Automobile insurance requirements by state are a crucial aspect of responsible driving in the United States. Each state mandates specific coverage levels to protect drivers, passengers, and other road users in the event of an accident. Understanding these requirements is essential for all motorists, as failure to comply can result in hefty fines and even license suspension.
Navigating the complex world of automobile insurance can be overwhelming. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental principles of automobile insurance, outlining the legal framework and coverage types. It provides a state-by-state breakdown of minimum requirements, highlighting unique exceptions and considerations. Additionally, we explore factors influencing insurance rates and offer strategies for potentially lowering costs.
Introduction to Automobile Insurance Requirements
Driving a car is a privilege and responsibility that comes with certain legal requirements, including automobile insurance. This insurance serves as a financial safety net, protecting drivers and their families from the potential financial consequences of accidents, injuries, or property damage.
In the United States, automobile insurance is generally mandatory, with each state having its own set of rules and regulations. This legal framework ensures that drivers have adequate financial coverage to compensate for any losses they might cause to others or themselves.
Core Elements of an Automobile Insurance Policy
An automobile insurance policy typically includes several core elements that provide coverage for various situations. These elements are designed to protect drivers and their vehicles in the event of accidents, injuries, or other unforeseen circumstances.
- Liability Coverage: This is the most essential component of an automobile insurance policy, as it covers the costs of damages or injuries caused to others in an accident. Liability coverage typically includes bodily injury liability and property damage liability.
- Collision Coverage: This coverage pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle if it is damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. Collision coverage is optional in most states, but it is often recommended to protect your financial investment in your vehicle.
- Comprehensive Coverage: This coverage protects your vehicle against damages caused by events other than accidents, such as theft, vandalism, fire, or natural disasters. Comprehensive coverage is also optional in most states, but it can be valuable for safeguarding your vehicle against unforeseen circumstances.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: This coverage protects you and your passengers if you are involved in an accident with a driver who is uninsured or underinsured. Uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage helps to compensate for damages and injuries that may not be fully covered by the other driver’s insurance.
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): Also known as “no-fault” insurance, PIP coverage helps pay for medical expenses and lost wages for you and your passengers, regardless of who is at fault in an accident. PIP coverage is mandatory in some states.
State-Specific Requirements

Each state in the US has its own set of minimum auto insurance requirements that drivers must comply with. These requirements are designed to ensure that drivers have sufficient financial protection in case of an accident.
Minimum Insurance Requirements by State
Here’s a table that Artikels the minimum insurance requirements for each state:
| State | Minimum Liability Coverage | Minimum Uninsured Motorist Coverage | Other Mandatory Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 25/50/25 | 25/50 | None |
| Alaska | 25/50/10 | 25/50 | None |
| Arizona | 15/30/10 | 15/30 | None |
| Arkansas | 25/50/25 | 25/50 | None |
| California | 15/30/5 | 15/30 | None |
| Colorado | 25/50/15 | 25/50 | None |
| Connecticut | 20/40/10 | 20/40 | None |
| Delaware | 30/60/5 | 30/60 | None |
| Florida | 10/20/10 | 10/20 | Personal Injury Protection (PIP) |
| Georgia | 25/50/25 | 25/50 | None |
| Hawaii | 20/40/10 | 20/40 | None |
| Idaho | 25/50/15 | 25/50 | None |
| Illinois | 20/40/15 | 20/40 | None |
| Indiana | 25/50/10 | 25/50 | None |
| Iowa | 20/40/15 | 20/40 | None |
| Kansas | 25/50/10 | 25/50 | None |
| Kentucky | 25/50/10 | 25/50 | None |
| Louisiana | 15/30/10 | 15/30 | None |
| Maine | 50/100/25 | 50/100 | None |
| Maryland | 30/60/15 | 30/60 | None |
| Massachusetts | 20/40/5 | 20/40 | None |
| Michigan | 20/40/10 | 20/40 | None |
| Minnesota | 30/60/10 | 30/60 | None |
| Mississippi | 25/50/25 | 25/50 | None |
| Missouri | 25/50/10 | 25/50 | None |
| Montana | 25/50/10 | 25/50 | None |
| Nebraska | 25/50/25 | 25/50 | None |
| Nevada | 15/30/10 | 15/30 | None |
| New Hampshire | 25/50/25 | 25/50 | None |
| New Jersey | 15/30/5 | 15/30 | None |
| New Mexico | 25/50/10 | 25/50 | None |
| New York | 25/50/10 | 25/50 | None |
| North Carolina | 30/60/25 | 30/60 | None |
| North Dakota | 25/50/25 | 25/50 | None |
| Ohio | 25/50/10 | 25/50 | None |
| Oklahoma | 25/50/10 | 25/50 | None |
| Oregon | 25/50/20 | 25/50 | None |
| Pennsylvania | 15/30/5 | 15/30 | None |
| Rhode Island | 25/50/25 | 25/50 | None |
| South Carolina | 25/50/25 | 25/50 | None |
| South Dakota | 25/50/25 | 25/50 | None |
| Tennessee | 25/50/15 | 25/50 | None |
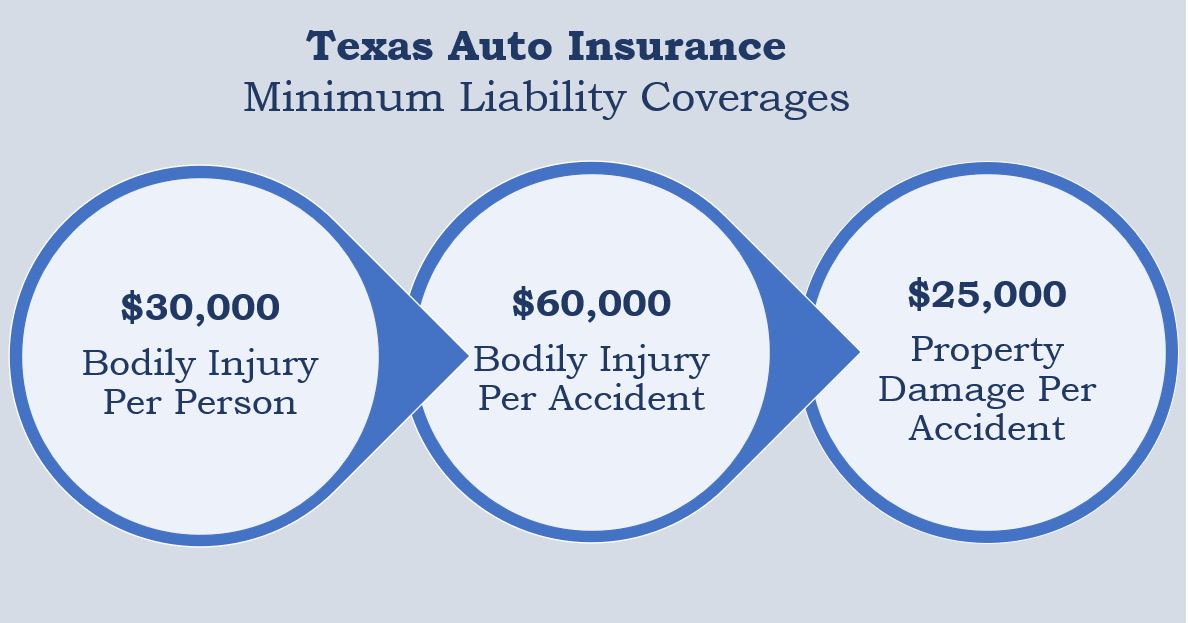
| Texas | 30/60/25 | 30/60 | None |
| Utah | 25/65/15 | 25/65 | None |
| Vermont | 25/50/10 | 25/50 | None |
| Virginia | 25/50/20 | 25/50 | None |
| Washington | 25/50/10 | 25/50 | None |
| West Virginia | 25/50/10 | 25/50 | None |
| Wisconsin | 25/50/10 | 25/50 | None |
| Wyoming | 25/50/10 | 25/50 | None |
Unique Requirements and Exceptions
– Florida: In addition to minimum liability coverage, Florida requires drivers to carry Personal Injury Protection (PIP) coverage. This coverage helps pay for medical expenses and lost wages after an accident, regardless of fault.
– New Jersey: New Jersey requires drivers to carry a minimum of $15,000 in uninsured motorist coverage, which is higher than the minimum liability coverage requirement.
– Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania has a unique “no-fault” insurance system. This means that drivers are required to file claims with their own insurance company, regardless of who caused the accident.
Coverage Types
Automobile insurance policies offer a range of coverage types to protect you and your vehicle in different situations. These coverages are designed to provide financial protection against potential losses, such as damage to your vehicle, injuries to yourself or others, or legal expenses arising from accidents. Understanding the different types of coverage available is crucial for ensuring you have the right level of protection to meet your specific needs and comply with state regulations.
Liability Coverage
Liability coverage is a fundamental component of most automobile insurance policies. It protects you financially if you are at fault in an accident that causes damage to another person’s property or injuries to another person. This coverage covers the costs of:
- Bodily injury liability: This coverage pays for medical expenses, lost wages, and other damages incurred by the other driver and passengers if you are at fault in an accident.
- Property damage liability: This coverage pays for repairs or replacement costs for the other driver’s vehicle or property if you are at fault in an accident.
Liability coverage is usually expressed as a set of limits, such as 100/300/50. This means that the policy will pay up to $100,000 per person for bodily injury, up to $300,000 per accident for bodily injury, and up to $50,000 per accident for property damage. The minimum liability coverage limits required by each state vary. It is essential to carry sufficient liability coverage to protect yourself from significant financial losses in the event of an accident.
Collision Coverage
Collision coverage pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle if it is damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. This coverage applies to accidents involving another vehicle, a stationary object, or even a single-car accident.
Collision coverage is optional in most states, but it is often required if you have a loan or lease on your vehicle. This is because the lender or leasing company wants to ensure that their investment is protected in the event of an accident. Collision coverage typically has a deductible, which is the amount you pay out of pocket before the insurance company covers the remaining costs. The deductible amount can be adjusted to affect your premium, with higher deductibles generally resulting in lower premiums.
Comprehensive Coverage
Comprehensive coverage protects your vehicle from damages caused by events other than accidents. This includes events such as theft, vandalism, fire, hail, floods, and animal collisions.
Like collision coverage, comprehensive coverage is usually optional. However, it is often required if you have a loan or lease on your vehicle. It also typically has a deductible, which can be adjusted to affect your premium.
Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage
Uninsured/underinsured motorist (UM/UIM) coverage provides financial protection if you are involved in an accident with a driver who has no insurance or insufficient insurance to cover your losses. This coverage can help pay for your medical expenses, lost wages, and other damages, even if the other driver is at fault.
UM/UIM coverage is typically optional, but it is highly recommended. It provides a crucial safety net in situations where the other driver’s insurance is inadequate or nonexistent. UM/UIM coverage can also cover your losses if you are injured by a hit-and-run driver.
Personal Injury Protection (PIP)
Personal injury protection (PIP) coverage, also known as no-fault insurance, covers your medical expenses and lost wages, regardless of who is at fault in an accident. It provides financial protection for you and your passengers, regardless of whether the other driver is insured.
PIP coverage is required in some states, but it is optional in others. The amount of coverage available under PIP varies by state and policy.
Factors Affecting Insurance Rates
Your driving record, age, vehicle type, and location are some of the key factors that determine your car insurance premiums. Insurance companies use these factors to assess your risk of being involved in an accident.
Driving History
Your driving history is a major factor in determining your insurance rates. A clean driving record with no accidents or violations will result in lower premiums. Conversely, a history of accidents, speeding tickets, or DUI convictions will significantly increase your rates.
Insurance companies use a system called a “risk score” to assess your driving history. This score is based on factors such as the number and severity of your accidents, traffic violations, and driving experience.
Age
Your age is another significant factor in determining your insurance rates. Young drivers, especially those under 25, are statistically more likely to be involved in accidents. Insurance companies typically charge higher premiums for young drivers due to their lack of experience and higher risk. As drivers age and gain experience, their premiums tend to decrease.
Vehicle Type
The type of vehicle you drive also plays a role in determining your insurance rates. Insurance companies consider factors such as the vehicle’s safety features, cost of repairs, and theft risk. For example, a luxury car with advanced safety features will likely have a lower insurance rate than a high-performance sports car with a history of theft.
Location, Automobile insurance requirements by state
The location where you live can also affect your insurance rates. Insurance companies consider factors such as the density of traffic, crime rates, and weather conditions in your area. For example, drivers living in urban areas with high traffic density and higher crime rates may face higher insurance premiums compared to those living in rural areas.
Understanding Your Policy: Automobile Insurance Requirements By State

Your automobile insurance policy is a legally binding contract that Artikels the terms and conditions of your coverage. Understanding its contents is crucial to ensure you have the protection you need and to avoid any surprises when you need to file a claim.
Policy Terms and Definitions
Insurance policies often use specialized terminology. Familiarizing yourself with common terms and definitions will help you decipher the language and make informed decisions.
- Deductible: The amount you pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. A higher deductible typically results in lower premiums.
- Premium: The amount you pay for your insurance coverage, usually on a monthly or annual basis.
- Coverage Limits: The maximum amount your insurance company will pay for a covered loss.
- Exclusions: Specific events or circumstances that are not covered by your policy.
- Endorsements: Additional coverage options that can be added to your policy for a fee.
Navigating Your Policy
Reading your policy thoroughly is essential, but it can seem overwhelming. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate and interpret your policy document:
- Read the Declaration Page: This page summarizes your policy’s key details, including your name, policy number, coverage types, premium amount, and effective dates.
- Review the Coverage Sections: Each section describes a specific type of coverage, such as liability, collision, or comprehensive. Pay attention to coverage limits, deductibles, and exclusions.
- Understand the Exclusions: This section lists events or circumstances that are not covered by your policy. For example, most policies exclude coverage for damage caused by wear and tear or acts of war.
- Familiarize Yourself with Endorsements: If you have any additional coverage options, review the relevant endorsements to understand their terms and conditions.
- Contact Your Agent: If you have any questions or need clarification, don’t hesitate to reach out to your insurance agent. They are your best resource for understanding your policy.
Filing a Claim
Filing an automobile insurance claim is a process you may need to go through if you’re involved in an accident or experience a covered loss. Understanding the steps involved can help you navigate this process smoothly.
The Process for Filing a Claim
It’s essential to report an accident to your insurance company as soon as possible. This can be done by calling their 24-hour claims hotline or using their online portal. You will typically need to provide the following information:
- Your policy number
- The date, time, and location of the accident
- Details of the other vehicles involved, including their license plate numbers and insurance information
- A description of the accident and any injuries sustained
Required Documentation and Information
After you report the accident, your insurance company will guide you through the claim process. They will likely ask for additional documentation, including:
- A copy of the police report
- Photos of the damage to your vehicle
- Medical bills and documentation if you were injured
- Estimates from repair shops for the cost of repairs
- Proof of ownership of the vehicle
Steps Involved in Handling a Claim
Once you provide the necessary information and documentation, your insurance company will review your claim. They may contact the other party involved in the accident to gather their perspective. If your claim is approved, they will determine the amount of coverage you are entitled to.
Resolving Disputes
In some cases, you may disagree with your insurance company’s assessment of your claim. If this happens, you have the right to appeal their decision. You should follow the steps Artikeld in your insurance policy for filing an appeal.
If you are unable to resolve the dispute with your insurance company, you may need to seek assistance from an independent mediator or arbitrator.
Resources and Assistance
Navigating the complex world of automobile insurance can be daunting, but numerous resources are available to provide guidance and support. Whether you’re seeking general information, comparing quotes, or resolving a claim, there are reliable sources to help you make informed decisions.
Government Websites
Government websites are valuable resources for understanding state-specific insurance requirements, consumer protection laws, and available resources. These websites often provide information on:
- Minimum coverage requirements
- Insurance fraud prevention
- Consumer complaint processes
- Financial assistance programs
For example, the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) website offers a comprehensive overview of insurance regulations across all states.
Insurance Industry Organizations
Insurance industry organizations play a crucial role in promoting consumer education and advocating for fair insurance practices. These organizations provide information on:
- Insurance terminology and concepts
- Industry trends and best practices
- Consumer protection resources
The Insurance Information Institute (III) is a prominent organization that offers a wealth of information on various insurance topics, including automobile insurance.
Consumer Advocacy Groups
Consumer advocacy groups champion the rights of consumers and provide valuable insights into insurance industry practices. These groups often:
- Investigate consumer complaints
- Advocate for consumer protection laws
- Offer advice on insurance-related matters
The Consumer Federation of America (CFA) is a prominent consumer advocacy group that actively monitors insurance industry practices and advocates for consumer protection.
Insurance Agents and Brokers
Insurance agents and brokers serve as intermediaries between consumers and insurance companies. They provide guidance on:
- Selecting the right coverage
- Understanding policy terms and conditions
- Finding competitive insurance rates
- Filing claims
It is essential to choose an agent or broker who is licensed and knowledgeable about automobile insurance.
Finding Reliable Insurance Providers
Choosing a reliable and trustworthy insurance provider is crucial. Here are some tips:
- Check financial stability: Look for companies with strong financial ratings, indicating their ability to pay claims.
- Read customer reviews: Research online reviews and ratings from reputable sources to gauge customer satisfaction.
- Compare quotes: Obtain quotes from multiple insurance companies to compare coverage options and prices.
- Ask for referrals: Seek recommendations from trusted friends, family members, or financial advisors.
Last Word
Armed with knowledge of automobile insurance requirements by state, you can confidently navigate the road ahead. By understanding your obligations and making informed decisions about your coverage, you can ensure peace of mind and financial protection in the event of an unforeseen incident. Remember to review your policy regularly, seek professional guidance when needed, and prioritize safe driving practices to minimize risks and safeguard yourself and others on the road.
FAQ Insights
What happens if I get into an accident and don’t have the required insurance coverage?
You could face serious consequences, including fines, license suspension, and even legal action. You may also be held personally liable for damages, even if the accident wasn’t your fault.
Can I get a discount on my car insurance if I have a good driving record?
Yes, most insurance companies offer discounts for drivers with clean driving histories. You may also qualify for discounts for safety features in your vehicle, completing a defensive driving course, or bundling multiple insurance policies with the same provider.
How often should I review my car insurance policy?
It’s a good idea to review your policy at least annually, or more frequently if there are significant changes in your life, such as a new car purchase, a change in your driving habits, or a move to a new state.







