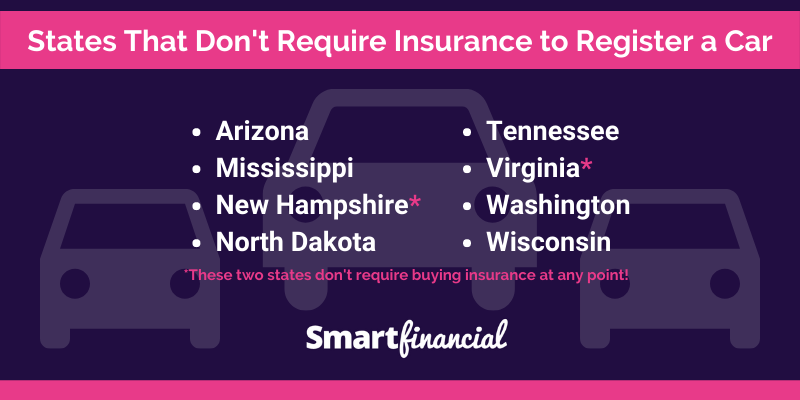
States that don’t need car insurance might seem like a dream come true for drivers, but the reality is far more complex. While a handful of states don’t mandate car insurance, they do require drivers to demonstrate financial responsibility in other ways. This means that even if you’re driving in a state without mandatory car insurance, you’re still responsible for any damages you cause in an accident. This article delves into the nuances of these states, exploring the legal requirements, potential risks, and alternative forms of financial protection.
Navigating the intricacies of driving without mandatory car insurance can be confusing, but understanding the potential risks and alternative options is crucial for making informed decisions. This guide will equip you with the knowledge to drive safely and responsibly, regardless of the state you reside in.
States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
While most states in the US mandate car insurance, there are a few exceptions. These states have chosen not to require drivers to carry car insurance, opting for a different approach to managing financial responsibility for accidents. This decision is often driven by a combination of factors, including economic considerations, political views, and the belief that individuals should be free to choose whether or not to purchase car insurance.
Legal Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
In states without mandatory car insurance, driving without insurance can have significant legal consequences. While these states do not require drivers to carry insurance, they still hold drivers financially responsible for any damages or injuries they cause in an accident. If you are involved in an accident without insurance, you could face a range of legal actions, including:
- Financial Responsibility Laws: These laws hold drivers accountable for damages caused by their vehicles. Even without insurance, you could be held personally liable for the full cost of repairs, medical bills, lost wages, and other damages incurred by the other party.
- Lawsuits: The injured party can file a lawsuit against you to recover their losses. This could result in significant financial hardship, including the possibility of having your assets seized to cover the judgment.
- License Suspension: Some states may suspend your driver’s license if you are found to be driving without insurance. This can severely impact your ability to drive legally and may result in additional fines and penalties.
- Jail Time: In some cases, driving without insurance may lead to criminal charges and potential jail time, especially if the accident results in serious injuries or death.
Financial Risks of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without insurance in a state that does not require it can expose you to significant financial risks. In the event of an accident, you could be responsible for covering all associated costs, including:
- Property Damage: Repairs or replacement costs for the other vehicle involved in the accident.
- Medical Expenses: Treatment costs for any injuries sustained by yourself or others involved in the accident.
- Lost Wages: Compensation for time missed from work due to injuries or vehicle repairs.
- Legal Fees: Costs associated with defending yourself in a lawsuit.
- Potential Bankruptcy: If the financial burden of an accident is too great, you could face bankruptcy, losing your assets and financial stability.
Financial Responsibility Laws in States Without Mandatory Insurance
While these states don’t require drivers to carry car insurance, they still have laws in place to ensure financial responsibility in case of an accident. These laws are designed to protect victims of accidents and ensure that they have access to compensation for their losses.
Types of Financial Responsibility Proof Accepted
States without mandatory car insurance typically accept several types of financial responsibility proof. These proofs demonstrate that a driver can cover the costs of potential accidents.
- Proof of Financial Responsibility: Drivers can demonstrate financial responsibility by providing evidence of insurance coverage, such as a copy of their insurance policy. This coverage must meet the minimum financial responsibility requirements of the state.
- Surety Bond: A surety bond is a financial guarantee provided by an insurance company. It acts as a promise to pay for damages in case of an accident, up to the bond’s limit.
- Cash Deposit: Some states allow drivers to deposit a certain amount of cash with the state. This deposit serves as a guarantee that they can pay for damages caused by an accident.
- Self-Insurance: In some states, drivers with significant assets may be able to self-insure. This means they agree to be financially responsible for any accidents they cause.
Financial Responsibility Requirements
Financial responsibility requirements vary across states that do not mandate car insurance. These requirements typically specify the minimum amounts of coverage a driver must have for liability, property damage, and personal injury.
- Liability Coverage: This coverage protects the driver from financial responsibility for injuries or property damage caused to others in an accident.
- Property Damage Coverage: This coverage pays for damages to the property of others involved in an accident.
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): While not mandatory in these states, PIP coverage pays for medical expenses, lost wages, and other expenses incurred by the driver and passengers of their own vehicle, regardless of fault.
The Importance of Car Insurance, Even in States Without Mandatory Coverage
While some states don’t mandate car insurance, it’s still crucial to have it. Even in states where it’s not required by law, car insurance provides significant protection against financial ruin in the event of an accident.
Financial Protection in Case of an Accident, States that don’t need car insurance
Car insurance can protect you from substantial financial losses in the event of an accident. Without insurance, you would be personally liable for all costs associated with the accident, including medical expenses, property damage, and legal fees. These costs can quickly escalate, potentially leading to significant financial hardship.
Examples of Situations Where Car Insurance is Essential
Even in states without mandatory coverage, there are numerous situations where car insurance is essential:
- Accidents Involving Other Drivers: If you’re involved in an accident with another driver who is uninsured or underinsured, your own insurance policy can cover your losses, ensuring you’re not left footing the bill.
- Hit-and-Run Accidents: If you’re hit by a driver who flees the scene, your insurance policy can help cover your medical expenses and property damage.
- Accidents Involving Property Damage: Even if you’re not at fault, your insurance can cover the cost of repairing or replacing your vehicle if it’s damaged in an accident.
- Unforeseen Events: Car insurance can protect you from unexpected events such as theft, vandalism, or natural disasters.
Alternative Forms of Financial Protection

While some states do not mandate car insurance, drivers in these states still face the risk of significant financial losses in case of an accident. Fortunately, several alternative forms of financial protection are available to mitigate these risks. These alternatives offer varying levels of coverage and may come with specific limitations. Understanding the nuances of these options is crucial for drivers in states without mandatory car insurance to make informed decisions about their financial protection.
Self-Insurance
Self-insurance is a common alternative in states without mandatory car insurance. It involves setting aside a specific amount of money to cover potential accident-related costs. This approach allows drivers to control their insurance expenses and avoid premiums.
How Self-Insurance Works
Drivers who opt for self-insurance must set aside a substantial sum of money, known as a self-insured retention, to cover potential liabilities arising from accidents. The amount should be sufficient to cover potential medical bills, property damage, and legal fees. In the event of an accident, the driver would use this self-insured retention to pay for the associated expenses.
Limitations of Self-Insurance
Self-insurance presents significant limitations. It requires drivers to have a substantial financial reserve to cover potential losses. Moreover, self-insurance does not provide coverage for damages exceeding the self-insured retention. If the accident results in substantial damages, the driver could face significant financial hardship.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Self-Insurance
Self-insurance offers the advantage of cost control, as drivers avoid insurance premiums. However, it exposes drivers to significant financial risks. If an accident occurs, they are fully responsible for covering all associated costs.
Financial Responsibility Laws
States without mandatory car insurance often have financial responsibility laws, which require drivers to prove their ability to cover accident-related costs. These laws typically involve demonstrating financial responsibility through various methods, such as:
- Proof of Financial Responsibility: Drivers may need to provide proof of financial responsibility by presenting a certificate of insurance, a surety bond, or a deposit of cash or securities. These documents demonstrate the driver’s ability to cover potential accident-related costs.
- Self-Insurance: Some states allow drivers to self-insure by demonstrating their ability to cover potential losses. This typically involves providing evidence of sufficient financial resources to cover the required amounts.
- High-Risk Insurance: Drivers with poor driving records or who have been involved in accidents may be required to obtain high-risk insurance, which offers limited coverage at higher premiums.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Financial Responsibility Laws
Financial responsibility laws provide a basic level of protection for victims of accidents. However, they do not guarantee full coverage for all damages. Furthermore, the requirements of these laws can vary significantly between states, making it challenging for drivers to understand their obligations.
Understanding the Risks of Driving Without Insurance
Even in states that don’t require car insurance, driving without coverage comes with significant risks. You’re not just risking a fine; you’re putting yourself and others in a precarious financial situation.
Financial Consequences of an Accident
The most immediate consequence of driving without insurance and being involved in an accident is the potential for substantial financial ruin. If you’re at fault, you’ll be responsible for covering the costs of repairs, medical bills, and other damages. This can quickly lead to significant debt, even if the accident is relatively minor.
Closure: States That Don’t Need Car Insurance
In conclusion, while some states may not mandate car insurance, it’s essential to remember that financial responsibility is still a crucial aspect of driving. Even in states without mandatory coverage, the potential risks associated with driving uninsured are significant. By understanding the legal requirements, exploring alternative forms of financial protection, and prioritizing safe driving practices, you can navigate the complexities of driving without mandatory car insurance and ensure peace of mind on the road.
FAQ Overview
What happens if I get into an accident in a state without mandatory car insurance?
If you cause an accident in a state without mandatory car insurance, you could face significant financial liability. You may be responsible for covering the costs of damages to other vehicles, injuries to other drivers and passengers, and even legal fees.
How do I prove financial responsibility in a state without mandatory car insurance?
Each state has its own specific requirements for proving financial responsibility. Common methods include providing proof of self-insurance, posting a bond, or having a surety company guarantee your ability to pay for damages. You should consult your state’s Department of Motor Vehicles for specific requirements.
Is it cheaper to drive without car insurance in a state without mandatory coverage?
It may seem like you can save money by not buying car insurance, but the potential risks outweigh any potential savings. If you get into an accident, you could face financial ruin. It’s always recommended to have at least the minimum level of car insurance coverage, even in states without mandatory requirements.