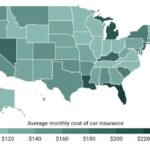
The Virginia State Insurance Commission plays a crucial role in safeguarding the interests of both consumers and the insurance industry within the Commonwealth. Established to ensure fair and responsible practices, the commission oversees a vast array of insurance products and services, from health and life insurance to property and casualty coverage. Its mission is to promote a stable and competitive insurance market while protecting consumers from unfair or deceptive practices.
The commission’s regulatory authority extends to licensing and overseeing insurance companies, ensuring they meet financial solvency requirements and adhere to strict consumer protection standards. It also provides resources and education to consumers, empowering them to make informed decisions about their insurance needs and navigate the complexities of the insurance landscape.
Overview of the Virginia State Insurance Commission
The Virginia State Insurance Commission (VSIC) is a regulatory body responsible for overseeing the insurance industry in the Commonwealth of Virginia. Established in 1906, the VSIC plays a crucial role in protecting consumers and ensuring the financial stability of the insurance market.
Mission and Purpose
The VSIC’s primary mission is to protect the public interest by regulating the insurance industry in Virginia. This includes ensuring the solvency of insurance companies, protecting consumers from unfair or deceptive practices, and promoting fair competition in the insurance market. The VSIC strives to achieve this mission by:
* Licensing and regulating insurance companies and agents: The VSIC ensures that insurance companies meet certain financial requirements and that agents are properly trained and qualified to sell insurance.
* Approving insurance rates and policies: The VSIC reviews insurance rates and policies to ensure they are fair and reasonable for consumers.
* Investigating consumer complaints: The VSIC investigates consumer complaints about insurance companies and agents and takes appropriate action to resolve issues.
* Educating the public about insurance: The VSIC provides information and resources to help consumers understand insurance products and make informed decisions.
Regulatory Powers and Responsibilities
The VSIC has broad regulatory powers and responsibilities, including:
* Licensing and regulating insurance companies, agents, and brokers: The VSIC licenses and regulates insurance companies, agents, and brokers operating in Virginia. This includes setting licensing requirements, conducting background checks, and monitoring their activities to ensure compliance with state laws and regulations.
* Approving insurance rates and policies: The VSIC reviews and approves insurance rates and policies to ensure they are fair and reasonable for consumers. This includes reviewing the actuarial basis of rates, ensuring that rates are not unfairly discriminatory, and ensuring that policies are clear and understandable.
* Investigating consumer complaints: The VSIC investigates consumer complaints about insurance companies and agents. This includes investigating allegations of unfair or deceptive practices, fraud, and other violations of state laws and regulations. The VSIC can take appropriate action to resolve consumer complaints, such as ordering the insurance company to make restitution to the consumer, imposing fines, or revoking the company’s license.
* Enforcing insurance laws and regulations: The VSIC enforces insurance laws and regulations through investigations, hearings, and administrative actions. This includes imposing penalties on insurance companies and agents who violate state laws and regulations.
* Promoting fair competition in the insurance market: The VSIC promotes fair competition in the insurance market by ensuring that insurance companies are not engaging in anti-competitive practices. This includes reviewing mergers and acquisitions to ensure they do not harm consumers.
Key Stakeholders
The VSIC interacts with various stakeholders in the insurance industry, including:
* Insurance companies: Insurance companies are regulated by the VSIC and must comply with its rules and regulations.
* Insurance agents and brokers: Insurance agents and brokers are licensed by the VSIC and are responsible for selling insurance products to consumers.
* Consumers: Consumers are protected by the VSIC, which ensures that they are treated fairly and receive adequate insurance coverage.
* The Virginia General Assembly: The Virginia General Assembly sets the legislative framework for the insurance industry in Virginia.
* The Virginia Department of Insurance: The Virginia Department of Insurance is responsible for administering the state’s insurance laws and regulations.
* The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC): The NAIC is a national organization that develops model laws and regulations for the insurance industry.
Insurance Regulation in Virginia

The Virginia State Insurance Commission (VSIC) plays a vital role in regulating the insurance industry within the state, ensuring fairness, transparency, and consumer protection. It oversees various aspects of insurance operations, including licensing, claims handling, and policy content.
Types of Insurance Regulated by the VSIC
The VSIC regulates a wide range of insurance products to protect Virginia residents and businesses. This includes:
- Life Insurance: Provides financial protection to beneficiaries upon the death of the insured. This includes term life, whole life, and universal life insurance.
- Health Insurance: Covers medical expenses, including hospital stays, doctor visits, and prescription drugs. This includes individual and group health plans, as well as Medicare supplement policies.
- Property and Casualty Insurance: Protects against financial losses from damage to property or liability arising from accidents. This includes homeowners, renters, auto, and business insurance.
- Workers’ Compensation Insurance: Provides benefits to employees injured on the job, covering medical expenses, lost wages, and rehabilitation costs.
- Disability Insurance: Offers financial support to individuals who become disabled and unable to work.
- Annuities: Provide a stream of income payments, either for a fixed period or for life.
- Long-Term Care Insurance: Helps cover the costs of long-term care services, such as nursing homes or assisted living facilities.
Licensing and Registration Requirements for Insurance Companies
To operate in Virginia, insurance companies must obtain a license from the VSIC. This process involves meeting specific requirements, including:
- Financial Stability: Companies must demonstrate sufficient financial resources to meet their obligations to policyholders.
- Operational Integrity: They must have a sound business plan and competent management team.
- Compliance with State Laws: Companies must adhere to Virginia’s insurance regulations.
- Background Checks: Key personnel undergo background checks to ensure their suitability.
Handling Insurance Claims and Disputes
The VSIC plays a crucial role in resolving insurance claims and disputes. It provides guidance and oversight to ensure fair and timely handling of claims.
- Claim Filing Process: Policyholders must file claims with their insurance company within a specified timeframe.
- Investigation and Evaluation: The insurance company investigates the claim and determines its validity and amount.
- Payment or Denial: The insurance company either pays the claim or provides a written explanation for denial.
- Appeals Process: Policyholders can appeal denied claims or disputes regarding claim payments.
- Mediation and Arbitration: The VSIC offers mediation and arbitration services to help resolve disputes between policyholders and insurance companies.
Types of Insurance Policies Regulated by the VSIC
The VSIC regulates various types of insurance policies, each designed to meet specific needs and risks. Some common types include:
- Auto Insurance: Provides coverage for damage to your vehicle and liability for accidents.
- Homeowners Insurance: Protects your home and belongings from damage caused by fire, theft, natural disasters, and other perils.
- Renters Insurance: Covers your personal belongings and liability in a rental property.
- Health Insurance: Offers coverage for medical expenses, including hospitalization, doctor visits, and prescription drugs.
- Life Insurance: Provides financial protection to your beneficiaries upon your death.
- Disability Insurance: Offers income replacement if you become disabled and unable to work.
- Long-Term Care Insurance: Helps cover the costs of long-term care services, such as nursing homes or assisted living facilities.
Consumer Protection and Education
The Virginia State Insurance Commission is committed to protecting consumers and ensuring they have access to the information they need to make informed decisions about their insurance. We understand that navigating the world of insurance can be confusing, and we strive to make it easier for you.
Understanding Insurance Policies
Understanding your insurance policy is crucial to ensuring you’re adequately protected. It’s essential to read through the policy carefully and understand its key features, including:
- Coverage: This Artikels what your policy covers and what it doesn’t. It includes the types of events, incidents, or situations that are covered, along with any limitations or exclusions.
- Limits and Deductibles: These determine how much you’ll pay out-of-pocket before your insurance kicks in and the maximum amount your insurance will cover for a specific event.
- Premiums: This is the amount you pay for your insurance coverage, typically on a monthly or annual basis. Factors such as your age, driving record, and location can influence your premium.
- Exclusions: These are specific events or situations that are not covered by your policy. It’s important to understand these exclusions to avoid surprises.
If you have any questions or need clarification, don’t hesitate to contact your insurance agent or the Virginia State Insurance Commission for assistance.
Common Insurance Scams and How to Avoid Them
Insurance scams can be costly and frustrating. It’s important to be aware of common scams and take steps to protect yourself. Here are some common scams and tips on how to avoid them:
- Phishing Scams: Be cautious of emails or phone calls claiming to be from your insurance company, especially if they ask for personal information. Never provide sensitive information over the phone or through unverified email addresses.
- Fake Insurance Agents: Beware of individuals who claim to be insurance agents but are not licensed or affiliated with a legitimate company. Verify their credentials and the company they represent before sharing any information.
- Unnecessary Coverage: Some unscrupulous agents may try to sell you unnecessary coverage or policies that don’t suit your needs. Carefully evaluate your needs and only purchase policies that provide the coverage you require.
- Bait and Switch: This involves offering a low initial premium that is later increased or changed without proper notice. Read the fine print and ask questions before signing any documents.
If you suspect you’re being scammed, report it to the Virginia State Insurance Commission or the appropriate authorities.
Resources for Resolving Insurance Issues, Virginia state insurance commission
If you’re facing an issue with your insurance company, several resources are available to help you:
- Your Insurance Agent: Your agent is your first point of contact for resolving any issues with your policy. They can help you understand your coverage and advocate on your behalf.
- Virginia State Insurance Commission: The commission is dedicated to protecting consumers’ rights and can assist you in resolving disputes with insurance companies. You can file a complaint with the commission online or by phone.
- The Virginia Department of Insurance: This department provides information and resources on insurance-related matters, including consumer rights and regulations.
- The Virginia Attorney General’s Office: If you believe you’ve been a victim of insurance fraud, you can report it to the Virginia Attorney General’s Office.
It’s important to document all interactions with your insurance company, including phone calls, emails, and letters. This documentation can be helpful if you need to file a complaint or pursue legal action.
Role of the Commission in Protecting Consumers’ Rights
The Virginia State Insurance Commission plays a crucial role in protecting consumers’ rights and ensuring a fair and competitive insurance market. The commission:
- Regulates Insurance Companies: The commission sets and enforces rules and regulations for insurance companies operating in Virginia, ensuring they comply with state laws and protect consumer interests.
- Educates Consumers: The commission provides information and resources to consumers about insurance policies, rights, and responsibilities. It also offers educational programs and workshops on various insurance topics.
- Resolves Disputes: The commission serves as a mediator in disputes between consumers and insurance companies. It investigates consumer complaints and works to find fair resolutions.
- Protects Against Fraud: The commission works to prevent and investigate insurance fraud, protecting consumers from scams and ensuring a fair and honest insurance market.
The commission is committed to protecting consumers and ensuring they have access to fair and affordable insurance. If you have any questions or concerns about your insurance, don’t hesitate to contact the commission for assistance.
Financial Stability and Solvency
The Virginia State Insurance Commission plays a crucial role in ensuring the financial stability of insurance companies operating within the state. This is essential to protect policyholders and maintain the integrity of the insurance market. The commission employs various methods to assess the solvency of insurance companies and implement regulations to address potential financial risks.
Methods for Assessing Solvency
The commission utilizes a comprehensive approach to assess the solvency of insurance companies. This involves analyzing various financial metrics, including:
- Capital adequacy: The commission evaluates the amount of capital held by insurance companies to ensure it is sufficient to cover potential losses and meet policy obligations. This is assessed through various ratios, such as the risk-based capital (RBC) ratio, which measures the company’s capital against its risk profile.
- Investment portfolio: The commission scrutinizes the investment strategies and holdings of insurance companies to assess their risk exposure and potential impact on financial stability. This includes evaluating the quality and diversification of investments, as well as the company’s ability to manage investment risks effectively.
- Underwriting performance: The commission analyzes the company’s underwriting practices, including the pricing of insurance products, the selection of risks, and the management of claims. This helps to assess the company’s ability to generate sufficient premiums to cover expected losses and expenses.
- Operational efficiency: The commission evaluates the company’s operational efficiency, including its management practices, administrative expenses, and fraud prevention measures. This helps to ensure that the company is well-managed and operating in a cost-effective manner.
Regulations for Handling Insurance Company Insolvencies
In the event of an insurance company insolvency, the commission has established regulations and procedures to protect policyholders and ensure the orderly liquidation of the company’s assets. These procedures include:
- Guaranty Fund: The Virginia Insurance Guaranty Association (VIGA) is a state-run fund that provides financial protection to policyholders of insolvent insurance companies. VIGA is funded by assessments on insurance companies operating in Virginia and provides coverage for unpaid claims, up to certain limits, for various types of insurance policies.
- Liquidation Process: The commission appoints a receiver to oversee the liquidation of the insolvent insurance company’s assets. The receiver collects assets, pays valid claims, and distributes any remaining funds to creditors. The commission closely monitors the liquidation process to ensure fairness and transparency.
- Reinsurance: The commission encourages insurance companies to maintain adequate reinsurance coverage to mitigate potential financial losses. Reinsurance is a mechanism where insurance companies transfer a portion of their risk to other insurers, thereby reducing their exposure to catastrophic events or large claims.
Key Indicators of Financial Stability
Several key indicators can help assess the financial stability of insurance companies:
- Capital adequacy ratios: As mentioned earlier, the RBC ratio is a crucial indicator of a company’s capital adequacy. A higher RBC ratio indicates a stronger financial position and greater ability to absorb potential losses.
- Profitability: Consistent profitability is a sign of a financially sound company. The commission analyzes a company’s underwriting and investment performance to assess its profitability and ability to generate sustainable earnings.
- Liquidity: Adequate liquidity is essential for insurance companies to meet their financial obligations. The commission evaluates a company’s cash flow and its ability to access funds when needed.
- Debt levels: High levels of debt can increase financial risk. The commission analyzes a company’s debt structure and its ability to manage its debt obligations.
Industry Trends and Challenges
The Virginia insurance industry, like its counterparts across the nation, is navigating a dynamic landscape shaped by technological advancements, evolving consumer expectations, and the need to adapt to emerging risks. Understanding these trends and challenges is crucial for the Virginia State Insurance Commission (VSIC) in its mission to ensure a stable and competitive insurance market that serves the best interests of Virginia’s residents and businesses.
Impact of Technology on the Insurance Industry
Technological advancements are fundamentally reshaping the insurance landscape in Virginia. These advancements are driving greater efficiency, personalization, and innovation in the industry.
- Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI): Insurers are leveraging data analytics and AI to gain deeper insights into risk profiles, personalize pricing, and streamline operations. This includes using AI-powered chatbots for customer service, automated claims processing, and fraud detection.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Connected devices are generating vast amounts of data, enabling insurers to offer usage-based insurance products and services. For example, telematics devices in vehicles can track driving behavior, leading to personalized premiums based on actual driving patterns.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain’s immutability and transparency are being explored for streamlining insurance transactions, simplifying claims processing, and enhancing data security. This technology could potentially revolutionize the way insurance policies are issued and managed.
Emerging Trends in Insurance Products and Services
The insurance industry is responding to changing consumer needs and technological advancements by developing innovative products and services.
- Insurtech: Insurtech startups are disrupting traditional insurance models with innovative solutions. These startups often leverage technology to offer more personalized, efficient, and affordable insurance products. Examples include online platforms for comparing insurance quotes and managing policies, as well as digital insurance brokers that offer specialized coverage.
- Microinsurance: This trend involves offering small, affordable insurance policies to individuals with limited financial resources. Microinsurance can help address the insurance gap in underserved communities by providing basic protection against unforeseen events.
- Cybersecurity Insurance: The growing threat of cyberattacks has led to a surge in demand for cybersecurity insurance. This type of insurance provides coverage for financial losses and expenses incurred due to data breaches, system failures, and other cyber-related incidents.
Challenges Faced by the Insurance Industry
While the insurance industry benefits from technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences, it also faces several challenges:
- Cybersecurity Threats: Cyberattacks pose a significant threat to insurers, potentially disrupting operations, compromising sensitive data, and leading to financial losses. The VSIC is working with insurers to promote best practices for cybersecurity and to enhance regulatory oversight in this area.
- Climate Change and Natural Disasters: The frequency and severity of natural disasters, exacerbated by climate change, are increasing insurance costs and creating challenges for insurers. The VSIC is actively engaged in research and collaboration with stakeholders to address the implications of climate change on the insurance industry.
- Rising Healthcare Costs: Rising healthcare costs are putting pressure on health insurance premiums, making coverage increasingly expensive for individuals and families. The VSIC is working with stakeholders to explore solutions that promote affordability and access to quality healthcare.
VSIC Initiatives to Address Industry Challenges
The VSIC plays a proactive role in addressing industry challenges by:
- Promoting Innovation: The VSIC encourages the development and adoption of innovative insurance products and services by providing guidance and support to insurers and Insurtech startups.
- Enhancing Cybersecurity: The VSIC works with insurers to promote cybersecurity best practices, conduct vulnerability assessments, and enhance regulatory oversight to mitigate cyber risks.
- Addressing Climate Change: The VSIC is actively engaged in research and collaboration with stakeholders to understand the impact of climate change on the insurance industry and to develop strategies for mitigating risks.
- Promoting Consumer Protection: The VSIC prioritizes consumer protection by ensuring that insurers operate fairly and transparently, providing consumers with access to clear and accurate information about their insurance policies.
Final Summary: Virginia State Insurance Commission
In conclusion, the Virginia State Insurance Commission serves as a vital guardian of consumer rights and a facilitator of a robust insurance market. Its comprehensive regulatory framework, consumer protection initiatives, and commitment to financial stability ensure a level playing field for both insurers and consumers. By promoting transparency, accountability, and fair practices, the commission fosters trust and confidence in the insurance industry, ultimately benefiting all stakeholders.
User Queries
How do I file a complaint against an insurance company?
You can file a complaint with the Virginia State Insurance Commission online, by mail, or by phone. The commission will investigate your complaint and attempt to resolve it.
What are the different types of insurance regulated by the commission?
The commission regulates a wide range of insurance products, including health, life, property, casualty, auto, and workers’ compensation insurance.
How can I find out if an insurance company is licensed in Virginia?
You can search the Virginia State Insurance Commission’s website for a list of licensed insurance companies.
What resources are available to consumers who have insurance issues?
The commission offers a variety of resources to consumers, including educational materials, complaint forms, and a consumer hotline.
What is the commission’s role in ensuring the financial stability of insurance companies?
The commission monitors the financial health of insurance companies to ensure they have enough capital to meet their obligations to policyholders. It also has the authority to take action against companies that are financially unstable.