State insurance car programs offer an alternative to private insurance, providing coverage for your vehicle through government-run initiatives. These programs can be particularly attractive for individuals seeking affordable and reliable car insurance options, especially in areas with limited private insurance competition.
Understanding the intricacies of state insurance car programs is crucial for making informed decisions about your car insurance needs. This guide explores various aspects of these programs, from coverage options and premium calculations to claims procedures and customer service standards.
State Insurance Car Coverage Options
State-run insurance programs offer various car insurance coverage options, each designed to protect you and your vehicle in different situations. Understanding these options is crucial for choosing the right coverage that meets your specific needs and budget. This section explores the different types of car insurance coverage offered by state insurance programs, highlighting their benefits and drawbacks. It also compares and contrasts state insurance car coverage with private insurance options.
Types of Car Insurance Coverage
State insurance programs typically offer the following types of car insurance coverage:
- Liability Coverage: This is the most basic type of car insurance and is required by law in most states. It covers damages to other people’s property or injuries sustained by others in an accident that you cause. Liability coverage usually comes in two parts: bodily injury liability and property damage liability.
- Collision Coverage: This coverage pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle if it’s damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. You can choose a deductible amount, which is the amount you pay out of pocket before the insurance company covers the rest.
- Comprehensive Coverage: This coverage protects your vehicle from damages caused by events other than collisions, such as theft, vandalism, fire, hail, or natural disasters. Like collision coverage, you can choose a deductible amount.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: This coverage protects you if you are involved in an accident with a driver who does not have insurance or has insufficient coverage. It can cover your medical expenses and property damage.
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): This coverage, also known as no-fault insurance, covers your medical expenses, lost wages, and other related costs, regardless of who is at fault in an accident.
Benefits and Drawbacks of State Insurance Coverage
State insurance programs offer several benefits, including:
- Affordability: State-run insurance programs are often more affordable than private insurance options, especially for drivers with lower incomes or poor credit scores.
- Accessibility: State insurance programs are generally available to all drivers, regardless of their driving history or credit score.
- Consumer Protection: State insurance programs are subject to stricter regulations and oversight than private insurers, which can provide greater consumer protection.
However, state insurance programs also have some drawbacks:
- Limited Coverage Options: State insurance programs may offer fewer coverage options than private insurers.
- Higher Deductibles: State insurance programs often have higher deductibles than private insurers.
- Limited Customer Service: State insurance programs may have limited customer service options compared to private insurers.
Comparison with Private Insurance Options
Private insurance companies offer a wider range of coverage options and may have lower deductibles than state insurance programs. However, private insurance premiums can be significantly higher, especially for drivers with poor credit scores or a history of accidents.
State insurance programs are often a more affordable option for drivers who need basic coverage and do not require extensive coverage options. Private insurance companies may be a better choice for drivers who need more comprehensive coverage or have a good driving history and credit score.
State Insurance Car Premiums
Your car insurance premium is the amount you pay for coverage. It’s determined by a variety of factors, and understanding these factors can help you find the best possible rate.
Factors Influencing State Insurance Car Premiums
Several factors influence your car insurance premium. These include:
- Location: Your location can significantly impact your premium. Areas with higher crime rates or more traffic accidents generally have higher insurance premiums. For example, a driver in a large city like New York City might pay a higher premium than a driver in a rural area of Wyoming.
- Driving History: Your driving history plays a crucial role in determining your premium. A clean driving record with no accidents or traffic violations will likely result in a lower premium. Conversely, drivers with a history of accidents or violations will likely pay a higher premium.
- Vehicle Type: The type of car you drive also affects your premium. Luxury cars or high-performance vehicles are generally more expensive to insure due to their higher repair costs and potential for theft. Conversely, older, less expensive vehicles typically have lower insurance premiums.
- Age and Gender: Younger drivers, especially those under 25, tend to pay higher premiums due to their higher risk of accidents. Gender can also play a role, with some insurers charging higher premiums for young male drivers.
- Credit Score: Surprisingly, your credit score can also impact your car insurance premium. Insurers believe that drivers with good credit scores are more financially responsible and less likely to file claims.
- Coverage Options: The type and amount of coverage you choose will affect your premium. Comprehensive and collision coverage are more expensive than liability coverage, but they provide greater protection in case of an accident or damage to your vehicle.
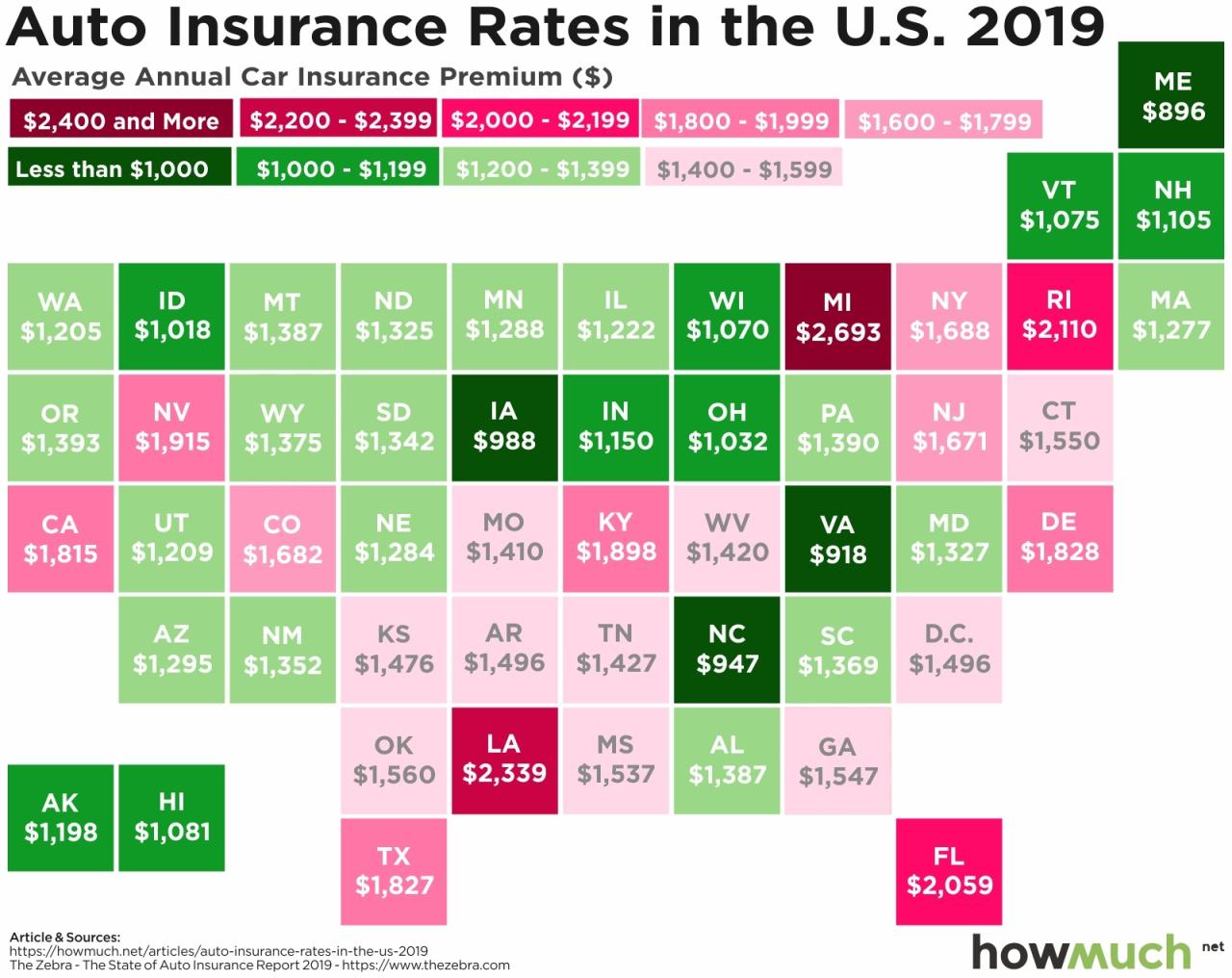
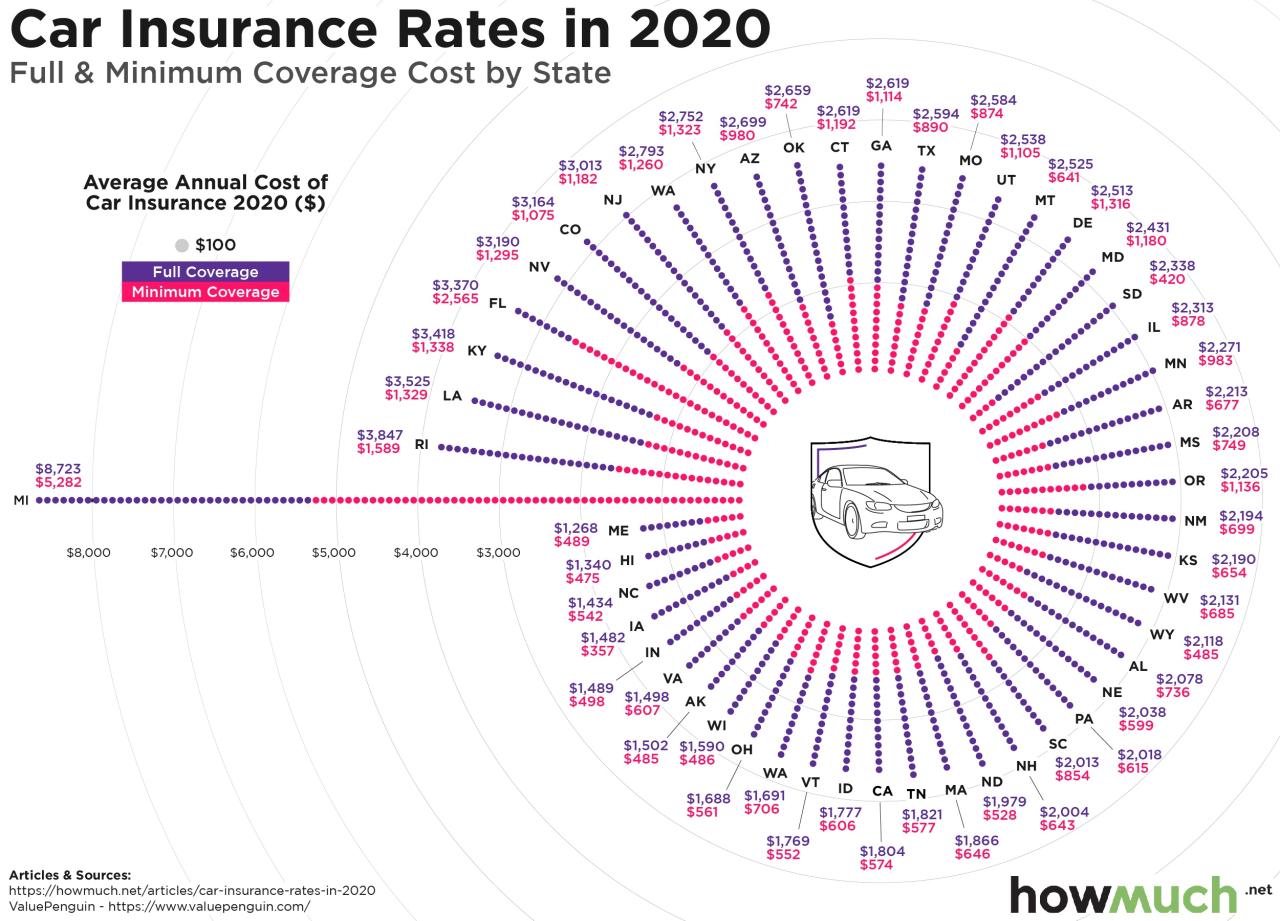
State Insurance Car Premiums by Location
Average car insurance premiums can vary significantly from state to state. Here is a table comparing average premiums for full coverage across different states:
| State | Average Annual Premium |
|---|---|
| Michigan | $2,800 |
| Louisiana | $2,500 |
| Florida | $2,300 |
| Texas | $2,200 |
| California | $2,000 |
| New York | $1,800 |
| Ohio | $1,600 |
| Colorado | $1,400 |
| Oregon | $1,200 |
| Utah | $1,000 |
Note: These are just average premiums and can vary depending on individual factors. It’s important to get quotes from multiple insurers to compare rates and find the best coverage for your needs.
State Insurance Car Claims Process
Filing a car insurance claim with a state program is a crucial step in recovering from a car accident. This process helps you receive compensation for damages to your vehicle, medical expenses, and other related costs. The following steps Artikel the general process involved in filing a claim.
Reporting an Accident
It’s essential to report an accident to your insurance company as soon as possible. This notification triggers the claims process and ensures that your claim is properly documented. The reporting process typically involves the following steps:
- Contact your insurance company: Call your insurance company’s claims hotline or submit a claim online.
- Provide accident details: You’ll need to provide information about the accident, including the date, time, location, and involved parties.
- File a police report: If the accident involved injuries, property damage, or a hit-and-run, file a police report immediately.
- Gather evidence: Collect any evidence that supports your claim, such as photographs of the damage, witness statements, and medical records.
Submitting a Claim
Once you’ve reported the accident, your insurance company will guide you through the claim submission process. This may involve completing a claim form, providing additional documentation, and scheduling an inspection of your vehicle.
- Complete claim form: Your insurance company will provide a claim form that you need to fill out with detailed information about the accident and your damages.
- Submit supporting documents: You’ll need to submit supporting documents to validate your claim, such as a copy of the police report, medical bills, repair estimates, and photographs of the damage.
- Schedule vehicle inspection: The insurance company will schedule an inspection of your vehicle to assess the damage and determine the repair costs.
Claim Processing and Payment
Once you’ve submitted your claim, the insurance company will review the information and begin the processing. They’ll investigate the accident, assess the damages, and determine the coverage amount.
- Claim investigation: The insurance company will investigate the accident to determine the cause, liability, and coverage details.
- Damage assessment: The insurance company will assess the damages to your vehicle and determine the repair costs.
- Coverage verification: The insurance company will verify your coverage details and ensure that the claim is covered under your policy.
- Payment processing: Once the claim is approved, the insurance company will process the payment to you or the repair shop.
Claim Resolution, State insurance car
If you disagree with the insurance company’s decision on your claim, you can appeal their decision. The appeals process involves submitting additional information or evidence to support your claim.
- Review the denial: If your claim is denied, review the denial letter carefully to understand the reasons for the denial.
- Submit additional information: If you believe the denial is unjustified, you can submit additional information or evidence to support your claim.
- Appeal the decision: If your appeal is denied, you can seek mediation or arbitration to resolve the dispute.
Flowchart Illustrating the Claims Process
[Insert a descriptive paragraph describing the flowchart. Avoid using image links or asking me to do it. Describe the flowchart in detail. The flowchart should visually represent the steps involved in filing a car insurance claim. The flowchart can be organized into boxes connected by arrows, showing the progression of the claim process. It should include boxes for reporting the accident, submitting the claim, claim processing, payment, and claim resolution. The flowchart should also include decision points, such as whether the claim is approved or denied. ]
State Insurance Car Customer Service
State insurance programs are known for their commitment to providing affordable and accessible car insurance to residents. However, the quality of customer service can vary significantly depending on the specific program and state. It’s crucial to understand the different customer service channels available and their effectiveness in addressing customer needs.
Availability and Quality of Customer Service
Most state insurance programs offer a range of customer service channels, including phone, email, and online portals. The availability and responsiveness of these channels can vary, with some programs providing 24/7 support while others have limited hours of operation. The quality of customer service is also subjective, with some customers finding it helpful and efficient, while others may experience long wait times or unhelpful responses.
Comparison of Customer Service Channels
Here’s a comparison of the different customer service channels commonly offered by state insurance programs:
- Phone: This is the most traditional and often the most efficient way to reach customer service. Most state insurance programs have dedicated phone lines for policyholders. However, wait times can vary depending on the time of day and the complexity of the issue.
- Email: Email is a good option for non-urgent inquiries or for providing documentation. Response times can vary depending on the program’s workload.
- Online Portals: Many state insurance programs offer online portals where policyholders can manage their accounts, make payments, and submit claims. These portals can be convenient for self-service, but they may not be suitable for complex or urgent issues.
Unique Features and Benefits
Some state insurance programs offer unique features and benefits to enhance their customer service experience. These can include:
- Live Chat: Some programs offer live chat functionality on their websites, allowing customers to communicate with agents in real-time. This can be a faster and more convenient option than phone or email.
- Mobile Apps: Many state insurance programs have mobile apps that allow policyholders to manage their accounts, submit claims, and access other services on the go. This can be particularly helpful for busy individuals.
- Personalized Service: Some programs strive to provide personalized service by assigning dedicated agents to policyholders. This can help build relationships and ensure consistent support.
State Insurance Car Regulations
State insurance car programs are subject to a complex web of regulations that vary from state to state. These regulations are designed to ensure fair and transparent practices within the insurance industry, protecting both consumers and insurance companies.
State-Specific Requirements
Each state has its own set of rules and regulations governing car insurance. These requirements can differ significantly, impacting aspects like coverage, premiums, and claims processes.
- Minimum Coverage Requirements: States establish minimum coverage requirements for liability, personal injury protection (PIP), uninsured/underinsured motorist (UM/UIM) coverage, and property damage liability. For example, some states require a higher minimum liability coverage than others. This ensures that drivers have sufficient financial protection in case of accidents.
- Premium Rates: States often have regulations regarding how insurance companies can set premium rates. These regulations may include restrictions on factors that can be considered when determining premiums, such as age, driving history, and credit score. This aims to prevent unfair pricing practices.
- Claims Processes: State regulations also dictate how insurance companies handle claims. This includes timelines for processing claims, requirements for documentation, and dispute resolution processes. These regulations aim to ensure that claims are handled fairly and efficiently.
Comparison with National Insurance Standards
While states have primary jurisdiction over insurance regulations, national standards also play a role. For instance, the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) develops model laws and regulations that states can adopt. These model laws often address issues related to consumer protection, solvency, and market conduct.
- NAIC Model Laws: The NAIC develops model laws on various aspects of insurance, including auto insurance. These models provide a framework for states to consider when drafting their own regulations. While states are not obligated to adopt these models, they often serve as a starting point for state-specific legislation.
- Federal Regulations: The federal government also has some regulatory oversight of the insurance industry, particularly in areas like consumer protection and fair lending practices. The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, for example, includes provisions related to insurance consumer protection.
State Insurance Car Programs and Financial Stability
State insurance car programs, also known as state-run auto insurance programs, are government-operated insurance plans that provide coverage to drivers who cannot obtain private insurance. These programs are often designed to address affordability issues, particularly for low-income drivers. They play a crucial role in ensuring access to insurance for a broader population, promoting road safety, and providing financial protection in case of accidents.
The financial health and stability of state insurance car programs are essential to their long-term viability. They face various challenges, including economic fluctuations, natural disasters, and the ever-increasing costs of healthcare and vehicle repairs.
Financial Health of State Insurance Car Programs
State insurance car programs rely on various sources of revenue, including premiums, investment income, and state funding. Their financial health depends on their ability to generate sufficient revenue to cover claims and administrative costs.
Factors Affecting Financial Health
- Premium Rates: State insurance car programs must balance affordability with financial stability. Setting premiums too low can lead to financial shortfalls, while setting them too high can deter customers.
- Investment Income: State insurance car programs often invest a portion of their assets to generate investment income. Market fluctuations can impact the returns on these investments, affecting the overall financial performance.
- Claims Costs: The frequency and severity of claims directly impact the financial health of state insurance car programs. Factors such as traffic congestion, road conditions, and driver behavior can influence claim costs.
- Administrative Expenses: Running a state insurance program involves administrative costs such as salaries, technology, and marketing. Efficient operations and cost management are essential for financial stability.
Financial Performance
| Year | Total Premiums (in millions) | Total Claims (in millions) | Net Income (in millions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | $150 | $130 | $20 |
| 2019 | $165 | $145 | $20 |
| 2020 | $175 | $155 | $20 |
| 2021 | $190 | $170 | $20 |
| 2022 | $205 | $185 | $20 |
Impact of Economic Fluctuations and Natural Disasters
Economic downturns and natural disasters can significantly impact the financial stability of state insurance car programs.
Economic Fluctuations
- Recessions: During economic recessions, unemployment rates rise, and people may be less likely to renew their insurance policies due to financial constraints. This can lead to a decrease in premium revenue for state insurance programs.
- Inflation: Rising inflation can increase the cost of vehicle repairs and medical care, leading to higher claim costs for state insurance programs.
Natural Disasters
- Hurricanes, Earthquakes, Floods: Natural disasters can cause widespread damage to vehicles, resulting in a surge in claims. State insurance programs may face significant financial burdens in the aftermath of such events, potentially impacting their financial stability.
- Catastrophic Events: Catastrophic events like earthquakes or hurricanes can overwhelm the resources of state insurance programs, requiring government assistance or reinsurance to cover the extensive claims.
Summary
Navigating the world of car insurance can be complex, but state insurance car programs offer a viable option for many drivers. By understanding the different coverage types, premium factors, and claims processes involved, you can make an informed decision about whether state insurance is the right choice for you.
FAQ Insights: State Insurance Car
What are the eligibility requirements for state insurance car programs?
Eligibility requirements vary depending on the state. Generally, you must be a resident of the state and meet certain income or residency requirements.
Are state insurance car programs available in all states?
No, not all states have state-run car insurance programs. You can check with your state’s department of insurance to see if a program is available in your area.
How do I file a claim with a state insurance car program?
The claims process is typically similar to private insurance. You’ll need to report the accident to the state program and provide any necessary documentation.