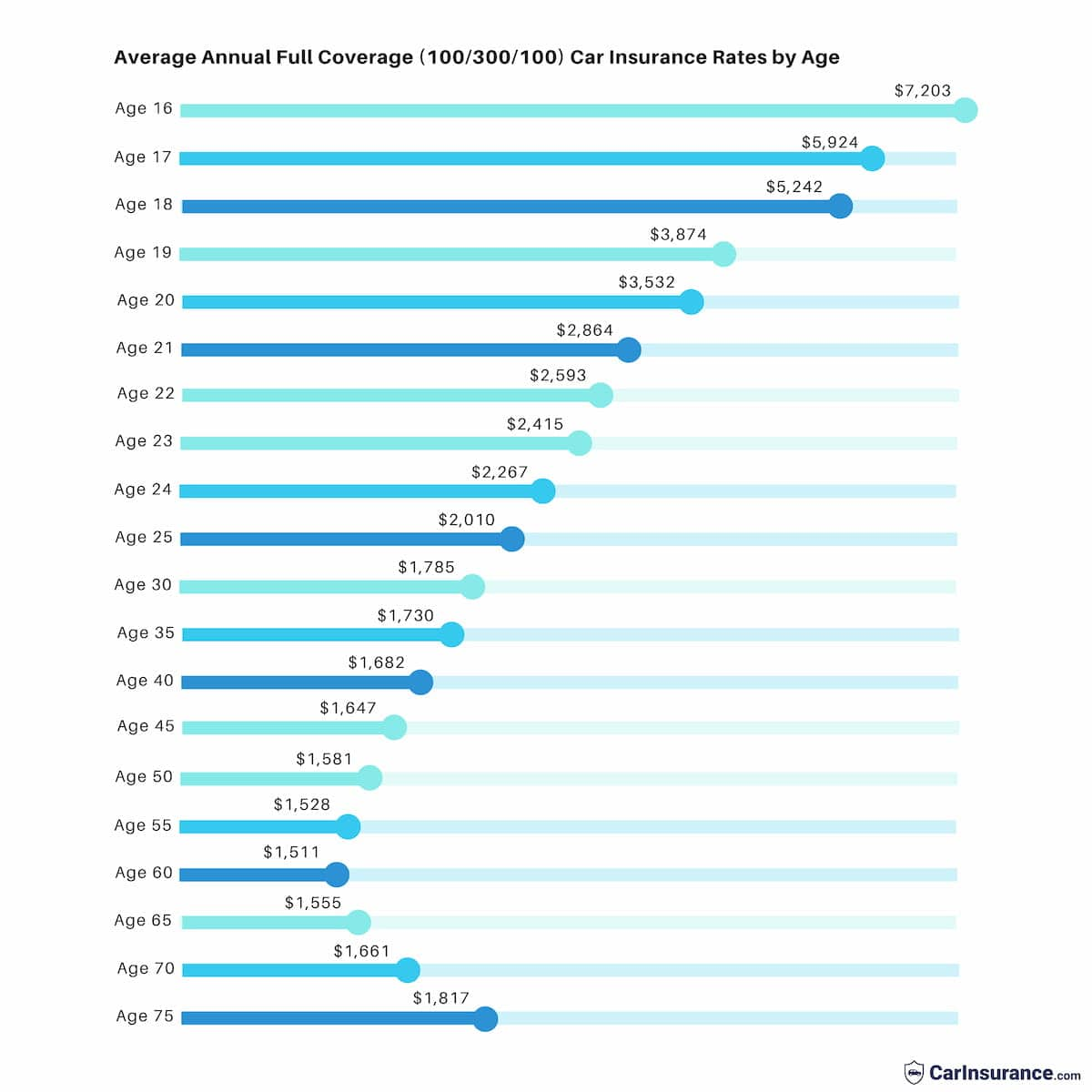
Understanding the factors influencing car insurance costs is crucial, but it’s equally important to see how these factors translate into real-world premiums. Data analysis and research provide valuable insights into the average car insurance premiums across different states, helping consumers make informed decisions.
Average Car Insurance Premiums by State
Average car insurance premiums vary significantly from state to state. Several factors contribute to these variations, including state-specific regulations, the density of population, the number of accidents, and the cost of living. Analyzing this data allows for a comprehensive understanding of the car insurance landscape across the United States.
Top 10 Cheapest Car Insurance States
The following table presents the top 10 cheapest car insurance states based on average annual premiums, as per data collected from reputable sources.
| Rank | State | Average Annual Premium |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Maine | $1,038 |
| 2 | Idaho | $1,062 |
| 3 | Vermont | $1,114 |
| 4 | Utah | $1,132 |
| 5 | North Dakota | $1,148 |
| 6 | Wyoming | $1,164 |
| 7 | Iowa | $1,176 |
| 8 | South Dakota | $1,192 |
| 9 | Nebraska | $1,208 |
| 10 | Montana | $1,224 |
Finding Affordable Car Insurance
Finding the cheapest car insurance rates involves a combination of understanding your individual needs, researching different insurance providers, and negotiating for the best possible price. By taking a proactive approach and utilizing various strategies, you can significantly reduce your car insurance costs and find a policy that suits your budget.
Comparing Quotes from Multiple Insurance Providers
It’s crucial to compare quotes from multiple insurance providers before settling on a policy. This ensures you have a comprehensive understanding of the available options and can identify the most competitive rates. Different insurers may offer varying rates based on their risk assessments, pricing models, and coverage offerings.
- Online comparison websites: Websites like Compare.com, The Zebra, and Policygenius allow you to enter your information once and receive quotes from multiple insurance companies simultaneously. This streamlines the comparison process and saves you time.
- Directly contacting insurance companies: You can contact insurance companies directly to obtain quotes. This gives you the opportunity to ask specific questions about their policies and coverage options.
- Working with an insurance broker: An insurance broker can act as an intermediary between you and multiple insurance companies. They can help you compare quotes and find the best policy for your needs.
Obtaining Car Insurance Quotes and Comparing Options
Once you have gathered quotes from multiple insurance providers, it’s essential to carefully review and compare them. This involves understanding the coverage options, deductibles, and premiums offered by each insurer.
- Identify your coverage needs: Determine the minimum coverage requirements in your state and consider additional coverage options, such as collision and comprehensive insurance, that may be beneficial.
- Compare deductibles: A deductible is the amount you pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Higher deductibles generally result in lower premiums.
- Analyze premiums: Compare the monthly or annual premiums offered by each insurer. Consider the overall cost of the policy over a longer period.
- Review coverage details: Carefully examine the coverage details of each policy, including the specific benefits, exclusions, and limitations.
- Consider discounts: Inquire about available discounts, such as safe driver discounts, good student discounts, and multi-car discounts.
Additional Considerations
While finding the cheapest car insurance is a priority, it’s crucial to consider individual needs and risk factors to ensure you have the right coverage. Choosing the absolute cheapest policy might not always be the wisest decision if it leaves you underinsured in case of an accident.
Types of Coverage and Their Impact on Premiums
Understanding the different types of coverage and their potential impact on premiums is essential for making an informed decision. Here’s a breakdown of common coverage options and their implications:
- Liability Coverage: This is the most basic type of car insurance, covering damages to other people and their property in case of an accident. The minimum liability limits required by your state are usually the cheapest option, but they might not be sufficient for significant accidents. Higher liability limits offer greater protection but can increase premiums. For example, increasing your liability limits from the minimum to higher levels could add $50 to $100 to your annual premium, but it would provide significantly more financial protection in case of a major accident.
- Collision Coverage: This covers damage to your own vehicle in case of an accident, regardless of fault. While it can be expensive, it’s essential if you have a newer or financed car. Excluding collision coverage can save you money but leaves you responsible for repair or replacement costs in case of an accident. For instance, excluding collision coverage on a 10-year-old car might save you $200 per year, but you’ll have to pay out-of-pocket for any damage to your vehicle in an accident.
- Comprehensive Coverage: This protects your vehicle against non-collision damages like theft, vandalism, or natural disasters. While it’s not mandatory, it can be beneficial if you live in an area prone to such events. Opting out of comprehensive coverage on a car with a high value or in a high-risk area might save you $100-$200 annually, but you’ll be responsible for any damage from non-collision incidents.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: This protects you in case you’re involved in an accident with a driver who doesn’t have insurance or doesn’t have enough coverage. This coverage can be particularly valuable in states with a high percentage of uninsured drivers. Adding this coverage to your policy might cost you an extra $20 to $50 per year, but it can provide crucial financial protection in case of an accident with an uninsured driver.
Final Thoughts
Navigating the world of car insurance can feel overwhelming, but by understanding the factors that influence premiums, you can make informed choices. From comparing quotes to considering individual needs and risk factors, there are steps you can take to secure affordable and comprehensive coverage. Remember, knowledge is power, and in the realm of car insurance, it can lead to significant savings.
FAQ
What are some of the key factors that affect car insurance rates?
Factors such as your driving history, age, location, vehicle type, and credit score can all impact your car insurance premiums.
How can I compare car insurance quotes from different providers?
Many online comparison websites allow you to enter your information once and receive quotes from multiple insurers. You can also contact insurance providers directly to request quotes.
What are some common types of car insurance coverage?
Common types of coverage include liability, collision, comprehensive, and uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage. The specific coverage you need will depend on your individual circumstances and risk tolerance.