American States Insurance plays a crucial role in the intricate tapestry of the US insurance market. This vast industry, encompassing a diverse range of providers and regulations, presents a complex landscape for both consumers and businesses. From auto and health to homeowners and life insurance, each state offers unique offerings and regulations, impacting availability, affordability, and consumer choices.
Understanding the nuances of state-level insurance is paramount for navigating this complex system. This exploration delves into the structure of the insurance industry, the various types of insurance offered, and the intricacies of state-specific regulations. We’ll examine the impact of these regulations on the economy and explore emerging trends shaping the future of American States Insurance.
Insurance Landscape in the United States
The United States insurance industry is a complex and dynamic sector, playing a vital role in the nation’s economy and financial stability. It encompasses a wide range of insurance products, including life, health, property, casualty, and liability insurance.
Key Players in the US Insurance Industry
The US insurance industry is characterized by a diverse range of players, each with specific roles and responsibilities. These include:
- Insurance Companies: These are the core entities that underwrite and sell insurance policies to individuals and businesses. They assess risks, determine premiums, and pay claims when covered events occur.
- Insurance Brokers: These act as intermediaries, connecting insurance buyers with insurance companies. They offer advice and guidance on selecting the right policies and negotiating favorable terms.
- Insurance Agents: These are typically employed by insurance companies and sell insurance products directly to customers. They provide information, answer questions, and process applications.
- Regulatory Bodies: The insurance industry is subject to extensive regulation at both the state and federal levels. State insurance departments are responsible for licensing insurers, overseeing their financial solvency, and ensuring compliance with state laws.
State-Level Regulation in the US Insurance Market
State-level regulation plays a crucial role in shaping the US insurance market. Each state has its own unique set of laws and regulations governing insurance companies operating within its borders. This approach to regulation, known as “state-based insurance regulation,” offers several advantages:
- Flexibility: States can tailor regulations to meet the specific needs of their local populations and insurance markets. This flexibility allows for greater responsiveness to regional variations in risk profiles, consumer preferences, and economic conditions.
- Competition: State-based regulation encourages competition among insurers, as companies must meet the requirements of multiple states to operate nationwide. This competition can drive innovation and lower premiums for consumers.
- Consumer Protection: State insurance departments are responsible for protecting consumers from unfair or deceptive practices by insurance companies. They investigate complaints, enforce regulations, and provide information to consumers about their rights and responsibilities.
Types of Insurance Offered by States

Each state in the United States has its own unique insurance landscape, with varying regulations, available insurance types, and prominent providers. This section delves into the specific types of insurance offered by states, highlighting key providers and notable features.
Types of Insurance Offered by States
The following table provides a general overview of major insurance categories offered by states, along with key providers and notable features.
| State | Type of Insurance | Key Providers | Notable Features |
|—|—|—|—|
| California | Auto, Health, Homeowners, Life | State Farm, Geico, Blue Shield of California | California has strict regulations regarding auto insurance, including mandatory coverage for personal injury protection (PIP). |
| Texas | Auto, Health, Homeowners, Life | State Farm, Allstate, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Texas | Texas has a competitive insurance market with a wide range of options for auto and health insurance. |
| New York | Auto, Health, Homeowners, Life | Geico, Progressive, Empire BlueCross BlueShield | New York requires all drivers to have auto insurance, and the state has a robust health insurance exchange. |
| Florida | Auto, Health, Homeowners, Life | State Farm, Geico, Florida Blue | Florida is known for its high auto insurance rates due to a high number of claims. |
| Illinois | Auto, Health, Homeowners, Life | State Farm, Allstate, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Illinois | Illinois has a strong health insurance market with a variety of plans available. |
State-Specific Insurance Regulations
The insurance industry in the United States is heavily regulated, with each state having its own set of rules and regulations governing insurance companies and products. These regulations aim to protect consumers, ensure fair competition, and maintain the financial stability of insurance companies.
Variations in Insurance Regulations
State insurance regulations vary significantly across the country, impacting insurance availability, affordability, and coverage options. These differences stem from factors such as:
- State-Specific Needs: Different states have unique demographic profiles, risk factors, and economic conditions, leading to tailored regulations to address specific needs.
- Political Landscape: Political ideologies and priorities influence regulatory approaches, resulting in variations in consumer protection, pricing, and coverage mandates.
- Historical Factors: Past experiences with insurance market failures or consumer abuses have shaped regulatory frameworks, leading to diverse regulations across states.
Coverage Requirements
State regulations define the minimum coverage requirements for various insurance lines, such as auto, health, and property insurance. For instance:
- Auto Insurance: States mandate minimum liability coverage for bodily injury and property damage, but these requirements vary considerably. Some states also require coverage for uninsured/underinsured motorists.
- Health Insurance: States have varying regulations regarding essential health benefits, coverage for pre-existing conditions, and affordability requirements for health insurance plans.
- Property Insurance: States often mandate coverage for specific perils, such as fire, windstorm, and hail, while others allow insurers to exclude certain risks.
Pricing Regulations, American states insurance
State regulations influence insurance pricing through:
- Rate Filing Requirements: Some states require insurers to file their rates for approval, while others allow insurers to use “file and use” systems, where rates are filed but not necessarily reviewed.
- Rate Regulation: States may impose limits on rate increases, prohibit discriminatory pricing practices, or require insurers to consider specific factors, such as credit scores, when setting rates.
- Risk Classification: States have different rules regarding how insurers can classify risks and group individuals for pricing purposes. This impacts affordability for individuals in certain risk categories.
Consumer Protection
States have implemented regulations to protect consumers from unfair or deceptive insurance practices. These include:
- Consumer Information Requirements: States require insurers to provide clear and understandable information about their policies, coverage, and pricing.
- Complaint Handling Procedures: States establish mechanisms for resolving consumer complaints against insurance companies, often through dedicated insurance departments or bureaus.
- Fair Claims Practices: States have regulations outlining insurers’ responsibilities in handling claims fairly and promptly, including timelines for investigations and payments.
Impact of State Regulations
State insurance regulations have a significant impact on insurance availability and affordability:
- Insurance Availability: Stringent regulations can increase costs for insurers, making it less attractive to offer coverage in certain states, especially for high-risk individuals or areas.
- Insurance Affordability: Regulations that limit rate increases or mandate coverage can make insurance less affordable for some consumers, particularly those in higher-risk categories.
- Innovation and Competition: Regulations can stifle innovation and competition in the insurance market, potentially leading to fewer choices for consumers and higher prices.
Consumer Considerations in State Insurance
Navigating the insurance landscape can be complex, especially when you consider the variations across different states. Understanding your specific state’s regulations and available options is crucial for making informed decisions that protect your financial well-being.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Insurance
When selecting insurance in a particular state, consumers should consider several key factors to ensure they choose a policy that meets their needs and budget.
- Your Specific Needs and Circumstances: Every individual’s insurance requirements differ. Consider factors such as your age, health, family size, property value, and driving record.
- Coverage Options and Limits: Compare the different types of coverage offered by various insurers and their limits. Ensure the policy provides sufficient protection for your assets and liabilities.
- Premiums and Deductibles: Carefully evaluate the cost of premiums and deductibles. Higher deductibles generally lead to lower premiums, but you’ll be responsible for paying more out-of-pocket in case of a claim.
- Financial Stability and Reputation of Insurers: Research the insurer’s financial stability and reputation. Look for companies with strong financial ratings and positive customer reviews.
- Customer Service and Claims Handling: Consider the insurer’s reputation for customer service and claims handling. Look for companies known for their responsiveness and fair claim processing.
Comparing Insurance Quotes
Obtaining and comparing insurance quotes from multiple insurers is essential for finding the best value.
- Use Online Comparison Tools: Numerous websites and apps allow you to compare quotes from various insurers simultaneously. This streamlines the process and helps you identify the most competitive offers.
- Contact Insurers Directly: Reach out to insurers directly to discuss your specific needs and obtain personalized quotes.
- Consider Bundling: Check if the insurer offers discounts for bundling multiple insurance policies, such as home and auto insurance.
- Review Policy Terms Carefully: Before committing to a policy, thoroughly review the terms and conditions, including exclusions, limitations, and cancellation policies.
Understanding Policy Terms
Understanding the terms and conditions of your insurance policy is crucial for maximizing its benefits.
- Deductible: This is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in.
- Premium: The regular payment you make to maintain your insurance coverage.
- Coverage Limits: The maximum amount your insurer will pay for a covered claim.
- Exclusions: Specific events or circumstances that are not covered by your policy.
- Co-Insurance: A percentage of the covered claim you are responsible for paying.
State-Level Resources and Consumer Protection Agencies
States provide valuable resources and consumer protection agencies to assist individuals with insurance-related matters.
- State Insurance Departments: These departments regulate insurance companies and provide information on consumer rights and insurance options.
- Consumer Protection Agencies: Organizations dedicated to protecting consumers from unfair business practices, including insurance fraud.
- State-Specific Websites: Many states have dedicated websites that provide information on insurance regulations, consumer protection, and available resources.
Impact of State Insurance on the Economy
The insurance industry plays a vital role in the economic well-being of individual states across the United States. Its influence extends beyond providing financial protection to encompass job creation, revenue generation, and the overall stability of state economies.
Economic Significance of the Insurance Industry
The insurance industry’s contribution to the economy is multifaceted, encompassing employment, revenue generation, and its role in fostering economic stability.
- Employment: The insurance industry is a significant employer in many states, providing jobs in various sectors such as underwriting, claims processing, sales, and customer service. The industry’s contribution to employment is substantial, particularly in states with large insurance hubs, such as New York, California, and Illinois.
- Revenue Generation: Insurance companies contribute significantly to state revenues through taxes on premiums, licensing fees, and other assessments. These revenues support state programs and services, including education, healthcare, and infrastructure development. The contribution of insurance companies to state coffers varies depending on the size and scope of the insurance market in each state.
- Economic Stability: The insurance industry plays a crucial role in economic stability by providing financial protection against various risks. In the event of natural disasters, accidents, or other unforeseen events, insurance companies provide financial compensation, helping to mitigate the economic impact of these events. This role in risk management contributes to the overall stability of state economies.
Contribution of Insurance to Employment
The insurance industry creates a wide range of job opportunities, contributing significantly to state economies.
- Direct Employment: Insurance companies directly employ a large number of individuals in various roles, including underwriters, claims adjusters, actuaries, sales agents, customer service representatives, and administrative staff. These jobs contribute to the local economy through wages and salaries.
- Indirect Employment: The insurance industry also generates indirect employment through its relationships with other businesses. For example, insurance companies rely on legal services, accounting firms, and technology providers, creating jobs in these sectors.
- Multiplier Effect: The employment generated by the insurance industry has a multiplier effect on the economy. When insurance companies hire employees, these employees spend their earnings, stimulating demand for goods and services in other sectors, leading to further job creation.
Revenue Generation through Insurance
State governments rely on insurance companies as a source of revenue through various taxes and fees.
- Premium Taxes: Many states impose taxes on insurance premiums, generating revenue for state budgets. These taxes vary depending on the type of insurance and the state’s tax structure.
- Licensing Fees: Insurance companies are required to obtain licenses to operate in each state. These licenses involve fees that contribute to state revenues.
- Assessments: In some cases, states may impose assessments on insurance companies to fund specific programs or initiatives, such as disaster relief funds.
Impact of State Insurance Regulations on Business and Investment
State insurance regulations play a crucial role in shaping the business environment for insurance companies and influencing investment decisions.
- Regulatory Environment: States have varying insurance regulations, which can impact the profitability and competitiveness of insurance companies. Stricter regulations may increase compliance costs and limit product offerings, while more lenient regulations may attract more investment.
- Investment Decisions: Insurance companies consider state insurance regulations when making investment decisions. States with favorable regulatory environments and strong consumer protection laws may attract more investment in the insurance sector.
- Innovation and Competition: State insurance regulations can impact innovation and competition in the industry. Regulations that promote competition and innovation can lead to better products and services for consumers.
Future Trends in State Insurance

The insurance landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, shifting consumer needs, and evolving regulatory environments. These trends are shaping the future of state insurance, impacting how insurers operate, how consumers access coverage, and the overall role of insurance in the economy.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are fundamentally changing the insurance industry. Artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics, and blockchain technology are transforming how insurers assess risk, personalize policies, and manage claims.
- AI-powered risk assessment: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict future events, leading to more accurate risk assessments and customized pricing for insurance policies. For example, AI can analyze driving data from telematics devices to assess individual driving habits and offer tailored auto insurance premiums.
- Personalized insurance products: By leveraging data analytics, insurers can develop highly personalized insurance products that cater to individual needs and preferences. For instance, insurers can use data to create customized health insurance plans based on a person’s medical history, lifestyle, and risk factors.
- Automated claims processing: Blockchain technology can streamline claims processing by providing a secure and transparent platform for tracking claims information and facilitating faster payments. This can improve customer satisfaction and reduce operational costs for insurers.
Changing Consumer Needs
Consumer expectations are also evolving, demanding greater transparency, personalization, and convenience in insurance services. This is driving insurers to adapt their offerings and service models.
- Digital-first experiences: Consumers are increasingly comfortable with digital interactions, and they expect insurance companies to provide seamless online experiences, from policy purchasing to claims filing. This is leading to the development of mobile apps, online portals, and chatbots for insurance transactions.
- Demand for value-added services: Consumers are seeking more than just basic insurance coverage. They want insurers to provide value-added services such as health and wellness programs, financial planning tools, and personalized risk management advice.
- Increased focus on sustainability: Consumers are increasingly concerned about environmental issues and are looking for insurers that offer sustainable products and services. This is driving the development of green insurance policies that cover risks related to climate change and environmental hazards.
Evolving State Regulations
State insurance regulators are playing a critical role in adapting to these changes and ensuring that the insurance market remains fair, stable, and accessible.
- Promoting innovation: Regulators are encouraging innovation in the insurance industry by supporting the development and adoption of new technologies. This includes providing guidance on data privacy, cybersecurity, and the use of AI in insurance.
- Ensuring consumer protection: Regulators are focused on protecting consumers by setting standards for transparency, fairness, and accessibility in insurance products and services. This includes regulations related to pricing, coverage, and claims handling.
- Addressing emerging risks: State insurance regulators are actively addressing emerging risks, such as those related to climate change, cybersecurity threats, and the growing use of autonomous vehicles. This involves developing new regulations and guidance to mitigate these risks and ensure the stability of the insurance market.
Future Role of State Insurance
In the future, state insurance will play a crucial role in supporting economic growth, promoting financial security, and protecting consumers.
- Supporting economic growth: State insurance plays a vital role in supporting economic growth by providing financial protection against risks that can disrupt businesses and individuals. This includes coverage for property damage, business interruption, and liability.
- Promoting financial security: State insurance helps individuals and families achieve financial security by providing coverage for health care, retirement, and other critical needs. This includes health insurance, life insurance, and long-term care insurance.
- Protecting consumers: State insurance regulators are responsible for ensuring that consumers are treated fairly and have access to affordable and comprehensive insurance coverage. This includes setting standards for pricing, coverage, and claims handling.
Closing Notes
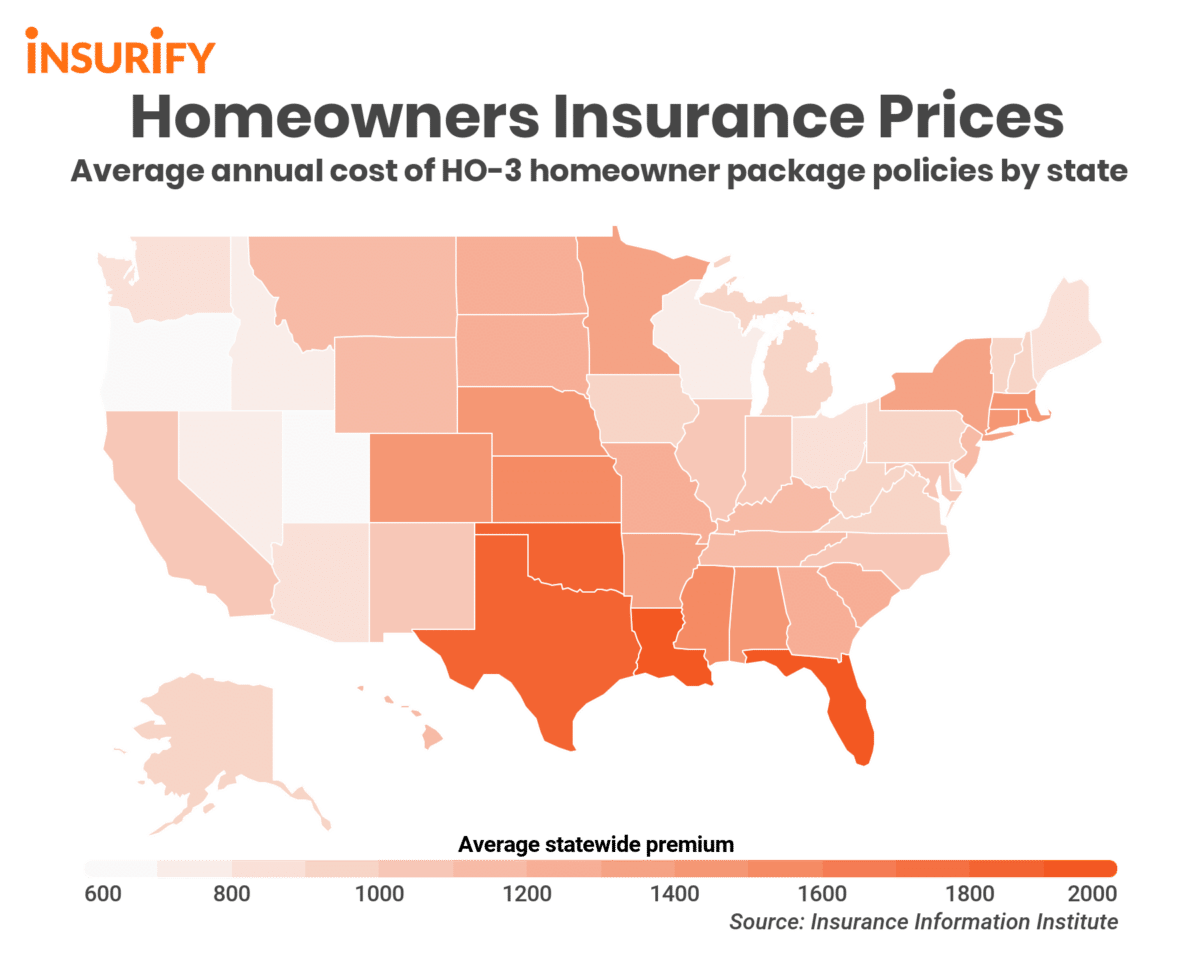
As we conclude our journey through the realm of American States Insurance, the interconnectedness of state-level regulations, consumer choices, and economic implications becomes evident. Navigating this landscape requires a keen understanding of the unique characteristics of each state, empowering individuals and businesses to make informed decisions. The future of American States Insurance is likely to be shaped by technological advancements, evolving consumer needs, and ongoing adjustments to state regulations. Staying informed about these developments will be crucial for all stakeholders in this dynamic sector.
General Inquiries: American States Insurance
What are the main types of insurance offered in the US?
The main types of insurance offered in the US include auto, health, homeowners, life, and commercial insurance. Each state may offer additional specialized insurance products as well.
How can I compare insurance quotes from different providers?
Many online comparison websites allow you to enter your information and receive quotes from multiple insurance providers. You can also contact insurance agents directly to obtain quotes.
What are some key factors to consider when choosing insurance?
Key factors to consider include coverage, price, deductibles, customer service, and financial stability of the insurance provider. It’s essential to compare policies and understand the terms and conditions before making a decision.
Are there any state-level resources available to help consumers with insurance?
Most states have consumer protection agencies and insurance departments that provide information and assistance to consumers regarding insurance issues.






