States that don’t require auto insurance present a unique situation in the American landscape. While most states mandate auto insurance to protect drivers and victims of accidents, a handful have chosen a different path. This decision, often driven by a combination of historical factors, economic considerations, and philosophical beliefs, has sparked ongoing debate about the pros and cons of such a system.
This exploration delves into the intricacies of states without mandatory auto insurance, examining the legal rationale behind their decisions, the potential financial implications for drivers, and the broader impact on road safety and accident rates. We’ll also discuss alternative insurance options and the legal framework surrounding liability in these states. Finally, we’ll consider future trends and potential changes in legislation as the auto insurance landscape continues to evolve.
States Without Mandatory Auto Insurance: States That Don’t Require Auto Insurance
In the United States, auto insurance is a crucial aspect of road safety and financial protection. While most states mandate auto insurance coverage, a handful of states have chosen to forgo this requirement. This decision is often based on a complex interplay of factors, including philosophical beliefs about individual responsibility, economic considerations, and the perceived effectiveness of insurance mandates.
Rationale Behind the Decision
The decision to not require auto insurance is rooted in various legal and philosophical arguments. These states often argue that individuals should be free to choose whether or not to purchase insurance, believing that this choice fosters personal responsibility and incentivizes safe driving practices. Proponents of this approach contend that mandatory insurance can lead to higher premiums and potentially discourage individuals from driving, particularly those with limited financial resources.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Not Requiring Auto Insurance
The absence of a mandatory auto insurance requirement presents both potential benefits and drawbacks.
- One potential benefit is that it can lead to lower insurance premiums for those who choose to purchase coverage. This is because insurance companies may face less risk in a state where all drivers are not required to be insured.
- Another potential benefit is that it can reduce the administrative burden on the state government, as it does not need to oversee and enforce a mandatory insurance program.
- However, a significant drawback is that it can lead to an increase in uninsured drivers. This can pose a financial risk to victims of accidents caused by uninsured drivers, as they may not be able to recover their losses.
- Furthermore, the lack of mandatory insurance can make it more challenging for injured parties to receive compensation for their injuries and damages.
Financial Responsibility Laws, States that don’t require auto insurance
States that do not require auto insurance typically have financial responsibility laws in place. These laws establish minimum financial requirements that drivers must meet to demonstrate their ability to cover potential damages resulting from accidents.
- These laws often require drivers to provide proof of financial responsibility, such as proof of insurance, a surety bond, or a deposit of a certain amount of money with the state.
- In states without mandatory auto insurance, the financial responsibility laws are typically less stringent than those in states with mandatory insurance.
- This means that drivers in these states may be required to carry less coverage, potentially leaving victims with fewer resources to recover their losses.
Financial Implications of Not Having Auto Insurance

Driving without auto insurance in states where it is not mandatory can seem like a way to save money. However, this decision comes with significant financial risks. The absence of insurance can leave you vulnerable to catastrophic financial burdens in the event of an accident, potentially leading to debt, financial instability, and even bankruptcy.
Financial Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
In the absence of insurance, you are personally liable for all costs associated with an accident, including:
- Medical Expenses: If you or another driver is injured, you will be responsible for covering all medical costs, including hospital bills, surgeries, rehabilitation, and ongoing medical care. Even minor accidents can result in substantial medical bills.
- Property Damage: You will be responsible for repairing or replacing any damaged vehicles or property involved in the accident. This includes your own vehicle and any other vehicles or property you may have damaged.
- Legal Fees: If you are involved in an accident, you may face legal action from the other party. You will be responsible for covering your own legal fees, as well as any legal settlements or judgments awarded to the other party.
Real-Life Examples of Financial Hardship
- A driver in Texas, who chose not to purchase insurance, was involved in a minor collision. The accident resulted in a $5,000 medical bill for the other driver and $2,000 in damage to their vehicle. The uninsured driver, unable to afford these costs, was forced to sell their car and take on substantial debt to cover the expenses.
- In Florida, a driver without insurance caused a major accident, injuring several people. The uninsured driver faced multiple lawsuits and was ordered to pay over $1 million in damages, leading to financial ruin and bankruptcy.
Financial Burden of Covering Accident Costs
The costs associated with an accident can be overwhelming, even in minor incidents. The financial burden of covering medical expenses, property damage, and legal fees without insurance can quickly drain your savings and lead to significant financial hardship.
“In many cases, the cost of an accident without insurance can be more than the cost of a lifetime of insurance premiums.”
Alternatives to Traditional Auto Insurance
In states that don’t mandate auto insurance, drivers have the option to explore alternatives to traditional insurance plans. These alternatives offer varying levels of financial protection and can be tailored to individual needs and risk tolerance.
Self-Insurance
Self-insurance involves setting aside a specific amount of money to cover potential costs associated with accidents or damages. This approach allows drivers to manage their own risk and avoid paying premiums to an insurance company.
- Pros:
- Potential for lower costs, as premiums are not paid.
- Greater control over how funds are managed.
- Cons:
- High financial risk, as drivers are fully responsible for all costs.
- Requires significant financial resources to cover potential liabilities.
- May not be suitable for individuals with limited financial resources or high risk tolerance.
Surety Bonds
Surety bonds are financial guarantees issued by a surety company that provide protection to third parties in case of financial losses caused by the insured. These bonds are typically required by states as proof of financial responsibility, and they ensure that the insured can cover damages caused to others.
- Pros:
- May be a more affordable option than traditional insurance for individuals with a clean driving record.
- Provides financial protection to third parties.
- Cons:
- May not cover all potential losses, such as medical expenses or property damage to the insured’s vehicle.
- Requires a surety company to issue the bond, which may involve additional fees.
Other Financial Responsibility Mechanisms
Some states offer alternative financial responsibility mechanisms, such as deposit accounts or cash bonds. These options typically involve depositing a specific amount of money with the state, which can be used to cover damages in the event of an accident.
- Pros:
- May be a less expensive option than traditional insurance.
- Provides financial protection to third parties.
- Cons:
- May not cover all potential losses, such as medical expenses or property damage to the insured’s vehicle.
- Requires a significant upfront investment.
Comparison of Insurance Options
| Insurance Option | Key Features | Costs | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Auto Insurance | Comprehensive coverage, including liability, collision, and comprehensive | Premiums vary based on factors such as driving history, vehicle type, and location | Wide range of coverage options, financial protection against significant losses, peace of mind |
| Self-Insurance | No premiums, full financial responsibility | Requires significant financial resources, potential for high out-of-pocket expenses | Potential for lower costs, greater control over funds |
| Surety Bonds | Financial guarantee to third parties | Bond premiums, may be more affordable than traditional insurance for individuals with a clean driving record | Provides financial protection to third parties, may be a less expensive option than traditional insurance |
| Other Financial Responsibility Mechanisms | Deposit accounts or cash bonds | Upfront investment, may be less expensive than traditional insurance | Provides financial protection to third parties, may be a less expensive option than traditional insurance |
Impact on Road Safety and Accidents
The absence of mandatory auto insurance in certain states raises concerns about its potential impact on road safety and accident-related issues. While some argue that it encourages personal responsibility and cost-conscious driving, others believe it can lead to a higher risk of accidents and financial hardship for victims.
Impact of Uninsured Drivers on Accident Rates
The presence or absence of mandatory auto insurance laws has a direct correlation with road safety and accident rates. Studies have shown that states without mandatory auto insurance laws tend to have higher rates of uninsured drivers. This leads to increased risk for other drivers on the road, as uninsured drivers are less likely to be financially responsible for the damages they cause.
- A study by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) found that states without mandatory auto insurance laws had a higher percentage of uninsured drivers. This, in turn, resulted in higher rates of hit-and-run accidents and a greater likelihood of drivers being unable to pay for damages caused in an accident.
- Another study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) revealed that uninsured drivers are more likely to be involved in fatal accidents. This is because they are less likely to be held accountable for their actions and are more likely to drive recklessly without fear of financial consequences.
Consequences of Uninsured Drivers on Claims Processing
Uninsured drivers pose significant challenges to the claims processing system, leading to delays, complications, and increased costs for insurance companies and victims.
- In the event of an accident involving an uninsured driver, the process of claiming compensation can be lengthy and complex. Victims may have to rely on their own insurance policies, which could lead to higher premiums and deductibles.
- Insurance companies may face increased costs and administrative burdens when dealing with claims involving uninsured drivers. They may have to pursue legal action to recover damages, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
Legal Considerations and Liability

Even though states without mandatory auto insurance do not require drivers to purchase coverage, they still have legal responsibilities in case of accidents. These responsibilities are Artikeld in the state’s financial responsibility laws, which aim to ensure that drivers are held accountable for any damages they cause.
Financial Responsibility Laws, States that don’t require auto insurance
States without mandatory auto insurance have financial responsibility laws that require drivers to demonstrate their ability to cover damages caused in an accident. These laws typically require drivers to:
- Provide proof of financial responsibility: This can be done through insurance coverage, a surety bond, or a cash deposit with the state.
- Meet minimum financial responsibility requirements: These requirements usually specify minimum coverage limits for bodily injury, property damage, and uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage.
- Comply with reporting requirements: Drivers are generally required to report accidents to the state within a certain timeframe, even if they are not at fault.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failing to comply with financial responsibility laws can have serious legal consequences, including:
- Suspension of driving privileges: The state may suspend a driver’s license if they fail to provide proof of financial responsibility or meet the minimum requirements.
- Fines and penalties: Drivers who violate financial responsibility laws may face fines and other penalties, which can vary depending on the state and the severity of the violation.
- Legal liability for damages: Even without insurance, drivers are still legally responsible for any damages they cause in an accident. This means they could be held personally liable for medical bills, property repairs, lost wages, and other expenses.
Legal Procedures for Accidents
In the event of an accident, drivers in states without mandatory auto insurance must follow specific legal procedures:
- Exchange information: Drivers involved in an accident are required to exchange contact and insurance information, even if they are not at fault.
- File a police report: It is crucial to file a police report, especially if there are injuries or significant property damage.
- Seek legal advice: Drivers who are involved in an accident without insurance should consult with an attorney to understand their legal rights and obligations.
Impact of Liability on Drivers
The legal framework surrounding liability in states without mandatory auto insurance emphasizes the importance of financial responsibility for drivers. Even though insurance is not required, drivers must be prepared to cover the costs of any damages they cause. This can include medical expenses, property repairs, lost wages, and legal fees. Drivers who fail to comply with financial responsibility laws may face serious legal consequences, including license suspension, fines, and personal liability for damages.
Future Trends and Potential Changes
While states without mandatory auto insurance may seem like an outlier, the landscape is constantly evolving. Several factors, including technological advancements, economic pressures, and societal shifts, could lead to changes in legislation and policies regarding auto insurance requirements in these states.
Factors Influencing Future Trends
The future of auto insurance regulation in states without mandatory coverage is influenced by a complex interplay of factors. These factors, often interconnected, can drive policy changes and shape the industry’s trajectory.
- Technological Advancements: The rise of autonomous vehicles and connected car technologies could drastically alter the risk profile of drivers. These advancements may lead to a decrease in accidents and injuries, potentially prompting reassessments of insurance requirements. For instance, with autonomous vehicles, the need for traditional liability coverage may be reevaluated as the risk of accidents decreases.
- Economic Conditions: Economic downturns can lead to a rise in uninsured drivers as individuals prioritize essential expenses over insurance premiums. This could put pressure on state legislatures to consider mandatory auto insurance requirements to ensure adequate financial protection for accident victims. Conversely, economic prosperity may encourage more people to purchase insurance, potentially lessening the need for mandatory coverage.
- Societal Concerns: Public perception of uninsured drivers and the potential risks they pose to other road users can influence policy decisions. Growing public awareness of the financial burden on accident victims and the healthcare system due to uninsured drivers could push for stricter regulations. For example, advocacy groups for accident victims might push for mandatory insurance requirements to ensure financial compensation for injuries and damages.
Potential Future Scenarios
Considering the factors above, here are potential future scenarios for states without mandatory auto insurance:
- Increased Regulation: In response to growing societal concerns and economic pressures, states may introduce mandatory minimum liability insurance requirements. This could be similar to existing requirements in other states, requiring drivers to carry a minimum amount of coverage for bodily injury and property damage.
- Hybrid Approaches: States might explore hybrid approaches that combine elements of mandatory insurance with alternative risk management strategies. This could involve mandatory financial responsibility laws requiring drivers to prove their ability to pay for damages, coupled with options for alternative insurance products or self-insurance.
- Technology-Driven Solutions: Advancements in autonomous vehicles and connected car technologies could lead to the development of innovative insurance models. These models may incorporate data from vehicle sensors and driving behavior to personalize premiums and potentially reduce the need for traditional liability coverage.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, the decision of whether or not to require auto insurance is a complex one with far-reaching implications. States that choose not to mandate insurance face unique challenges, including increased risk for uninsured drivers, potential financial hardship for victims of accidents, and the possibility of higher accident rates. However, these states also present a valuable case study for understanding the interplay between individual responsibility, government regulation, and the broader social contract surrounding road safety. As the auto insurance landscape continues to evolve, it will be interesting to observe how these states adapt and navigate the complexities of this issue.
Top FAQs
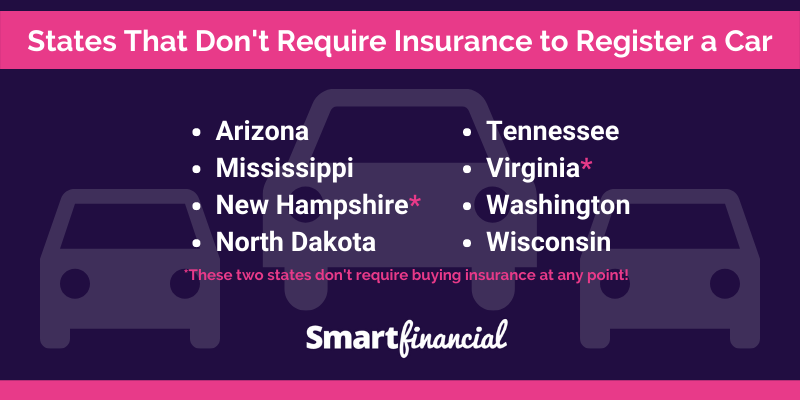
What are the states that don’t require auto insurance?
Currently, there are only two states in the US that do not require drivers to carry auto insurance: New Hampshire and Virginia. However, Virginia requires drivers to demonstrate financial responsibility through alternative means, such as surety bonds or self-insurance.
What happens if I get into an accident in a state that doesn’t require auto insurance?
If you are involved in an accident in a state that doesn’t require auto insurance, you may face significant financial hardship. Even if you are not at fault, you may be responsible for covering medical expenses, property damage, and legal fees. It is essential to understand the specific laws and regulations in each state and take steps to protect yourself financially.
Is it safe to drive without insurance?
Driving without insurance is generally considered unsafe and risky. Not only are you putting yourself at financial risk, but you are also potentially jeopardizing the safety of other drivers on the road. If you are involved in an accident, you could be held liable for significant damages, even if you are not at fault. It is always advisable to have adequate insurance coverage to protect yourself and others.







